1. Plot B-Spline Basis Function
When draw Bezier curve, you only need to know Bernstein basis function, life was easier.Bernstein basis function solely as a function of the number of control points. Now you have a lot more flexibility, but you also have a lot more to worry about. In addition to control points, the B-Spline basis function must account for the degree of the cruve, as well as the ranges defined by the knot vector. The resulting basis functions are defined not by Bernstein polynomials, but by the Cox-de Boor recursion formulas. [Ref. : Focus on Cruves and Surfaces]
當畫Bezier曲線時,事情要簡單些,因Bezier曲線由Bernstein基函數確定,而Bernstein基函數只與控制頂點數有關。當畫B-Spline曲線時,有了更多的靈活性,即有了局部修改能力,但是你需要考慮的事就更多了。除了控制頂點外,B-Spline曲線的基函數必須解釋曲線的次數和節點矢量定義的范圍。即B-Spline曲線的基函數由Cox-de Boor遞歸方法定義:
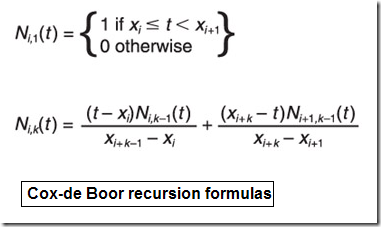
Imagine I want to draw a fourh-order(k=4) cubic curve with 4 control points and I choose a knot vector of [x]=[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]. The knot vector forces each control point to affect the entire curve.
假如我想畫一個四個控制頂點形成的四階三次曲線,選擇節點矢量為[x]=[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]。節點矢量迫使每個控制頂點的改變影響到整個曲線。
使用B樣條基函數的遞歸公式畫出各階基函數的圖形。MATLAB代碼如下:
1: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
2: % Imagine I want to draw a fourth-order cubic curve with 4 control points
3: % and I choose a knot vector of [x]=[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1].
4: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
5:
6: t=0:0.01:1; % knot vector range
7:
8: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
9: % 1. First-order basis functions for k=4 [x]=[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]
10: % N11=0;
11: % N21=0;
12: % N31=0;
13: % N41=1;
14: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
15:
16: N11=0;
17: N21=0;
18: N31=0;
19: N41=1;
20:
21: subplot(2,2,1);
22: plot(t,N11,t,N21,t,N31,t,N41);
23:
24: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
25: % 2. Second-order basis functions for k=4 [x]=[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]
26: % N12=0;
27: % N22=0;
28: % N32=1-t;
29: % N42=t;
30: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
31:
32: N12=0;
33: N22=0;
34: N32=1-t;
35: N42=t;
36:
37: subplot(2,2,2);
38: plot(t,N12,t,N22,t,N32,t,N42)
39:
40: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
41: % 3. Third-order basis functions for k=4 [x]=[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]
42: % N13=0;
43: % N23=(1-t)^2;
44: % N33=2t(1-t);
45: % N43=t^2;
46: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
47:
48: N13=0;
49: N23=(1-t).^2;
50: N33=2*t.*(1-t);
51: N43=t.^2;
52:
53: subplot(2,2,3);
54: plot(t,N13,t,N23,t,N33,t,N43);
55:
56: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
57: % 4. Fourth-order basis functions for k=4 [x]=[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]
58: % N14=(1-t)^3;
59: % N24=3t(1-t)^2;
60: % N34=3(1-t)t^2;
61: % N44=t^3;
62: %-------------------------------------------------------------------------
63:
64: N14=(1-t).^3;
65: N24=3*t.*(1-t).^2;
66: N34=3*(1-t).*t.^2;
67: N44=t.^3;
68:
69: subplot(2,2,4);
70: plot(t,N14,t,N24,t,N34,t,N44);
.csharpcode, .csharpcode pre
{
font-size: small;
color: black;
font-family: consolas, "Courier New", courier, monospace;
background-color: #ffffff;
/*white-space: pre;*/
}
.csharpcode pre { margin: 0em; }
.csharpcode .rem { color: #008000; }
.csharpcode .kwrd { color: #0000ff; }
.csharpcode .str { color: #006080; }
.csharpcode .op { color: #0000c0; }
.csharpcode .preproc { color: #cc6633; }
.csharpcode .asp { background-color: #ffff00; }
.csharpcode .html { color: #800000; }
.csharpcode .attr { color: #ff0000; }
.csharpcode .alt
{
background-color: #f4f4f4;
width: 100%;
margin: 0em;
}
.csharpcode .lnum { color: #606060; }
用MATLAB畫出各階基函數如下圖所示:
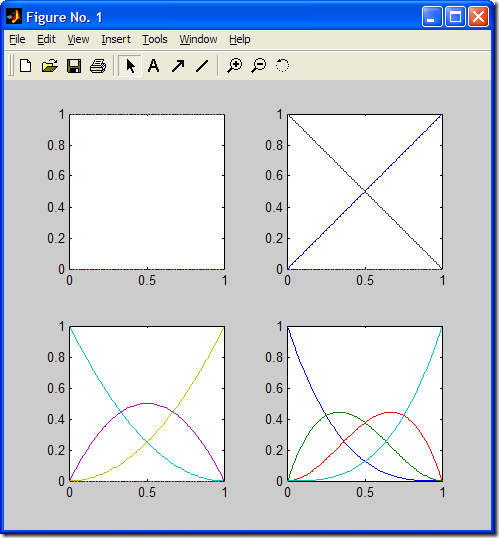
三次均勻B樣條基函數Ni,3(u)的圖形由MATLAB生成如下所示:
生成此圖形的MATLAB代碼如下:
1: %------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2: % 均勻B樣條基最簡單的形式是取節點為整數:Ti=i(i=0,1,2,...,n),
3: % 令:t-ti=u,則參數u的取值范圍為[0,1]。則得Ni,3(u)如下式:
4: % | u^3 / 6; u=[0,1]
5: % | (-3u^3 + 3u^2 + 3u + 1) / 6; u=[0,1]
6: % Ni,3(u) = | (3u^3 - 6u^2 + 4) / 6; u=[0,1]
7: % | (-u^3 + 3u^2 - 3u + 1) / 6; u=[0,1]
8: %
9: %------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10:
11: u=0:0.01:1;
12: N03=u.^3/6;
13: N13=(-3*u.^3 + 3*u.^2 + 3*u + 1)/6;
14: N23=(3*u.^3 - 6*u.^2 + 4) / 6;
15: N33=(-u.^3 + 3*u.^2 - 3*u + 1) / 6;
16:
17: line(u, N03, 'Color', 'r');
18: line(u+1, N13, 'Color', 'g');
19: line(u+2, N23, 'Color', 'b');
20: line(u+3, N33, 'Color', 'y');
.csharpcode, .csharpcode pre
{
font-size: small;
color: black;
font-family: consolas, "Courier New", courier, monospace;
background-color: #ffffff;
/*white-space: pre;*/
}
.csharpcode pre { margin: 0em; }
.csharpcode .rem { color: #008000; }
.csharpcode .kwrd { color: #0000ff; }
.csharpcode .str { color: #006080; }
.csharpcode .op { color: #0000c0; }
.csharpcode .preproc { color: #cc6633; }
.csharpcode .asp { background-color: #ffff00; }
.csharpcode .html { color: #800000; }
.csharpcode .attr { color: #ff0000; }
.csharpcode .alt
{
background-color: #f4f4f4;
width: 100%;
margin: 0em;
}
.csharpcode .lnum { color: #606060; }
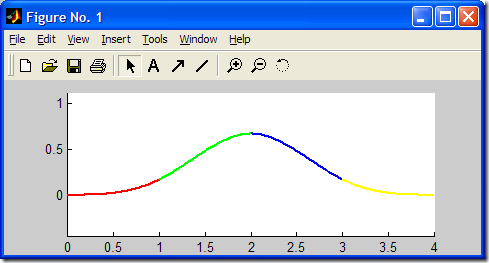
2. Plot B-Spline Curve
已知平面上五個頂點矢量V0(0,1), V1(1,1), V2(1,0), V3(1,-1), V4(2,-1), 要求構造一條三次均勻B樣條曲線,并做出圖形.
使用MATLAB代碼如下:
1: %-----------------------------------------------------------
2: % Plot Cubic Uniform B-Spline Curve.
3: % Just for Testing, Welcome your advice: eryar@163.com
4: %
5: % Date : 2011-12-28 21:31
6: %
7: %-----------------------------------------------------------
8:
9: % Knot Vector range.
10: u=0:0.01:1;
11:
12: % Control Points.
13: % You can change the control point's number and value
14: % to test the effect.
15: V0=[0 1];
16: V1=[1 1];
17: V2=[1 0];
18: V3=[1 -1];
19: V4=[2 -1];
20:
21: % Basis Functions.
22: N03=(-u.^3 + 3*u.^2 - 3*u + 1) / 6;
23: N13=(3*u.^3 - 6*u.^2 + 4) / 6;
24: N23=(-3*u.^3 + 3*u.^2 + 3*u + 1)/6;
25: N33=u.^3/6;
26:
27: % Calculate every segment.
28: r0x=N03 * V0(1) + N13 * V1(1) + N23 * V2(1) + N33 * V3(1);
29: r0y=N03 * V0(2) + N13 * V1(2) + N23 * V2(2) + N33 * V3(2);
30: r1x=N03 * V1(1) + N13 * V2(1) + N23 * V3(1) + N33 * V4(1);
31: r1y=N03 * V1(2) + N13 * V2(2) + N23 * V3(2) + N33 * V4(2);
32:
33: % Plot the Control Polygon.
34: plot(V0(1), V0(2), 'Marker', 'o'); hold on;
35: plot(V0(1), V0(2), 'Marker', 'o'); hold on;
36: plot(V1(1), V1(2), 'Marker', 'o'); hold on;
37: plot(V2(1), V2(2), 'Marker', 'o'); hold on;
38: plot(V3(1), V3(2), 'Marker', 'o'); hold on;
39:
40: % Plot the Uniform B-Spline Curve.
41: line('XData', r0x, 'YData', r0y, 'Color', 'r'); 42: line('XData', r1x, 'YData', r1y, 'Color', 'g');
.csharpcode, .csharpcode pre
{
font-size: small;
color: black;
font-family: consolas, "Courier New", courier, monospace;
background-color: #ffffff;
/*white-space: pre;*/
}
.csharpcode pre { margin: 0em; }
.csharpcode .rem { color: #008000; }
.csharpcode .kwrd { color: #0000ff; }
.csharpcode .str { color: #006080; }
.csharpcode .op { color: #0000c0; }
.csharpcode .preproc { color: #cc6633; }
.csharpcode .asp { background-color: #ffff00; }
.csharpcode .html { color: #800000; }
.csharpcode .attr { color: #ff0000; }
.csharpcode .alt
{
background-color: #f4f4f4;
width: 100%;
margin: 0em;
}
.csharpcode .lnum { color: #606060; }
生成圖形如下所示:
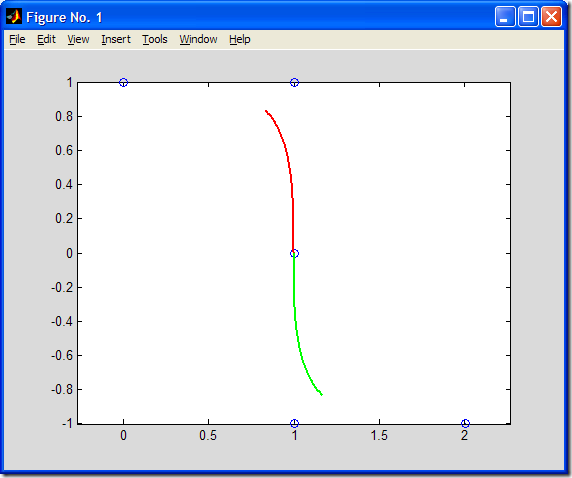
如圖所示,B樣條曲線由兩段組成,控制頂點由“0”標出。
試求由特征頂點V0=[-1,1], V1=[1,1], V2=[1,-1], V3=[-1,-1]決定的閉合的三次均勻B樣條曲線,并做出圖形。適當修改上述MATLAB代碼,即可得到所求B樣條曲線,如下圖所示:
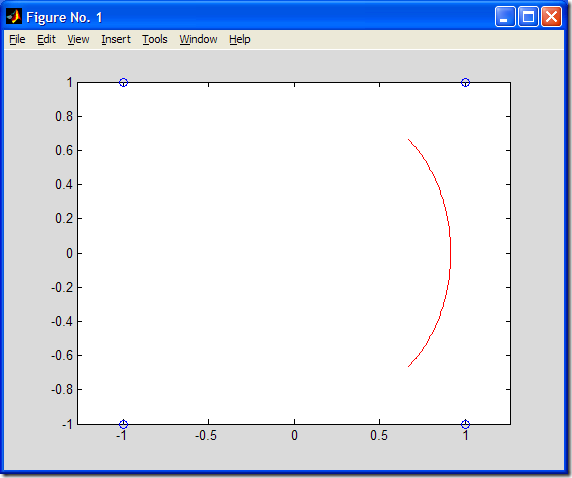
3.結論:
對于均勻B樣條基函數,由于節點矢量均勻遞增,所以在每兩個節點組成的區間的距離相等。利用基函數的的遞推公式可以計算出每個區間上的函數表達式。對于上例中的均勻B樣條基每個區間取值范圍都是從0到1,通過偏移X軸,可畫出B樣條的基函數。
通過MATLAB畫出B樣條曲線的基函數,操作簡單,便于對B樣條基函數的理解。在理解B樣條基函數后,會對B樣條曲線的理解更加深刻。繼續加油!!