Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的最短路徑路由算法,用于計算一個節點到其他所有節點的最短路徑。主要特點是以起始點為中心向外層層擴展,直到擴展到終點為止。
Dijkstra算法能得出最短路徑的最優解,但由于它遍歷計算的節點很多,所以效率低。
Dijkstra算法是很有代表性的最短路算法,在很多專業課程中都作為基本內容有詳細的介紹,如數據結構,圖論,運籌學等等。
其基本思想是,設置頂點集合S并不斷地作貪心選擇來擴充這個集合。一個頂點屬于集合S當且僅當從源到該頂點的最短路徑長度已知。
初始時,S中僅含有源。設u是G的某一個頂點,把從源到u且中間只經過S中頂點的路稱為從源到u的特殊路徑,并用數組dist記錄當前每個頂點所對應的最短特殊路徑長度。Dijkstra算法每次從V-S中取出具有最短特殊路長度的頂點u,將u添加到S中,同時對數組dist作必要的修改。一旦S包含了所有V中頂點,dist就記錄了從源到所有其它頂點之間的最短路徑長度。
例如,對下圖中的有向圖,應用Dijkstra算法計算從源頂點1到其它頂點間最短路徑的過程列在下表中。
Dijkstra算法的迭代過程:
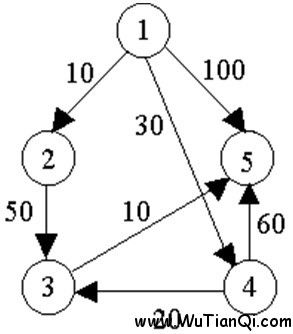
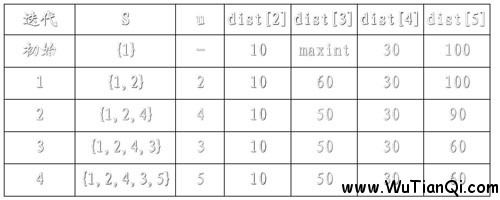
主題好好理解上圖!
以下是具體的實現(C/C++):
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 const int maxnum = 100;
5 const int maxint = 999999;
6
7 // 各數組都從下標1開始
8 int dist[maxnum]; // 表示當前點到源點的最短路徑長度
9 int prev[maxnum]; // 記錄當前點的前一個結點
10 int c[maxnum][maxnum]; // 記錄圖的兩點間路徑長度
11 int n, line; // 圖的結點數和路徑數
12
13 // n -- n nodes
14 // v -- the source node
15 // dist[] -- the distance from the ith node to the source node
16 // prev[] -- the previous node of the ith node
17 // c[][] -- every two nodes' distance
18 void Dijkstra(int n, int v, int *dist, int *prev, int c[maxnum][maxnum])
19 {
20 bool s[maxnum]; // 判斷是否已存入該點到S集合中
21 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
22 {
23 dist[i] = c[v][i];
24 s[i] = 0; // 初始都未用過該點
25 if(dist[i] == maxint)
26 prev[i] = 0;
27 else
28 prev[i] = v;
29 }
30 dist[v] = 0;
31 s[v] = 1;
32
33 // 依次將未放入S集合的結點中,取dist[]最小值的結點,放入結合S中
34 // 一旦S包含了所有V中頂點,dist就記錄了從源點到所有其他頂點之間的最短路徑長度
35 // 注意是從第二個節點開始,第一個為源點
36 for(int i=2; i<=n; ++i)
37 {
38 int tmp = maxint;
39 int u = v;
40 // 找出當前未使用的點j的dist[j]最小值
41 for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
42 if((!s[j]) && dist[j]<tmp)
43 {
44 u = j; // u保存當前鄰接點中距離最小的點的號碼
45 tmp = dist[j];
46 }
47 s[u] = 1; // 表示u點已存入S集合中
48
49 // 更新dist
50 for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
51 if((!s[j]) && c[u][j]<maxint)
52 {
53 int newdist = dist[u] + c[u][j];
54 if(newdist < dist[j])
55 {
56 dist[j] = newdist;
57 prev[j] = u;
58 }
59 }
60 }
61 }
62
63 // 查找從源點v到終點u的路徑,并輸出
64 void searchPath(int *prev,int v, int u)
65 {
66 int que[maxnum];
67 int tot = 1;
68 que[tot] = u;
69 tot++;
70 int tmp = prev[u];
71 while(tmp != v)
72 {
73 que[tot] = tmp;
74 tot++;
75 tmp = prev[tmp];
76 }
77 que[tot] = v;
78 for(int i=tot; i>=1; --i)
79 if(i != 1)
80 cout << que[i] << " -> ";
81 else
82 cout << que[i] << endl;
83 }
84
85 int main()
86 {
87 freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
88 // 各數組都從下標1開始
89
90 // 輸入結點數
91 cin >> n;
92 // 輸入路徑數
93 cin >> line;
94 int p, q, len; // 輸入p, q兩點及其路徑長度
95
96 // 初始化c[][]為maxint
97 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
98 for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
99 c[i][j] = maxint;
100
101 for(int i=1; i<=line; ++i)
102 {
103 cin >> p >> q >> len;
104 if(len < c[p][q]) // 有重邊
105 {
106 c[p][q] = len; // p指向q
107 c[q][p] = len; // q指向p,這樣表示無向圖
108 }
109 }
110
111 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
112 dist[i] = maxint;
113 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
114 {
115 for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
116 printf("%8d", c[i][j]);
117 printf("\n");
118 }
119
120 Dijkstra(n, 1, dist, prev, c);
121
122 // 最短路徑長度
123 cout << "源點到最后一個頂點的最短路徑長度: " << dist[n] << endl;
124
125 // 路徑
126 cout << "源點到最后一個頂點的路徑為: ";
127 searchPath(prev, 1, n);
128 }
輸入數據:
5
7
1 2 10
1 4 30
1 5 100
2 3 50
3 5 10
4 3 20
4 5 60
輸出數據:
999999 10 999999 30 100
10 999999 50 999999 999999
999999 50 999999 20 10
30 999999 20 999999 60
100 999999 10 60 999999
源點到最后一個頂點的最短路徑長度: 60
源點到最后一個頂點的路徑為: 1 -> 4 -> 3 -> 5
本文轉自:http://www.wutianqi.com/?p=1890
其他連接:http://2728green-rock.blog.163.com/blog/static/43636790200901211848284/
posted on 2012-06-30 16:12
王海光 閱讀(565)
評論(0) 編輯 收藏 引用 所屬分類:
算法