Posted on 2010-08-10 20:48
MiYu 閱讀(1135)
評論(5) 編輯 收藏 引用 所屬分類:
ACM ( 組合 ) 、
ACM ( 博弈 )

MiYu原創, 轉帖請注明 : 轉載自 ______________白白の屋
題目地址:
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2147
題目描述:
kiki's game
Time Limit: 5000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 40000/1000 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1806 Accepted Submission(s): 1055
Problem Description
Recently kiki has nothing to do. While she is bored, an idea appears in his mind, she just playes the checkerboard game.The size of the chesserboard is n*m.First of all, a coin is placed in the top right corner(1,m). Each time one people can move the coin into the left, the underneath or the left-underneath blank space.The person who can't make a move will lose the game. kiki plays it with ZZ.The game always starts with kiki. If both play perfectly, who will win the game?
Input
Input contains multiple test cases. Each line contains two integer n, m (0<n,m<=2000). The input is terminated when n=0 and m=0.
Output
If kiki wins the game printf "Wonderful!", else "What a pity!".
Sample Input
5 3
5 4
6 6
0 0
Sample Output
What a pity!
Wonderful!
Wonderful!
題目分析:
一直WA , 分析也沒分析出來 , 百度了一下別人的解題報告后.............我承認....我被征服了.....................
分析如下:
P點:就是P個石子的時候,對方拿可以贏(自己輸的)
N點:就是N個石子的時候,自己拿可以贏
現在關于P,N的求解有三個規則
(1):最終態都是P
(2):按照游戲規則,到達當前態的前態都是N的話,當前態是P
(3):按照游戲規則,到達當前態的前態至少有一個P的話,當前態是N
題意:
在一個m*n的棋盤內,從(1,m)點出發,每次可以進行的移動是:左移一,下移一,左下移一。然后kiki每次先走,判斷kiki時候會贏(對方無路可走的時候)。
我們可以把PN狀態的點描繪出來::
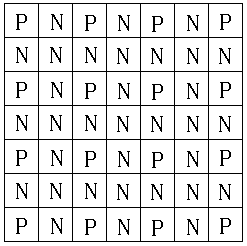
這些點的描繪有一個程序::
【
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
bool map[2001][2001];//1 P 0 N;
int main(){
int i,j,k;
map[1][1]=1;
for(i=2;i<=2000;i++)
{
if(map[i-1][1])
map[i][1]=0;
else map[i][1]=1;
for(j=2;j<i;j++){
if(!map[i][j-1]&&!map[i-1][j-1]&&!map[i-1][j])
map[i][j]=1;
else map[i][j]=0;
}
if(map[1][i-1])
map[1][i]=0;
else map[1][i]=1;
for(j=2;j<i;j++){
if(!map[j-1][i]&&!map[j-1][i-1]&&!map[j][i-1])
map[j][i]=1;
else map[j][i]=0;
}
if(!map[i][i-1]&&!map[i-1][i-1]&&!map[i-1][i])
map[i][i]=1;
else map[i][i]=0;
}
int M,N;
for(i=1;i<=10;i++){
for(j=1;j<=10;j++)
printf("%c ",map[i][j]?'P':'N');
printf("\n");
}
while(scanf("%d%d",&M,&N)&&M&&N){
if(map[M][N]) printf("What a pity!\n");
else printf("Wonderful!\n");
}
return 0;
}
】
具體代碼如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int n,m;
while ( cin >> n >> m , n + m )
{
puts ( n%2 && m % 2 ? "What a pity!" : "Wonderful!");
}
return 0;
}