OpenCASCADE Chamfer 2D
eryar@163.com
二維的倒角Chamfer功能可以將兩個不平行的曲線進行倒角。如下圖所示為QCAD中進行倒角的效果圖:選擇要倒角的兩個邊,及設置兩個邊上的倒角距離。
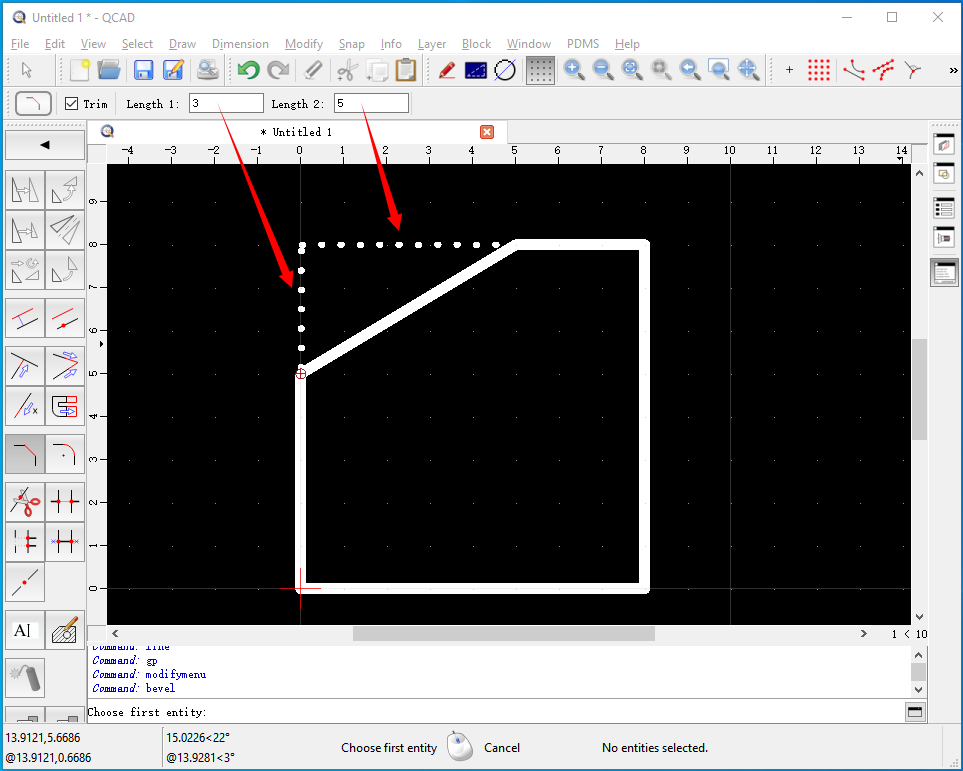
在OpenCASCADE中也提供了這個二維曲線倒角功能,使用Tcl腳本在DRAW中顯示如下:
polyline p 0 0 0 10 0 0 10 10 0
chamfer2d r p 3 5
vdisplay r

在源文件BRepTest_Fillet2DCommands.cxx中找到命令chamfer2d的實現:
//=======================================================================
//function : chamfer2d
//purpose : Chamfer 2d.
//usage : chamfer2d result wire (or edge1 edge2) length1 length2
//=======================================================================
static Standard_Integer chamfer2d(Draw_Interpretor& di, Standard_Integer n, const char** a)
{
if (n != 5 && n != 6)
{
di << "Usage : chamfer2d result wire (or edge1 edge2) length1 length2";
return 1;
}
TopoDS_Shape W;
TopoDS_Shape E1, E2;
if (n == 6)
{
// Get the edges.
E1 = DBRep::Get(a[2], TopAbs_EDGE, Standard_True);
E2 = DBRep::Get(a[3], TopAbs_EDGE, Standard_True);
}
else
{
W = DBRep::Get(a[2], TopAbs_WIRE, Standard_True);
}
// Get the lengths.
const Standard_Real length1 = (n == 6) ? Atof(a[4]) : Atof(a[3]);
const Standard_Real length2 = (n == 6) ? Atof(a[5]) : Atof(a[4]);
// Algo.
ChFi2d_ChamferAPI algo;
if (n == 6)
{
const TopoDS_Edge& e1 = TopoDS::Edge(E1);
const TopoDS_Edge& e2 = TopoDS::Edge(E2);
algo.Init(e1, e2);
}
else
{
const TopoDS_Wire& w = TopoDS::Wire(W);
algo.Init(w);
}
// Prepare the chamfer.
algo.Perform();
// Get the result.
TopoDS_Edge M1, M2; // modified E1 and E2
TopoDS_Edge chamfer = algo.Result(M1, M2, length1, length2);
if (chamfer.IsNull())
{
di << "Error: the algrithm produced no result.";
return 1;
}
if (n == 6)
{
// Set result for DRAW.
DBRep::Set(a[1], chamfer);
// Update neighbour edges in DRAW.
DBRep::Set(a[2], M1);
DBRep::Set(a[3], M2);
}
else // recreate the wire using the chamfer
{
BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire mkWire(M1, chamfer, M2);
if (mkWire.IsDone())
DBRep::Set(a[1], mkWire.Wire());
else
DBRep::Set(a[1], chamfer);
}
return 0;
}
從上述源碼可以看出,二維曲線倒角功能主要是由類ChFi2d_ChamferAPI實現。OpenCASCADE中的算法類的大致套路就是:
l Init():初始化:數據輸入。給定幾種條件的初始化函數,對應幾種情況的數據輸入。
l Perform():執行計算。根據輸入數據,計算出結果;
l Result()/Get():得到計算結果。
二維曲線的倒角功能是相對簡單的功能,所以找到類ChFi2d_ChamferAPI中源碼看看實現過程:
// Constructs a chamfer edge.
// Returns true if the edge is constructed.
Standard_Boolean ChFi2d_ChamferAPI::Perform()
{
myCurve1 = BRep_Tool::Curve(myEdge1, myStart1, myEnd1);
myCurve2 = BRep_Tool::Curve(myEdge2, myStart2, myEnd2);
// searching for common points
if (myCurve1->Value(myStart1).IsEqual(myCurve2->Value(myEnd2), Precision::Confusion()))
{
myCommonStart1 = true;
myCommonStart2 = false;
}
else
{
if (myCurve1->Value(myEnd1).IsEqual(myCurve2->Value(myStart2), Precision::Confusion()))
{
myCommonStart1 = false;
myCommonStart2 = true;
}
else
{
if (myCurve1->Value(myEnd1).IsEqual(myCurve2->Value(myEnd2), Precision::Confusion()))
{
myCommonStart1 = false;
myCommonStart2 = false;
}
else
{
myCommonStart1 = true;
myCommonStart2 = true;
}
}
}
return Standard_True;
}
執行計算函數Perform中,根據邊EDGE中的曲線數據,判斷兩個曲線的端點處是不是相連接的,并記錄下連接狀態:是首首連接、首尾連接等。這里面判斷兩個點是不是相等使用的gp_Pnt的IsEqual()函數,這個是根據兩個點之間的距離來判斷的,需要計算出兩個點之間的距離。這里可以使用距離的平方來判斷SquareDistance來判斷兩個點是不是相等,可以提高性能。因為計算距離需要要開方,開方比較耗時。關于開方的數值算法,還有個傳奇故事:一個Sqrt函數引發的血案 https://www.cnblogs.com/pkuoliver/archive/2010/10/06/sotry-about-sqrt.html
// Returns the result (chamfer edge, modified edge1, modified edge2).
TopoDS_Edge ChFi2d_ChamferAPI::Result(TopoDS_Edge& theEdge1, TopoDS_Edge& theEdge2,
const Standard_Real theLength1, const Standard_Real theLength2)
{
TopoDS_Edge aResult;
if (Abs(myEnd1 - myStart1) < theLength1)
return aResult;
if (Abs(myEnd2 - myStart2) < theLength2)
return aResult;
Standard_Real aCommon1 = (myCommonStart1?myStart1:myEnd1) + (((myStart1 > myEnd1)^myCommonStart1)?theLength1:-theLength1);
Standard_Real aCommon2 = (myCommonStart2?myStart2:myEnd2) + (((myStart2 > myEnd2)^myCommonStart2)?theLength2:-theLength2);
// make chamfer edge
GC_MakeLine aML(myCurve1->Value(aCommon1), myCurve2->Value(aCommon2));
BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge aBuilder(aML.Value(), myCurve1->Value(aCommon1), myCurve2->Value(aCommon2));
aResult = aBuilder.Edge();
// divide first edge
BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge aDivider1(myCurve1, aCommon1, (myCommonStart1?myEnd1:myStart1));
theEdge1 = aDivider1.Edge();
// divide second edge
BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge aDivider2(myCurve2, aCommon2, (myCommonStart2?myEnd2:myStart2));
theEdge2 = aDivider2.Edge();
return aResult;
}
這個代碼很好理解,根據Perform()函數中計算到的相連狀態,再結合參數曲線計算出倒角得到的線aResult,及倒角后的兩條邊。
二維曲線倒角算法相對簡單,在理解二維曲線倒角的基礎上再去深入理解三維倒角原理。
因為OpenCASCADE的BREP結構中沒有保存從Vertex到Edger的關系,所以查找兩條邊EDGE的相連關系時只能從幾何點之間的距離來處理。
對于距離的比較,能直接用平方距離比較的情況下盡量避免開方,可以提高性能。
為了方便大家在移動端也能看到我的博文和討論交流,現已注冊微信公眾號,歡迎大家掃描下方二維碼關注。
