OpenCascade Matrix
eryar@163.com
摘要Abstract:本文對矩陣作簡要介紹,并結合代碼說明OpenCascade矩陣計算類的使用方法。
關鍵字Key Words:OpenCascade、Matrix、C++
一、引言Introduction
矩陣的研究歷史悠久,拉丁方陣和幻方在史前年代已有人研究。作為解決線性方程的工具,矩陣也有不短的歷史。1693年,微積分的發現者之一萊布尼茨建立了行列式論(theory of determinants)。1750年,克拉默又定下了克拉默法則。1800年代,高斯和威廉若爾當建立了高斯-若爾當消去法。
從其發展歷史可以看出,從行列式論的提出到克拉默法則總共歷時50多年之久,而在我們《線性代數》的課本中,也就是一章的內容,學習時間可能只有一個星期。難怪這些概念這么抽象晦澀,也是情有可原的,哈哈。不過,當理解這些概念,也就掌握了一個強大的工具,因為它也使有些計算統一、簡單。
矩陣是高等代數中的常見工具,也常見于統計分析等應用數學學科中。在物理學中,矩陣用于電路學、力學、光學和量子物理中都有應用;計算機科學中,三維變換就是使用了矩陣的線性變換。矩陣的運算是數值分析領域的重要問題。
在計算機圖形相關的軟件中,矩陣是必不可少的重要工具。如:OpenGL、DirectX中的變換都是用矩陣實現的;OpenCascade中就有矩陣計算類(math_Matrix);OpenSceneGraph中也有矩陣的計算類(osg::Matrix)等等。矩陣在計算中主要用來表達線性變換,統一三維空間中物體的位置和方向變換。
本文主要介紹OpenCascade中矩陣類的使用方法。
二、矩陣的運算 Matrix Calculation
矩陣的運算主要有矩陣的加法、數與矩陣相乘、矩陣與矩陣相乘、矩陣的轉置、方陣的行列式、共軛矩陣、逆矩陣。還有通過矩陣來求解線性方程組的解問題。
1. 矩陣的加法 Matrix Addition
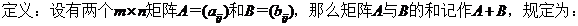
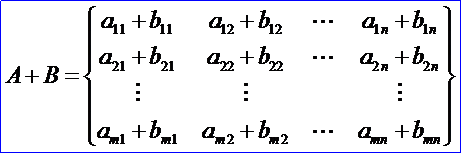
應該注意,只有當兩個矩陣是同型矩陣時,才能進行加法運算。矩陣加法滿足下列運算規律:設A、B、C都是m×n矩陣:

2. 數與矩陣相乘 Matrix Multiplication
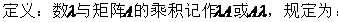

數乘矩陣滿足下列運算規律(設A、B為m×n矩陣,λ、μ為數):
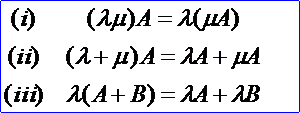
矩陣相加與矩陣相乘合起來,統稱為矩陣的線性運算。
3. 矩陣與矩陣相乘 Matrix Multiplication
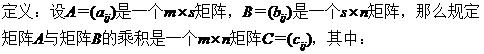
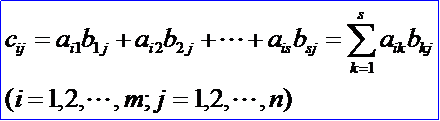
并把此乘積記作:C = AB
按此定義,一個1×s行矩陣與一個s×1列矩陣的乘積是一個1階方陣,也就是一個數:
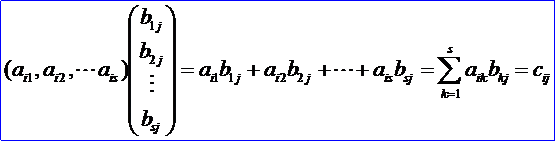
由此表明乘積矩陣AB=C的(i,j)元cij就是A的第i行與B的第j列的乘積。必須注意:只有當每一個矩陣(左矩陣)的列數等于第二個矩陣(右矩陣)的行數時,兩個矩陣才能相乘。
矩陣的乘法雖不滿足交換律,但仍滿足下列結合律和分配律(假設運算都是可行的):
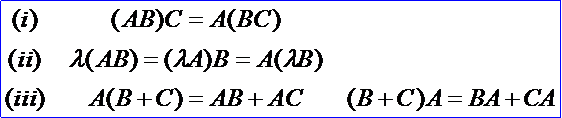
4. 矩陣的轉置 Matrix Transpose
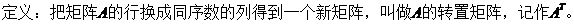
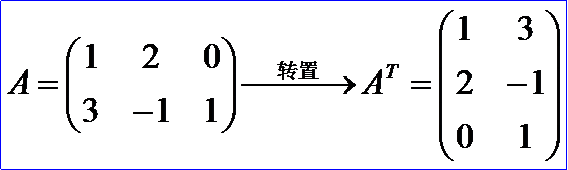
矩陣轉置也是一種運算,滿足下列運算規律(假設運算都是可行的):
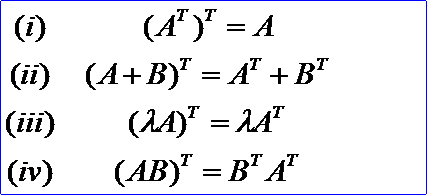
5. 方陣的行列式 Determinant of the Square Matrix

應該注意,方陣與行列式是兩個不同的概念,n階方陣是n×n個數按一定方式排列成的數表,而n階行列式是這些數(也就是數表A)按一定的運算法則所確定的一個數。
由A確定|A|的這個運算滿足下述運算規律(設A、B為n階方陣,λ為數):

6. 逆矩陣 Inverse of Matrix
定義:對于n階矩陣A,如果一個n階矩陣B,使AB=BA=E,則說矩陣A是可逆的,并把矩陣B稱為A的逆矩陣,簡稱逆陣。
方陣的逆矩陣滿足下列運算規律:

7. 線性方程組的數值解法
在自然科學和工程中有很多問題的解決都歸結為求解線性方程組或者非線性方程組的數學問題。例如,電學中的網絡問題,用最小二乘法求實驗數據的網線擬合問題,三次樣條的插值問題,用有限元素法計算結構力學中的一些問題或用差分法解橢圓型偏微分方程的邊值問題等等。
求解線性方程組的直接法主要有選主元高斯消去法、平方根法、追趕法等。如果計算過程中沒有舍入誤差,則此種方法經過有限步算術運算可求得方程組的精確解,但實際計算中由于舍入誤差的存在和影響,這種方法也只能求得方程組的近似解。目前這種方法是計算機上解低階稠密矩陣的有效方法。
高斯消去法是一個古老的求解線性方程組的方法,但由于它改進得到的選主元的高斯消去法則是目前計算機上常用的解低階稠密矩陣方程組的有效方法。
用高斯消去法解方程組的基本思想是用矩陣行的初等變換將系數矩陣化為具有簡單形式的矩陣,即三角形矩陣,再通過回代過程,求出方程組的解。
三、OpenCascade矩陣計算
在OpenCascade中,矩陣的計算類是math_Matrix,它可以有任意的行數和列數,實現了矩陣大部分的運算。以下通過程序實例來說明math_Matrix的使用方法:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
*
* File : Main.cpp
* Author : eryar@163.com
* Date : 2013-07-17 21:46
* Version : 1.0v
*
* Description : Demonstrate how to use math_Matrix class.
* 題目來自《線性代數》同濟 第四版
*
*/
#include <math_Matrix.hxx>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
math_Matrix A(1, 3, 1, 3);
math_Matrix B(1, 3, 1, 3);
math_Matrix C(1, 3, 1, 3);
// 1. Test Matrix Transpose and multiply.
// 題目來自P53習題二 第3題
// Set value of Matrix A
A.Init(1);
A(2, 3) = -1;
A(3, 2) = -1;
// Set value of Matrix B
B(1, 1) = 1; B(1, 2) = 2; B(1, 3) = 3;
B(2, 1) = -1; B(2, 2) = -2; B(2, 3) = 4;
B(3, 1) = 0; B(3, 2) = 5; B(3, 3) = 1;
C.TMultiply(A, B);
cout<<"Matrix A: "<<endl;
cout<<A<<endl;
cout<<"Matrix B: "<<endl;
cout<<B<<endl;
cout<<"Matrix C: "<<endl;
cout<<C<<endl;
// 2. Test the Determinant of the Matrix.
// 題目來自P12 例7
math_Matrix D(1, 4, 1, 4);
D(1, 1) = 3; D(1, 2) = 1; D(1, 3) = -1; D(1, 4) = 2;
D(2, 1) = -5; D(2, 2) = 1; D(2, 3) = 3; D(2, 4) = -4;
D(3, 1) = 2; D(3, 2) = 0; D(3, 3) = 1; D(3, 4) = -1;
D(4, 1) = 1; D(4, 2) = -5; D(4, 3) = 3; D(4, 4) = -3;
cout<<"Matrix D: "<<endl;
cout<<D<<endl;
cout<<"Determinant of Matrix D: "<<D.Determinant()<<endl;
// 3. Calculate Inverse of the Matrix.
// 題目來自P54 11題(3) 和P56 30題(1)
math_Matrix E(1, 3, 1, 3);
E(1, 1) = 1; E(1, 2) = 2; E(1, 3) = -1;
E(2, 1) = 3; E(2, 2) = 4; E(2, 3) = -2;
E(3, 1) = 5; E(3, 2) = -4; E(3, 3) = 1;
cout<<"Inverse of the Matrix E: "<<endl;
cout<<E.Inverse()<<endl;
// P56 30題(1)
math_Matrix F(1, 4, 1, 4);
F(1, 1) = 5; F(1, 2) = 2;
F(2, 1) = 2; F(2, 2) = 1;
F(3, 3) = 8; F(3, 4) = 3;
F(4, 3) = 5; F(4, 4) = 2;
cout<<"Inverse of the Matrix F: "<<endl;
cout<<F.Inverse()<<endl;
return 0;
}
計算結果為:
1 Matrix A:
2 math_Matrix of RowNumber = 3 and ColNumber = 3
3 math_Matrix ( 1, 1 ) = 1
4 math_Matrix ( 1, 2 ) = 1
5 math_Matrix ( 1, 3 ) = 1
6 math_Matrix ( 2, 1 ) = 1
7 math_Matrix ( 2, 2 ) = 1
8 math_Matrix ( 2, 3 ) = -1
9 math_Matrix ( 3, 1 ) = 1
10 math_Matrix ( 3, 2 ) = -1
11 math_Matrix ( 3, 3 ) = 1
12
13 Matrix B:
14 math_Matrix of RowNumber = 3 and ColNumber = 3
15 math_Matrix ( 1, 1 ) = 1
16 math_Matrix ( 1, 2 ) = 2
17 math_Matrix ( 1, 3 ) = 3
18 math_Matrix ( 2, 1 ) = -1
19 math_Matrix ( 2, 2 ) = -2
20 math_Matrix ( 2, 3 ) = 4
21 math_Matrix ( 3, 1 ) = 0
22 math_Matrix ( 3, 2 ) = 5
23 math_Matrix ( 3, 3 ) = 1
24
25 Matrix C:
26 math_Matrix of RowNumber = 3 and ColNumber = 3
27 math_Matrix ( 1, 1 ) = 0
28 math_Matrix ( 1, 2 ) = 5
29 math_Matrix ( 1, 3 ) = 8
30 math_Matrix ( 2, 1 ) = 0
31 math_Matrix ( 2, 2 ) = -5
32 math_Matrix ( 2, 3 ) = 6
33 math_Matrix ( 3, 1 ) = 2
34 math_Matrix ( 3, 2 ) = 9
35 math_Matrix ( 3, 3 ) = 0
36
37 Matrix D:
38 math_Matrix of RowNumber = 4 and ColNumber = 4
39 math_Matrix ( 1, 1 ) = 3
40 math_Matrix ( 1, 2 ) = 1
41 math_Matrix ( 1, 3 ) = -1
42 math_Matrix ( 1, 4 ) = 2
43 math_Matrix ( 2, 1 ) = -5
44 math_Matrix ( 2, 2 ) = 1
45 math_Matrix ( 2, 3 ) = 3
46 math_Matrix ( 2, 4 ) = -4
47 math_Matrix ( 3, 1 ) = 2
48 math_Matrix ( 3, 2 ) = 0
49 math_Matrix ( 3, 3 ) = 1
50 math_Matrix ( 3, 4 ) = -1
51 math_Matrix ( 4, 1 ) = 1
52 math_Matrix ( 4, 2 ) = -5
53 math_Matrix ( 4, 3 ) = 3
54 math_Matrix ( 4, 4 ) = -3
55
56 Determinant of Matrix D: 40
57 Inverse of the Matrix E:
58 math_Matrix of RowNumber = 3 and ColNumber = 3
59 math_Matrix ( 1, 1 ) = -2
60 math_Matrix ( 1, 2 ) = 1
61 math_Matrix ( 1, 3 ) = -8.88178e-017
62 math_Matrix ( 2, 1 ) = -6.5
63 math_Matrix ( 2, 2 ) = 3
64 math_Matrix ( 2, 3 ) = -0.5
65 math_Matrix ( 3, 1 ) = -16
66 math_Matrix ( 3, 2 ) = 7
67 math_Matrix ( 3, 3 ) = -1
68
69 Inverse of the Matrix F:
70 math_Matrix of RowNumber = 4 and ColNumber = 4
71 math_Matrix ( 1, 1 ) = 1
72 math_Matrix ( 1, 2 ) = -2
73 math_Matrix ( 1, 3 ) = 0
74 math_Matrix ( 1, 4 ) = 0
75 math_Matrix ( 2, 1 ) = -2
76 math_Matrix ( 2, 2 ) = 5
77 math_Matrix ( 2, 3 ) = -0
78 math_Matrix ( 2, 4 ) = -0
79 math_Matrix ( 3, 1 ) = 0
80 math_Matrix ( 3, 2 ) = 0
81 math_Matrix ( 3, 3 ) = 2
82 math_Matrix ( 3, 4 ) = -3
83 math_Matrix ( 4, 1 ) = -0
84 math_Matrix ( 4, 2 ) = -0
85 math_Matrix ( 4, 3 ) = -5
86 math_Matrix ( 4, 4 ) = 8
87
88 Press any key to continue . . .
線性方程組的計算方法請參考另一篇blog:
使用OpenCASCADE的Math功能解線性方程組
http://www.shnenglu.com/eryar/archive/2012/06/21/179629.html
四、結論 Conclusion
OpenCascade的math_Matrix實現了矩陣的大部分運算,也可以作為一個小型的C++矩陣計算庫來使用,在沒有安裝Matlab、Mathematica等軟件的情況下,可以使用這個庫進行一些計算。
另外,對《計算方法》中算法感興趣的讀者可以參考OpenCascade其中代碼的實現,加深對相關算法的理解。
五、參考文獻 Bibliography
1. 同濟大學應用數學系 線性代數 高等教育出版社 2003
2. 易大義,沈云寶,李有法 計算方法 浙江大學出版社 2002