Bounding Volume Hierarchy BVH in OpenCASCADE
eryar@163.com
Abstract. Bounding Volume Hierarchy(BVH) organizes geometric objects in the tree based on spatial relationships. Each node in the tree contains an axis-aligned bounding box of all the objects below it. Bounding volume hierarchies are used in many algorithms to support efficient operations on the sets of geometric objects, such as collision detection, ray-tracing, searching of nearest objects, and view frustum culling. The paper focus on the usage of BVH on TopoDS_Shape, and its application.
Key Words. BVH, Bounding Volume Hierarchy, Collision Detection
1.Introduction
層次包圍盒(Bounding Volume Hierarchy, BVH)是一種基于物體的場景管理技術(shù),廣泛用于碰撞檢測,光線追蹤,視錐體物體剔除等場合。對于三維場景的實時渲染來說,BVH是最常用的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)。場景以層次樹形結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行組織,包含一個根節(jié)點、內(nèi)部節(jié)點、葉子節(jié)點。樹中的每個節(jié)點,包括葉子節(jié)點都有一個包圍體,可以將其子樹的所有幾何體包圍起來,這就是BVH名字的由來。如下圖所示:
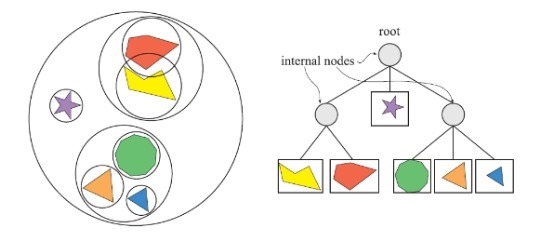
Figure 1. Simple Scene(left), BVH Scene Graph(right)
本文主要介紹OpenCASCADE中的BVH包及其應(yīng)用,如碰撞檢測。
2.Build BVH
在BVH包中的頭文件里面找到BVH的作者:Denis BOGOLEPOV, Danila ULYANOV,在網(wǎng)上搜到他們的一篇論文:Real-Time SAH BVH Construction for Ray Tracing Dynamic Scenes. 因此,可知BVH中是應(yīng)用SAH(Surface Area Heuristic)策略來構(gòu)造BVH樹的。根據(jù)BVH_BinnedBuilder頭文件中的注釋可知:
//! Performs construction of BVH tree using binned SAH algorithm. Number
//! of bins controls BVH quality in cost of construction time (greater
//! better). For optimal results, use 32 - 48 bins. However, reasonable
//! performance is provided even for 4 - 8 bins (it is only 10-20% lower
//! in comparison with optimal settings). Note that multiple threads can
//! be used only with thread safe BVH primitive sets.
OpenCASCADE中也提供了其他的構(gòu)造方法,如類BVH_LinearBuilder中使用了Spatial Morton codes方法:
//! Performs fast BVH construction using LBVH building approach.
//! Algorithm uses spatial Morton codes to reduce the BVH construction
//! problem to a sorting problem (radix sort -- O(N) complexity). This
//! Linear Bounding Volume Hierarchy (LBVH) builder produces BVH trees
//! of lower quality compared to SAH-based BVH builders but it is over
//! an order of magnitude faster (up to 3M triangles per second).
//!
//! For more details see:
//! C. Lauterbach, M. Garland, S. Sengupta, D. Luebke, and D. Manocha.
//! Fast BVH construction on GPUs. Eurographics, 2009.
3.Traversal BVH
由類BVH_TreeBase可知,當(dāng)?shù)玫紹VH樹后,可以取出節(jié)點索引的數(shù)組。下面給出將TopoDS_Shape的BVH樹顯示出來的示例代碼:
/*
Copyright(C) 2017 Shing Liu(eryar@163.com)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files(the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and / or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions :
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
*/
// Visual Studio 2013 & OpenCASCADE7.1.0
// 2017-04-18 20:52
#include <BRepExtrema_TriangleSet.hxx>
#include <BRepTools.hxx>
#include <BRep_Builder.hxx>
#include <TopoDS.hxx>
#include <TopExp_Explorer.hxx>
#include <BRepPrimAPI_MakeBox.hxx>
#include <BRepMesh_IncrementalMesh.hxx>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG2d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomAlgo.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKBRep.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKPrim.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMesh.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKTopAlgo.lib")
void testBvh(const std::string& theFileName)
{
BRep_Builder aBuilder;
TopoDS_Compound aCompound;
TopoDS_Shape aShape;
BRepTools::Read(aShape, theFileName.c_str(), aBuilder);
BRepExtrema_ShapeList aFaceList;
for (TopExp_Explorer i(aShape, TopAbs_FACE); i.More(); i.Next())
{
aFaceList.Append(TopoDS::Face(i.Current()));
}
aBuilder.MakeCompound(aCompound);
BRepMesh_IncrementalMesh aMesher(aShape, 1.0);
BRepExtrema_TriangleSet aTriangleSet(aFaceList);
const NCollection_Handle<BVH_Tree<Standard_Real, 3> >& aBvh = aTriangleSet.BVH();
for (int i = 0; i < aBvh->Length(); i++)
{
const BVH_Vec4i& aNodeData = aBvh->NodeInfoBuffer()[i];
if (aNodeData.x() == 0)
{
// inner node.
const BVH_Vec3d& aP1 = aBvh->MinPoint(aNodeData.y());
const BVH_Vec3d& aP2 = aBvh->MaxPoint(aNodeData.y());
const BVH_Vec3d& aQ1 = aBvh->MinPoint(aNodeData.z());
const BVH_Vec3d& aQ2 = aBvh->MaxPoint(aNodeData.z());
try
{
BRepPrimAPI_MakeBox aBoxMaker(gp_Pnt(aP1.x(), aP1.y(), aP1.z()),
gp_Pnt(aP2.x(), aP2.y(), aP2.z()));
for (TopExp_Explorer i(aBoxMaker.Shape(), TopAbs_EDGE); i.More(); i.Next())
{
aBuilder.Add(aCompound, i.Current());
}
}
catch (Standard_Failure f)
{
}
try
{
BRepPrimAPI_MakeBox aBoxMaker(gp_Pnt(aQ1.x(), aQ1.y(), aQ1.z()),
gp_Pnt(aQ2.x(), aQ2.y(), aQ2.z()));
for (TopExp_Explorer i(aBoxMaker.Shape(), TopAbs_EDGE); i.More(); i.Next())
{
aBuilder.Add(aCompound, i.Current());
}
}
catch (Standard_Failure f)
{
}
}
else
{
// leaves node.
const BVH_Vec3d& aP1 = aBvh->MinPoint(i);
const BVH_Vec3d& aP2 = aBvh->MaxPoint(i);
try
{
BRepPrimAPI_MakeBox aBoxMaker(gp_Pnt(aP1.x(), aP1.y(), aP1.z()),
gp_Pnt(aP2.x(), aP2.y(), aP2.z()));
aBuilder.Add(aCompound, aBoxMaker.Shape());
}
catch (Standard_Failure f)
{
}
}
}
BRepTools::Write(aCompound, "d:/bvh.brep");
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc > 1)
{
testBvh(argv[1]);
}
return 0;
}
由上述代碼可知,當(dāng)?shù)玫焦?jié)點信息
const BVH_Vec4i& aNodeData = aBvh->NodeInfoBuffer()[i];
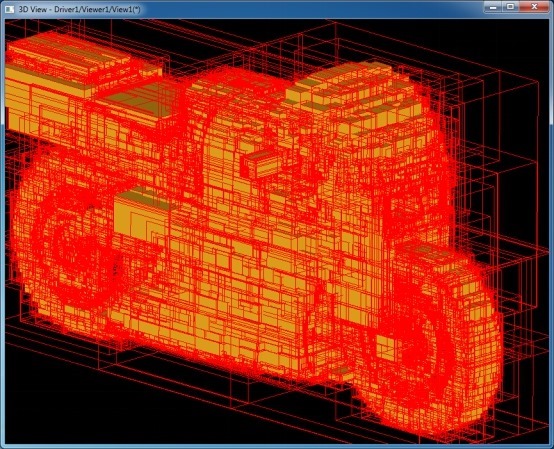
后,通過判斷aNodeData.x()分量來確定此節(jié)點是內(nèi)部節(jié)點還是葉子節(jié)點。顯示OCC自帶的螺旋槳模型的BVH如下圖所示:
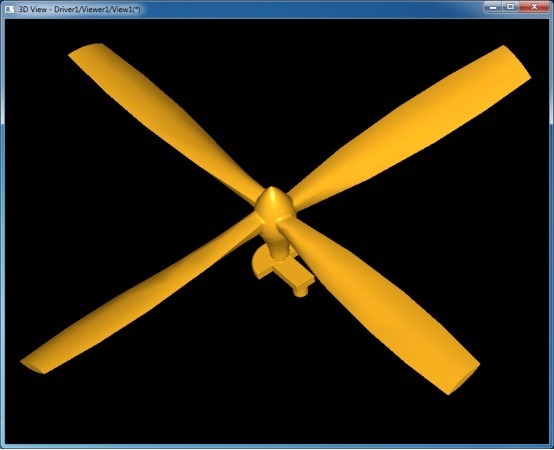
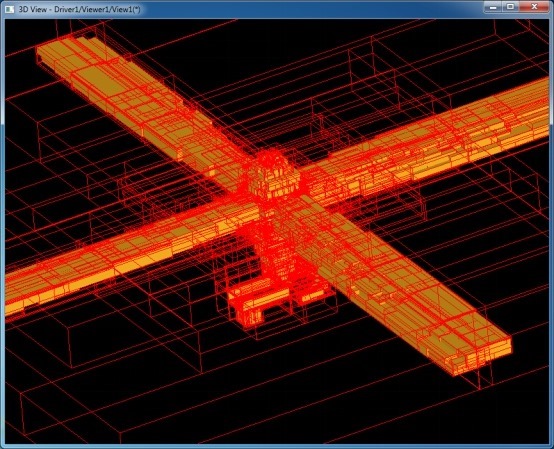
其中紅色線框為內(nèi)部節(jié)點,黃色實體模型是葉子節(jié)點。
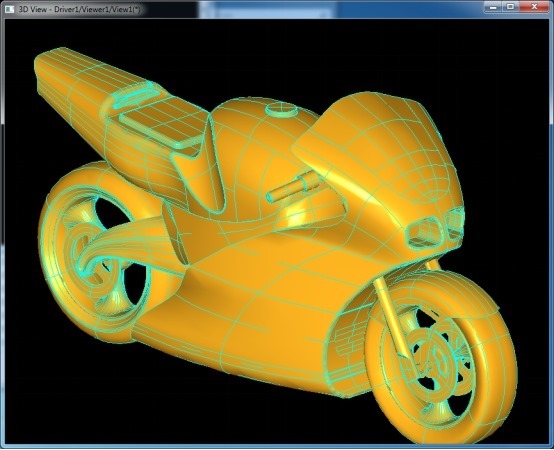
4.BVH Application
BVH在OpenCASCADE中也有廣泛地應(yīng)用,如開源版本中的模型快速碰撞檢測,使用類BRepExtrema_ShapeProximity. 模型選擇操作,光線跟蹤等算法中都有應(yīng)用。
5.Conclusion
因為OpenCASCADE中構(gòu)造BVH時依賴模型的網(wǎng)格三角形,所以BVH算法的應(yīng)用的結(jié)果就依賴于網(wǎng)格化算法的質(zhì)量了。如兩個Topo形狀碰撞檢測時,網(wǎng)格化的質(zhì)量越高,結(jié)果精度越高。如果用解析算法去對兩個Topo形狀做碰撞檢測,也會涉及到解析算法的精度問題。
BVH結(jié)構(gòu)廣泛應(yīng)用于碰撞檢測、光線跟蹤等算法中,大大提高程序性能。本文只是拋磚引玉,對BVH感興趣的童鞋可以參考相關(guān)資料及OpenCASCADE中的代碼實現(xiàn),去深入學(xué)習(xí)應(yīng)用。
6.References
1. Dmitry Sopin, Denis Bogolepov, Danila Ulyanov. Real-Time SAH BVH Construction for Ray Tracing Dynamic Scenes. http://graphicon.ru/html/2011/conference/gc2011Sopin.pdf
2. BVH with SAH. http://www.cnblogs.com/lookof/p/3546320.html
3. 3D游戲引擎中常見的三維場景管理方法. http://www.cnblogs.com/wangchengfeng/p/3495954.html