[Cocoa]深入淺出Cocoa之 Method Swizzling
CC許可,轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)注明出處
在前文深入淺出Cocoa之消息中,我簡(jiǎn)要介紹了ObjC 中消息的基本情況,包括SEL查找,緩存以及消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)等。在本文中,我要介紹一個(gè)很有趣的技術(shù),Method swizzling,通過這個(gè)手法,我們可以動(dòng)態(tài)修改方法的實(shí)現(xiàn),從而達(dá)到修改類行為的目的。當(dāng)然,還有其他辦法(如 ClassPosing,Category)也可以達(dá)到這個(gè)目的。ClassPosing 是針對(duì)類級(jí)別的,是重量級(jí)的手法,Category 也差不多,比較重量級(jí),此外 Category 還無法避免下面的遞歸死循環(huán)(如果你的代碼出現(xiàn)了如下形式的遞歸調(diào)用,應(yīng)該考慮一下你的設(shè)計(jì),而不是使用在這里介紹的 Method Swizzling 手法,:))。
// Bar
//
@implementation Bar
- (void) testMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Bar testMethod");
}
@end
// Bar(BarCategory)
//
@implementation Bar(BarCategory)
- (void) altRecursionMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Bar(BarCategory) recursionMethod");
[self altRecursionMethod];
}
@end
在前文深入淺出Cocoa之消息中提到,ObjC 中的類(class)和實(shí)例(instance)都是對(duì)象,類對(duì)象有自己的類方法列表,實(shí)例對(duì)象有自己的實(shí)例方法列表,這些方法列表(struct objc_method_list)是存儲(chǔ)在 struct objc_class 中的。每個(gè)方法列表存儲(chǔ)近似 SEL:Method 的對(duì),Method 是一個(gè)對(duì)象,包含方法的具體實(shí)現(xiàn) impl。由此可知,我們只需要修改 SEL 對(duì)應(yīng)的 Method 的 impl 既可以達(dá)到修改消息行為的目的。下面來看代碼:
void PerformSwizzle(Class aClass, SEL orig_sel, SEL alt_sel, BOOL forInstance)
{
// First, make sure the class isn't nil
if (aClass != nil) {
Method orig_method = nil, alt_method = nil;
// Next, look for the methods
if (forInstance) {
orig_method = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, orig_sel);
alt_method = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, alt_sel);
} else {
orig_method = class_getClassMethod(aClass, orig_sel);
alt_method = class_getClassMethod(aClass, alt_sel);
}
// If both are found, swizzle them
if ((orig_method != nil) && (alt_method != nil)) {
IMP temp;
temp = orig_method->method_imp;
orig_method->method_imp = alt_method->method_imp;
alt_method->method_imp = temp;
} else {
#if DEBUG
NSLog(@"PerformSwizzle Error: Original %@, Alternate %@",(orig_method == nil)?@" not found":@" found",(alt_method == nil)?@" not found":@" found");
#endif
}
} else {
#if DEBUG
NSLog(@"PerformSwizzle Error: Class not found");
#endif
}
}
void MethodSwizzle(Class aClass, SEL orig_sel, SEL alt_sel)
{
PerformSwizzle(aClass, orig_sel, alt_sel, YES);
}
void ClassMethodSwizzle(Class aClass, SEL orig_sel, SEL alt_sel)
{
PerformSwizzle(aClass, orig_sel, alt_sel, NO);
}
讓我們來分析上面代碼:
1,首先,區(qū)分類方法和實(shí)例方法;
2,取得 SEL 對(duì)應(yīng)的 Method;
3,修改 Method 的 impl,在這里是通過交換實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
上面的代碼是可以工作的,但還不夠完善。Apple 10.5 提供了交換 Method 實(shí)現(xiàn)的 API: method_exchangeImplementations 。下面我們使用這個(gè)新 API,并以 NSObject category的形式給出新的實(shí)現(xiàn)方式:
#if TARGET_OS_IPHONE
#import <objc/runtime.h>
#import <objc/message.h>
#else
#import <objc/objc-class.h>
#endif
// NSObject (MethodSwizzlingCategory)
//
@interface NSObject (MethodSwizzlingCategory)
+ (BOOL)swizzleMethod:(SEL)origSel withMethod:(SEL)altSel;
+ (BOOL)swizzleClassMethod:(SEL)origSel withClassMethod:(SEL)altSel;
@end
@implementation NSObject (MethodSwizzlingCategory)
+ (BOOL)swizzleMethod:(SEL)origSel withMethod:(SEL)altSel
{
Method origMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, origSel);
if (!origSel) {
NSLog(@"original method %@ not found for class %@", NSStringFromSelector(origSel), [self class]);
return NO;
}
Method altMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, altSel);
if (!altMethod) {
NSLog(@"original method %@ not found for class %@", NSStringFromSelector(altSel), [self class]);
return NO;
}
class_addMethod(self,
origSel,
class_getMethodImplementation(self, origSel),
method_getTypeEncoding(origMethod));
class_addMethod(self,
altSel,
class_getMethodImplementation(self, altSel),
method_getTypeEncoding(altMethod));
method_exchangeImplementations(class_getInstanceMethod(self, origSel), class_getInstanceMethod(self, altSel));
return YES;
}
+ (BOOL)swizzleClassMethod:(SEL)origSel withClassMethod:(SEL)altSel
{
Class c = object_getClass((id)self);
return [c swizzleMethod:origSel withMethod:altSel];
}
@end
代碼就不用多解釋了,下面我們來看如何使用。先看輔助類Foo:
Foo.h
//
// Foo.h
// MethodSwizzling
//
// Created by LuoZhaohui on 1/5/12.
// Copyright (c) 2012 http://www.shnenglu.com/kesalin/. All rights reserved.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
// Foo
//
@interface Foo : NSObject
- (
void) testMethod;
- (
void) baseMethod;
- (
void) recursionMethod;
@end
// Bar
//
@interface Bar : Foo
- (
void) testMethod;
@end
// Bar(BarCategory)
//
@interface Bar(BarCategory)
- (
void) altTestMethod;
- (
void) altBaseMethod;
- (
void) altRecursionMethod;
@end
Foo.m
//
// Foo.m
// MethodSwizzling
//
// Created by LuoZhaohui on 1/5/12.
// Copyright (c) 2012 . All rights reserved.
//
#import "Foo.h"
// Foo
//
@implementation Foo
- (
void) testMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Foo testMethod");
}
- (
void) baseMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Foo baseMethod");
}
- (
void) recursionMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Foo recursionMethod");
}
@end
// Bar
//
@implementation Bar
- (
void) testMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Bar testMethod");
}
@end
// Bar(BarCategory)
//
@implementation Bar(BarCategory)
- (
void) altTestMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Bar(BarCategory) altTestMethod");
}
- (
void) altBaseMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Bar(BarCategory) altBaseMethod");
}
- (
void) altRecursionMethod
{
NSLog(@" >> Bar(BarCategory) recursionMethod");
[self altRecursionMethod];
}
@end
下面是具體的使用示例:
// Main
//
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool
{
Foo * foo = [[[Foo alloc] init] autorelease];
Bar * bar = [[[Bar alloc] init] autorelease];
NSLog(@"========= Method Swizzling test 1 =========");
NSLog(@" Step 1");
[foo testMethod];
[bar testMethod];
[bar altTestMethod];
NSLog(@" Step 2");
[Bar swizzleMethod:@selector(testMethod) withMethod:@selector(altTestMethod)];
[foo testMethod];
[bar testMethod];
[bar altTestMethod];
NSLog(@"========= Method Swizzling test 2 =========");
NSLog(@" Step 1");
[foo baseMethod];
[bar baseMethod];
[bar altBaseMethod];
NSLog(@" Step 2");
[Bar swizzleMethod:@selector(baseMethod) withMethod:@selector(altBaseMethod)];
[foo baseMethod];
[bar baseMethod];
[bar altBaseMethod];
NSLog(@"========= Method Swizzling test 3 =========");
[Bar swizzleMethod:@selector(recursionMethod) withMethod:@selector(altRecursionMethod)];
[bar recursionMethod];
}
return 0;
}
輸出結(jié)果為下表。注意,test 3 中調(diào)用了遞歸調(diào)用“自己”的方法,你能理解為什么沒有出現(xiàn)死循環(huán)么?
========= Method Swizzling test 1 =========
Step 1
>> Foo testMethod
>> Bar testMethod
>> Bar(BarCategory) altTestMethod
Step 2
>> Foo testMethod
>> Bar(BarCategory) altTestMethod
>> Bar testMethod
========= Method Swizzling test 2 =========
Step 1
>> Foo baseMethod
>> Foo baseMethod
>> Bar(BarCategory) altBaseMethod
Step 2
>> Foo baseMethod
>> Bar(BarCategory) altBaseMethod
>> Foo baseMethod
========= Method Swizzling test 3 =========
>> Bar(BarCategory) recursionMethod
>> Foo recursionMethod
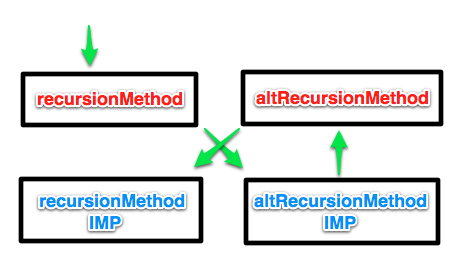
test3 解釋:在函數(shù)體 {} 之間的部分是真正的 IMP,而在這之前的是 SEL。通常情況下,SEL 是與 IMP 匹配的,但在 swizzling 之后,情況就不同了。下圖就是調(diào)用的時(shí)序圖。
 rentzsch 寫了一個(gè)完善的開源類 jrswizzle 來處理 Method Swizzling,如果你在工程中使用到 Method Swizzling 手法,應(yīng)該優(yōu)先使用這個(gè)類庫,:)。
rentzsch 寫了一個(gè)完善的開源類 jrswizzle 來處理 Method Swizzling,如果你在工程中使用到 Method Swizzling 手法,應(yīng)該優(yōu)先使用這個(gè)類庫,:)。
Refference: