PlaneGCS-平面幾何約束求解器用法
eryar@163.com
1 Introduction
在傳統的機械設計軟件中���,一般使用幾何約束求解器來畫草圖��,再通過對草圖進行拉伸旋轉等生成特征實現建模功能?�;趨祷瘹v史特征方式來建模的軟件繞不開幾何約束求解器,目前主流商用軟件一般使用西門子D-Cubed DCM及達索的CGM�����。開源世界也有兩款幾何約束求解器:SolveSpace和PlaneGCS���。
PlaneGCS字面意思是平面幾何約束求解器��,主要用于繪制二維草圖��。因為PlaneGCS代碼相對清晰,功能簡單��,只能處理平面幾何元素的約束�,本文主要結合示例代碼介紹PlaneGCS的使用方法,在會用的基礎上去理解源碼的實現邏輯���。
2 PlaneGCS
PlaneGCS主要包含三部分:
- 幾何元素數據結構文件:h/Geo.cpp
- 約束條件文件:h/Constraints.cpp
- 約束求解實現文件:h/GCS.cpp
其中幾何元素數據結構中定義的幾何元素如下圖所示:
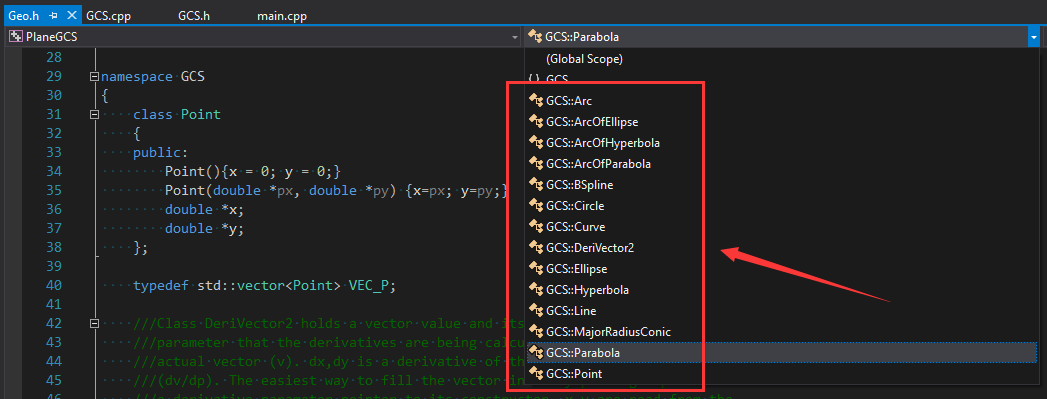
從上圖可以看到,目前支持的幾何元素有點Point�,直線Line,圓Circle�,橢圓Ellipse����,雙曲線Hyperbola����,拋物線Parabola,圓弧Arc/ArcOfEllipse/ArcOfHyperbola/ArcOfParabola���,及B樣條曲線BSpline,不過看代碼BSpline部分函數沒有實現�,應該是不支持的�����。
約束條件文件定義的約束類型如下圖所示:
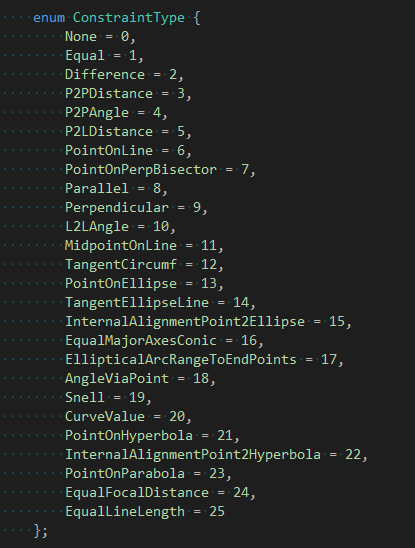
從約束求解文件中可以看到����,其中數學計算主要使用Eigen中非線性方程組求解算法和boost的圖graph算法���,從中可以推測出實現平面幾何約束求解器中需要的關鍵技術��。先掌握PlaneGCS的用法�,然后再分析其背后的實現原理細節�����。
3 Code Example
這里給出一個簡單的示例程序,先讓大家對PlaneGCS有個認識。示例程序中演示了給兩條直線加上水平和垂直約束���。為了便于查看約束后的結果��,在代碼中生成Draw Test Harness腳本文件。
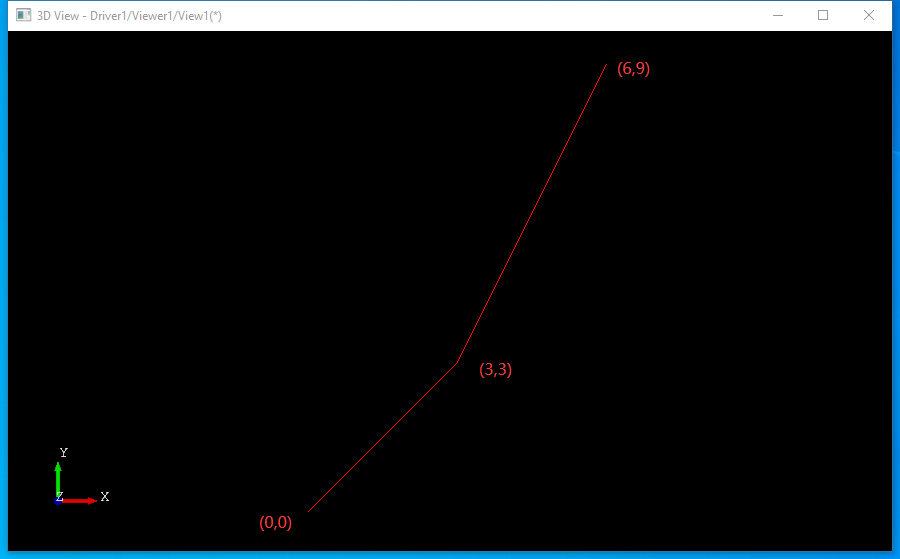
程序代碼如下所示:
/*
Copyright(C) 2023 Shing Liu(eryar@163.com)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files(the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and / or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions :
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
*/
#include "GCS.h"
#include <fstream>
void test()
{
double aPx1 = 0.0;
double aPy1 = 0.0;
double aPx2 = 3.0;
double aPy2 = 3.0;
double aPx3 = 6.0;
double aPy3 = 9.0;
GCS::VEC_pD aParameters;
aParameters.push_back(&aPx1);
aParameters.push_back(&aPy1);
aParameters.push_back(&aPx2);
aParameters.push_back(&aPy2);
aParameters.push_back(&aPx3);
aParameters.push_back(&aPy3);
GCS::Point aP1(&aPx1, &aPy1);
GCS::Point aP2(&aPx2, &aPy2);
GCS::Point aP3(&aPx3, &aPy3);
GCS::Line aLine1;
GCS::Line aLine2;
aLine1.p1 = aP1;
aLine1.p2 = aP2;
aLine2.p1 = aP2;
aLine2.p2 = aP3;
std::ofstream aTclFile("d:/gcs.tcl");
aTclFile << "# 2 lines before PlaneGCS solve" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vinit" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vertex aP1 " << aPx1 << " " << aPy1 << " 0" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vertex aP2 " << aPx2 << " " << aPy2 << " 0" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vertex aP3 " << aPx3 << " " << aPy3 << " 0" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "polyvertex aPolyline1 aP1 aP2 aP3" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vdisplay aPolyline1 " << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vsetcolor aPolyline1 RED" << std::endl;
GCS::System aSolver;
aSolver.addConstraintHorizontal(aLine1);
aSolver.addConstraintVertical(aLine2);
if (aSolver.solve(aParameters) == GCS::Success)
{
aSolver.applySolution();
aTclFile << "# 2 lines after PlaneGCS solve" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vertex aV1 " << aPx1 << " " << aPy1 << " 0" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vertex aV2 " << aPx2 << " " << aPy2 << " 0" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vertex aV3 " << aPx3 << " " << aPy3 << " 0" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "polyvertex aPolyline2 aV1 aV2 aV3" << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vdisplay aPolyline2 " << std::endl;
aTclFile << "vsetcolor aPolyline2 GREEN" << std::endl;
}
aTclFile.close();
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
test();
return 0;
}
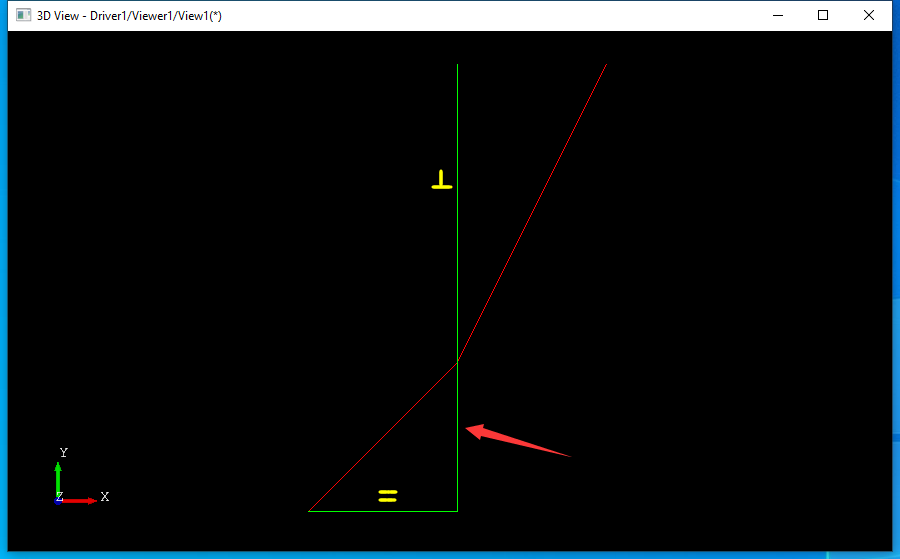
從程序代碼中可以看出PlaneGCS的使用先要定義需要計算的參數aParameters,這些參數是幾何元素中的數據,都是使用的指針���。然后將約束加入到GCS::System中����,最后代入參數調用solve函數進行求解���。求解成功后使用applySolution()函數應用求解結果��。求解結果在Draw中顯示的綠色的線如下圖所示:
4 Conclusion
本文結合示例代碼演示如何使用PlaneGCS����,主要使用了水平和垂直約束。PlaneGCS中還支持其他約束類型�����,童鞋們可以自己探索一下��。幾何造型內核和幾何約束求解器常被看作是工業CAD軟件的卡脖子技術�,開源庫一般功能不太完善���,但是用來探索背后的實現原理還是有參考借鑒意義的����。希望有更多的童鞋去了解背后的原理���,共同來提高國內三維CAD軟件開發水平��。