OpenCASCADE Linear Extrusion Surface
eryar@163.com
Abstract. OpenCASCADE linear extrusion surface is a generalized cylinder. Such a surface is obtained by sweeping a curve (called the “extruded curve” or “basis”) in a given direction (referred to as the direction of extrusion and defined by a unit vector). The u parameter is along the extruded curve. The v parameter is along the direction of extrusion. The form of a surface of linear extrusion is generally a ruled surface. It can be a cylindrical surface, or a planar surface.
Key Words. OpenCASCADE, Extrusion Surface, Sweeping
1. Introduction
一般柱面(The General Cylinder)可以由一段或整個圓弧沿一個方向偏移一定的距離得到����。如下圖所示:
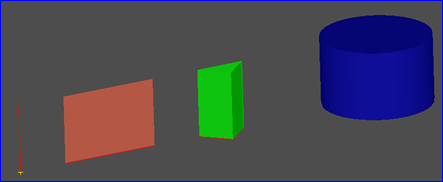
Figure 1.1 Extrusion Shapes
當將頂點拉伸時����,會生成一條邊����;當將邊拉伸時,會生成面;當將Wire拉伸時,會生成Shell����,當將面拉伸時�,會生成體�。當將曲線沿一個方向拉伸時,會形成一個曲面,如果此方向為直線����,則會生成一般柱面�。如果此方向是曲線時��,會生成如下圖所示曲面:
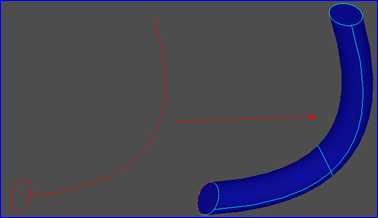
Figure 1.2 Swept surface/ loft surface
本文主要介紹將曲線沿直線方向拉伸的算法��,即一般柱面生成算法。并將生成的曲面在OpenSceneGraph中進行顯示。
2.Cylinder Surface Definition
設W是一個單位向量,C(u)是定義在節點矢量U上,權值為wi的p次NURBS曲線。我們要得到一般柱面S(u,v)的表達式,S(u,v)是通過將C(u)沿方向W平行掃描(sweep)距離d得到的����。記掃描方向的參數為v, 0<v<1�,顯然����,S(u,v)必須滿足以下兩個條件:
v 對于固定的u0, S(u0, v)為由C(u0)到C(u0)+dW的直線段;
v 對于固定的v0:
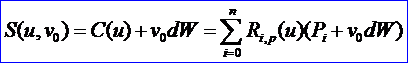
所要求的柱面的表達式為:
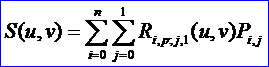
S(u,v)定義在節點矢量U和V上,這里V={0�,0����,1��,1}��,U為C(u)的節點矢量�。控制頂點由Pi,0=Pi和Pi,1=Pi+dW給出����,權值wi,0=wi,1=wi����。如下圖所示為一般柱面:
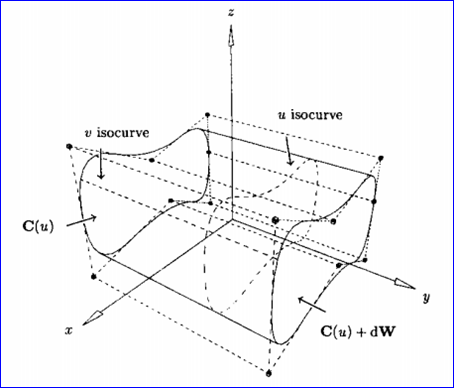
Figure 2.1 A general cylinder obtained by translating C(u) a distance d along W.
其中OpenCASCADE中一般柱面的表達式如下所示:
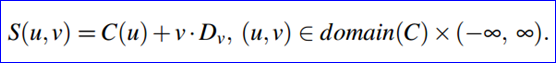
其取值范圍的代碼如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : Bounds
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
void Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion::Bounds ( Standard_Real& U1,
Standard_Real& U2,
Standard_Real& V1,
Standard_Real& V2 ) const {
V1 = -Precision::Infinite(); V2 = Precision::Infinite();
U1 = basisCurve->FirstParameter(); U2 = basisCurve->LastParameter();
}
由上代碼可知�,參數在v方向上是趨于無窮的;在u方向上參數的范圍為曲線的范圍����。計算柱面上點的方法代碼如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : D0
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
void Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion::D0 (const Standard_Real U,
const Standard_Real V,
Pnt& P) const {
XYZ Pxyz = direction.XYZ();
Pxyz.Multiply (V);
Pxyz.Add (basisCurve->Value (U).XYZ());
P.SetXYZ(Pxyz);
}
即將柱面上點先按V方向來計算��,再按U方向來計算,最后將兩個方向的值相加即得到柱面上的點�。
由上述代碼可知����,OpenCASCADE中一般柱面沒有使用NURBS曲面來表示�。根據這個方法,可以將任意曲線沿給定的方向來得到一個柱面�,這個曲線可以是直線�、圓弧����、圓、橢圓等�。關于柱面上更多算法�,如求微分等�,可以參考源程序。
3.Display the Surface
還是在OpenSceneGraph中來對一般柱面進行可視化�,來驗證結果����。因為OpenSceneGraph的簡單易用��,顯示曲面的程序代碼如下所示:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2013 to current year. All Rights Reserved.
*
* File : Main.cpp
* Author : eryar@163.com
* Date : 2014-11-23 10:18
* Version : OpenCASCADE6.8.0
*
* Description : Test the Linear Extrusion Surface of OpenCASCADE.
*
* Key Words : OpenCascade, Linear Extrusion Surface, General Cylinder
*
*/
// OpenCASCADE.
#define WNT
#include <Precision.hxx>
#include <gp_Circ.hxx>
#include <Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion.hxx>
#include <GC_MakeCircle.hxx>
#include <GC_MakeSegment.hxx>
#include <GC_MakeArcOfCircle.hxx>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib")
// OpenSceneGraph.
#include <osgViewer/Viewer>
#include <osgViewer/ViewerEventHandlers>
#include <osgGA/StateSetManipulator>
#pragma comment(lib, "osgd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgGAd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgViewerd.lib")
const double TOLERANCE_EDGE = 1e-6;
const double APPROXIMATION_DELTA = 0.05;
/**
* @brief Render 3D geometry surface.
*/
osg::Node* BuildSurface(const Handle_Geom_Surface& theSurface)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geode> aGeode = new osg::Geode();
Standard_Real aU1 = 0.0;
Standard_Real aV1 = 0.0;
Standard_Real aU2 = 0.0;
Standard_Real aV2 = 0.0;
Standard_Real aDeltaU = 0.0;
Standard_Real aDeltaV = 0.0;
theSurface->Bounds(aU1, aU2, aV1, aV2);
// trim the parametrical space to avoid infinite space.
Precision::IsNegativeInfinite(aU1) ? aU1 = -1.0 : aU1;
Precision::IsInfinite(aU2) ? aU2 = 1.0 : aU2;
Precision::IsNegativeInfinite(aV1) ? aV1 = -1.0 : aV1;
Precision::IsInfinite(aV2) ? aV2 = 1.0 : aV2;
// Approximation in v direction.
aDeltaU = (aU2 - aU1) * APPROXIMATION_DELTA;
aDeltaV = (aV2 - aV1) * APPROXIMATION_DELTA;
for (Standard_Real u = aU1; (u - aU2) <= TOLERANCE_EDGE; u += aDeltaU)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> aLine = new osg::Geometry();
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> aPoints = new osg::Vec3Array();
for (Standard_Real v = aV1; (v - aV2) <= TOLERANCE_EDGE; v += aDeltaV)
{
gp_Pnt aPoint = theSurface->Value(u, v);
aPoints->push_back(osg::Vec3(aPoint.X(), aPoint.Y(), aPoint.Z()));
}
// Set vertex array.
aLine->setVertexArray(aPoints);
aLine->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, 0, aPoints->size()));
aGeode->addDrawable(aLine.get());
}
// Approximation in u direction.
for (Standard_Real v = aV1; (v - aV2) <= TOLERANCE_EDGE; v += aDeltaV)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> aLine = new osg::Geometry();
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> aPoints = new osg::Vec3Array();
for (Standard_Real u = aU1; (u - aU2) <= TOLERANCE_EDGE; u += aDeltaU)
{
gp_Pnt aPoint = theSurface->Value(u, v);
aPoints->push_back(osg::Vec3(aPoint.X(), aPoint.Y(), aPoint.Z()));
}
// Set vertex array.
aLine->setVertexArray(aPoints);
aLine->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, 0, aPoints->size()));
aGeode->addDrawable(aLine.get());
}
return aGeode.release();
}
/**
* @brief Build the test scene.
*/
osg::Node* BuildScene(void)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Group> aRoot = new osg::Group();
// test the linear extrusion surface.
// test linear extrusion surface of a line.
Handle_Geom_Curve aSegment = GC_MakeSegment(gp_Pnt(3.0, 0.0, 0.0), gp_Pnt(6.0, 0.0, 0.0));
Handle_Geom_Surface aPlane = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(aSegment, gp::DZ());
aRoot->addChild(BuildSurface(aPlane));
// test linear extrusion surface of a arc.
Handle_Geom_Curve aArc = GC_MakeArcOfCircle(gp_Circ(gp::ZOX(), 2.0), 0.0, M_PI, true);
Handle_Geom_Surface aSurface = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(aArc, gp::DY());
aRoot->addChild(BuildSurface(aSurface));
// test linear extrusion surface of a circle.
Handle_Geom_Curve aCircle = GC_MakeCircle(gp::XOY(), 1.0);
Handle_Geom_Surface aCylinder = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(aCircle, gp::DZ());
aRoot->addChild(BuildSurface(aCylinder));
return aRoot.release();
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
osgViewer::Viewer aViewer;
aViewer.setSceneData(BuildScene());
aViewer.addEventHandler(new osgGA::StateSetManipulator(
aViewer.getCamera()->getOrCreateStateSet()));
aViewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::StatsHandler);
aViewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::WindowSizeHandler);
return aViewer.run();
return 0;
}
上述顯示方法只是顯示線框的最簡單的算法,只為驗證一般柱面結果��,不是高效算法����。顯示結果如下圖所示:
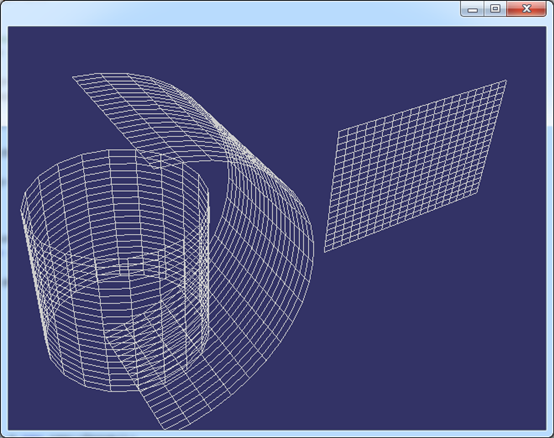
Figure 3.1 General Cylinder for: Circle, Arc, Line
如上圖所示分別為對圓、圓弧和直線進行拉伸得到的一般柱面����。根據這個原理可以將任意曲線沿給定方向進行拉伸得到一個柱面�。
4.Conclusion
通過對OpenCASCADE中一般柱面的類中代碼進行分析可知,OpenCASCADE的這個線性拉伸柱面Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion是根據一般柱面的定義實現的�,并不是使用NURBS曲面來表示的����。當需要用NURBS曲面來表示一般柱面時��,需要注意控制頂點及權值的計算取值�。
5. References
1. 趙罡�,穆國旺,王拉柱譯. 非均勻有理B樣條. 清華大學出版社. 2010
2. Les Piegl, Wayne Tiller. The NURBS Book. Springer-Verlag. 1997
3. OpenCASCADE Team, OpenCASCADE BRep Format. 2014
4. Donald Hearn, M. Pauline Baker. Computer Graphics with OpenGL. Prentice Hall. 2009
5. 莫蓉����,常智勇. 計算機輔助幾何造型技術. 科學出版社. 2009