新建網頁 1
13
構造了一個地形以后,我們想要有移動攝像機的能力,以便模擬在地形上行走的效果。我們需要調整攝像機的高度,這依賴于地形部分的知識,好的,繼續往下看。我們首先需要找到照相機所在的方格的位置,并給出x軸和z軸坐標,cTerrain::get_height函數能做到這些,它能提供x軸、z軸坐標參數,返回攝像機需要被設置在地形上的高度值,現在看實現部分。
float cTerrain::get_height(float x, float z)
{
// Translate on xz-plane by the transformation that takes the terrain START point to the origin,
// note that we negative z value so positive z-axis will be down in logical.
x = m_width/2.0f + x;
z = m_depth/2.0f - z;
// Scale down by the transformation that makes the cell_spacing equal to one.
x /= m_cell_spacing;
z /= m_cell_spacing;
We first translate by the transformation that takes the start point of the terrain to the origin. Next, we scale by the inverse of the cell spacing variable; this scaling sets the cell spacing to 1. Then we switch to a new frame of reference where the positive z-axis points “down.” Of course, there is no code that changes the frame of reference, but it is now understood that +z goes down. Figure 13.9 shows these steps graphically.
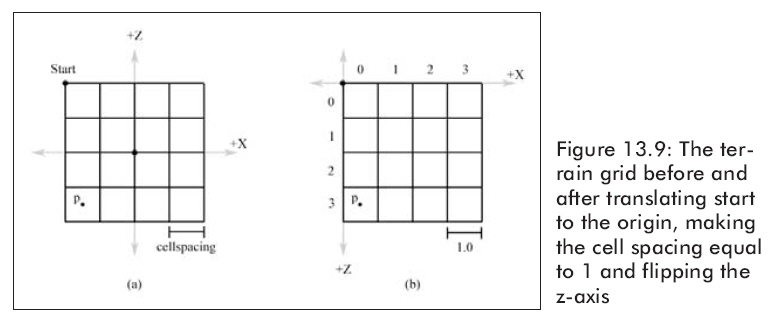
We see that our changed coordinate system matches the ordering of a matrix. That is, the upper-left corner is at the origin, the column count increases in the right direction, and the row count increases in the down direction. Thus, by Figure 13.9 and knowing the cell spacing is equal to 1, we can immediately see that the row and column of the cell we are in is given by:
// From now on, we will interpret our positive z-axis as going in the 'down' direction,
// rather than the 'up' direction. This allows to extract the row and column simply by
// 'flooring' x and z:
float col = floorf(x);
float row = floorf(z);
// ensures row and col are valid
if(row < 0)
row = 0;
if(row >= m_num_cells_per_col - 1)
row = m_num_cells_per_col - 1;
if(col < 0)
col = 0;
if(col >= m_num_cells_per_row)
col = m_num_cells_per_row;
現在我們將取得方格的四個頂點的高度。
// get the heights of the quad we're in:
//
// A B
// *---*
// | / |
// *---*
// C D
float AHeight = get_height_map_entry(row, col);
float BHeight = get_height_map_entry(row, col+1);
float CHeight = get_height_map_entry(row+1, col);
float DHeight = get_height_map_entry(row+1, col+1);
現在我們知道了方格的四個頂點的高度,我們需要找到照相機所在的位置的方格的高度,因為一個方格可能同時向幾個方向傾斜,這可能會稍微難一點,見圖 13.10:
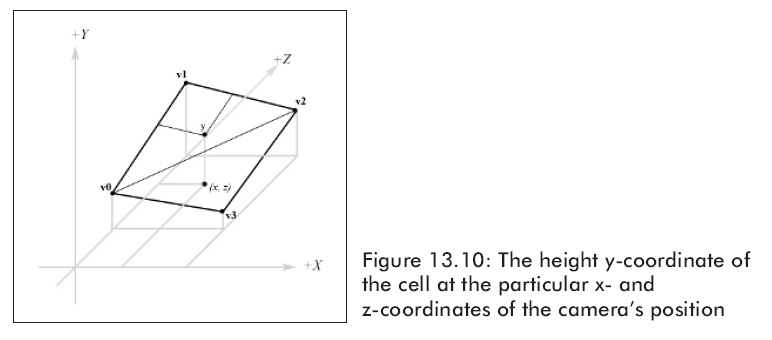
為了找到高度,我們需要知道我們在方格中的哪個三角形里。方格是由二個三角形渲染成的,找到我們所在的三角形,我們要取得我們所在的方格并且轉換它,它的左上點是原點。
自從用行和列來描述我們所在的方格左上頂點的位置以來,我們必須沿x軸平移-col個單位,并沿z軸平移-row個單位。沿著x軸和z軸的平移過程用如下代碼表示。
//
// Find the triangle we are in:
//
// Translate by the transformation that takes the upper-left corner of the cell we are in
// to the origin. Recall that our cell_spacing was nomalized to 1. Thus we have a unit square
// at the origin of our +x -> 'right' and +z -> 'down' system.
float dx = x - col;
float dz = z - row;
float height = 0.0f;
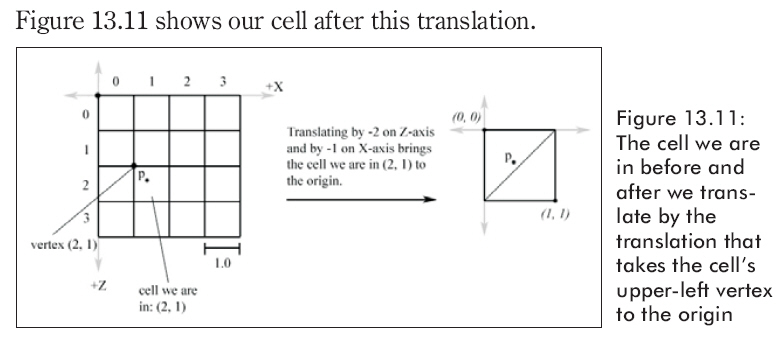
Then, if dx < 1.0 – dx we are in the “upper” triangle v0v1v2. Otherwise, we are in the “lower” triangle v0v2v3 (see Figure 13.10).
Now we explain how to find the height if we are in the “upper” triangle. The process is similar for the “lower” triangle, and of course the code for both follows shortly. To find the height if we are in the “upper”triangle, we construct two vectors, u = (cellSpacing, B – A, 0) and v = (0, C – A, – cellSpacing), on the sides of the triangle and originating at the terminal point of the vector q = (qx, A, qz) as Figure 13.12.a shows. Then we linearly interpolate along u by dx, and we linearly interpolate along v by dz. Figure 13.12.b illustrates these interpolations. The y-coordinate of the vector (q + dxu + dzv) gives the height based on the given x- and z-coordinates; recall the geometric interpretation of vector addition to see this.
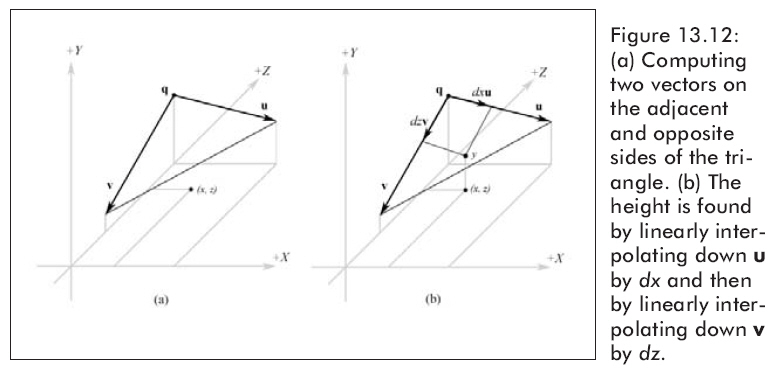
注意:我們只關心改變的高度值,我們只修改y值,忽視其他部分,因此,Height=A + dxuy + dzvy
float height = 0.0f;
if(dz < 1.0f - dx) // upper triangle ABC
{
float uy = BHeight - AHeight; // A->B
float vy = CHeight - AHeight; // A->C
// Linearly interpolate on each vector. The height is the vertex height the vectors u and v
// originate from {A}, plus the heights found by interpolating on each vector u and v.
height = AHeight + lerp(0.0f, uy, dx) + lerp(0.0f, vy, dz);
}
else // lower triangle DCB
{
float uy = CHeight - DHeight; // D->C
float vy = BHeight - DHeight; // D->B
// Linearly interpolate on each vector. The height is the vertex height the vectors u and v
// originate from {D}, plus the heights found by interpolating on each vector u and v.
height = DHeight + lerp(0.0f, uy, 1.0f - dx) + lerp(0.0f, vy, 1.0f - dz);
}
return height;
}
Lerp函數是一個沿著一維直線的基本線性插值算法,實現如下:
float lerp(float a, float b, float t)
{
return a * (1 - t) + (b * t);
}
繪制函數:
void cTerrain::draw(D3DXMATRIX* world_matrix, bool draw_triangle)
{
if(m_device == NULL)
return;
m_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, world_matrix);
m_device->SetStreamSource(0, m_vertex_buffer, 0, sizeof(cTerrainVertex));
m_device->SetFVF(TERRAIN_VERTEX_FVF);
m_device->SetIndices(m_index_buffer);
m_device->SetTexture(0, m_texture);
m_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_LIGHTING, FALSE); // trun off lighting since we're lighting it ourselves
m_device->DrawIndexedPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST, 0, 0, m_num_vertices, 0, m_num_triangles);
m_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_LIGHTING, TRUE);
if(draw_triangle)
{
m_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_FILLMODE, D3DFILL_WIREFRAME);
m_device->DrawIndexedPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST, 0, 0, m_num_vertices, 0, m_num_triangles);
m_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_FILLMODE, D3DFILL_SOLID);
}
}