Geometry Curve of OpenCascade BRep
eryar@163.com
摘要Abstract:幾何曲線是參數表示的曲線 ,在邊界表示中其數據存在于BRep_TEdge中,BRep_TEdge中不僅包括了幾何曲線,還包含其他類型的幾何信息。本文主要對OpenCascade的BRep表示中幾何曲線進行說明,將在后面分析Topology部分的讀寫程序時來說明這三種拓樸結構中分別包括哪些幾何信息。
關鍵字Key Words:OpenCascade BRep, Geometry Curve, Topology, Refactoring
一、引言 Introduction
邊界表示(Boundary Representation)也稱為BRep表示,它是幾何造型中最成熟、無二義的表示法。實體的邊界通常是由面的并集來表示,而每個面又由它所在的曲面的定義加上其邊界來表示,面的邊界是邊的并集,而邊又是由點來表示的。
邊界表示的一個重要特征是描述形體的信息包括幾何信息(Geometry)和拓樸信息(Topology)兩個方面。拓樸信息描述形體上的頂點、邊、面的連接關系,它形成物體邊界表示的“骨架”。形體的幾何信息猶如附著在“骨架”上的肌肉。例如,形體的某個面位于某一個曲面上,定義這一曲面方程的數據就是幾何信息。此外,邊的形狀、頂點在三維空間中的位置(點的坐標)等都是幾何信息,一般來說,幾何信息描述形體的大小、尺寸、位置和形狀等。
OpenCascade中幾何(Geometry)與拓樸(Topology)的關系也是按上述方式組織的。即幾何信息在BRep中并不是單獨存在的,而是依附于拓樸存在的。通過繼承TopoDS包中的抽象的拓樸類實現了邊界表示(BRep)模型。如下圖所示:
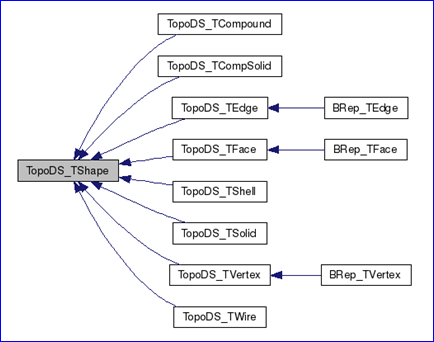
Figure 1.1 Topology data structure in OpenCascade
從上面的類圖可以看出只有三種拓樸對象有幾何數據:頂點(vertex)、邊(edge)、面(face),分別為BRep_TVertex、BRep_TEdge、BRep_TFace。BRep_TVertex中主要包含一個空間點(x, y, z)數據;幾何曲線數據主要存在于BRep_TEdge中,BRep_TEdge中不僅包括了幾何曲線,還包含其他類型的幾何信息;BRep_TFace中主要包含幾何曲面及其他的幾何數據,如面的三角剖分等。本文主要對OpenCascade的BRep表示中幾何曲線進行說明,將在后面分析Topology部分的讀寫程序時來說明這三種拓樸結構中分別包括哪些幾何信息。
Draw Test Harness是OpenCascade提供的一種靈活和簡便的測試與演示OCCT造型庫的工具。他不僅可以使用交互的方式來創建、顯示和修改曲線、曲面和拓樸形狀,還可以以腳本(script)的方式來使用,OpenCascade就是用腳本的方式來對其造型內核進行自動化測試(Tests)。本文將示例程序的幾何曲線在Draw Test Harness進行創建與顯示,結合圖形的直觀顯示便于對抽象概念的理解。
二、示例程序 Example Code
在OpenCascade提供的文檔《BRep Format Description White Paper》對其BRep文件數據進行了說明。BRep文件的幾何部分包含了三維曲線,根據文檔中提供的數據,利用其提供的類來將示例數據進行輸出,再調試其相關代碼來分析其實現。示例程序如下所示:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
*
* File : Main.cpp
* Author : eryar@163.com
* Date : 2013-11-11 21:46
* Version : 1.0v
*
* Description : Demonstrate the geometry 3d curve section
* of the BRep file of OpenCascade.
*
* KeyWords : OpenCascade, BRep File, Geometry Curve
*
*/
// OpenCascade library.
#define WNT
#include <Geom_Line.hxx>
#include <Geom_Circle.hxx>
#include <Geom_Ellipse.hxx>
#include <Geom_Parabola.hxx>
#include <Geom_Hyperbola.hxx>
#include <Geom_BezierCurve.hxx>
#include <Geom_BSplineCurve.hxx>
#include <Geom_TrimmedCurve.hxx>
#include <Geom_OffsetCurve.hxx>
#include <TColgp_Array1OfPnt.hxx>
#include <TColStd_Array1OfReal.hxx>
#include <TColStd_Array1OfInteger.hxx>
#include <GeomTools.hxx>
#include <GeomTools_CurveSet.hxx>
#pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib")
int main(void)
{
gp_Ax2 axis(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 3), gp::DZ());
std::ofstream dumpFile("geometryCurve.txt");
// 3D curve record 1: Line.
// Example: 1 1 0 3 0 1 0
Handle_Geom_Line theLine = new Geom_Line(gp_Pnt(1, 0, 3), gp_Dir(0, 1, 0));
GeomTools::Write(theLine, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theLine, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theLine, std::cout);
// 3D curve record 2: Circle.
// Example: 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
Handle_Geom_Circle theCircle = new Geom_Circle(axis, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theCircle, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theCircle, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theCircle, std::cout);
// 3D curve record 3: Ellipse.
// Example: 3 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 5 4
Handle_Geom_Ellipse theEllipse = new Geom_Ellipse(axis, 5.0, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theEllipse, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theEllipse, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theEllipse, std::cout);
// 3D curve record 4: Parabola.
// Example: 4 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 16
Handle_Geom_Parabola theParabola = new Geom_Parabola(axis, 16.0);
GeomTools::Write(theParabola, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theParabola, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theParabola, std::cout);
// 3D curve record 5: Hyperbola.
// Example: 5 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 5 4
Handle_Geom_Hyperbola theHyperbola = new Geom_Hyperbola(axis, 5.0, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theHyperbola, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theHyperbola, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theHyperbola, std::cout);
// 3D curve record 6: Bezier Curve.
// Example: 6 1 2 0 1 0 4 1 -2 0 5 2 3 0 6
TColgp_Array1OfPnt poles(1, 3);
TColStd_Array1OfReal weights(1, 3);
poles.SetValue(1, gp_Pnt(0, 1, 0));
poles.SetValue(2, gp_Pnt(1, -2, 0));
poles.SetValue(3, gp_Pnt(2, 3, 0));
weights.SetValue(1, 4.0);
weights.SetValue(2, 5.0);
weights.SetValue(3, 6.0);
Handle_Geom_BezierCurve theBezierCurve = new Geom_BezierCurve(poles, weights);
GeomTools::Write(theBezierCurve, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theBezierCurve, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theBezierCurve, std::cout);
// 3D curve record 7: B-Spline Curve.
// Example: 7 1 0 1 3 5 0 1 0 4 1 -2 0 5 2 3 0 6
// 0 1 0.25 1 0.5 1 0.75 1 1 1
Standard_Integer degree = 1;
TColStd_Array1OfReal knots(1, 5);
TColStd_Array1OfInteger multiplicities(1, 5);
knots.SetValue(1, 0);
knots.SetValue(2, 0.25);
knots.SetValue(3, 0.5);
knots.SetValue(4, 0.75);
knots.SetValue(5, 1.0);
// all knots multiplicity of the B-spline is 1.
multiplicities.Init(1);
Handle_Geom_BSplineCurve theBSplineCurve = new Geom_BSplineCurve(poles, weights, knots, multiplicities, degree);
GeomTools::Write(theBSplineCurve, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theBSplineCurve, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theBSplineCurve, std::cout);
// 3D curve record 8: Trimmed Curve.
// Example: 8 -4 5
// 1 1 2 3 1 0 0
Handle_Geom_Line theBaseCurve = new Geom_Line(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 3), gp_Dir(1, 0, 0));
Handle_Geom_TrimmedCurve theTrimmedCurve = new Geom_TrimmedCurve(theBaseCurve, -4, 5);
GeomTools::Write(theTrimmedCurve, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theTrimmedCurve, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theTrimmedCurve, std::cout);
// 3D curve record 9: Offset Curve.
// Example: 9 2
// 0 1 0
// 1 1 2 3 1 0 0
Handle_Geom_OffsetCurve theOffsetCurve = new Geom_OffsetCurve(theBaseCurve, 2.0, gp::DY());
GeomTools::Write(theOffsetCurve, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theOffsetCurve, dumpFile);
GeomTools::Dump(theOffsetCurve, std::cout);
return 0;
}
上述程序將《BRep Format Description White Paper》中的幾何部分(Geometry Section)的三維曲線(3D Curves)示例數據分別使用類GeomTools的靜態函數輸出到屏幕和文件。
當使用GeomTools::Write()時輸出的內容與BRep文件中一致,當使用GeomTools::Dump()時輸出更易讀的信息。為了便于對比理解,將兩種形式都輸出到文件geometryCurve.txt中,輸出數據如下所示:
1 1 0 3 0 1 0
Line
Origin :1, 0, 3
Axis :0, 1, 0
2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
Circle
Center :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radius :4
3 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 5 4
Ellipse
Center :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radii :5, 4
4 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 16
Parabola
Center :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Focal :16
5 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 5 4
Hyperbola
Center :1, 2, 3
Axis :0, 0, 1
XAxis :1, 0, -0
YAxis :-0, 1, 0
Radii :5, 4
6 1 2 0 1 0 4 1 -2 0 5 2 3 0 6
BezierCurve rational
Degree :2
1 : 0, 1, 0 4
2 : 1, -2, 0 5
3 : 2, 3, 0 6
7 1 0 1 3 5 0 1 0 4 1 -2 0 5 2 3 0 6
0 1 0.25 1 0.5 1 0.75 1 1 1
BSplineCurve rational
Degree 1, 3 Poles, 5 Knots
Poles :
1 : 0, 1, 0 4
2 : 1, -2, 0 5
3 : 2, 3, 0 6
Knots :
1 : 0 1
2 : 0.25 1
3 : 0.5 1
4 : 0.75 1
5 : 1 1
8 -4 5
1 1 2 3 1 0 0
Trimmed curve
Parameters : -4 5
Basis curve :
Line
Origin :1, 2, 3
Axis :1, 0, 0
9 2
0 1 0
1 1 2 3 1 0 0
OffsetCurveOffset : 2
Direction : 0, 1, 0
Basis curve :
Line
Origin :1, 2, 3
Axis :1, 0, 0
三、程序說明 Example Description
3.1 直線 Line
示例:
// 3D curve record 1: Line.
// Example: 1 1 0 3 0 1 0
Handle_Geom_Line theLine = new Geom_Line(gp_Pnt(1, 0, 3), gp_Dir(0, 1, 0));
GeomTools::Write(theLine, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 1>描述的直線數據包含一個三維點P和三維方向D,其參數方程為:
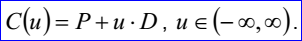
示例數據表示的直線為經過點(1,0,3)且方向D為(0,1,0)的直線,其參數方程表示為:
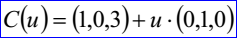
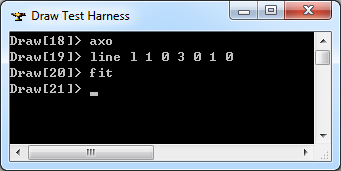
在Draw Test Harness中創建并顯示直線如下所示:

3.2 圓 Circle
示例:
// 3D curve record 2: Circle.
// Example: 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4
gp_Ax2 axis(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 3), gp::DZ());
Handle_Geom_Circle theCircle = new Geom_Circle(axis, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theCircle, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 2>描述的圓的數據包含表示圓心坐標的三維點P,三個方向N,Dx,Dy表示的坐標系和半徑r。其參數方程如下所示:
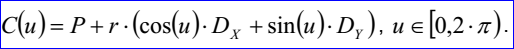
示例數據表示的圓是圓心坐標為(1,2,3),半徑r為(4),圓所在平面的法向N為(0,0,1),圓的X方向(1,0,0)和Y方向為(0,1,0),其參數方程為:
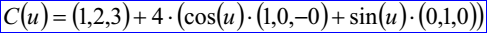
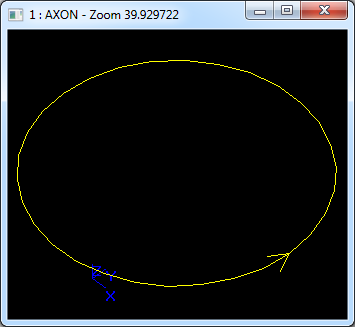
在Draw Test Harness中創建并顯示圓如下所示:
3.3 橢圓 Ellipse
示例:
// 3D curve record 3: Ellipse.
// Example: 3 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 5 4
Handle_Geom_Ellipse theEllipse = new Geom_Ellipse(axis, 5.0, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theEllipse, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 3>定義了橢圓。橢圓的數據包含三維點P,三維正交坐標系N、Dmaj、Dmin和兩個非負實數rmaj和rmin,且rmin<=rmaj。橢圓位于中心點P,法向量為N的平面上,且長軸、短軸的方向分別為Dmaj, Dmin,長軸、短軸上的半徑分別為rmaj, rmin。橢圓的參數方程定義如下所示:
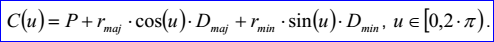
示例數據表示的橢圓的中心點P=(1,2,3),平面的法向量N=(0,0,1),長軸方向Dmaj=(1,0,-0),短軸方向Dmin=(-0,1,0),長軸半徑為5,短軸半徑為4,
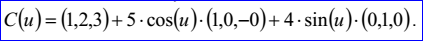
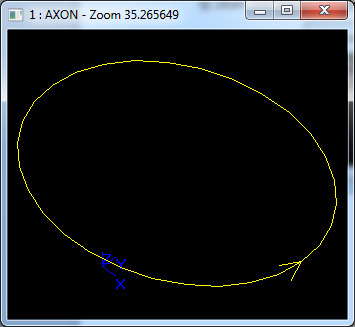
在Draw Test Harness中創建并顯示橢圓如下所示:
3.4 拋物線 Parabola
示例:
// 3D curve record 4: Parabola.
// Example: 4 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 16
Handle_Geom_Parabola theParabola = new Geom_Parabola(axis, 16.0);
GeomTools::Write(theParabola, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 4>定義了拋物線。拋物線數據包含三維點P,三維正交坐標系坐標軸方向N,Dx,Dy和一個非負的實數f。拋物線通過點P,且位于法向量為N的平面上,焦點長度為f,其參數方程如下所示:
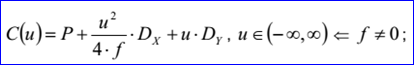
示例數據表示的拋物線過點P=(1,2,3),位于平面的法向N=(0,0,1),拋物線的另兩個軸方向Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(-0,1,0),焦點長度f=16。參數方程為:
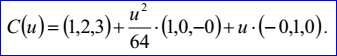
在Draw Test Harness中創建并顯示拋物線如下所示:
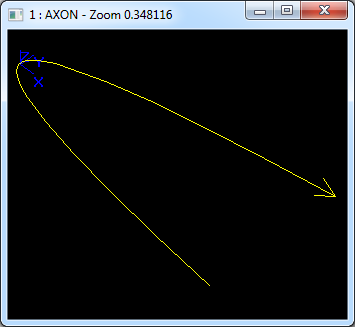
3.5 雙曲線 Hyperbola
示例:
// 3D curve record 5: Hyperbola.
// Example: 5 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 5 4
Handle_Geom_Hyperbola theHyperbola = new Geom_Hyperbola(axis, 5.0, 4.0);
GeomTools::Write(theHyperbola, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 5>定義了雙曲線。雙曲線定義數據有三維點P,三維正交坐標系坐標軸方向為N,Dx,Dy和兩個非負實數Kx,Ky。雙曲線過P點且法向量為N的平面上,其參數方程如下所示:
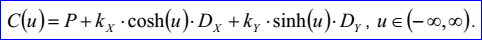
示例數據表示的雙曲線過點P=(1,2,3)且位于的平面的法向N=(0,0,1),其它的數據Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(-0,1,0),Kx=5和Ky=4。其參數方程為:
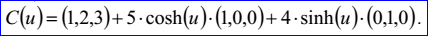
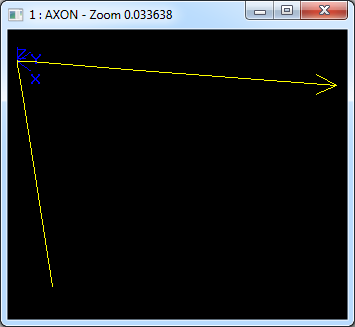
在Draw Test Harness中創建并顯示雙曲線如下所示:
3.6 Bezier曲線 Bezier Curve
示例:
// 3D curve record 6: Bezier Curve.
// Example: 6 1 2 0 1 0 4 1 -2 0 5 2 3 0 6
TColgp_Array1OfPnt poles(1, 3);
TColStd_Array1OfReal weights(1, 3);
poles.SetValue(1, gp_Pnt(0, 1, 0));
poles.SetValue(2, gp_Pnt(1, -2, 0));
poles.SetValue(3, gp_Pnt(2, 3, 0));
weights.SetValue(1, 4.0);
weights.SetValue(2, 5.0);
weights.SetValue(3, 6.0);
Handle_Geom_BezierCurve theBezierCurve = new Geom_BezierCurve(poles, weights);
GeomTools::Write(theBezierCurve, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 6>定義了Bezier曲線。Bezier曲線數據包含有理標志r,曲線的次數m(degree m <= 25查看源代碼可知OpenCascade可處理的B樣條次數不超過25)和帶權的控制點(weight poles)。當有理標志位r=0時,weight poles就是m+1個三維點:B0,B1...Bn;當有理標志位r=1時,weight poles就是帶權的控制點B0 h0... Bm hm。Bi是三維點,hi是[0,m]正實數,即權因子。當有理標志位r=0時,即不是有理Bezier曲線時,hi=1。Bezier曲線參數方程如下所示:
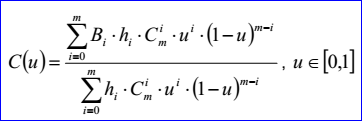
示例數據表示的Bezier曲線是有理Bezier曲線,因其有理標志位r=1,次數m=2,帶權控制點及權因子分別為:B0=(0,1,0),h0=4,B1=(1,-2,0),h1=5,B2=(2,3,0),h2=6。Bezier曲線的參數方程如下所示:
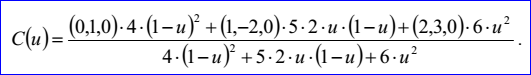
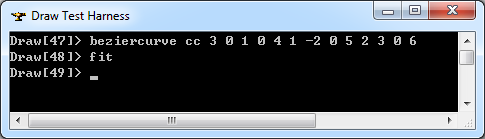
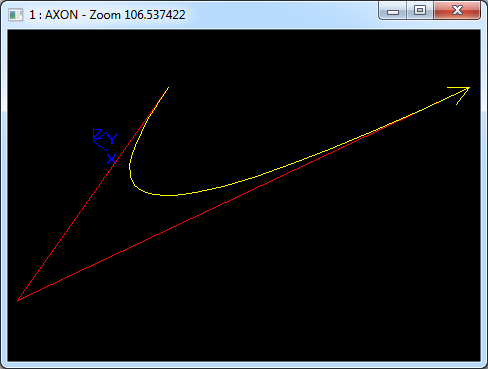
在Draw Test Harness中創建并顯示Bezier曲線如下所示:
3.7 B樣條曲線 B-Spline Curve
示例:
// 3D curve record 7: B-Spline Curve.
// Example: 7 1 0 1 3 5 0 1 0 4 1 -2 0 5 2 3 0 6
// 0 1 0.25 1 0.5 1 0.75 1 1 1
Standard_Integer degree = 1;
TColStd_Array1OfReal knots(1, 5);
TColStd_Array1OfInteger multiplicities(1, 5);
knots.SetValue(1, 0);
knots.SetValue(2, 0.25);
knots.SetValue(3, 0.5);
knots.SetValue(4, 0.75);
knots.SetValue(5, 1.0);
// all knots multiplicity of the B-spline is 1.
multiplicities.Init(1);
Handle_Geom_BSplineCurve theBSplineCurve = new Geom_BSplineCurve(poles, weights, knots, multiplicities, degree);
GeomTools::Write(theBSplineCurve, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 7>定義了B-Spline曲線。B-Spline曲線包含了有理標志位r,曲線次數m<=25,控制點數n>=2,節點數k,帶權控制點wieght poles和節點重數multiplicity knots。
當有理標志位r=0時,是非有理B樣條曲線,weight poles有n個三維點B1,...,Bn;當有理標志位r=1時,是有理B樣條曲線,weight poles是n個帶權控制點對:B1, h1, .... Bn, hn。這里Bi表示一個三維點,hi表示一個[0,1]正實數。當有理標志位r=0時,hi=1。
重節點有k對u1, q1, ... uk, qk。這里ui是重復度為qi>=1的節點。
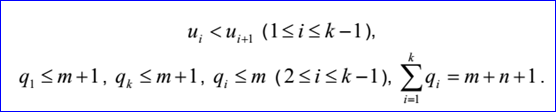
B-Spline曲線的參數方程如下所示:
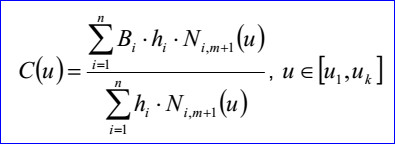
其中基函數Ni,j有如下的遞歸定義:
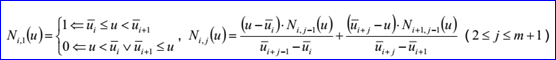
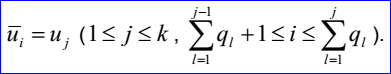
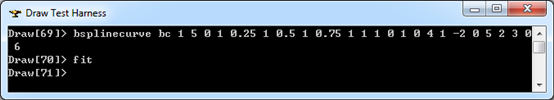
示例數據表示的B樣條曲線為:有理標志位r=1,次數m=1,控制點數n=3,節點數k=5,帶權控制點:B1=(0,1,0),h1=4,B2=(1,-2,0),h2=5,B3=(2,3,0),h3=6;節點及其重數u1=0,q1=1,u2=0.25,q2=1,u3=0.5,q3=1,u4=0.75,q4=1,u5=1,q5=1。B-Spline曲線的參數方程如下所示:
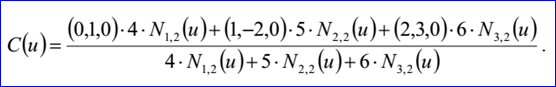
在Draw Test Harness中創建并顯示B-Spline曲線如下所示:
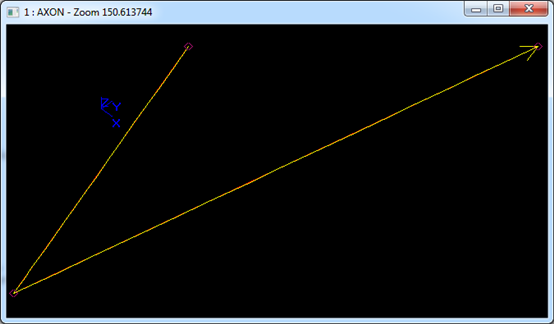
3.8 裁剪曲線 Trimmed Curve
示例:
// 3D curve record 8: Trimmed Curve.
// Example: 8 -4 5
// 1 1 2 3 1 0 0
Handle_Geom_Line theBaseCurve = new Geom_Line(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 3), gp_Dir(1, 0, 0));
Handle_Geom_TrimmedCurve theTrimmedCurve = new Geom_TrimmedCurve(theBaseCurve, -4, 5);
GeomTools::Write(theTrimmedCurve, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 8>定義了裁剪曲線(trimmed curve)。裁剪曲線數據包含:兩個實數umin,umax和<3D curve record>,且umin<umax。裁剪曲線是將<3D curve record>描述的曲線B限制在[umin,umax]。裁剪曲線的參數方程如下所示:
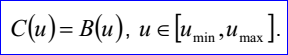
示例數據表示的裁剪曲線為:umin=-4,umax=5,曲線B(u)=(1,2,3)+u(1,0,0)。裁剪曲線的參數方程如下所示:
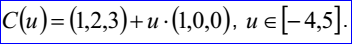
3.9 偏移曲線 Offset Curve
示例:
// 3D curve record 9: Offset Curve.
// Example: 9 2
// 0 1 0
// 1 1 2 3 1 0 0
Handle_Geom_OffsetCurve theOffsetCurve = new Geom_OffsetCurve(theBaseCurve, 2.0, gp::DY());
GeomTools::Write(theOffsetCurve, dumpFile);
<3D curve record 9>定義了偏移曲線(offset curve)。偏移曲線的數據包含偏移距離d,偏移方向D和曲線數據<3D curve record>。偏移曲線是將<3D curve record>描述的曲線沿矢量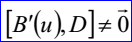 偏移距離d后的結果。偏移曲線的參數方程如下所示:
偏移距離d后的結果。偏移曲線的參數方程如下所示:
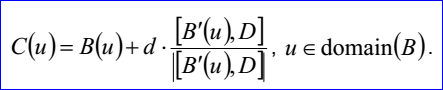
示例數據表示的偏移曲線為偏移距離d=2,方向D=(0,1,0),基曲線B(u)=(1,2,3)+u(1,0,0),其參數方程如下所示:
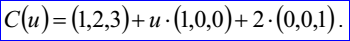
四、程序分析 Refactoring the Code
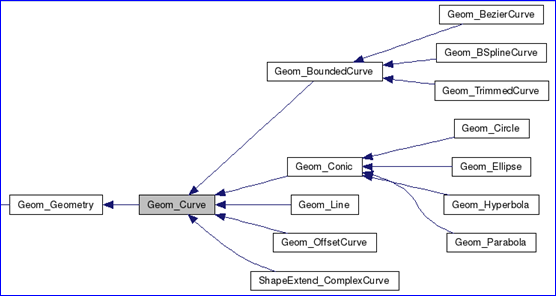
Figure 4.1 Class diagram of Geom_Curve
根據幾何曲線的類圖可知,幾何曲線有個共同的基類Geom_Curve。而在對幾何數據進行輸出與讀入時,用了很多條件判斷。輸出部分程序代碼如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : Print
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
void GeomTools_CurveSet::PrintCurve(const Handle(Geom_Curve)& C,
Standard_OStream& OS,
const Standard_Boolean compact)
{
Handle(Standard_Type) TheType = C->DynamicType();
if ( TheType ==STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_Line)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_Line)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_Circle)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_Circle)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_Ellipse)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_Ellipse)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_Parabola)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_Parabola)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_Hyperbola)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_Hyperbola)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_BezierCurve)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_BezierCurve)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_BSplineCurve)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_BSplineCurve)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_TrimmedCurve)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_TrimmedCurve)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else if ( TheType == STANDARD_TYPE(Geom_OffsetCurve)) {
Print(Handle(Geom_OffsetCurve)::DownCast(C),OS,compact);
}
else {
GeomTools::GetUndefinedTypeHandler()->PrintCurve(C,OS,compact);
//if (!compact)
// OS << "****** UNKNOWN CURVE TYPE ******\n";
//else
// cout << "****** UNKNOWN CURVE TYPE ******" << endl;
}
}
讀入部分的程序代碼如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : ReadCurve
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
Standard_IStream& GeomTools_CurveSet::ReadCurve(Standard_IStream& IS,
Handle(Geom_Curve)& C)
{
Standard_Integer ctype;
try {
OCC_CATCH_SIGNALS
IS >> ctype;
switch (ctype) {
case LINE :
{
Handle(Geom_Line) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
case CIRCLE :
{
Handle(Geom_Circle) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
case ELLIPSE :
{
Handle(Geom_Ellipse) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
case PARABOLA :
{
Handle(Geom_Parabola) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
case HYPERBOLA :
{
Handle(Geom_Hyperbola) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
case BEZIER :
{
Handle(Geom_BezierCurve) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
case BSPLINE :
{
Handle(Geom_BSplineCurve) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
case TRIMMED :
{
Handle(Geom_TrimmedCurve) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
case OFFSET :
{
Handle(Geom_OffsetCurve) CC;
IS >> CC;
C = CC;
}
break;
default:
{
Handle(Geom_Curve) CC;
GeomTools::GetUndefinedTypeHandler()->ReadCurve(ctype,IS,CC);
C = CC;
}
}
}
catch(Standard_Failure) {
#ifdef DEB
Handle(Standard_Failure) anExc = Standard_Failure::Caught();
cout <<"EXCEPTION in GeomTools_CurveSet::ReadCurve(..)!!!" << endl;
cout << anExc << endl;
#endif
C = NULL;
}
return IS;
}
正如《Refactoring-Improving the Design of Existing Code》書中以多態取代條件表達式(Replace Conditional with Polymorphism)所說,在面向對象術語中,聽上去最高貴的詞非“多態”莫屬。多態最根本的好處就是如果你需要根據對象的不同類型而采取不同的行為,多態使你不必編寫明顯的條件表達式。正因為有了多態,所以你會發現“類型碼的switch語句”以及“基于類型名稱的if-then-else語句”在面向對象程序中很少出現。
多態能夠帶給你很多好處。如果同一組條件表達式在程序許多地方出現,那么使用多態的收益是最大的。使用條件表達式時,如果你想添加一種新類型,就必須查找并更新所有條件表達式。但如果改用多態,只需要一個新的子類,并在其中提供適當的函數就行了。類的用戶不需要了解這個子類,這就大降低了系統各部分之間的依賴,使系統升級更容易。
OpenCascade的幾何曲線已經有一個基類Geom_Curve了,可將輸出做為虛函數,就不需要做判斷了。在讀入(創建)時引入工廠模式,對于UndefinedTypeHandler()可以引入Null對象。經過這樣重構之后的程序可讀性應該會更好吧!
五、結論 Conclusion
在邊界表示BRep的形狀中,參數表示的幾何曲線并不會孤立存在,他總是依附于拓樸邊中。在OpenCascade的BRep格式的文件中三維幾何曲線共有九種,通過將這九種幾何曲線輸出,理解參數表示的幾何曲線的數據結構。
通過查看其讀寫幾何曲線的源程序,提出重構的方法。當在面向對象的程序中出現很條件表達式時,那么程序就有“壞味道”了,需要進行重構改進。
六、參考資料 References
1. OpenCascade. BRep Format Description White Paper
2. Martin Fowler. Refactoring:Improving the Design of Existing Code. Addison-Wesley
3. Les Piegl, Wayne Tiller. The NURBS Book. Springer-Verlag