布爾數據 邊的相交
eryar@163.com
1 Introduction
在OpenCASCADE中對于邊的相交分為三類:邊與點,邊與邊,邊與面,邊與點的相交已經歸結為點與邊的相交處理了,邊的相交主要處理邊與邊,邊與面的相交。邊與邊、邊與面的相交會引入一個新的數據結構-公共部分Common Part,用于保存重疊的公共部分數據。
2 Edge/Edge Interferences
對于兩條邊的相交是指在兩條邊的某些地方的距離小于邊的容差之和,主要分為兩種情況,一種是兩條邊只有一個交點的情況;一種是有重疊部分的情況;先看只有一個交點情況:

我們在DRAW中通過腳本構造最簡單的情況來測試。
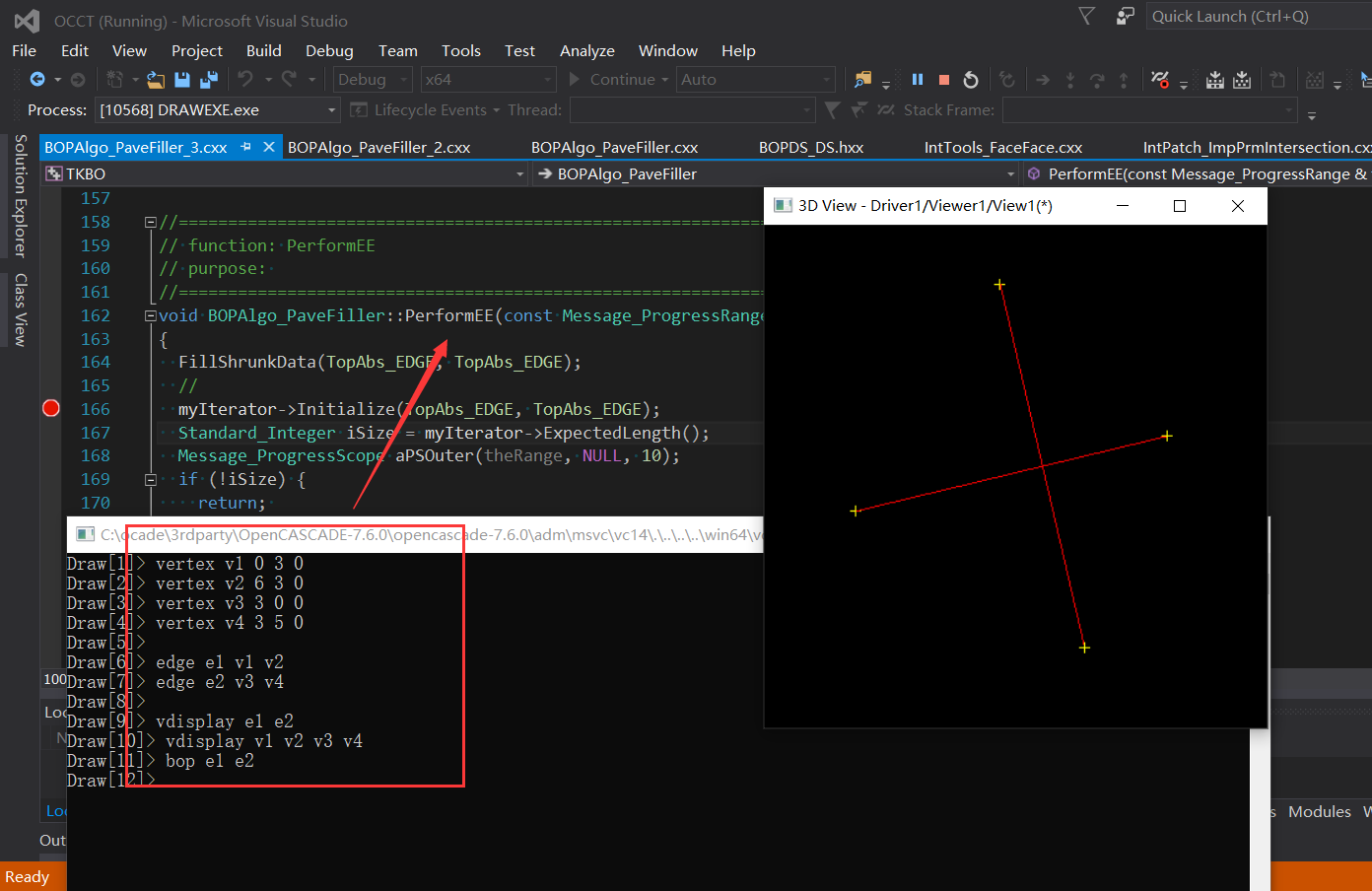
在處理邊與邊相交的函數BOPAlgo_PaveFiller::PerformEE()中,對每兩條邊調用BOPAlgo_EdgeEdge進行求交。從這里可以看到Pave Block的使用,相當于對每兩條邊上的每對Pave Block部分進行求交。這里有一些優化空間,目前是使用的兩個循環處理,可以嘗試使用BVH來提升一些性能。當每對Pave Block對應的點的索引號一致時,即每對Pave Block的端點重疊時,使用快速計算的算法來判斷是否有重疊。
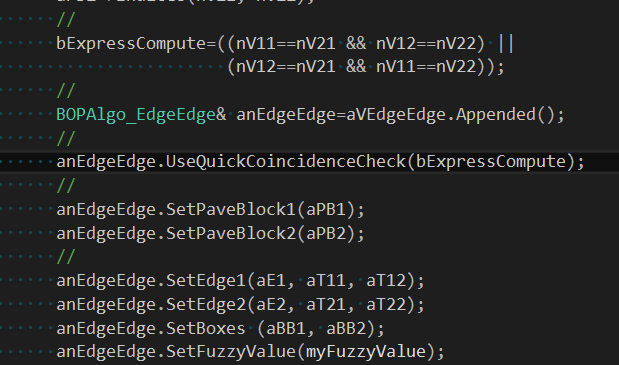
對于邊的求交結果保存到BOPDS_InterfEE中,都會保存是哪兩條邊相交及相交的公共部分。對于相交于一點的公共部分的類型為TopAbs_VERTEX,對于有重疊部分的公共部分類型為TopAbs_EDGE:

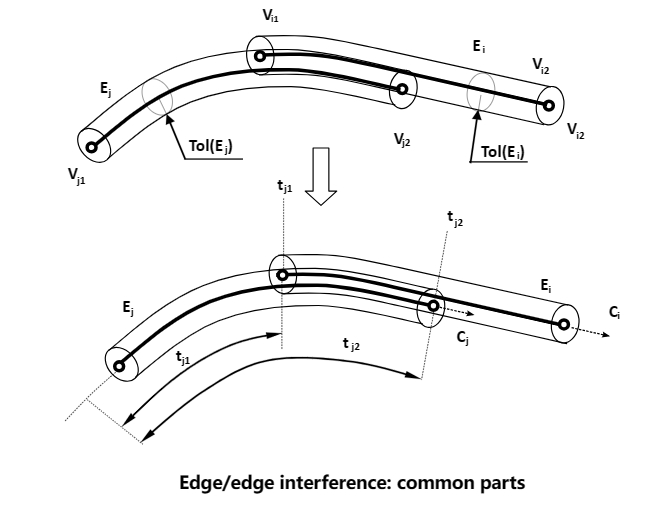
當兩邊條有重疊部分時,如下圖所示:
如何檢測兩條邊的公共部分呢?在函數IntTools_EdgeEdge::IsCoincident()中實現:
//=======================================================================
//function : IsCoincident
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
Standard_Boolean IntTools_EdgeEdge::IsCoincident()
{
Standard_Integer i, iCnt, aNbSeg, aNbP2;
Standard_Real dT, aT1, aCoeff, aTresh, aD;
Standard_Real aT11, aT12, aT21, aT22;
GeomAPI_ProjectPointOnCurve aProjPC;
gp_Pnt aP1;
//
aTresh=0.5;
aNbSeg=23;
myRange1.Range(aT11, aT12);
myRange2.Range(aT21, aT22);
//
aProjPC.Init(myGeom2, aT21, aT22);
//
dT=(aT12-aT11)/aNbSeg;
//
iCnt=0;
for(i=0; i <= aNbSeg; ++i) {
aT1 = aT11+i*dT;
myGeom1->D0(aT1, aP1);
//
aProjPC.Perform(aP1);
aNbP2=aProjPC.NbPoints();
if (!aNbP2) {
continue;
}
//
aD=aProjPC.LowerDistance();
if(aD < myTol) {
++iCnt;
}
}
//
aCoeff=(Standard_Real)iCnt/((Standard_Real)aNbSeg+1);
return aCoeff > aTresh;
}
從上述代碼可以看出,對于重疊部分的檢測是將一條邊根據檢測范圍分成23段采樣點,計算每個點到另一條邊的距離,滿足條件的采樣點的數量超過12個,基本認為是重疊的。從這里可以看出這樣檢測重疊稍微有點不嚴謹。固定采樣點數量對于小段曲線來說數量過大,對于很長的曲線來說數量又偏小,這里有待提高。如果重疊,則將公共部分的數據保存起來:

對于測試的TCL腳本不會走這個通用的判斷流程,會直接有IntTools_EdgeEdge::ComputeLineLine()函數來處理這種特殊情況:
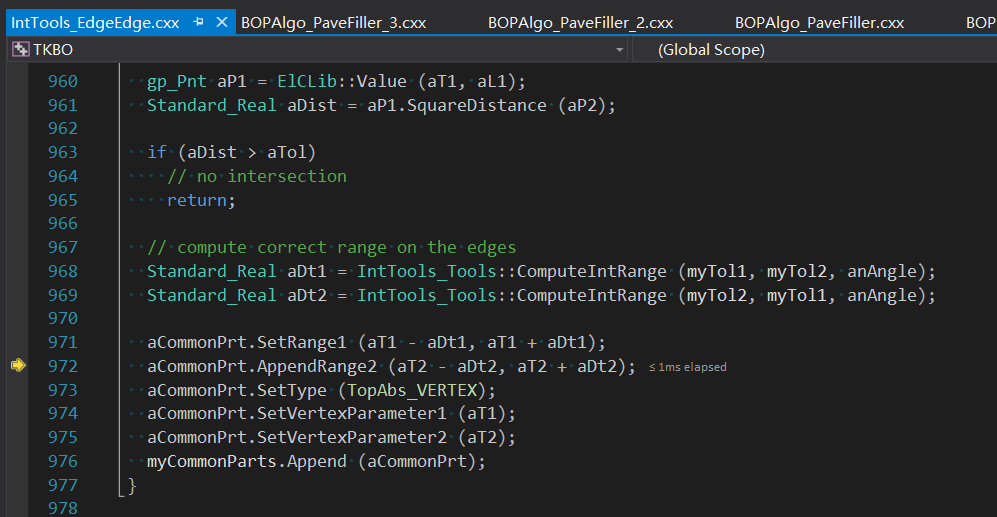
從保存的數據可以看出,公共部分的相交類型為TopAbs_VERTEX,及交點分別在兩條邊上的參數。關于有重疊部分的兩條邊相交,同學們可以自行使用DRAW腳本來測試一下。
3 Edge/Face Interferences
邊與面的相交會遇到和邊與邊相交類似的情況,即會有重疊部分Common Part。也分為兩種情況,一種情況是邊與面只有一個交點的情況,交點可能會有多個;一種情況是有重疊部分的情況。
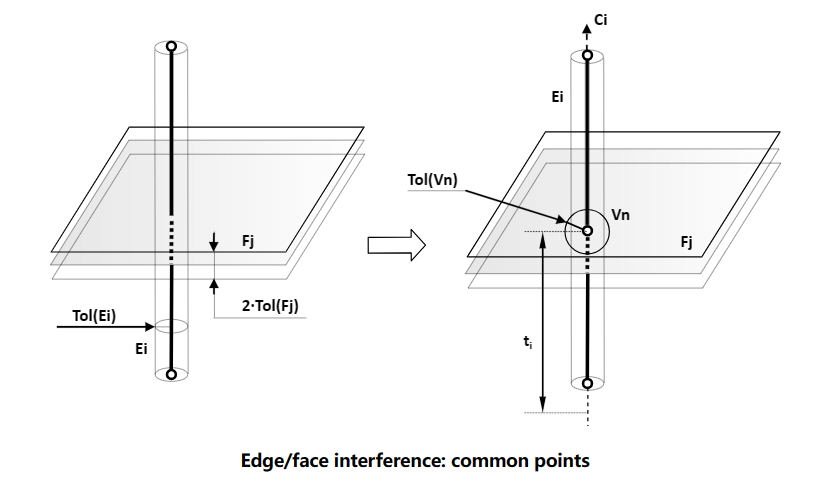
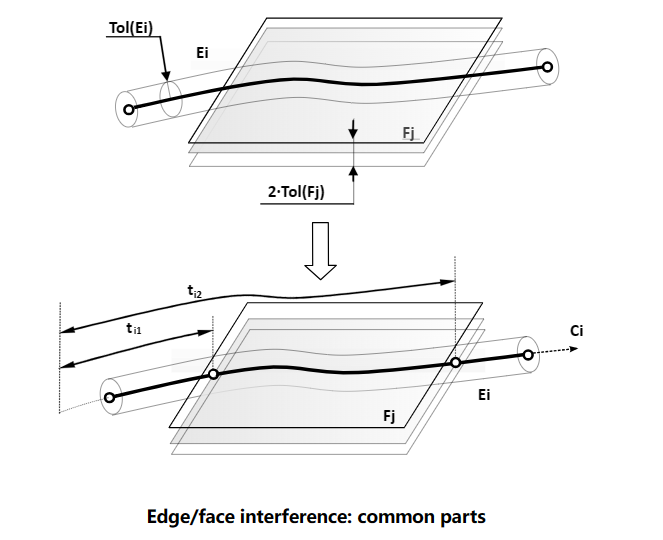
我們可以在使用腳本來測試一下重疊的情況:
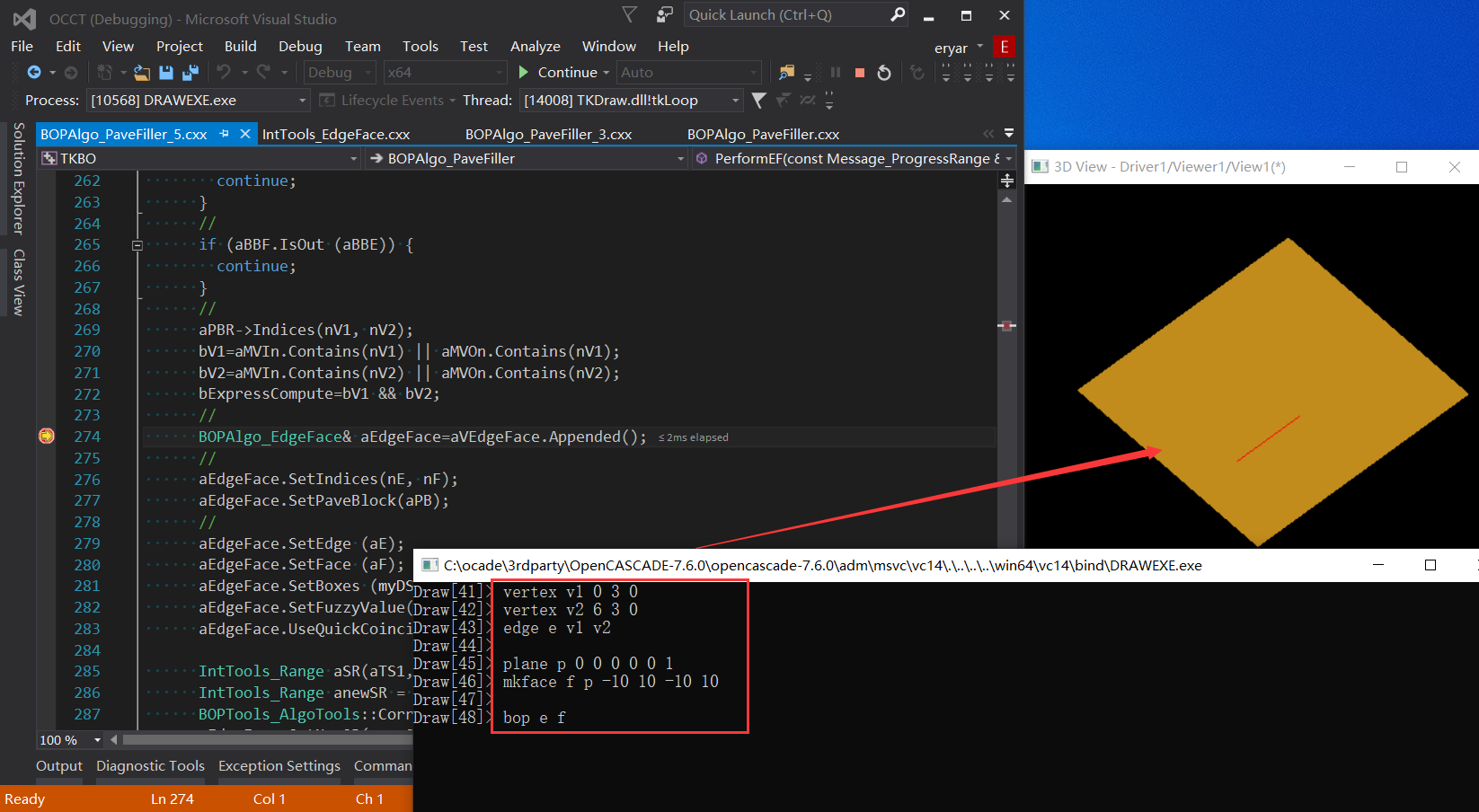
從代碼中可以看出當邊的端點在面上時,則會判斷邊與面會不會重疊Coincidence。判斷邏輯與判斷邊是否重疊類似,都是使用固定23個采樣點的方式處理,并加上定位器來判斷點是否在面上,因為面上可能會有孔洞:
//=======================================================================
//function : IsCoincident
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
Standard_Boolean IntTools_EdgeFace::IsCoincident()
{
Standard_Integer i, iCnt;
Standard_Real dT, aT, aD, aT1, aT2, aU, aV;
gp_Pnt aP;
TopAbs_State aState;
gp_Pnt2d aP2d;
//
GeomAPI_ProjectPointOnSurf& aProjector=myContext->ProjPS(myFace);
Standard_Integer aNbSeg=23;
if (myC.GetType() == GeomAbs_Line &&
myS.GetType() == GeomAbs_Plane)
aNbSeg = 2; // Check only three points for Line/Plane intersection
const Standard_Real aTresh = 0.5;
const Standard_Integer aTreshIdxF = RealToInt((aNbSeg+1)*0.25),
aTreshIdxL = RealToInt((aNbSeg+1)*0.75);
const Handle(Geom_Surface) aSurf = BRep_Tool::Surface(myFace);
aT1=myRange.First();
aT2=myRange.Last();
Standard_Real aBndShift = 0.01 * (aT2 - aT1);
//Shifting first and last curve points in order to avoid projection
//on surface boundary and rejection projection point with minimal distance
aT1 += aBndShift;
aT2 -= aBndShift;
dT=(aT2-aT1)/aNbSeg;
//
Standard_Boolean isClassified = Standard_False;
iCnt=0;
for(i=0; i <= aNbSeg; ++i) {
aT = aT1+i*dT;
aP=myC.Value(aT);
//
aProjector.Perform(aP);
if (!aProjector.IsDone()) {
continue;
}
//
aD=aProjector.LowerDistance();
if (aD > myCriteria) {
if (aD > 100. * myCriteria)
return Standard_False;
else
continue;
}
//
++iCnt;
//We classify only three points: in the begin, in the
//end and in the middle of the edge.
//However, exact middle point (when i == (aNbSeg + 1)/2)
//can be unprojectable. Therefore, it will not be able to
//be classified. Therefore, points with indexes in
//[aTreshIdxF, aTreshIdxL] range are made available
//for classification.
//isClassified == TRUE if MIDDLE point has been chosen and
//classified correctly.
if(((0 < i) && (i < aTreshIdxF)) || ((aTreshIdxL < i ) && (i < aNbSeg)))
continue;
if(isClassified && (i != aNbSeg))
continue;
aProjector.LowerDistanceParameters(aU, aV);
aP2d.SetX(aU);
aP2d.SetY(aV);
IntTools_FClass2d& aClass2d=myContext->FClass2d(myFace);
aState = aClass2d.Perform(aP2d);
if(aState == TopAbs_OUT)
return Standard_False;
if(i != 0)
isClassified = Standard_True;
}
//
const Standard_Real aCoeff=(Standard_Real)iCnt/((Standard_Real)aNbSeg+1);
return (aCoeff > aTresh);
}
求交結果與邊與邊相交類型,會保存邊與面的索引,及公共部分的數據。除了保存這些數據以外,還和點與面相交一樣,更新面上的信息FaceInfo,即有哪些邊在面上。
4 Conclusion
綜上所述,邊與邊、邊與面相交會得到公共部分Common Part,公共部分可能是點,也可能是重疊的邊。在過濾相交的邊與邊、邊與面時都有一定的優化空間,即使用BVH來加速檢測相交部分。在快速判斷邊與邊是否重疊、邊與面是否重疊部分的代碼采用固定數量的采樣點的處理方式不太嚴謹。將相交的結果及過程數據都保存到BOPDS_DS中作為后面算法使用。