Geometry Surface of OpenCascade BRep
eryar@163.com
摘要Abstract:幾何曲面是參數(shù)表示的曲面 ,在邊界表示中其數(shù)據(jù)存在于BRep_TFace中,BRep_TFace中不僅包括了幾何曲線,還包含用于顯示的離散幾何信息,如三角剖分數(shù)據(jù)。本文主要對OpenCascade的BRep表示中幾何曲面進行說明,將在后面分析Topology部分的讀寫程序時來說明包含幾何數(shù)據(jù)的三種拓樸結(jié)構(gòu)中分別包括哪些幾何信息。
關(guān)鍵字Key Words:OpenCascade BRep, Geometry Surface, Topology
一、引言 Introduction
邊界表示(Boundary Representation)也稱為BRep表示,它是幾何造型中最成熟、無二義的表示法。實體的邊界通常是由面的并集來表示,而每個面又由它所在的曲面的定義加上其邊界來表示,面的邊界是邊的并集,而邊又是由點來表示的。
邊界表示的一個重要特征是描述形體的信息包括幾何信息(Geometry)和拓樸信息(Topology)兩個方面。拓樸信息描述形體上的頂點、邊、面的連接關(guān)系,它形成物體邊界表示的“骨架”。形體的幾何信息猶如附著在“骨架”上的肌肉。例如,形體的某個面位于某一個曲面上,定義這一曲面方程的數(shù)據(jù)就是幾何信息。此外,邊的形狀、頂點在三維空間中的位置(點的坐標)等都是幾何信息,一般來說,幾何信息描述形體的大小、尺寸、位置和形狀等。
OpenCascade中幾何(Geometry)與拓樸(Topology)的關(guān)系也是按上述方式組織的。即幾何信息在BRep中并不是單獨存在的,而是依附于拓樸存在的。通過繼承TopoDS包中的抽象的拓樸類實現(xiàn)了邊界表示(BRep)模型。如下圖所示:
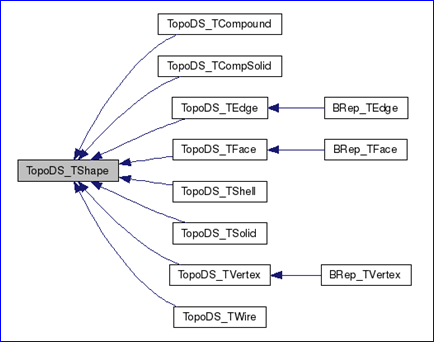
Figure 1.1 Topology data structure in OpenCascade
從上面的類圖可以看出只有三種拓樸對象有幾何數(shù)據(jù):頂點(vertex)、邊(edge)、面(face),分別為BRep_TVertex、BRep_TEdge、BRep_TFace。BRep_TVertex中主要包含一個空間點(x, y, z)數(shù)據(jù);幾何曲線數(shù)據(jù)主要存在于BRep_TEdge中,BRep_TEdge中不僅包括了幾何曲線,還包含其他類型的幾何信息;BRep_TFace中主要包含幾何曲面及其他的幾何數(shù)據(jù),如面的三角剖分等。本文主要對OpenCascade的BRep表示中幾何曲面進行說明,將在后面分析Topology部分的讀寫程序時來說明這三種拓樸結(jié)構(gòu)中分別包括哪些幾何信息。
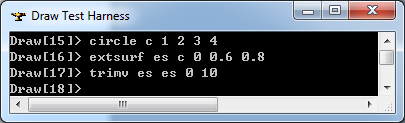
Draw Test Harness是OpenCascade提供的一種靈活和簡便的測試與演示OCCT造型庫的工具。他不僅可以使用交互的方式來創(chuàng)建、顯示和修改曲線、曲面和拓樸形狀,還可以以腳本(script)的方式來使用,OpenCascade就是用腳本的方式來對其造型內(nèi)核進行自動化測試(Tests)。本文將示例程序的幾何曲面在Draw Test Harness進行創(chuàng)建與顯示,結(jié)合圖形的直觀顯示便于對抽象概念的理解。
二、示例程序 Example Code
在OpenCascade提供的文檔《BRep Format Description White Paper》對其BRep文件數(shù)據(jù)進行了說明。BRep文件的幾何部分包含了參數(shù)曲面,根據(jù)文檔中提供的數(shù)據(jù),利用其提供的類來將示例數(shù)據(jù)進行輸出,再調(diào)試其相關(guān)代碼來分析其實現(xiàn)。示例程序如下所示:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
*
* File : Main.cpp
* Author : eryar@163.com
* Date : 2013-12-01 12:18
* Version : 1.0v
*
* Description : Demonstrate the geometry surface section
* of the BRep file of OpenCascade.
* KeyWords : OpenCascade, BRep File, Geometry Surface
*
*/
// OpenCascade library.
#define WNT
#include <Geom_Plane.hxx>
#include <Geom_CylindricalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_ConicalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_SphericalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_ToroidalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion.hxx>
#include <Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution.hxx>
#include <Geom_BezierSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_BSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_OffsetSurface.hxx>
#include <TColgp_Array2OfPnt.hxx>
#include <TColStd_Array1OfReal.hxx>
#include <TColStd_Array2OfReal.hxx>
#include <TColStd_Array1OfInteger.hxx>
#include <GeomTools.hxx>
#include <Geom_Circle.hxx>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib")
int main(void)
{
gp_Ax2 axis(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 3), gp::DZ());
std::ofstream dumpFile("geometrySurface.txt");
// Surface record 1 - Plane.
// Example: 1 0 0 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
Handle_Geom_Plane thePlane = new Geom_Plane(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 3), gp_Dir(0, 0, 1));
GeomTools::Write(thePlane, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(thePlane, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(thePlane, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(thePlane, std::cout);
// Surface record 2 - Cylinder.
// Example: 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_CylindricalSurface theCylinder = new Geom_CylindricalSurface(axis, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theCylinder, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theCylinder, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theCylinder, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theCylinder, std::cout);
// Surface record 3 - Cone.
// Example: 3 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 4
// 0.75
Handle_Geom_ConicalSurface theCone = new Geom_ConicalSurface(axis, 0.75, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theCone, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theCone, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theCone, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theCone, std::cout);
// Surface record 4 - Sphere.
// Example: 4 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_SphericalSurface theSphere = new Geom_SphericalSurface(axis, 4);
GeomTools::Write(theSphere, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theSphere, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theSphere, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theSphere, std::cout);
// Surface record 5 - Torus.
// Example: 5 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 8 4
Handle_Geom_ToroidalSurface theTorus = new Geom_ToroidalSurface(axis, 8, 4);
GeomTools::Write(theTorus, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theTorus, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theTorus, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theTorus, std::cout);
// Surface record 6 - Linear Extrusion.
// Example: 6 0 0.6 0.8
// 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_Circle baseCurve = new Geom_Circle(axis, 4.0);
Handle_Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion theExtrusion = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(baseCurve, gp_Dir(0, 0.6, 0.8));
GeomTools::Write(theExtrusion, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theExtrusion, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theExtrusion, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theExtrusion, std::cout);
// Surface record 7 - Revolution Surface.
// Example: 7 -4 0 3 0 1 0
// 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution theRevolution = new Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution(baseCurve, gp::OY());
theRevolution->SetLocation(gp_Pnt(-4, 0, 3));
GeomTools::Write(theRevolution, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theRevolution, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theRevolution, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theRevolution, std::cout);
// Surface record 8 - Bezier Surface.
// Example: 8 1 1 2 1 0 0 1 7 1 0 -4 10
// 0 1 -2 8 1 1 5 11
// 0 2 3 9 1 2 6 12
TColgp_Array2OfPnt poles(1, 3, 1, 2);
TColStd_Array2OfReal weights(1, 3, 1, 2);
poles.SetValue(1, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 0, 1)); weights.SetValue(1, 1, 7.0);
poles.SetValue(1, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 0, -4)); weights.SetValue(1, 2, 10.0);
poles.SetValue(2, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 1, -2)); weights.SetValue(2, 1, 8.0);
poles.SetValue(2, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 1, 5)); weights.SetValue(2, 2, 11.0);
poles.SetValue(3, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 2, 3)); weights.SetValue(3, 1, 9.0);
poles.SetValue(3, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 2, 6)); weights.SetValue(3, 2, 12.0);
Handle_Geom_BezierSurface theBezierSurface = new Geom_BezierSurface(poles, weights);
GeomTools::Write(theBezierSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theBezierSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theBezierSurface, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theBezierSurface, std::cout);
// Surface record 9 - B-spline Surface.
// Example: 9 1 1 0 0 1 1 3 2 5 4 0 0 1 7 1 0 -4 10
// 0 1 -2 8 1 1 5 11
// 0 2 3 9 1 2 6 12
//
// 0 1
// 0.25 1
// 0.5 1
// 0.75 1
// 1 1
//
// 0 1
// 0.3 1
// 0.7 1
// 1 1
Standard_Integer uDegree = 1;
Standard_Integer vDegree = 1;
Standard_Boolean uPeriodic = Standard_False;
Standard_Boolean vPeriodic = Standard_False;
TColStd_Array1OfReal uKnots(1, 5);
TColStd_Array1OfReal vKnots(1, 4);
TColStd_Array1OfInteger uMults(1, 5);
TColStd_Array1OfInteger vMults(1, 4);
uKnots.SetValue(1, 0);
uKnots.SetValue(2, 0.25);
uKnots.SetValue(3, 0.5);
uKnots.SetValue(4, 0.75);
uKnots.SetValue(5, 1.0);
vKnots.SetValue(1, 0);
vKnots.SetValue(2, 0.3);
vKnots.SetValue(3, 0.7);
vKnots.SetValue(4, 1.0);
// Multiplicity of u and v are 1.
uMults.Init(1);
vMults.Init(1);
Handle_Geom_BSplineSurface theBSplineSurface = new Geom_BSplineSurface(poles, weights, uKnots, vKnots, uMults, vMults, uDegree, vDegree, uPeriodic, vPeriodic);
GeomTools::Write(theBSplineSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theBSplineSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theBSplineSurface, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theBSplineSurface, std::cout);
// Surface record 10 - Rectangular Trim Surface.
// Example: 10 -1 2 -3 4
// 1 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
Handle_Geom_Plane baseSurface = new Geom_Plane(axis);
Handle_Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface theTrimmedSurface = new Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface(baseSurface, -1.0, 2.0, -3.0, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theTrimmedSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theTrimmedSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theTrimmedSurface, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theTrimmedSurface, std::cout);
// Surface record 11 - Offset Surface.
// Example: 11 -2
// 1 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
Handle_Geom_OffsetSurface theOffsetSurface = new Geom_OffsetSurface(baseSurface, -2.0);
GeomTools::Write(theOffsetSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theOffsetSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Write(theOffsetSurface, std::cout);
GeomTools::Dump(theOffsetSurface, std::cout);
return 0;
}
上述程序?qū)ⅰ禕Rep Format Description White Paper》中的幾何部分(Geometry Section)的參數(shù)曲面(Surfaces)示例數(shù)據(jù)分別使用類GeomTools的靜態(tài)函數(shù)輸出到屏幕和文件。
當使用GeomTools::Write()時輸出的內(nèi)容與BRep文件中一致,當使用GeomTools::Dump()時輸出更易讀的信息。為了便于對比理解,將兩種形式都輸出到文件geometrySurface.txt中,輸出數(shù)據(jù)如下所示:
1 0 0 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
Plane
Origin :0, 0, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
CylindricalSurface
Origin :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radius :4
3 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
0.75
ConicalSurface
Origin :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radius :4
Angle :0.75
4 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
SphericalSurface
Center :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radius :4
5 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 8 4
ToroidalSurface
Origin :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radii :8 4
6 0 0.6 0.8
2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion
Direction :0, 0.6, 0.8
Basis curve :
Circle
Center :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radius :4
7 -4 0 3 0 1 0
2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
SurfaceOfRevolution
Origin :-4, 0, 3
Direction :0, 1, 0
Basis curve :
Circle
Center :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radius :4
8 1 1 2 1 0 0 1 7 1 0 -4 10
0 1 -2 8 1 1 5 11
0 2 3 9 1 2 6 12
BezierSurface urational vrational
Degrees :2 1
1, 1 : 0, 0, 1 7
1, 2 : 1, 0, -4 10
2, 1 : 0, 1, -2 8
2, 2 : 1, 1, 5 11
3, 1 : 0, 2, 3 9
3, 2 : 1, 2, 6 12
9 1 1 0 0 1 1 3 2 5 4 0 0 1 7 1 0 -4 10
0 1 -2 8 1 1 5 11
0 2 3 9 1 2 6 12
0 1
0.25 1
0.5 1
0.75 1
1 1
0 1
0.3 1
0.7 1
1 1
BSplineSurface urational vrational
Degrees :1 1
NbPoles :3 2
NbKnots :5 4
Poles :
1, 1 : 0, 0, 1 7
1, 2 : 1, 0, -4 10
2, 1 : 0, 1, -2 8
2, 2 : 1, 1, 5 11
3, 1 : 0, 2, 3 9
3, 2 : 1, 2, 6 12
UKnots :
1 : 0 1
2 : 0.25 1
3 : 0.5 1
4 : 0.75 1
5 : 1 1
VKnots :
1 : 0 1
2 : 0.3 1
3 : 0.7 1
4 : 1 1
10 -1 2 -3 4
1 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
RectangularTrimmedSurface
Parameters : -1 2 -3 4
BasisSurface :
Plane
Origin :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
11 -2
1 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
OffsetSurface
Offset : -2
BasisSurface :
Plane
Origin :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
三、程序說明 Example Description
3.1 平面 Plane
示例:
// Surface record 1 - Plane.
// Example: 1 0 0 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
Handle_Geom_Plane thePlane = new Geom_Plane(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 3), gp_Dir(0, 0, 1));
GeomTools::Write(thePlane, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(thePlane, dumpFile);
<surface record 1>定義了平面。平面數(shù)據(jù)包含三維點P和三維正交坐標系N,Du,Dv。平面通過點P,且其法向量為N。其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
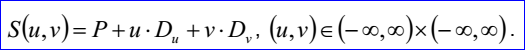
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的平面為通過點P=(0,0,3),法向量N=(0,0,1),其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
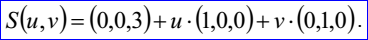
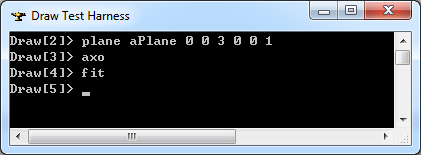
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示平面如下所示:
3.2 圓柱面 Cylinder
示例:
// Surface record 2 - Cylinder.
// Example: 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_CylindricalSurface theCylinder = new Geom_CylindricalSurface(axis, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theCylinder, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theCylinder, dumpFile);
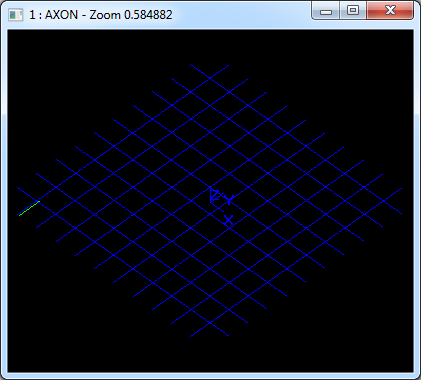
<surface record 2>定義了圓柱面。圓柱面的數(shù)據(jù)包含三維點P,三維正交坐標系Dv,Dx,Dy和一個非負實數(shù)r。圓柱面的軸通過點P,方向為Dv,圓柱面的半徑為r,其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
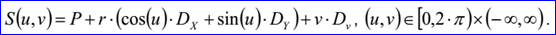
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的圓柱面為軸通過點P=(1,2,3),軸的方向Dv=(0,0,1),方向Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(-0,1,0),半徑r=4,其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
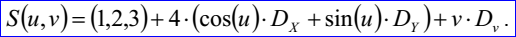
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示圓柱面如下所示:
3.3 圓錐面 Cone
示例:
// Surface record 3 - Cone.
// Example: 3 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 4
// 0.75
Handle_Geom_ConicalSurface theCone = new Geom_ConicalSurface(axis, 0.75, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theCone, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theCone, dumpFile);
<surface record 3>定義了圓錐面。圓錐面的數(shù)據(jù)包含三維點P,正交坐標系Dz,Dx,Dy,非負實數(shù)r和實數(shù)ψ(范圍為(-π/2, π/2))。圓錐面通過點P且軸的方向為Dz。過點P且與方向Dx,Dy平行的平面為圓錐面的參考平面(referenced plane)。參考平面截圓錐面為一個圓,其半徑為r。其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
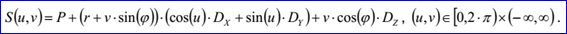
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的圓錐面的軸通過點P=(1,2,3),方向Dz=(0,0,1)。圓錐面的其他數(shù)據(jù)是Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(-0,1,0),半徑r=4,角度ψ=0.75。其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
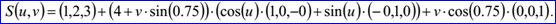
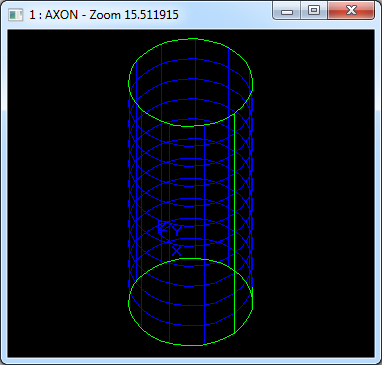
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示圓錐面如下所示:
3.4 球面 Sphere
示例:
// Surface record 4 - Sphere.
// Example: 4 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_SphericalSurface theSphere = new Geom_SphericalSurface(axis, 4);
GeomTools::Write(theSphere, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theSphere, dumpFile);
<surface record 4>定義了球面。球面的數(shù)據(jù)包含三維點P,三維正交坐標系Dz,Dx,Dy和非負實數(shù)r。即球面的球心為點P,半徑為r,其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
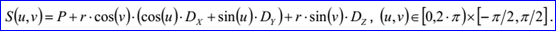
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的球面為球心過點P=(1,2,3),方向分別為Dz=(0,0,1),Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(-0,1,0),半徑r=4。其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
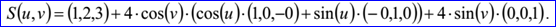
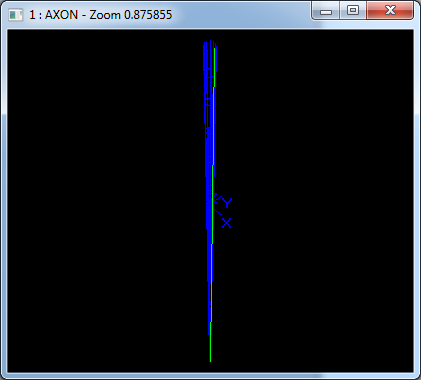
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示球面如下所示:
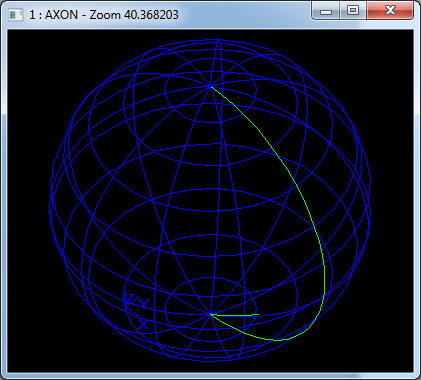
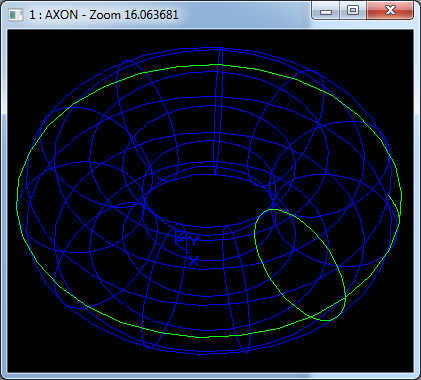
3.5 圓環(huán)面 Torus
示例:
// Surface record 5 - Torus.
// Example: 5 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 8 4
Handle_Geom_ToroidalSurface theTorus = new Geom_ToroidalSurface(axis, 8, 4);
GeomTools::Write(theTorus, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theTorus, dumpFile);
<surface record 5>定義了圓環(huán)面。圓環(huán)面的數(shù)據(jù)包含三維點P,三維正交坐標系Dz,Dx,Dy和非負實數(shù)r1,r2。圓環(huán)面的軸通過點P,方向為Dz,r1是從圓環(huán)面的圓的中心到點P的距離,圓環(huán)面的圓的半徑為r2。圓環(huán)面的參數(shù)方程如下所示:
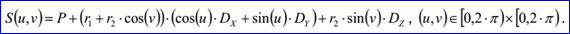
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的圓環(huán)面的軸通過點P=(1,2,3),軸的方向為Dz=(0,0,1)。其它數(shù)據(jù)為Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(0,1,0),r1=8,r2=4,其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
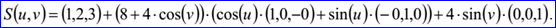
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示圓環(huán)面如下所示:
3.6 線性拉伸面 Linear Extrusion
示例:
// Surface record 6 - Linear Extrusion.
// Example: 6 0 0.6 0.8
// 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_Circle baseCurve = new Geom_Circle(axis, 4.0);
Handle_Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion theExtrusion = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(baseCurve, gp_Dir(0, 0.6, 0.8));
GeomTools::Write(theExtrusion, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theExtrusion, dumpFile);
<surface record 6>定義了線性拉伸面。線性拉伸面的數(shù)據(jù)包含三維方向Dv和三維曲線<3D curve record>。其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
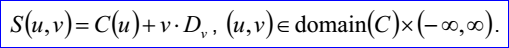
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的線性拉伸面的拉伸方向Dv=(0,0.6,0.8),拉伸曲線為圓。拉伸面的參數(shù)方程如下所示:
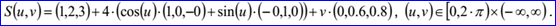
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示線性拉伸面如下所示:
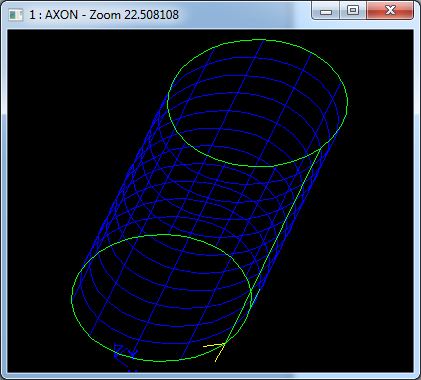
3.7 旋轉(zhuǎn)面 Revolution Surface
示例:
// Surface record 7 - Revolution Surface.
// Example: 7 -4 0 3 0 1 0
// 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution theRevolution = new Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution(baseCurve, gp::OY());
theRevolution->SetLocation(gp_Pnt(-4, 0, 3));
GeomTools::Write(theRevolution, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theRevolution, dumpFile);
<surface record 7>定義了旋轉(zhuǎn)面。旋轉(zhuǎn)面的數(shù)據(jù)包含三維點P,三維方向D和三維曲線。旋轉(zhuǎn)曲面的軸通過點P且方向為D,旋轉(zhuǎn)曲線為C與旋轉(zhuǎn)軸共面。旋轉(zhuǎn)曲面的參數(shù)方程如下所示:
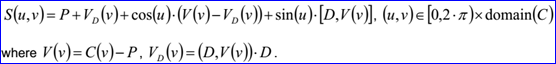
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的旋轉(zhuǎn)曲面的旋轉(zhuǎn)軸通過點P=(-4,0,3),方向D=(0,1,0),旋轉(zhuǎn)曲線是一個圓。其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
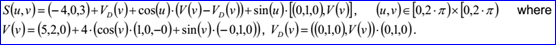
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示旋轉(zhuǎn)面如下所示:
3.8 Bezier曲面 Bezier Surface
示例:
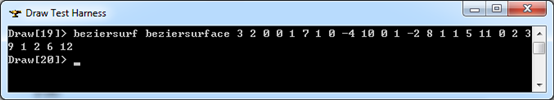
// Surface record 8 - Bezier Surface.
// Example: 8 1 1 2 1 0 0 1 7 1 0 -4 10
// 0 1 -2 8 1 1 5 11
// 0 2 3 9 1 2 6 12
TColgp_Array2OfPnt poles(1, 3, 1, 2);
TColStd_Array2OfReal weights(1, 3, 1, 2);
poles.SetValue(1, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 0, 1)); weights.SetValue(1, 1, 7.0);
poles.SetValue(1, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 0, -4)); weights.SetValue(1, 2, 10.0);
poles.SetValue(2, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 1, -2)); weights.SetValue(2, 1, 8.0);
poles.SetValue(2, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 1, 5)); weights.SetValue(2, 2, 11.0);
poles.SetValue(3, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 2, 3)); weights.SetValue(3, 1, 9.0);
poles.SetValue(3, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 2, 6)); weights.SetValue(3, 2, 12.0);
Handle_Geom_BezierSurface theBezierSurface = new Geom_BezierSurface(poles, weights);
GeomTools::Write(theBezierSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theBezierSurface, dumpFile);
<surface record 8>定義了Bezier曲面。曲面的數(shù)據(jù)包含u有理標志位ru,v有理標志位rv,曲面次數(shù)mu, mv,和weight poles。u,v的次數(shù)都不能大于25。
當ru+rv=0時,weight poles是(mu+1)(mv+1)個三維點Bi,j((i,j)∈{0,...,mu}x{0,...,mv}),hi,j=1((i,j)∈{0,...,mu}x{0,...,mv});
當ru+rv≠0時,weight poles是(mu+1)(mv+1)個帶權(quán)控制點對Bi,j,hi,j。Bi,j是三維點,hi,j是權(quán)因子,正實數(shù)。
Bezier曲面的參數(shù)方程如下所示:
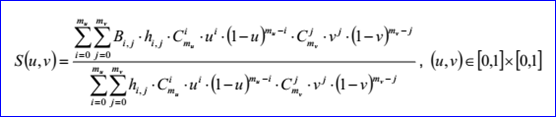
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的Bezier曲面為:u有理標志位ru=1,v有理標志位rv=1,次數(shù)mu=2,mv=1,weight poles為:B0,0=(0,0,1),h0,0=7,B0,1=(1,0,-4),h0,1=10,B1,0=(0,1,-2),h1,0=8,B1,1=(1,1,5),h1,1=11,B2,0=(0,2,3),h2,0=9,B2,1=(1,2,6),h2,1=12。曲面的參數(shù)方程為:
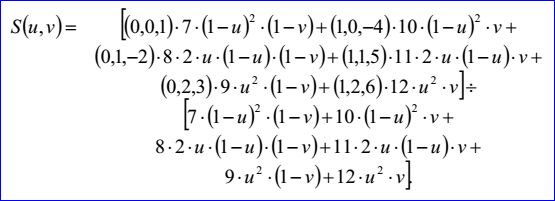
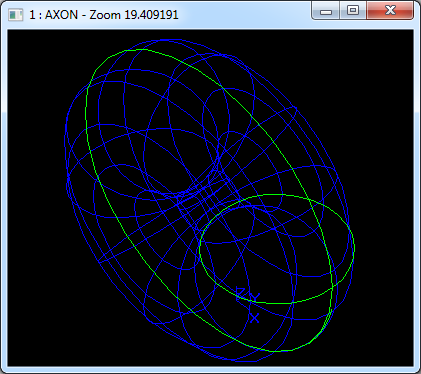
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示Bezier曲面如下所示:
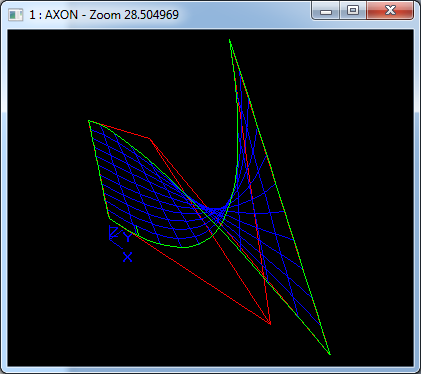
3.9 B樣條曲面 B-spline Surface
示例:
// Surface record 9 - B-spline Surface.
// Example: 9 1 1 0 0 1 1 3 2 5 4 0 0 1 7 1 0 -4 10
// 0 1 -2 8 1 1 5 11
// 0 2 3 9 1 2 6 12
//
// 0 1
// 0.25 1
// 0.5 1
// 0.75 1
// 1 1
//
// 0 1
// 0.3 1
// 0.7 1
// 1 1
Standard_Integer uDegree = 1;
Standard_Integer vDegree = 1;
Standard_Boolean uPeriodic = Standard_False;
Standard_Boolean vPeriodic = Standard_False;
TColStd_Array1OfReal uKnots(1, 5);
TColStd_Array1OfReal vKnots(1, 4);
TColStd_Array1OfInteger uMults(1, 5);
TColStd_Array1OfInteger vMults(1, 4);
uKnots.SetValue(1, 0);
uKnots.SetValue(2, 0.25);
uKnots.SetValue(3, 0.5);
uKnots.SetValue(4, 0.75);
uKnots.SetValue(5, 1.0);
vKnots.SetValue(1, 0);
vKnots.SetValue(2, 0.3);
vKnots.SetValue(3, 0.7);
vKnots.SetValue(4, 1.0);
// Multiplicity of u and v are 1.
uMults.Init(1);
vMults.Init(1);
Handle_Geom_BSplineSurface theBSplineSurface = new Geom_BSplineSurface(poles, weights, uKnots, vKnots, uMults, vMults, uDegree, vDegree, uPeriodic, vPeriodic);
GeomTools::Write(theBSplineSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theBSplineSurface, dumpFile);
<surface record 9>定義了B-Spline曲面。B樣條曲面數(shù)據(jù)包含u有理標志位ru,v有理標志位rv,u次數(shù)mu<=25;v次數(shù)mv<=25,u控制點數(shù)nu>=2,v控制點數(shù)nv>=2,u重節(jié)點數(shù)ku,v重節(jié)點數(shù)kn,weight poles,u重節(jié)點,v重節(jié)點。
當ru+rv=0時,weight poles是(mu+1)(mv+1)個三維點Bi,j((i,j)∈{0,...,mu}x{0,...,mv}),hi,j=1((i,j)∈{0,...,mu}x{0,...,mv});
當ru+rv≠0時,weight poles是(mu+1)(mv+1)個帶權(quán)控制點對Bi,j,hi,j。Bi,j是三維點,hi,j是權(quán)因子,正實數(shù)。
u重節(jié)點及其重數(shù)有ku對:u1,q1,...,uku,qku。這里ui是重數(shù)為qi>=1的節(jié)點:
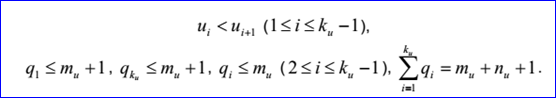
v重節(jié)點及其重數(shù)有kv對:u1,q1,...,ukv,qkv。這里vi是重數(shù)為qi>=1的節(jié)點:
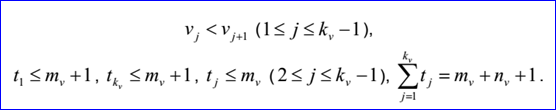
B-Spline曲面的參數(shù)方程如下所示:
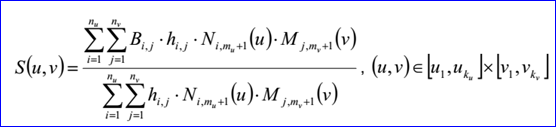
基函數(shù)Ni,j和Mi,j有如下的遞歸定義:
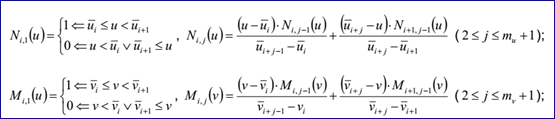
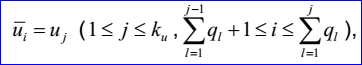
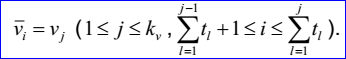
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的B-Spline曲面為:u有理標志位ru=1,v有理標志位rv=1,u次數(shù)mu=1,v次數(shù)mv=1,u控制點數(shù)nu=3,v控制點數(shù)nv=2,u有重復(fù)度的節(jié)點數(shù)ku=5,v有重復(fù)度節(jié)點數(shù)kv=4,帶權(quán)控制點B1,1=(0,0,1),h1,1=7,B1,2=(1,0,-4),h1,2=10,B2,1=(0,1,-2),h2,1=8,B2,2=(1,1,5),h2,2=11,B3,1=(0,2,3),h3,1=9,B3,2=(1,2,6),h3,2=12,u有重復(fù)度節(jié)點u1=0,q1=1,u2=0.25,q2=1,u3=0.5,q3=1,u4=0.75,q4=1,u5=1,q5=1,v有重度度節(jié)點v1=0,r1=1,v2=0.3,r2=1,v3=0.7,r3=1,v4=1,r4=1。B-Spline曲面的參數(shù)方程如下所示:
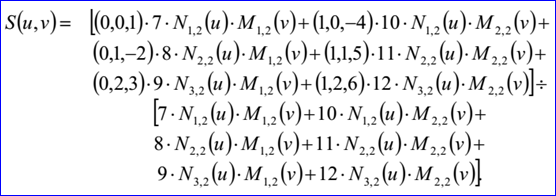
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示B樣條曲面如下所示:
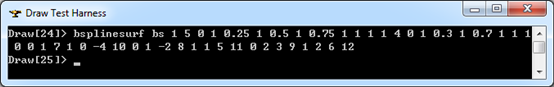
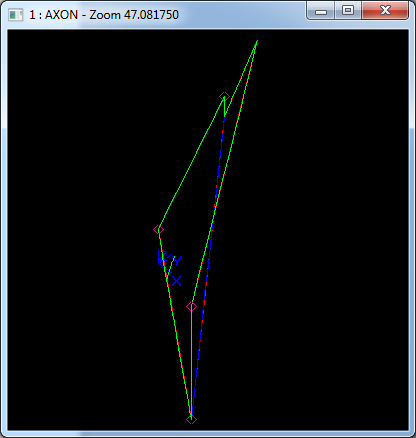
3.10 矩形裁剪曲面 Rectangular Trim Surface
示例:
// Surface record 10 - Rectangular Trim Surface.
// Example: 10 -1 2 -3 4
// 1 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
Handle_Geom_Plane baseSurface = new Geom_Plane(axis);
Handle_Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface theTrimmedSurface = new Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface(baseSurface, -1.0, 2.0, -3.0, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theTrimmedSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theTrimmedSurface, dumpFile);
<surface record 10>定義了矩形裁剪曲面。矩形裁剪曲面的數(shù)據(jù)包含實數(shù)umin,umax,vmin,vmax和一個曲面。矩形裁剪曲面是將曲面限制在矩形區(qū)域[umin,umax]x[vmin,vmax]內(nèi)得到的曲面。曲面的參數(shù)方程如下所示:
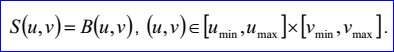
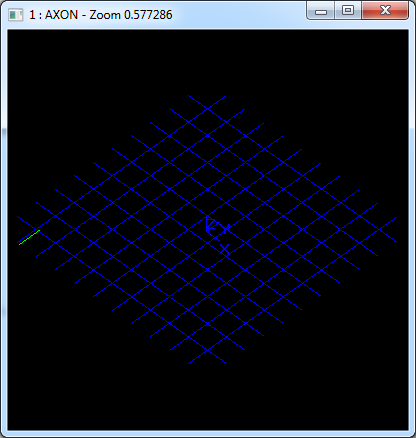
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的矩形裁剪曲面的矩形裁剪區(qū)域為[-1,2]x[-3,4],被裁剪曲面B(u,v)=(1,2,3)+u(1,0,0)+v(0,1,0)。其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
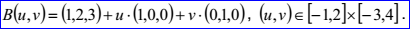
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示矩形裁剪曲面如下所示:
3.11 偏移曲面 Offset Surface
示例:
// Surface record 11 - Offset Surface.
// Example: 11 -2
// 1 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0
Handle_Geom_OffsetSurface theOffsetSurface = new Geom_OffsetSurface(baseSurface, -2.0);
GeomTools::Write(theOffsetSurface, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theOffsetSurface, dumpFile);
<surface record 11>定義了偏移曲面。偏移曲面的數(shù)據(jù)包含偏移距離d和曲面。偏移曲面的就將基準曲面B沒曲面的法向N上偏移距離d得到的曲面。偏移曲面的參數(shù)方程如下所示:
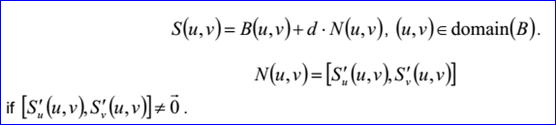
示例數(shù)據(jù)表示的偏移曲面的偏移距離d=-2,基準曲面B(u,v)=(1,2,3)+u(1,0,0)+v(0,1,0)。其參數(shù)方程如下所示:
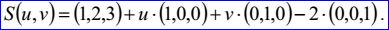
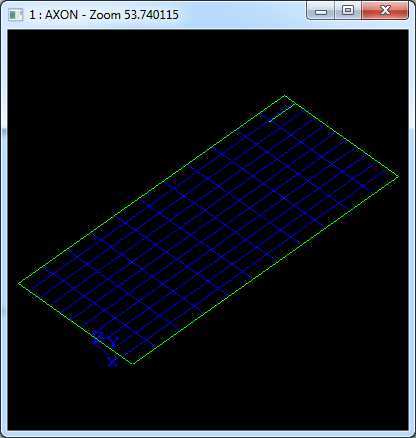
在Draw Test Harness中創(chuàng)建并顯示偏移曲面如下所示:
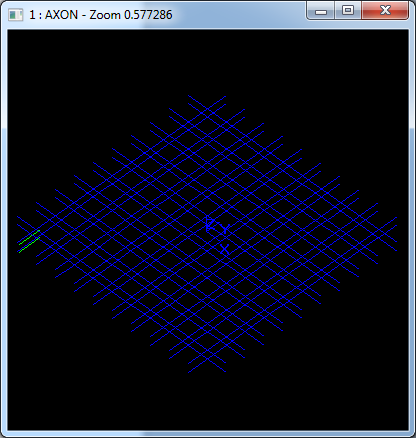
注:當偏移-2時,效果不明顯示,所以偏移了-20,這樣看上去比較明顯。
四、程序分析 Refactoring the Code
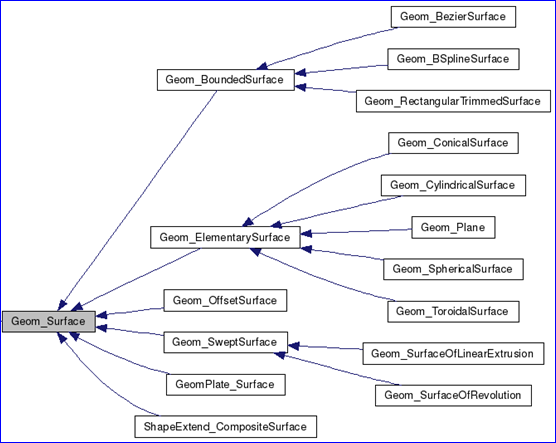
Figure 4.1 Class diagram of Geom_Surface
根據(jù)幾何曲面的類圖可知,幾何曲面有個共同的基類Geom_Surface。而在對幾何數(shù)據(jù)進行輸出與讀入時,用了很多條件判斷。輸出部分程序代碼如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : PrintSurface
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
void GeomTools_SurfaceSet::PrintSurface(const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S,
Standard_OStream& OS,
const Standard_Boolean compact)
{
Handle(Standard_Type) TheType = S->DynamicType();
if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_Plane)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_Plane)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_CylindricalSurface)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_CylindricalSurface)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_ConicalSurface)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_ConicalSurface)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_SphericalSurface)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_SphericalSurface)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_ToroidalSurface)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_ToroidalSurface)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_BezierSurface)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_BezierSurface)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_BSplineSurface)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_OffsetSurface)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_OffsetSurface)::DownCast(S),OS,compact);
}
else {
GeomTools::GetUndefinedTypeHandler()->PrintSurface(S,OS,compact);
//if (!compact)
// OS << "***** Unknown Surface ********\n";
//else
// cout << "***** Unknown Surface ********"<<endl;
}
}
讀入部分的程序代碼如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : ReadSurface
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
Standard_IStream& GeomTools_SurfaceSet::ReadSurface(Standard_IStream& IS,
Handle(Geom_Surface)& S)
{
Standard_Integer stype;
try {
OCC_CATCH_SIGNALS
IS >> stype;
switch (stype) {
case PLANE :
{
Handle(Geom_Plane) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case CYLINDER :
{
Handle(Geom_CylindricalSurface) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case CONE :
{
Handle(Geom_ConicalSurface) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case SPHERE :
{
Handle(Geom_SphericalSurface) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case TORUS :
{
Handle(Geom_ToroidalSurface) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case LINEAREXTRUSION :
{
Handle(Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case REVOLUTION :
{
Handle(Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case BEZIER :
{
Handle(Geom_BezierSurface) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case BSPLINE :
{
Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case RECTANGULAR :
{
Handle(Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
case OFFSET :
{
Handle(Geom_OffsetSurface) SS;
IS >> SS;
S = SS;
}
break;
default :
{
Handle(Geom_Surface) SS;
GeomTools::GetUndefinedTypeHandler()->ReadSurface(stype,IS,SS);
S = SS;
}
break;
}
}
catch(Standard_Failure) {
#ifdef DEB
Handle(Standard_Failure) anExc = Standard_Failure::Caught();
cout <<"EXCEPTION in GeomTools_SurfaceSet::ReadSurface(..)!!!" << endl;
cout << anExc << endl;
#endif
S = NULL;
}
return IS;
}
正如《Refactoring-Improving the Design of Existing Code》書中以多態(tài)取代條件表達式(Replace Conditional with Polymorphism)所說,在面向?qū)ο笮g(shù)語中,聽上去最高貴的詞非“多態(tài)”莫屬。多態(tài)最根本的好處就是如果你需要根據(jù)對象的不同類型而采取不同的行為,多態(tài)使你不必編寫明顯的條件表達式。正因為有了多態(tài),所以你會發(fā)現(xiàn)“類型碼的switch語句”以及“基于類型名稱的if-then-else語句”在面向?qū)ο蟪绦蛑泻苌俪霈F(xiàn)。
多態(tài)能夠帶給你很多好處。如果同一組條件表達式在程序許多地方出現(xiàn),那么使用多態(tài)的收益是最大的。使用條件表達式時,如果你想添加一種新類型,就必須查找并更新所有條件表達式。但如果改用多態(tài),只需要一個新的子類,并在其中提供適當?shù)暮瘮?shù)就行了。類的用戶不需要了解這個子類,這就大降低了系統(tǒng)各部分之間的依賴,使系統(tǒng)升級更容易。
OpenCascade的幾何曲面已經(jīng)有一個基類Geom_Surface了,可將輸出做為虛函數(shù),就不需要做判斷了。在讀入(創(chuàng)建)時引入工廠模式,對于UndefinedTypeHandler()可以引入Null對象。經(jīng)過這樣重構(gòu)之后的程序可讀性應(yīng)該會更好吧!
五、結(jié)論 Conclusion
在邊界表示BRep的形狀中,參數(shù)表示的幾何曲面并不會孤立存在,他總是依附于拓樸面中。在OpenCascade的BRep格式的文件中三維幾何曲面共有十一種,通過將這十一種幾何曲面輸出,理解參數(shù)表示的幾何曲面的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)。
通過查看其讀寫幾何曲面的源程序,提出重構(gòu)的方法。當在面向?qū)ο蟮某绦蛑谐霈F(xiàn)很條件表達式時,那么程序就有“壞味道”了,需要進行重構(gòu)改進。
六、參考資料 References
1. OpenCascade. BRep Format Description White Paper
2. Martin Fowler. Refactoring:Improving the Design of Existing Code. Addison-Wesley
3. Les Piegl, Wayne Tiller. The NURBS Book. Springer-Verlag