GLUT Trackball Demo
eryar@163.com
1.Introduction
在三維場景中建立模型后,為了方便用戶從各個角度觀察模型,從而需要對三維視圖進行控制。常見的視圖交互控制方式有:Trackball控制器、飛行控制器,還有三維游戲常用的第一人稱控制器。這些視圖控制器的根本是對模型視圖矩陣MODELVIEW進行變換。
Trackball控制器以一種用戶友好的交互方式來變換視圖,原理是由Trackball激發,Trackball如下圖所示:
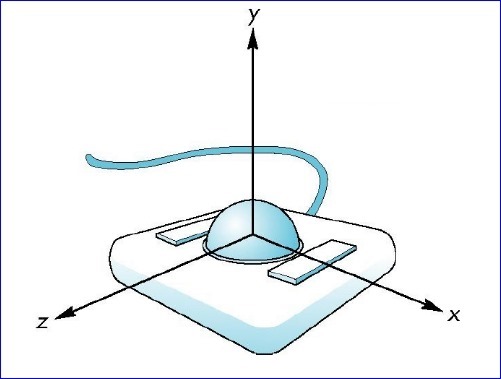
Figure 1. Trackball
通過手指在球面上滾動,就可以對三維視圖進行控制。現在需要用鼠標的拖動來模擬Trackball以實現對三維視圖的控制。在OpenGL中實現Trackball控制視圖分為以下幾步:
1.將鼠標移動時的屏幕坐標點映射到單位球上;
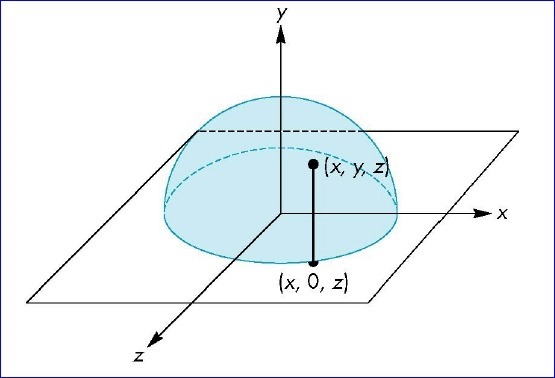
2.將開始旋轉視圖時鼠標點到球心的向量與鼠標移動過程中的坐標點球心的向量叉乘,即可得到旋轉軸;
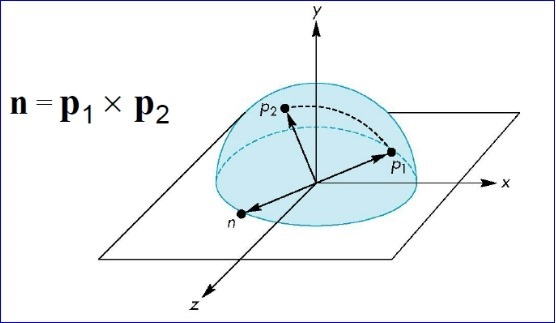
根據叉乘的定義,可以得到旋轉角度:
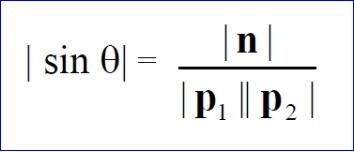
有了旋轉軸和旋轉角度,就可以對視圖進行旋轉操作了。
2.GLUT Test
為了簡明地說明Trackball的原理,這里只使用了GLUT庫和OpenCASCADE中的四元數和向量相關的類。如果其他開源庫也有向量計算和四元數據計算類,也可以將代碼很快移植到使用其他庫,如矩陣計算庫Eigen等。下面給出GLUT的示例代碼:
/*
Copyright(C) 2017 Shing Liu(eryar@163.com)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files(the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and / or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions :
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
*/
#include <gp_XYZ.hxx>
#include <gp_Trsf.hxx>
#include <gp_Quaternion.hxx>
#include <gl/glut.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
GLint VIEWPORT_WIDTH = 0;
GLint VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = 0;
gp_XYZ U;
gp_XYZ V;
gp_Quaternion R;
gp_Quaternion Q;
void init(void)
{
GLfloat aSpecularMaterial[] = {1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f};
GLfloat aLightPosition[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0};
GLfloat aWhiteLight[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
GLfloat aModelAmbient[] = {0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 1.0};
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH);
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_SPECULAR, aSpecularMaterial);
glMaterialf(GL_FRONT, GL_SHININESS, 60.0);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, aLightPosition);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_SPECULAR, aWhiteLight);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_DIFFUSE, aWhiteLight);
glLightModelfv(GL_LIGHT_MODEL_AMBIENT, aModelAmbient);
// Enable lighting
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
glEnable(GL_LIGHT0);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
}
void display(void)
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glutSolidTeapot(1.0);
// draw mouse motion point.
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex3f(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glVertex3f(U.X() * 2.0, U.Y() * 2.0, U.Z() * 2.0);
glEnd();
glutSwapBuffers();
}
void reshape(GLint theWidth, GLint theHeight)
{
VIEWPORT_WIDTH = theWidth;
VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = theHeight;
// Reset viewport and projection parameter
glViewport(0, 0, theWidth, theHeight);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
if (theWidth <= theHeight)
{
glOrtho(-1.5, 1.5, -1.5 * theHeight / theWidth, 1.5 * theHeight / theWidth, -10.0, 10.0);
}
else
{
glOrtho(-1.5 * theWidth / theHeight, 1.5 * theWidth / theHeight, -1.5, 1.5, -10.0, 10.0);
}
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
}
void mapToSphere(GLint theX, GLint theY, gp_XYZ& thePnt)
{
GLfloat aX = (theX - 0.5 * VIEWPORT_WIDTH) / VIEWPORT_WIDTH;
GLfloat aY = (0.5 * VIEWPORT_HEIGHT - theY) / VIEWPORT_HEIGHT;
GLfloat aSinx = sin(M_PI * aX * 0.5);
GLfloat aSiny = sin(M_PI * aY * 0.5);
GLfloat aSxy2 = aSinx * aSinx + aSiny * aSiny;
thePnt.SetX(aSinx);
thePnt.SetY(aSiny);
thePnt.SetZ(aSxy2 < 1.0 ? sqrt(1.0 - aSxy2) : 0.0);
}
void mouse(GLint theButton, GLint theState, GLint theX, GLint theY)
{
mapToSphere(theX, theY, U);
glutPostRedisplay();
}
void motion(GLint theX, GLint theY)
{
mapToSphere(theX, theY, V);
gp_XYZ W = U.Crossed(V);
if (W.Modulus() < gp::Resolution())
{
return;
}
GLfloat aAngle = W.Modulus() / (U.Modulus() * V.Modulus());
aAngle = asin(aAngle);
glRotatef(aAngle * 180.0 / M_PI, W.X(), W.Y(), W.Z());
glutPostRedisplay();
U = V;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA);
glutInitWindowSize(500, 300);
glutCreateWindow("Trackball Demo");
init();
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutReshapeFunc(reshape);
glutMouseFunc(mouse);
glutMotionFunc(motion);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
上述程序運行結果如下動圖所示:
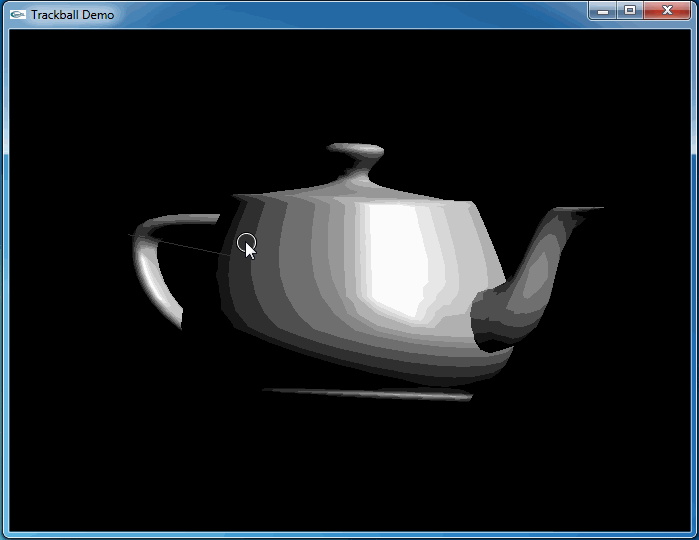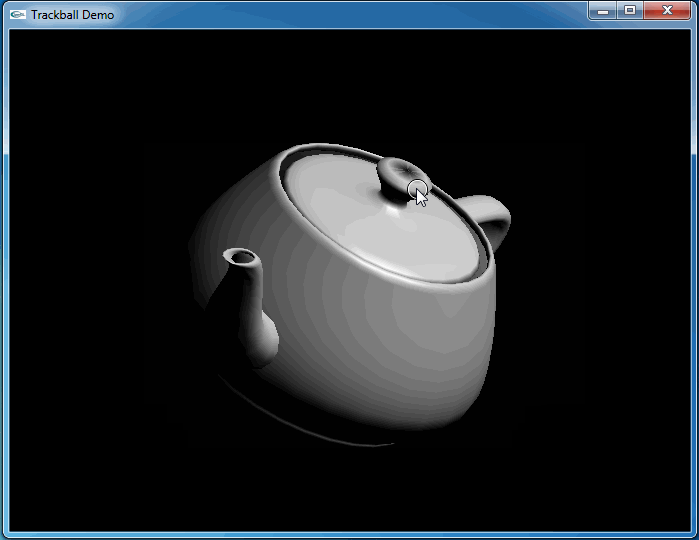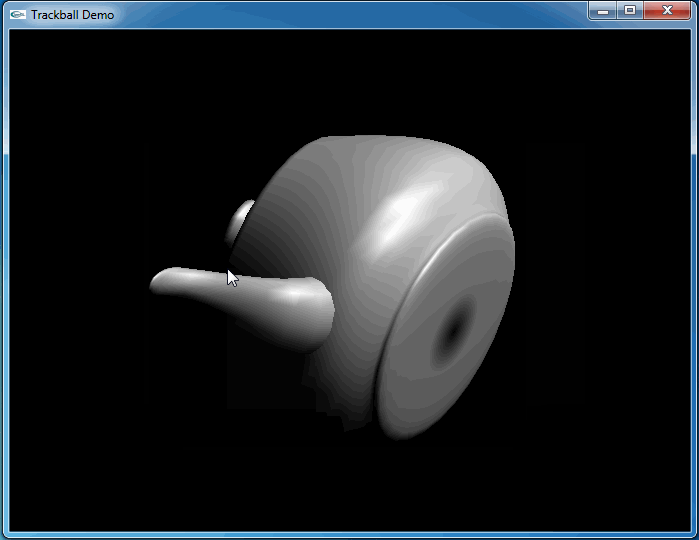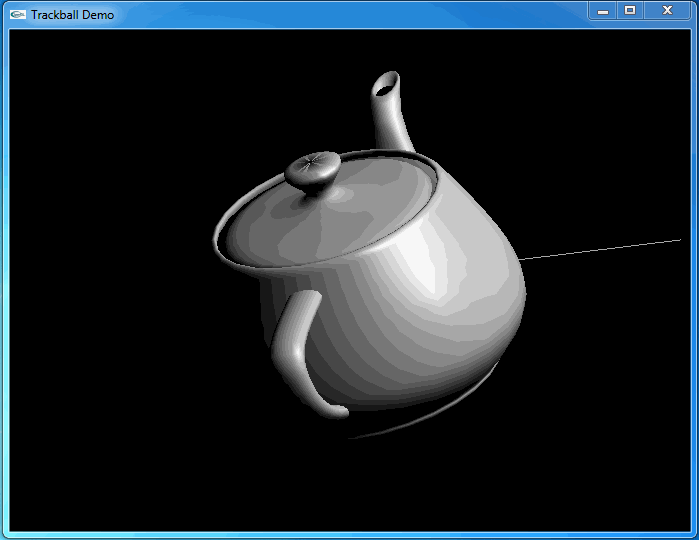
從上圖可知,當旋轉幾次后視圖并沒有得到預期的結果。因為程序將鼠標映射后坐標與球心得到的向量進行了顯示,發現當旋轉幾次后,這個向量并沒有跟隨鼠標。
3.Transform
通過觀察上面代碼程序運行的結果,可以發現鼠標映射函數得到的映射點始終是位于XOY平面上的一個半球面上。當視圖被旋轉后,視圖的坐標系已經發生了變化,而映射點并沒有。為了跟蹤這個變換用四元數進行累乘來記錄這一系列的旋轉變換。最后在映射函數中將映射點變換到已經改變的視圖坐標系中。
即在鼠標移動處理函數中增加記錄變換:
gp_Quaternion q(W, aAngle);
R.Multiply(q);
在mapToSphere函數中增加:
gp_Trsf aTrsf;
aTrsf.SetRotation(Q.Inverted());
aTrsf.Transforms(thePnt);
列出升級后的全部代碼如下所示:
/*
Copyright(C) 2017 Shing Liu(eryar@163.com)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files(the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and / or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions :
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
*/
#include <gp_XYZ.hxx>
#include <gp_Trsf.hxx>
#include <gp_Quaternion.hxx>
#include <gl/glut.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
GLint VIEWPORT_WIDTH = 0;
GLint VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = 0;
gp_XYZ U;
gp_XYZ V;
gp_Quaternion R;
gp_Quaternion Q;
void init(void)
{
GLfloat aSpecularMaterial[] = {1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f};
GLfloat aLightPosition[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0};
GLfloat aWhiteLight[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
GLfloat aModelAmbient[] = {0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 1.0};
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH);
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_SPECULAR, aSpecularMaterial);
glMaterialf(GL_FRONT, GL_SHININESS, 60.0);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, aLightPosition);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_SPECULAR, aWhiteLight);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_DIFFUSE, aWhiteLight);
glLightModelfv(GL_LIGHT_MODEL_AMBIENT, aModelAmbient);
// Enable lighting
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
glEnable(GL_LIGHT0);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
}
void display(void)
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glutSolidTeapot(1.0);
// draw mouse motion point.
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex3f(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glVertex3f(U.X() * 2.0, U.Y() * 2.0, U.Z() * 2.0);
glEnd();
glutSwapBuffers();
}
void reshape(GLint theWidth, GLint theHeight)
{
VIEWPORT_WIDTH = theWidth;
VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = theHeight;
// Reset viewport and projection parameter
glViewport(0, 0, theWidth, theHeight);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
if (theWidth <= theHeight)
{
glOrtho(-1.5, 1.5, -1.5 * theHeight / theWidth, 1.5 * theHeight / theWidth, -10.0, 10.0);
}
else
{
glOrtho(-1.5 * theWidth / theHeight, 1.5 * theWidth / theHeight, -1.5, 1.5, -10.0, 10.0);
}
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
}
void mapToSphere(GLint theX, GLint theY, gp_XYZ& thePnt)
{
GLfloat aX = (theX - 0.5 * VIEWPORT_WIDTH) / VIEWPORT_WIDTH;
GLfloat aY = (0.5 * VIEWPORT_HEIGHT - theY) / VIEWPORT_HEIGHT;
GLfloat aSinx = sin(M_PI * aX * 0.5);
GLfloat aSiny = sin(M_PI * aY * 0.5);
GLfloat aSxy2 = aSinx * aSinx + aSiny * aSiny;
thePnt.SetX(aSinx);
thePnt.SetY(aSiny);
thePnt.SetZ(aSxy2 < 1.0 ? sqrt(1.0 - aSxy2) : 0.0);
gp_Trsf aTrsf;
aTrsf.SetRotation(Q.Inverted());
aTrsf.Transforms(thePnt);
}
void mouse(GLint theButton, GLint theState, GLint theX, GLint theY)
{
mapToSphere(theX, theY, U);
Q = R;
glutPostRedisplay();
}
void motion(GLint theX, GLint theY)
{
mapToSphere(theX, theY, V);
gp_XYZ W = U.Crossed(V);
if (W.Modulus() < gp::Resolution())
{
return;
}
GLfloat aAngle = W.Modulus() / (U.Modulus() * V.Modulus());
aAngle = asin(aAngle);
glRotatef(aAngle * 180.0 / M_PI, W.X(), W.Y(), W.Z());
glutPostRedisplay();
gp_Quaternion q(W, aAngle);
R.Multiply(q);
U = V;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA);
glutInitWindowSize(500, 300);
glutCreateWindow("Trackball Demo");
init();
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutReshapeFunc(reshape);
glutMouseFunc(mouse);
glutMotionFunc(motion);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
這次程序運行和預期結果一致,旋轉很流暢:
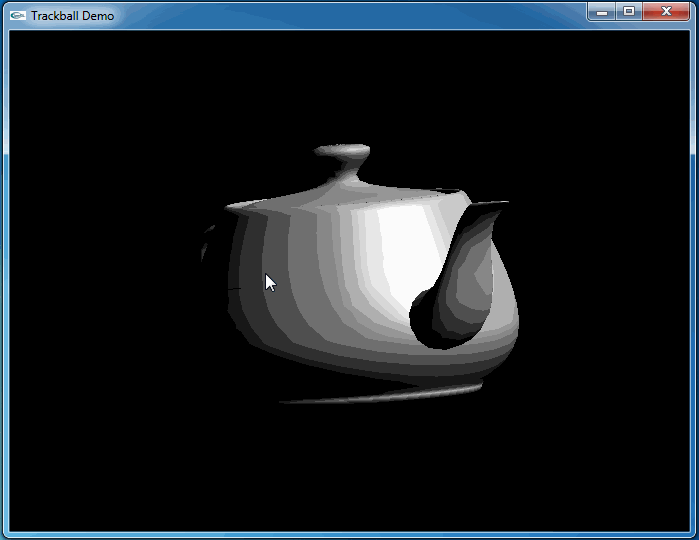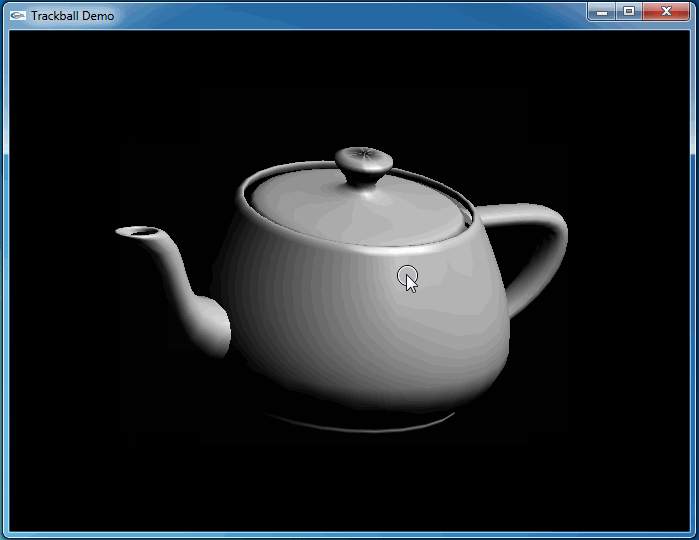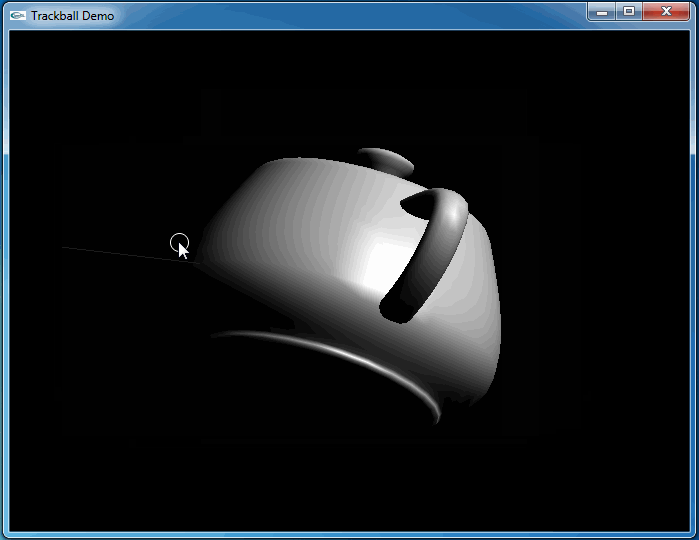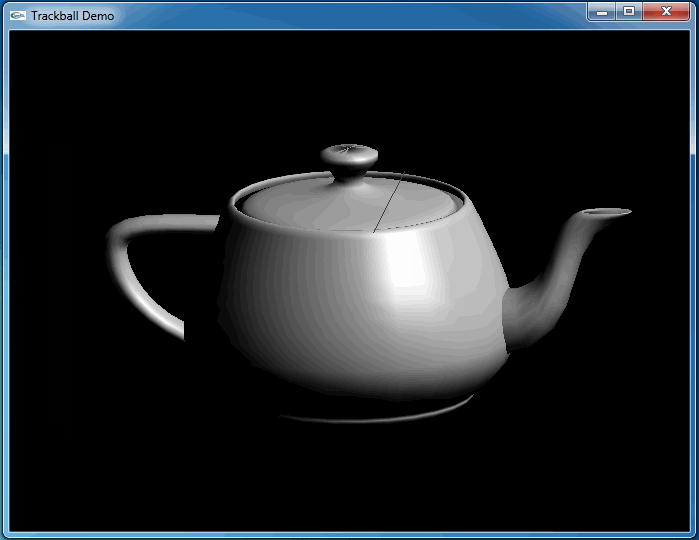
4.Conclusion
程序員總是有很強的控制欲,希望一切盡在掌握之中。在三維場景中建立模型后,如何對視圖進行控制來方便地觀察模型呢?最常見的控制方式就是Trackball. OpenSceneGraph、Eigen等開源庫都有相關的實現。
Trackball的實現主要是將鼠標點映射到一個球面上,然后使用叉乘得到旋轉軸和旋轉角度。為了旋轉的流暢,使用四元數記錄了一系列的旋轉變換,最后通過將映射點進行坐標變換得到滿意的效果。
5.References
1. Virtual Trackball. http://gukewen.sdu.edu.cn/panrj/courses/4-AngelCGE2-Virtual-Trackball.pdf
2. Object Mouse Trackball https://www.khronos.org/opengl/wiki/Object_Mouse_Trackball