OpenCASCADE 參數曲面面積
eryar@163.com
Abstract. 本文介紹了參數曲面的第一基本公式�,并應用曲面的第一基本公式����,結合OpenCASCADE中計算多重積分的類�,對任意參數曲面的面積進行計算。
Key Words. Parametric Curve, Parametric Surface, Gauss Integration, Global Properties
1.Introduction
我們知道一元函數y=f(x)的圖像是一條曲線,二元函數z=f(x,y)的圖像是一張曲面�。但是����,把曲線曲面表示成參數方程則更加便利于研究����,這種表示方法首先是由歐洲瑞士數學家Euler引進的。例如,在空間中的一條曲線可以表示為三個一元函數:
X=x(t), Y=y(t), Z=z(t)
在向量的概念出現后����,空間中的一條曲線可以自然地表示為一個一元向量函數:
r=r(t)=(x(t), y(t), z(t))
用向量函數來表示曲線和曲面后��,使曲線曲面一些量的計算方式比較統一。如曲線可以表示為一元向量函數��,曲面可以表示為二元向量函數�。
本文結合OpenCASCADE來介紹參數曲線曲面積分分別計算曲線弧長和曲面的面積。結合《微分幾何》來更好地理解曲線曲面相關知識�。
2.Curve Natural Parametric Equations
設曲線C的參數方程是r=r(t)�,命:
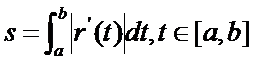
則s是該曲線的一個不變量����,即它與空間中的坐標系的選擇無關,也與該曲線的參數變換無關。前者是因為在笛卡爾直角坐標變換下��,切向量的長度|r’(t)|是不變的��,故s不變�。關于后者可以通過積分的變量的替換來證明�,設參數變換是:
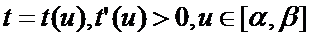
并且
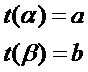
因此
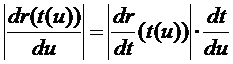
根據積分的變量替換公式有:
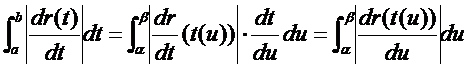
不變量s的幾何意義就是曲線段的弧長。這說明曲線參數t可以是任意的,但選擇不同的參數得到的參數方程會有不同�,但是曲線段的弧長是不變的��。以曲線弧長作為曲線方程的參數,這樣的方程稱為曲線的自然參數方程Natural Parametric Equations。
由曲線的參數方程可知�,曲線弧長的計算公式為:
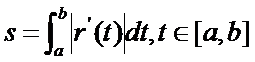
幾何意義就是在每個微元處的切向量的長度求和�。
3.Gauss Integration for Arc Length
曲線弧長的計算就是一元函數的積分�。OpenCASCADE中是如何計算任意曲線弧長的呢��?直接找到相關的源碼列舉如下:(在類CPnts_AbscissaPoint中)
// auxiliary functions to compute the length of the derivative
static Standard_Real f3d(const Standard_Real X, const Standard_Address C)
{
gp_Pnt P;
gp_Vec V;
((Adaptor3d_Curve*)C)->D1(X,P,V);
return V.Magnitude();
}
static Standard_Real f2d(const Standard_Real X, const Standard_Address C)
{
gp_Pnt2d P;
gp_Vec2d V;
((Adaptor2d_Curve2d*)C)->D1(X,P,V);
return V.Magnitude();
}
//==================================================================
//function : Length
//purpose : 3d with parameters
//==================================================================
Standard_Real CPnts_AbscissaPoint::Length(const Adaptor3d_Curve& C,
const Standard_Real U1,
const Standard_Real U2)
{
CPnts_MyGaussFunction FG;
//POP pout WNT
CPnts_RealFunction rf = f3d;
FG.Init(rf,(Standard_Address)&C);
// FG.Init(f3d,(Standard_Address)&C);
math_GaussSingleIntegration TheLength(FG, U1, U2, order(C));
if (!TheLength.IsDone()) {
throw Standard_ConstructionError();
}
return Abs(TheLength.Value());
}
//==================================================================
//function : Length
//purpose : 2d with parameters
//==================================================================
Standard_Real CPnts_AbscissaPoint::Length(const Adaptor2d_Curve2d& C,
const Standard_Real U1,
const Standard_Real U2)
{
CPnts_MyGaussFunction FG;
//POP pout WNT
CPnts_RealFunction rf = f2d;
FG.Init(rf,(Standard_Address)&C);
// FG.Init(f2d,(Standard_Address)&C);
math_GaussSingleIntegration TheLength(FG, U1, U2, order(C));
if (!TheLength.IsDone()) {
throw Standard_ConstructionError();
}
return Abs(TheLength.Value());
}
上述代碼的意思是直接對曲線的一階導數的長度求積分�,即是弧長��。OpenCASCADE的代碼寫得有點難懂�,根據意思把對三維曲線求弧長的代碼改寫下����,更便于理解:
//! Function for curve length evaluation.
class math_LengthFunction : public math_Function
{
public:
math_LengthFunction(const Handle(Geom_Curve)& theCurve)
: myCurve(theCurve)
{
}
virtual Standard_Boolean Value(const Standard_Real X, Standard_Real& F)
{
gp_Pnt aP;
gp_Vec aV;
myCurve->D1(X, aP, aV);
F = aV.Magnitude();
return Standard_True;
}
private:
Handle(Geom_Curve) myCurve;
};
4.First Fundamental Form of a Surface
曲面參數方程是個二元向量函數。根據《微分幾何》中曲面的第一基本公式(First Fundamental Form of a Surface)可知,曲面上曲線的表達式為:
r=r(u(t), v(t)) = (x(t), y(t), z(t))
若以s表示曲面上曲線的弧長,則由復合函數求導公式可得弧長微分公式:
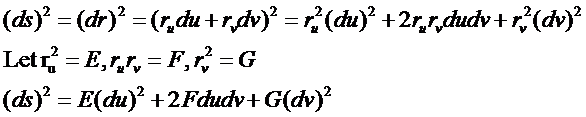
在古典微分幾何中,上式稱為曲面的第一基本公式��,E��、F��、G稱為第一基本量。在曲面上����,每一點的第一基本量與參數化無關�。
利用曲面第一基本公式可以用于計算曲面的面積��。參數曲面上與u,v參數空間的元素dudv對應的面積元為:

由參數曲面法向的計算可知�,曲面的面積元素即為u,v方向上的偏導數的乘積的模�。
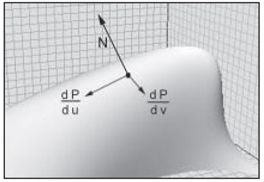
其幾何意義可以理解為參數曲面的面積微元是由u,v方向的偏導數的向量圍成的一個四邊形的面積,則整個曲面的面積即是對面積元素求積分�。由于參數曲面有兩個參數��,所以若要計算曲面的面積,只需要對面積元素計算二重積分即可����。
5.Gauss Integration for Area
OpenCASCADE的math包中提供了多重積分的計算類math_GaussMultipleIntegration�,由類名可知積分算法采用了Gauss積分算法����。下面通過具體代碼來說明OpenCASCADE中計算曲面積分的過程。要計算積分�,先要定義被積函數��。因為參數曲面與參數曲線不同�,參數曲線只有一個參數,而參數曲面有兩個參數����,所以是一個多元函數����。
//! 2D variable function for surface area evaluation.
class math_AreaFunction : public math_MultipleVarFunction
{
public:
math_AreaFunction(const Handle(Geom_Surface)& theSurface)
: mySurface(theSurface)
{
}
virtual Standard_Integer NbVariables() const
{
return 2;
}
virtual Standard_Boolean Value(const math_Vector& X, Standard_Real& Y)
{
gp_Pnt aP;
gp_Vec aDu;
gp_Vec aDv;
mySurface->D1(X(1), X(2), aP, aDu, aDv);
Y = aDu.Crossed(aDv).Magnitude();
return Standard_True;
}
private:
Handle(Geom_Surface) mySurface;
};
由于參數曲面是多元函數,所以從類math_MultipleVarFunction派生��,并在虛函數NbVariables()中說明有兩個變量����。在虛函數Value()中計算面積元素的值,即根據曲面第一基本公式中面積元素的定義�,對參數曲面求一階導數��,計算兩個偏導數向量的叉乘的模。
有了被積函數�,只需要在定義域對其計算二重積分�,相應代碼如下所示:
void evalArea(const Handle(Geom_Surface)& theSurface, const math_Vector& theLower, const math_Vector& theUpper)
{
math_IntegerVector aOrder(1, 2, math::GaussPointsMax());
math_AreaFunction aFunction(theSurface);
math_GaussMultipleIntegration anIntegral(aFunction, theLower, theUpper, aOrder);
if (anIntegral.IsDone())
{
anIntegral.Dump(std::cout);
}
}
通過theLower和theUpper指定定義域����,由于采用了Gauss-Legendre算法計算二重積分,所以需要指定階數����,且階數越高積分結果精度越高�,這里使用了OpenCASCADE中最高的階數����。
下面通過對基本曲面的面積計算來驗證結果的正確性,并將計算結果和OpenCASCADE中計算面積的類BRepGProp::SurfaceProperties()結果進行對比�。
6.Elementary Surface Area Test
下面通過對OpenCASCADE中幾個初等曲面的面積進行計算����,代碼如下所示:
/*
Copyright(C) 2017 Shing Liu(eryar@163.com)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files(the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and / or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions :
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
*/
#include <gp_Pnt.hxx>
#include <gp_Vec.hxx>
#include <math.hxx>
#include <math_Function.hxx>
#include <math_MultipleVarFunction.hxx>
#include <math_GaussMultipleIntegration.hxx>
#include <Geom_Plane.hxx>
#include <Geom_ConicalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_CylindricalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_SphericalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_ToroidalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_BSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface.hxx>
#include <GeomConvert.hxx>
#include <GProp_GProps.hxx>
#include <TopoDS_Face.hxx>
#include <BRepGProp.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace.hxx>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG2d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomAlgo.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKBRep.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKTopAlgo.lib")
//! 2D variable function for surface area evaluation.
class math_AreaFunction : public math_MultipleVarFunction
{
public:
math_AreaFunction(const Handle(Geom_Surface)& theSurface)
: mySurface(theSurface)
{
}
virtual Standard_Integer NbVariables() const
{
return 2;
}
virtual Standard_Boolean Value(const math_Vector& X, Standard_Real& Y)
{
gp_Pnt aP;
gp_Vec aDu;
gp_Vec aDv;
Standard_Real E = 0.0;
Standard_Real F = 0.0;
Standard_Real G = 0.0;
mySurface->D1(X(1), X(2), aP, aDu, aDv);
E = aDu.Dot(aDu);
F = aDu.Dot(aDv);
G = aDv.Dot(aDv);
Y = Sqrt(E * G - F * F);
//Y = aDu.Crossed(aDv).Magnitude();
return Standard_True;
}
private:
Handle(Geom_Surface) mySurface;
};
void evalArea(const Handle(Geom_Surface)& theSurface, const math_Vector& theLower, const math_Vector& theUpper)
{
math_IntegerVector aOrder(1, 2, math::GaussPointsMax());
math_AreaFunction aFunction(theSurface);
math_GaussMultipleIntegration anIntegral(aFunction, theLower, theUpper, aOrder);
if (anIntegral.IsDone())
{
anIntegral.Dump(std::cout);
}
}
void evalArea(const Handle(Geom_BoundedSurface)& theSurface)
{
math_IntegerVector aOrder(1, 2, math::GaussPointsMax());
math_Vector aLower(1, 2, 0.0);
math_Vector aUpper(1, 2, 0.0);
theSurface->Bounds(aLower(1), aUpper(1), aLower(2), aUpper(2));
math_AreaFunction aFunction(theSurface);
math_GaussMultipleIntegration anIntegral(aFunction, aLower, aUpper, aOrder);
if (anIntegral.IsDone())
{
anIntegral.Dump(std::cout);
}
}
void testFace(const TopoDS_Shape& theFace)
{
GProp_GProps aSurfaceProps;
BRepGProp::SurfaceProperties(theFace, aSurfaceProps);
std::cout << "Face area: " << aSurfaceProps.Mass() << std::endl;
}
void testPlane()
{
std::cout << "====== Test Plane Area =====" << std::endl;
Handle(Geom_Plane) aPlaneSurface = new Geom_Plane(gp::XOY());
math_Vector aLower(1, 2);
math_Vector aUpper(1, 2);
// Parameter U range.
aLower(1) = 0.0;
aUpper(1) = 2.0;
// Parameter V range.
aLower(2) = 0.0;
aUpper(2) = 3.0;
evalArea(aPlaneSurface, aLower, aUpper);
// Convert to BSpline Surface.
Handle(Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface) aTrimmedSurface =
new Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface(aPlaneSurface, aLower(1), aUpper(1), aLower(2), aUpper(2));
Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface) aBSplineSurface = GeomConvert::SurfaceToBSplineSurface(aTrimmedSurface);
evalArea(aBSplineSurface);
// Test Face.
TopoDS_Face aFace = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace(aTrimmedSurface, Precision::Confusion()).Face();
testFace(aFace);
aFace = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace(aBSplineSurface, Precision::Confusion()).Face();
testFace(aFace);
}
void testCylinder()
{
std::cout << "====== Test Cylinder Area =====" << std::endl;
Handle(Geom_CylindricalSurface) aCylindrialSurface = new Geom_CylindricalSurface(gp::XOY(), 1.0);
math_Vector aLower(1, 2);
math_Vector aUpper(1, 2);
aLower(1) = 0.0;
aUpper(1) = M_PI * 2.0;
aLower(2) = 0.0;
aUpper(2) = 3.0;
evalArea(aCylindrialSurface, aLower, aUpper);
// Convert to BSpline Surface.
Handle(Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface) aTrimmedSurface =
new Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface(aCylindrialSurface, aLower(1), aUpper(1), aLower(2), aUpper(2));
Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface) aBSplineSurface = GeomConvert::SurfaceToBSplineSurface(aTrimmedSurface);
evalArea(aBSplineSurface);
// Test Face.
TopoDS_Face aFace = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace(aTrimmedSurface, Precision::Confusion()).Face();
testFace(aFace);
aFace = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace(aBSplineSurface, Precision::Confusion()).Face();
testFace(aFace);
}
void testSphere()
{
std::cout << "====== Test Sphere Area =====" << std::endl;
Handle(Geom_SphericalSurface) aSphericalSurface = new Geom_SphericalSurface(gp::XOY(), 1.0);
math_Vector aLower(1, 2);
math_Vector aUpper(1, 2);
aSphericalSurface->Bounds(aLower(1), aUpper(1), aLower(2), aUpper(2));
evalArea(aSphericalSurface, aLower, aUpper);
// Convert to BSpline Surface.
Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface) aBSplineSurface = GeomConvert::SurfaceToBSplineSurface(aSphericalSurface);
evalArea(aBSplineSurface);
// Test Face.
TopoDS_Face aFace = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace(aSphericalSurface, Precision::Confusion()).Face();
testFace(aFace);
aFace = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace(aBSplineSurface, Precision::Confusion()).Face();
testFace(aFace);
}
void test()
{
testPlane();
testSphere();
testCylinder();
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
test();
return 0;
}
計算結果如下圖所示:
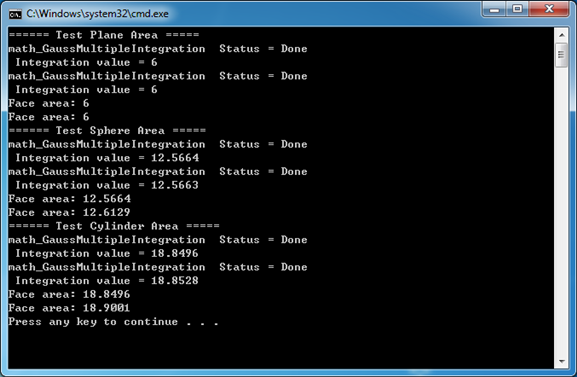
上述代碼計算了曲面的面積����,再將曲面轉換成B樣條曲面����,再使用算法計算面積。再將曲面和轉換的B樣條曲面生成拓樸面��,利用OpenCASCADE中計算曲面面積功能進行對比�。使用自定義函數math_AreaFunction利用多重積分類計算的結果與OpenCASCADE中計算曲面面積的值是一致的。當把曲面轉換成B樣條曲面后����,OpenCASCADE計算的曲面面積偏大�。
7.Conclusion
在學習《高等數學》的積分時�,其主要的一個應用就是計算弧長、面積和體積等����。學習高數抽象概念時�,總會問學了高數有什么用��?就從計算機圖形方面來看��,可以利用數學工具對任意曲線求弧長,對任意曲面計算面積等,更具一般性。
通過自定義被積函數再利用積分算法來計算任意曲面的面積��,將理論與實踐結合起來了�。即將曲面的第一基本公式與具體的代碼甚至可以利用OpenCASCADE生成對應的圖形,這樣抽象的理論就直觀了,更便于理解相應的概念�。
8.References
1.朱心雄. 自由曲線曲面造型技術. 科學出版社. 2000
2.陳維桓. 微分幾何. 北京大學出版社. 2006
3.同濟大學數學教研室. 高等數學. 高等教育出版社. 1996