Undo/Redo for Qt Tree Model
eryar@163.com
Abstract. Qt contains a set of item view classes that use a model/view architecture to manage the relationship between data and the way it is presented to the user. The separation of functionality introduced by this architecture gives developers greater flexibility to customize the presentation of items, and provides a standard model interface to allow a wide range of data sources to be used with existing item views. Model 3D aided design software such as AVEVA Plant/PDMS, Marine use the architecture to manage the design data source. The article demonstrate the Undo/Redo on the Qt Tree model.
Key Words. Model/View, MVC pattern, Undo/Redo, Tree Model
1. Introduction
現(xiàn)代稍微大型一點(diǎn)的軟件,要處理的數(shù)據(jù)量通常會(huì)比較大。這時(shí)就需要有一個(gè)唯一的數(shù)據(jù)源,且會(huì)對(duì)這個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)源中的數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行增、刪、改的操作。如果沒有統(tǒng)一的數(shù)據(jù)源,數(shù)據(jù)會(huì)隨意地被創(chuàng)建和刪除,且創(chuàng)建和刪除的用戶界面也不統(tǒng)一,不利于軟件管理。基于唯一的數(shù)據(jù)源,并在這個(gè)基礎(chǔ)上提供統(tǒng)一的增刪改接口,不僅有利于軟件數(shù)據(jù)管理,還有利于事務(wù)的處理,即Undo/Redo功能。若引入腳本語(yǔ)言,如Tcl或Python,甚至可實(shí)現(xiàn)腳本命令對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)的操作,為程序增加二次開發(fā)功能。
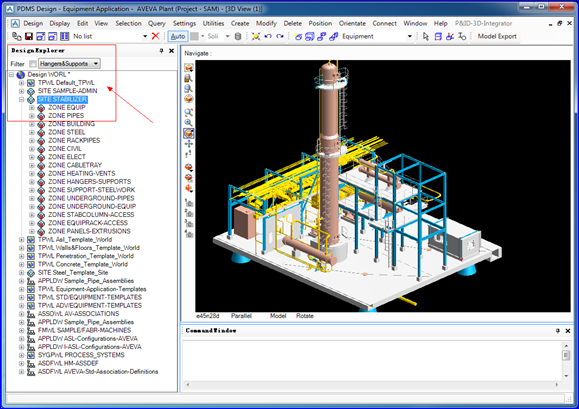
Figure 1. AVEVA Plant/PDMS Software
如上圖1所示為英國(guó)劍橋大學(xué)CADCENTRE出品的AVEVA Plant/PDMS軟件。PDMS使用了統(tǒng)一的數(shù)據(jù)源,左邊的導(dǎo)航樹及右邊的三維模型都是這個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)源的一種展示方式,可以在導(dǎo)航樹上創(chuàng)建及刪除數(shù)據(jù);也可以在三維視圖中進(jìn)行交互,方便地創(chuàng)建及修改模型。這種方式與GoF描述的Observer觀察者模式相似,即:
定義對(duì)象間的一種一對(duì)多的依賴關(guān)系,當(dāng)一個(gè)對(duì)象的狀態(tài)發(fā)生改變時(shí),所有依賴于它的對(duì)象都得到通知并被自動(dòng)更新。
對(duì)應(yīng)上面的軟件,即對(duì)于唯一的數(shù)據(jù)源這個(gè)對(duì)象,導(dǎo)航樹及三維視圖都依賴于他。當(dāng)數(shù)據(jù)源這個(gè)對(duì)象中有數(shù)據(jù)的增刪改時(shí),導(dǎo)航樹及三維視圖都會(huì)得到通知并自動(dòng)更新了。
圖1右下角的CommandWindow中可以輸入命令,即PML,也可以對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)源進(jìn)行修改。引入Observer模式,即可實(shí)現(xiàn)這些功能。
Qt中包含了一系列的Model/View類,這些類都是基于MVC架構(gòu)的,這種將數(shù)據(jù)與視圖分開的處理,使同一個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)源可以不同的視圖中進(jìn)行展示,且不需要修改數(shù)據(jù)源的結(jié)構(gòu)。Qt中基于Command命令模式實(shí)現(xiàn)了一個(gè)Undo/Redo的框架,將Undo/Redo框架應(yīng)用于Model/View的類,即可得到與AVEVA Plant/PDMS中類似的功能。
本文主要對(duì)Qt中的model/view及undo/redo框架進(jìn)行介紹,及如何將Undo/Redo框架應(yīng)用到model/view中去,實(shí)現(xiàn)對(duì)以層次方式組織數(shù)據(jù)的樹模型進(jìn)行undo/redo,進(jìn)而實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)三維CAD工廠設(shè)計(jì)的原型。
2.Tree Model
軟件中使用層次方式來(lái)組織數(shù)據(jù),可護(hù)展性好。如OpenCASCADE中的OCAF框架的數(shù)據(jù)也是樹形方式組織:

Figure 2.1 OpenCASCADE OCAF data tree
每個(gè)Label中可以存放屬性,還包含子Label,這樣就提供了一個(gè)通用的程序框架,靈活使用,可以用一種統(tǒng)一的方式來(lái)存放數(shù)據(jù)。有一個(gè)缺點(diǎn)就是每個(gè)Label中的屬性類型只能包含一種,這種方式相對(duì)于AVEVA的自定義屬性UDA來(lái)說(shuō),就顯得很不方便了,需要提前對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)的存儲(chǔ)進(jìn)行規(guī)劃,擴(kuò)展起來(lái)稍有不便。
AVEVA中對(duì)每個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)Element都提供了自定義屬性(User Definable Attribute),每種類型的屬性(數(shù)值型、字符串型等)都可以包含任意數(shù)量,沒有限制。所以可擴(kuò)展性更好。
Qt中基于MVC模式的model/view架構(gòu)提供了一些預(yù)定義的模型及視圖,如列表模型及對(duì)應(yīng)的視圖,樹模型及樹視圖等。在model/view架構(gòu)中,為model提供了統(tǒng)一的訪問(wèn)數(shù)據(jù)的方式,即Model Index。對(duì)于列表model,通過(guò)QModelIndex::row()即可訪問(wèn)。對(duì)于表格model,需要QModelIndex::row()和QModelIndex::column()。對(duì)于樹model,除了上述兩個(gè)函數(shù),還需要提供QModelIndex::parent()來(lái)對(duì)父節(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行訪問(wèn)。如下圖2.2所示:
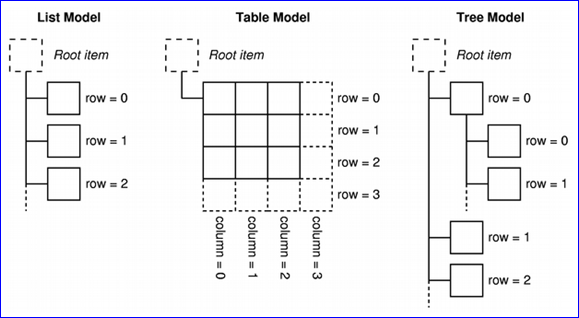
Figure 2.2 Schematic view of Qt’s Models
若需要對(duì)列表及表格model應(yīng)用Undo框架,還是很方便的,只要記住數(shù)據(jù)操作的對(duì)應(yīng)的row或row及column即可。若要對(duì)樹形model進(jìn)行undo,原理也是一樣的,即在redo中生成數(shù)據(jù)在undo中恢復(fù)數(shù)據(jù)。
3.Key Points
將undo框架與model/view結(jié)合有兩種方式:
v 通過(guò)在undo/redo命令中調(diào)用QAbstractItemModel的API來(lái)改變底層數(shù)據(jù);
v 自定義model使其創(chuàng)建命令并推送到undo棧Stack中去;
第一種方式看起來(lái)要容易些,且可與任意model結(jié)合。The first approach seems simpler, as it works with any model and gives the undo framework total control --- you can create as many different types of commands as you want and each of them can call a number of methods from the model API in their undo() and redo() routines.
當(dāng)model中有delete操作時(shí),會(huì)將index內(nèi)部的數(shù)據(jù)刪除。對(duì)于這種情況,需要注意。Qt給出了兩個(gè)解決辦法:
There are two things to remember. The first is that, if you delete items, rows or columns, you should save the data of all the items getting deleted(including children) somewhere so that you can later revert the deletion. The second is that it would be nice to be able to set meaningful descriptions of commands pushed on the stack. To do that you can provide methods in the model, that are called each time a command is pushed onto the stack, which should each return a description based on the parameters of the command being executed.
基于上述思想,實(shí)現(xiàn)了Tree Model與Undo Framework結(jié)合的一個(gè)小例子:
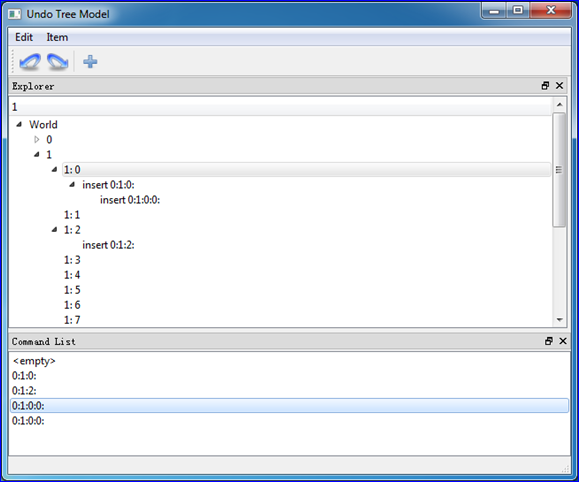
Figure 3. Undo/Redo and Tree Model
4.Conclusion
Qt中基于Command命令模式的Undo框架,需要對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)操作及恢復(fù)仔細(xì)考量。尤其對(duì)于有刪除數(shù)據(jù)的操作,若以QModelIndex作為參考依據(jù),則會(huì)出錯(cuò)。對(duì)于此Qt提供了兩個(gè)解決思路。
基于Qt的model/view及undo框架,也可以方便實(shí)現(xiàn)OpenCASCADE中的OCAF框架許多類似的功能,且Qt的代碼可讀性更高。若要快速開發(fā)程序,可以考慮使用Qt的model/view框架。
感謝曉天的建議。
5. References
1. Using Undo/Redo with Item Views. http://doc.qt.digia.com/qq/qq25-undo.html
2. OpenCASCADE. OCAF User’s Guide. 2014
3. GoF. Design Patterns-Element of Reusable Object-Oriented Software. 1995