性能提升-BVH層次包圍體
eryar@163.com
Abstract. OpenCASCADE provides BVH to achieve high performance in AIS of visualization module. To understand BVH usage will help us to understand many code of opencascade.
Key Words. BVH, Bounding Volume Hierarchy, LBVH, SAH Algorithm
1 Introduction
層次包圍體技術 (BVH) 指的是將所有包圍體分層逐次地再次包圍,獲得一個更大的包圍體,直到包圍住所有物體。實際上,它是一個樹形結構,因此可以仿照樹的結構,將兩個或三個小的包圍體包圍成一個更大的包圍體,以此類推。
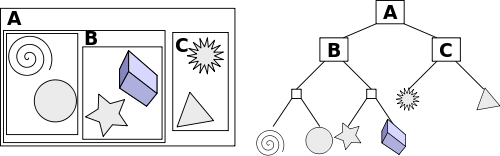
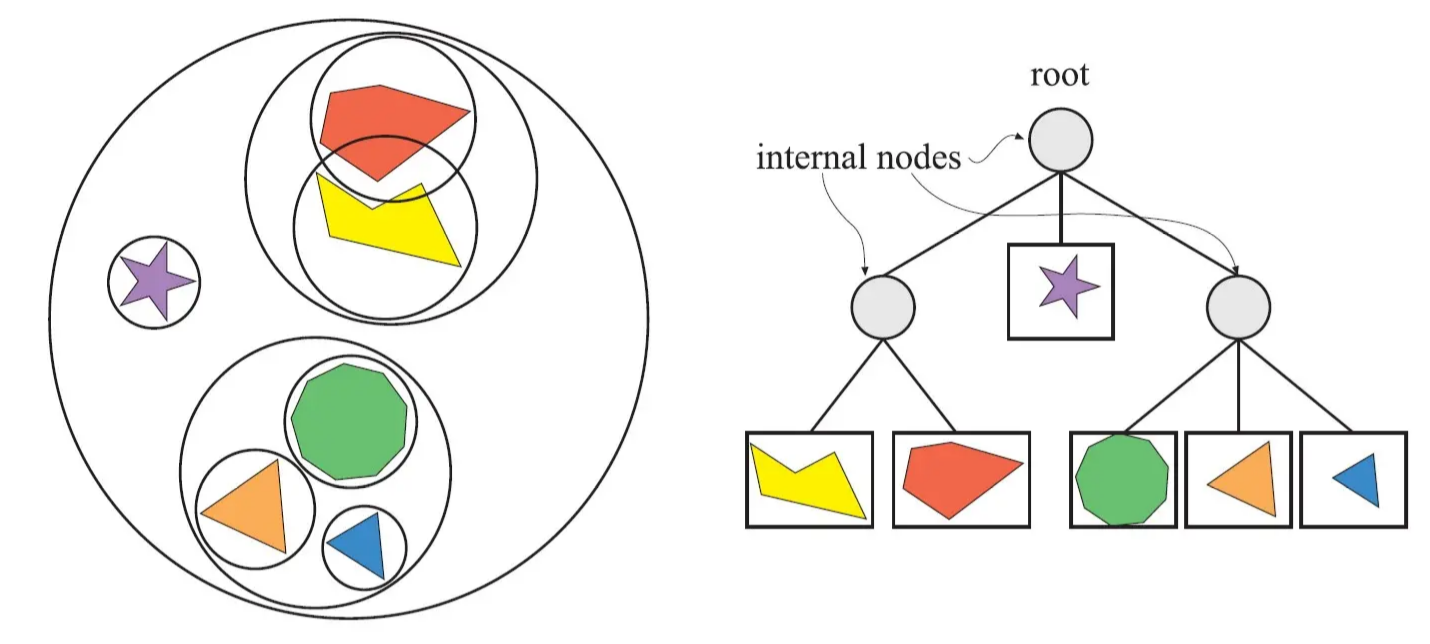
BVH是一種以物體BV為基礎進行劃分的結構。它由根節(jié)點、內部節(jié)點和葉子節(jié)點組成。其中葉子節(jié)點存放物體,每個非葉子節(jié)點都有包圍體,父節(jié)點可以把子節(jié)點包圍起來。每個非葉子節(jié)點的包圍體大小,是它所包含的所有物體的包圍體的總和,所以它在空間上比較緊湊,非常適用于需要大量求相交測試的應用場景,如光線追蹤、碰撞檢測、射線相交測試之類的應用場合中。
BVH在OpenCASCADE中也有廣泛地應用,如開源版本中的模型快速碰撞檢測,使用類BRepExtrema_ShapeProximity. 模型選擇操作,光線跟蹤等算法中都有應用。在
https://www.cnblogs.com/opencascade/p/6804446.html
中介紹如何遍歷BVH樹,本文主要介紹BVH使用方法。
2 BVH
OpenCASCADE中的BVH是相對獨立的一個包,是作者根據論文實現(xiàn)的純C++版本移植過來的。在DRAW中的QA品質保證Bugs中提供了BVH的使用示例。
2.1 BVH_Set
首先要定義層次包圍盒的集合Set來構造BVH樹,從BVH_Set基類派生的集合是可以直接使用的:
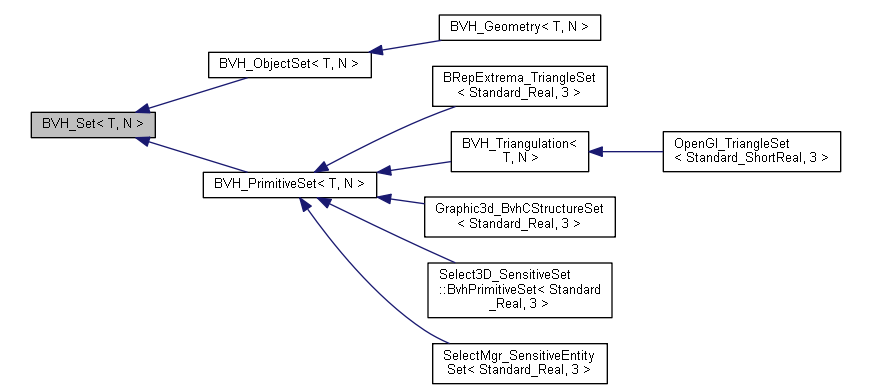
如可以直接使用BVH_Triangulation,也可以直接使用BVH_BoxSet:

從這些類名中,我們可以看出在求模型間極值距離Extrema,三維可視化Graphic3d及Select3D拾取及布爾操作BOPTools中都有BVH的應用。
將元素通過Add函數(shù)添加到BVH集合后,調用BVH()函數(shù)就可以構造BVH樹。
2.2 BVH_Traverse
對于單個BVH的遍歷提供類BVH_Traverse,一般的應用場景如求距離一點P最近的模型,或者位于某個空間范圍內的所有模型。代碼如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : ShapeSelector
//purpose : Implement the simplest shape's selector
//=======================================================================
class ShapeSelector :
public BVH_Traverse <Standard_Real, 3, BVH_BoxSet <Standard_Real, 3, TopoDS_Shape>, Standard_Boolean>
{
public:
//! Constructor
ShapeSelector() {}
//! Sets the Box for selection
void SetBox (const Bnd_Box& theBox)
{
myBox = Bnd_Tools::Bnd2BVH (theBox);
}
//! Returns the selected shapes
const NCollection_List<TopoDS_Shape>& Shapes () const { return myShapes; }
public:
//! Defines the rules for node rejection by bounding box
virtual Standard_Boolean RejectNode (const BVH_Vec3d& theCornerMin,
const BVH_Vec3d& theCornerMax,
Standard_Boolean& theIsInside) const Standard_OVERRIDE
{
Standard_Boolean hasOverlap;
theIsInside = myBox.Contains (theCornerMin, theCornerMax, hasOverlap);
return !hasOverlap;
}
//! Defines the rules for leaf acceptance
virtual Standard_Boolean AcceptMetric (const Standard_Boolean& theIsInside) const Standard_OVERRIDE
{
return theIsInside;
}
//! Defines the rules for leaf acceptance
virtual Standard_Boolean Accept (const Standard_Integer theIndex,
const Standard_Boolean& theIsInside) Standard_OVERRIDE
{
if (theIsInside || !myBox.IsOut (myBVHSet->Box (theIndex)))
{
myShapes.Append (myBVHSet->Element (theIndex));
return Standard_True;
}
return Standard_False;
}
protected:
BVH_Box <Standard_Real, 3> myBox; //!< Selection box
NCollection_List <TopoDS_Shape> myShapes; //!< Selected shapes
};
主要是從類BVH_Traverse派生并重寫兩個虛函數(shù)RejectNode()和Accept(),即在RejectNode()中定義排除結點的規(guī)則,在Accept()中處理滿足條件的情況。
2.3 BVH_PairTraverse
對于兩個BVH的遍歷提供類BVH_PairTraverse,一般的應用場景有求兩個Mesh之間的最近距離,判斷兩個Mesh之間是否有碰撞等。
//=======================================================================
//function : MeshMeshDistance
//purpose : Class to compute the distance between two meshes
//=======================================================================
class MeshMeshDistance : public BVH_PairDistance<Standard_Real, 3, BVH_BoxSet<Standard_Real, 3, Triangle>>
{
public:
//! Constructor
MeshMeshDistance() {}
public:
//! Defines the rules for leaf acceptance
virtual Standard_Boolean Accept (const Standard_Integer theIndex1,
const Standard_Integer theIndex2) Standard_OVERRIDE
{
const Triangle& aTri1 = myBVHSet1->Element (theIndex1);
const Triangle& aTri2 = myBVHSet2->Element (theIndex2);
Standard_Real aDistance = TriangleTriangleSqDistance (aTri1._Node1, aTri1._Node2, aTri1._Node3,
aTri2._Node1, aTri2._Node2, aTri2._Node3);
if (aDistance < myDistance)
{
myDistance = aDistance;
return Standard_True;
}
return Standard_False;
}
};
主要也是從BVH_PairTraverse派生并重寫兩個虛函數(shù)RejectNode()和Accept()。
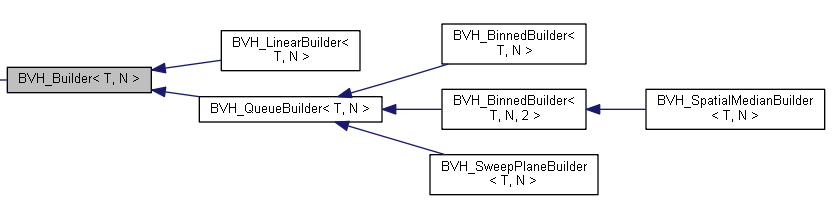
2.4 BVH_Builder
關于BVH的構造提供多種Builder,默認是使用基于SAH算法的BVH_BinnedBuilder來構造BVH樹,如果要切換不同的構造器,可以在BVH集合的構造函數(shù)中傳入一個。
下面給出求兩個Mesh之間最近距離的示例代碼:
// Define BVH Builder
opencascade::handle <BVH_LinearBuilder <Standard_Real, 3> > aLBuilder =
new BVH_LinearBuilder <Standard_Real, 3>();
// Create the ShapeSet
opencascade::handle <BVH_BoxSet <Standard_Real, 3, Triangle> > aTriangleBoxSet[2];
for (Standard_Integer i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
aTriangleBoxSet[i] = new BVH_BoxSet <Standard_Real, 3, Triangle> (aLBuilder);
TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape aMapShapes;
TopExp::MapShapes (aShape[i], TopAbs_FACE, aMapShapes);
for (Standard_Integer iS = 1; iS <= aMapShapes.Extent(); ++iS)
{
const TopoDS_Face& aF = TopoDS::Face (aMapShapes(iS));
TopLoc_Location aLoc;
const Handle(Poly_Triangulation)& aTriangulation = BRep_Tool::Triangulation(aF, aLoc);
const int aNbTriangles = aTriangulation->NbTriangles();
for (int iT = 1; iT <= aNbTriangles; ++iT)
{
const Poly_Triangle aTriangle = aTriangulation->Triangle (iT);
// Nodes indices
Standard_Integer id1, id2, id3;
aTriangle.Get (id1, id2, id3);
const gp_Pnt aP1 = aTriangulation->Node (id1).Transformed (aLoc.Transformation());
const gp_Pnt aP2 = aTriangulation->Node (id2).Transformed (aLoc.Transformation());
const gp_Pnt aP3 = aTriangulation->Node (id3).Transformed (aLoc.Transformation());
BVH_Vec3d aBVHP1 (aP1.X(), aP1.Y(), aP1.Z());
BVH_Vec3d aBVHP2 (aP2.X(), aP2.Y(), aP2.Z());
BVH_Vec3d aBVHP3 (aP3.X(), aP3.Y(), aP3.Z());
BVH_Box<Standard_Real, 3> aBox;
aBox.Add (aBVHP1);
aBox.Add (aBVHP2);
aBox.Add (aBVHP3);
aTriangleBoxSet[i]->Add (Triangle (aBVHP1, aBVHP2, aBVHP3), aBox);
}
}
// Build BVH
aTriangleBoxSet[i]->Build();
}
// Initialize selector
MeshMeshDistance aDistTool;
// Select the elements
aDistTool.SetBVHSets (aTriangleBoxSet[0].get(), aTriangleBoxSet[1].get());
Standard_Real aSqDist = aDistTool.ComputeDistance();
if (!aDistTool.IsDone())
std::cout << "Not Done" << std::endl;
else
theDI << "Distance " << sqrt (aSqDist) << "\n";
3 Conclusion
準確、穩(wěn)定、高效是高品質幾何內核的目標,我們在開發(fā)軟件時,也要時刻追求這個目標。而BVH層次包圍盒技術是提升性能的一種方式,理解BVH的使用,我們可以理解opencascade中快速求極值Extrema,交互選擇SelectMgr等很多代碼。甚至我們也可以參與貢獻,如將
Standard_Boolean BRepExtrema_Poly::Distance (const TopoDS_Shape& S1, const TopoDS_Shape& S2,
gp_Pnt& P1, gp_Pnt& P2, Standard_Real& dist)
這個O(N^2)的改造成BVH的來對比一下性能。