OpenCASCADE曲面求交之網(wǎng)格離散法1
eryar@163.com
1 Introduction
由朱心雄等著《自由曲線曲面造型技術(shù)》書中對(duì)曲面求交之網(wǎng)格離散法描述如下:該法的基本思想是先將曲面離散為由小平面片組成的網(wǎng)格,當(dāng)網(wǎng)格足夠密時(shí),可以認(rèn)為已經(jīng)非常接近真實(shí)曲面,對(duì)分別表示不同曲面的兩張網(wǎng)格,利用平面片求交法求得的交線,并以此交線近似代表曲面間的交線。這種方法原理簡(jiǎn)明,便于實(shí)現(xiàn),適用范圍廣,任意參數(shù)曲面均可利用該法求交。但為獲取精確地交線,則必須生成非常細(xì)密的網(wǎng)格,這將導(dǎo)致占用內(nèi)存多,計(jì)算花費(fèi)大。因此,實(shí)際工作中很少單一使用離散網(wǎng)格法,而常將其與其他方法結(jié)合使用。
OpenCASCADE中對(duì)于曲面求交也提供離散網(wǎng)格法,其中曲面的離散網(wǎng)格由類IntPatch_Polyhedron表示,兩個(gè)網(wǎng)格面求交使用類IntPatch_InterferencePolyhedron。本文主要介紹曲面的網(wǎng)格表示類IntPatch_Polyhedron。
2 Polyhedron
OpenCASCADE用于曲面求交的網(wǎng)格離散算法相對(duì)BRepMesh中的算法要簡(jiǎn)單很多,主要思路是根據(jù)參數(shù)U,V方向上的采樣點(diǎn)數(shù)量來計(jì)算曲面上的點(diǎn),再根據(jù)固定公式將采樣點(diǎn)連成三角形。其中生成采樣點(diǎn)代碼如下所示:
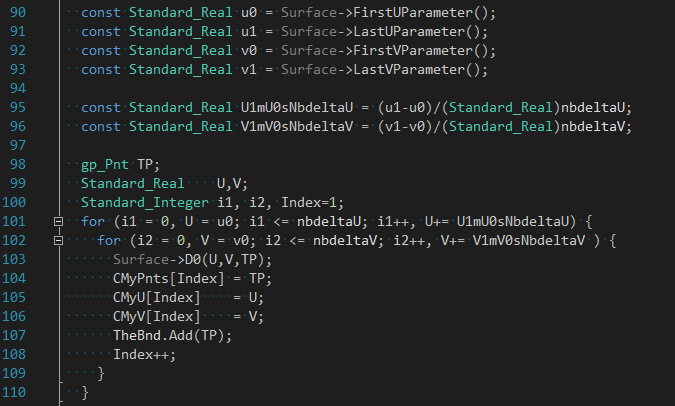
成員變量CMyPnts是采樣點(diǎn)數(shù)組,CMyU和CMyV是采樣點(diǎn)在曲面上的參數(shù)。將采樣點(diǎn)連成三角形函數(shù)如下圖所示:
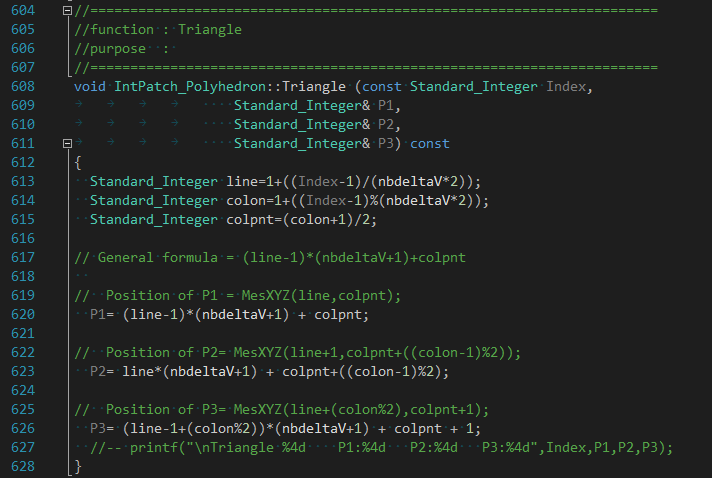
根據(jù)上述生成采樣點(diǎn)及三角形函數(shù),對(duì)于平面生成的三角形如下圖所示:
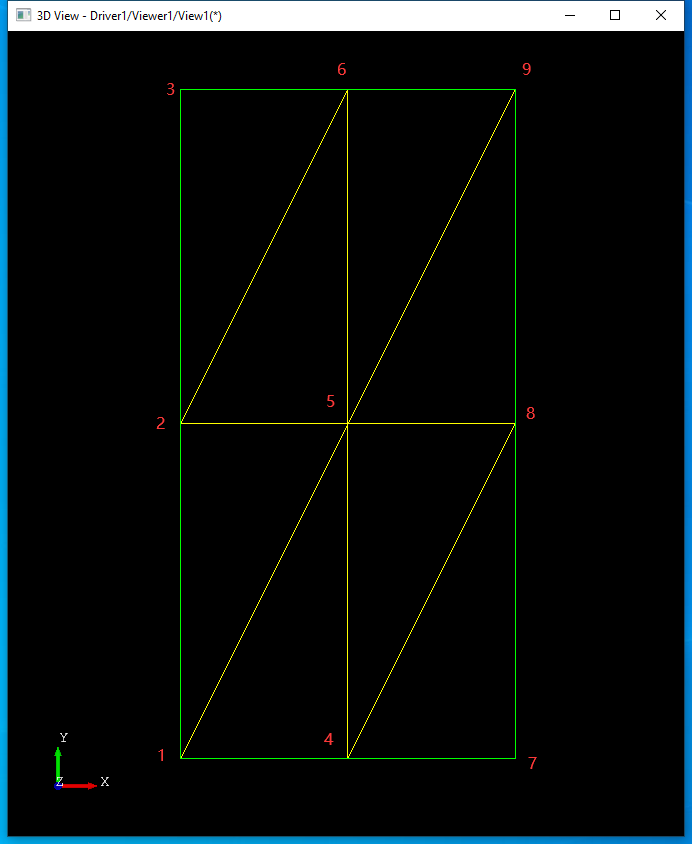
其中Triangle()函數(shù)中變量line表示參數(shù)u方向上第幾條線,代入具體的索引Index來看規(guī)律:
當(dāng)參數(shù)索引 Index為1時(shí),line為1,得到的三角形為1-4-5;
當(dāng)參數(shù)索引Index為2時(shí),line為1,得到的三角形為1-5-2;
當(dāng)參數(shù)索引Index為3時(shí),line為1,得到的三角形為2-5-6;
當(dāng)參數(shù)索引Index為4時(shí),line為1,得到的三角形為2-6-3;
當(dāng)參數(shù)索引Index為5時(shí),line為2,得到的三角形為4-7-8;
當(dāng)參數(shù)索引Index為6時(shí),line為2,得到的三角形為4-8-5;
從上可以得到生成三角形的規(guī)律,即根據(jù)索引Index計(jì)算正在處理的三角形是參數(shù)u方向上第幾條線line,生成這條線上在參數(shù)v方向上的所有的三角形。生成的三角形都是逆時(shí)針的。
下面我們看看對(duì)于一些基本曲面,這種離散網(wǎng)格算法生成的網(wǎng)格效果:
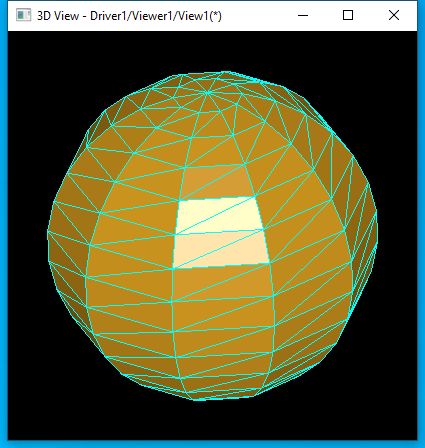
球面的離散網(wǎng)格
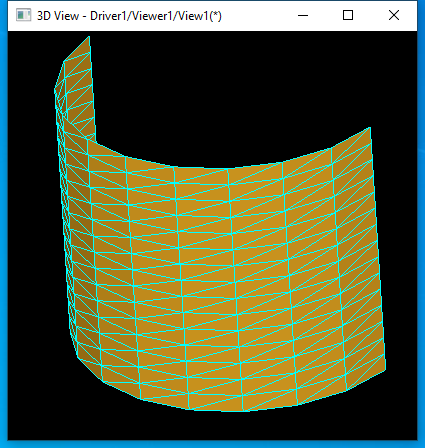
圓柱面的離散網(wǎng)格
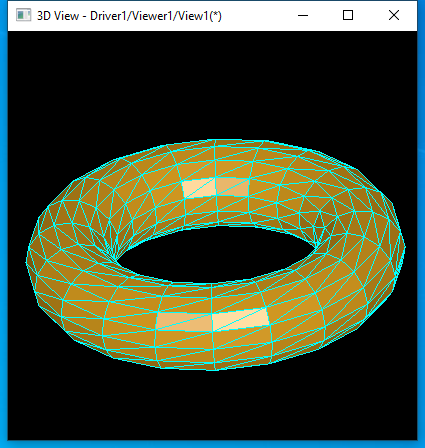
圓環(huán)面的離散網(wǎng)格
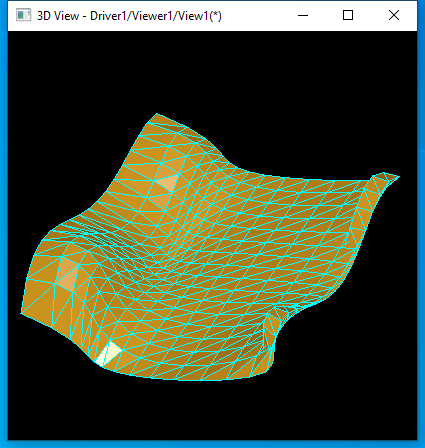
B樣條曲面
3 Conclusion
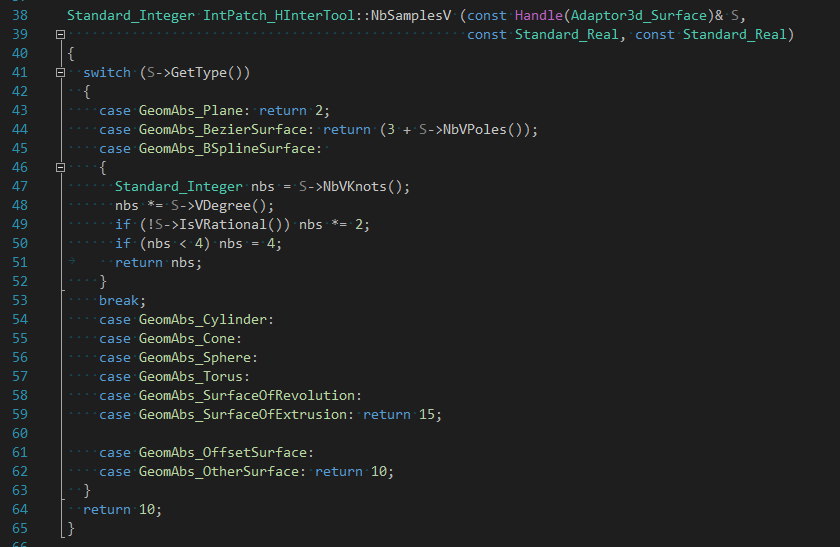
綜上所述,類IntPatch_Polyhedron中生成網(wǎng)格的算法主要依賴曲面在參數(shù)U,V上的采樣點(diǎn)數(shù)量。默認(rèn)采樣點(diǎn)數(shù)量是根據(jù)函數(shù)NbSamplesV()和NbSamplesU()生成。
也可以指定采樣點(diǎn)數(shù)量,當(dāng)采樣點(diǎn)數(shù)量越多,則生成的三角形越多,網(wǎng)格越密。當(dāng)然這種方式也可用來生成曲面的顯示數(shù)據(jù),生成速度很快,唯一的缺陷是生成顯示用網(wǎng)格的精度只能通過采樣點(diǎn)數(shù)量來控制,對(duì)于曲率變化大的曲面,若指定多的采樣點(diǎn),則會(huì)生成大量三角形,占用大量內(nèi)存空間。
附上測(cè)試代碼:
#include <TColgp_Array2OfPnt.hxx>
#include <Geom_Plane.hxx>
#include <Geom_CylindricalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_ConicalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_SphericalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_ToroidalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_BSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <GeomAdaptor_Surface.hxx>
#include <GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <IntPatch_Polyhedron.hxx>
#include <IntPatch_InterferencePolyhedron.hxx>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG2d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomAlgo.lib")
void makeSurface(Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface)& theSurface)
{
TColgp_Array2OfPnt aPoints(1, 5, 1, 5);
aPoints.SetValue(1, 1, gp_Pnt(-4, -4, 5));
aPoints.SetValue(1, 2, gp_Pnt(-4, -2, 5));
aPoints.SetValue(1, 3, gp_Pnt(-4, 0, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(1, 4, gp_Pnt(-4, 2, 5));
aPoints.SetValue(1, 5, gp_Pnt(-4, 4, 5));
aPoints.SetValue(2, 1, gp_Pnt(-2, -4, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(2, 2, gp_Pnt(-2, -2, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(2, 3, gp_Pnt(-2, 0, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(2, 4, gp_Pnt(-2, 2, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(2, 5, gp_Pnt(-2, 5, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(3, 1, gp_Pnt(0, -4, 3.5));
aPoints.SetValue(3, 2, gp_Pnt(0, -2, 3.5));
aPoints.SetValue(3, 3, gp_Pnt(0, 0, 3.5));
aPoints.SetValue(3, 4, gp_Pnt(0, 2, 3.5));
aPoints.SetValue(3, 5, gp_Pnt(0, 5, 3.5));
aPoints.SetValue(4, 1, gp_Pnt(2, -4, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(4, 2, gp_Pnt(2, -2, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(4, 3, gp_Pnt(2, 0, 3.5));
aPoints.SetValue(4, 4, gp_Pnt(2, 2, 5));
aPoints.SetValue(4, 5, gp_Pnt(2, 5, 4));
aPoints.SetValue(5, 1, gp_Pnt(4, -4, 5));
aPoints.SetValue(5, 2, gp_Pnt(4, -2, 5));
aPoints.SetValue(5, 3, gp_Pnt(4, 0, 5));
aPoints.SetValue(5, 4, gp_Pnt(4, 2, 6));
aPoints.SetValue(5, 5, gp_Pnt(4, 5, 5));
theSurface = GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface(aPoints).Surface();
}
void writeStl(const IntPatch_Polyhedron& thePolyhedron, const std::string& theFileName)
{
// Dump surface polyhedron to STL file.
std::ofstream aStlFile(theFileName);
aStlFile << "solid polyhedron" << std::endl;
// Dump triangles.
for (Standard_Integer t = 1; t <= thePolyhedron.NbTriangles(); ++t)
{
Standard_Integer aPi1 = 0;
Standard_Integer aPi2 = 0;
Standard_Integer aPi3 = 0;
thePolyhedron.Triangle(t, aPi1, aPi2, aPi3);
const gp_Pnt& aP1 = thePolyhedron.Point(aPi1);
const gp_Pnt& aP2 = thePolyhedron.Point(aPi2);
const gp_Pnt& aP3 = thePolyhedron.Point(aPi3);
aStlFile << "facet" << std::endl;
aStlFile << "outer loop" << std::endl;
aStlFile << "vertex " << aP1.X() << " " << aP1.Y() << " " << aP1.Z() << std::endl;
aStlFile << "vertex " << aP2.X() << " " << aP2.Y() << " " << aP2.Z() << std::endl;
aStlFile << "vertex " << aP3.X() << " " << aP3.Y() << " " << aP3.Z() << std::endl;
aStlFile << "endloop" << std::endl;
aStlFile << "endfacet" << std::endl;
}
aStlFile << "endsolid polyhedron" << std::endl;
aStlFile.close();
}
void testPolyhedron()
{
// Plane surface polyhedron.
Handle(Geom_Plane) aPlane = new Geom_Plane(gp::XOY());
Handle(GeomAdaptor_Surface) aSurfaceAdaptor = new GeomAdaptor_Surface(aPlane, 0.0, 10.0, 0.0, 20.0);
IntPatch_Polyhedron aPlanePolyhedron(aSurfaceAdaptor);
writeStl(aPlanePolyhedron, "d:/plane.stl");
// Spherical surface polyhedron.
Handle(Geom_SphericalSurface) aSphericalSurface = new Geom_SphericalSurface(gp::XOY(), 3.0);
aSurfaceAdaptor = new GeomAdaptor_Surface(aSphericalSurface);
IntPatch_Polyhedron aSphericalPolyhedron(aSurfaceAdaptor);
writeStl(aSphericalPolyhedron, "d:/spherical.stl");
// Cylindrical surface polyhedron.
Handle(Geom_CylindricalSurface) aCylindricalSurface = new Geom_CylindricalSurface(gp::XOY(), 5.0);
aSurfaceAdaptor = new GeomAdaptor_Surface(aCylindricalSurface, 0.0, M_PI, 0.0, 8.0);
IntPatch_Polyhedron aCylindricalPolyhedron(aSurfaceAdaptor);
writeStl(aCylindricalPolyhedron, "d:/cylindrical.stl");
// Toroidal Surface polyhedron.
Handle(Geom_ToroidalSurface) aToroidalSurface = new Geom_ToroidalSurface(gp::XOY(), 10.0, 3.0);
aSurfaceAdaptor = new GeomAdaptor_Surface(aToroidalSurface);
IntPatch_Polyhedron aToroidalPolyhedron(aSurfaceAdaptor);
writeStl(aToroidalPolyhedron, "d:/toroidal.stl");
// BSpline surface polyhedron.
Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface) aBSplineSurface;
makeSurface(aBSplineSurface);
aSurfaceAdaptor = new GeomAdaptor_Surface(aBSplineSurface);
IntPatch_Polyhedron aPolyhedron(aSurfaceAdaptor);
writeStl(aPolyhedron, "d:/bspline.stl");
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
testPolyhedron();
return 0;
}