音樂(lè)就是一系列的音符,這些音符在不同的時(shí)間用不同的幅度被播放或者停止。有非常多的指令被用來(lái)播放音樂(lè),但是這些指令的操作基本相同,都在使用各種各樣不同的音符。在計(jì)算機(jī)上進(jìn)行作曲,實(shí)際上是存儲(chǔ)了很多組音樂(lè),回放時(shí)由音頻硬件將這些音符播放出來(lái)。
Midi格式(文件擴(kuò)展名是.MID)是存儲(chǔ)數(shù)字音樂(lè)的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)格式。
DirectMusic 音樂(lè)片段(music segments)使用.SGT文件擴(kuò)展名,其他的相關(guān)文件包括樂(lè)隊(duì)文件(band file .BND),這種文件里面包含樂(lè)器信息;弦映射表文件(chordmaps
file .CDM)包含在回放時(shí)修改音樂(lè)的和弦指令;樣式文件(styles file .STY)包含回放樣式信息;模板文件(templates file .TPL)包含創(chuàng)造音樂(lè)片段的模板。
Midi是一種非常強(qiáng)大的音樂(lè)格式,惟一的不利因素是音樂(lè)品質(zhì)依賴于音樂(lè)合成器的性能,因?yàn)镸idi
僅僅記錄了音符,其播放的品質(zhì)由播放音樂(lè)的軟硬件決定。MP3文件(文件后綴為.MP3)是一種類似于波表文件的文件格式,但是MP3文件和WAV文件最大的區(qū)別在于MP3文件將聲音壓縮到了最小的程度,但是音質(zhì)卻基本不變。可以用DirectShow組件播放MP3文件,DirectShow組件是一個(gè)非常強(qiáng)大的多媒體組件,用DirectShow幾乎可以播放任何媒體文件,包括聲音和音頻文件,部分聲音文件我們只能用DirectShow播放。
Direct Audio是一個(gè)復(fù)合組件,它由DirectSound和DirectMusic兩個(gè)組件組成,如下圖所示:
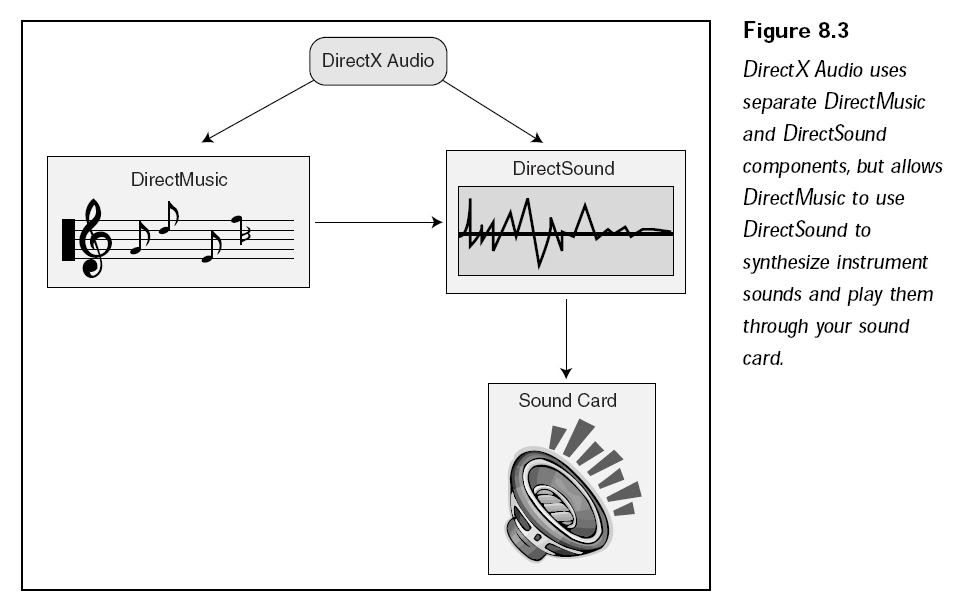
DirectMusic在DirectX8中得到了巨大的增強(qiáng),但是DirectSound基本保持原有的狀態(tài)。DirectSound是主要的數(shù)字聲音回放組件。DirectMusic處理所有的樂(lè)曲格式,包括MIDI、DirectMusic本地格式文件和波表文件。DirectMusic處理完之后將它們送入DirectSound中做其他處理,這意味著回放MIDI的時(shí)候可以使用數(shù)字化的樂(lè)器。
使用DirectSound
使用時(shí)需要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建一個(gè)和聲卡通訊的COM對(duì)象,用這個(gè)COM對(duì)象再創(chuàng)造一些獨(dú)立的聲音數(shù)據(jù)緩沖區(qū)(被稱之為輔助音頻緩沖區(qū) secondary sound
buffers)來(lái)存儲(chǔ)音頻數(shù)據(jù)。緩沖區(qū)中的這些數(shù)據(jù)在主混音緩存(稱之為主音頻緩存 primary sound
buffer)中被混合,然后可以用指定的任何格式播放出來(lái)。回放格式通過(guò)采樣頻率、聲道數(shù)、采樣精度排列,可能的采樣頻率有8000HZ,
11025HZ,22050HZ和44100HZ(CD音質(zhì))。
對(duì)于聲道數(shù)可以有兩個(gè)選擇:?jiǎn)瓮ǖ赖膯温暤缆曇艉碗p通道的立體聲聲音。采樣精度被限制在兩種選擇上:8位的低質(zhì)量聲音和16位的高保真聲音。在沒(méi)有修改的情況下,DirectSound主緩沖區(qū)的默認(rèn)設(shè)置是22025HZ采樣率、8位精度、立體聲。在DirectSound中可以調(diào)整聲音的播放速度(這同樣會(huì)改變聲音的音調(diào)),調(diào)整音量
、循環(huán)播放等。甚至還可以在一個(gè)虛擬的
3D環(huán)境中播放,以模擬一個(gè)實(shí)際環(huán)繞在周圍的聲音。
需要做的是將聲音數(shù)據(jù)充滿緩沖區(qū),如果聲音數(shù)據(jù)太大的話,必須創(chuàng)建流播放方法,加載聲音數(shù)據(jù)中的一小塊,當(dāng)這一小塊播放完畢以后,再加載另外的小塊數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)緩沖區(qū),一直持續(xù)這個(gè)過(guò)程,直到聲音被處理完畢。在緩沖區(qū)中調(diào)整播放位置可以實(shí)現(xiàn)流式音頻,當(dāng)播放完成通知應(yīng)用程序更新音頻數(shù)據(jù)。這個(gè)通知更新的過(guò)程我們稱之為“通告”。在同一時(shí)間被播放的緩存數(shù)目雖然沒(méi)有限制,但是仍然需要保證緩沖區(qū)數(shù)目不要太多,因?yàn)槊吭黾右粋€(gè)緩沖區(qū),就要消耗很多內(nèi)存和CPU資源。
在項(xiàng)目中使用DirectSound和DirectMusic,需要添加頭文件dsound.h和dmsuic.h,并且需要鏈接DSound.lib到包含庫(kù)中,添加DXGuid.lib庫(kù)可以讓DirectSound更容易使用。
以下是DirectSound COM接口:
IDirectSound8:DirectSound接口。
IDirectSoundBuffer8:主緩沖區(qū)和輔助緩沖區(qū)接口,保存數(shù)據(jù)并控制回放。
IDirectSoundNotify8:通知對(duì)象,通知應(yīng)用程序指定播放位置已經(jīng)達(dá)到。
各個(gè)對(duì)象間的關(guān)系如下圖所示:
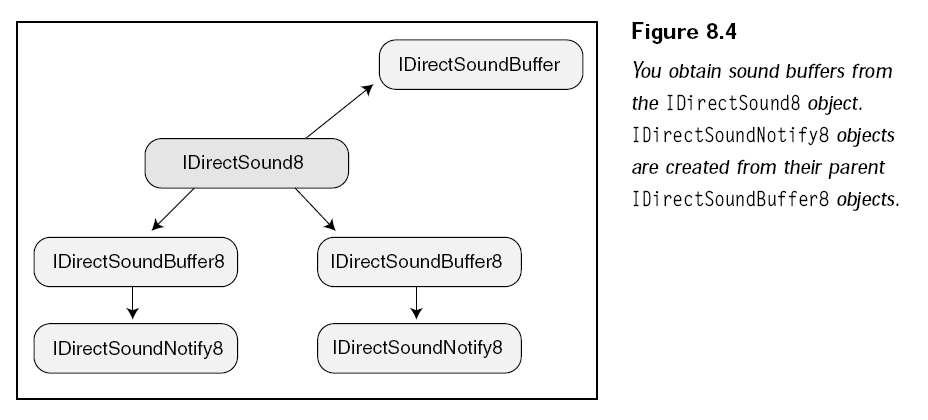
IDirectSound8是主接口,用它來(lái)創(chuàng)建緩沖區(qū)(IDirectSoundBuffer8),然后用緩沖區(qū)接口創(chuàng)建通告接口(IDirectSoundNotify8),通告接口告訴應(yīng)用程序指定的位置已經(jīng)到達(dá),通告接口在流化音頻文件時(shí)非常有用。
初始化DirectSound
使用 DirectSound的第一步是創(chuàng)建IDirectSound8對(duì)象,IDirectSound8起到控制音頻硬件設(shè)備的作用,可以通過(guò)
DirectSoundCreate8函數(shù)來(lái)創(chuàng)建。
The
DirectSoundCreate8 function creates and initializes an object that supports the
IDirectSound8 interface.
HRESULT DirectSoundCreate8(
LPCGUID lpcGuidDevice,
LPDIRECTSOUND8 * ppDS8,
LPUNKNOWN pUnkOuter
);
Parameters
- lpcGuidDevice
- Address of the GUID that identifies the
sound device. The value of this parameter must be one of the GUIDs returned
by DirectSoundEnumerate, or NULL for the default device, or one of the
following values.
|
Value |
Description |
|
DSDEVID_DefaultPlayback |
System-wide default audio playback
device. Equivalent to NULL. |
|
DSDEVID_DefaultVoicePlayback |
Default voice playback device. |
- ppDS8
- Address of a variable to receive an
IDirectSound8 interface pointer.
- pUnkOuter
- Address of the controlling object's
IUnknown interface for COM aggregation. Must be NULL, because aggregation is
not supported.
Return Values
If the function
succeeds, it returns DS_OK. If it fails, the return value may be one of the
following.
|
Return Code |
|
DSERR_ALLOCATED |
|
DSERR_INVALIDPARAM |
|
DSERR_NOAGGREGATION |
|
DSERR_NODRIVER |
|
DSERR_OUTOFMEMORY |
Remarks
The application
must call the IDirectSound8::SetCooperativeLevel method immediately after
creating a device object.
創(chuàng)建主音頻緩沖區(qū)
用 IDirectSoundBuffer對(duì)象控制主音頻緩沖區(qū),創(chuàng)建主緩沖區(qū)不需要DirectX8的接口,因?yàn)檫@個(gè)接口從來(lái)沒(méi)有改變。用來(lái)創(chuàng)建音頻緩沖區(qū)的函數(shù)是IDirectSound8::CreateSoundBuffer。
The CreateSoundBuffer method
creates a sound buffer object to manage audio samples.
HRESULT CreateSoundBuffer(
LPCDSBUFFERDESC pcDSBufferDesc,
LPDIRECTSOUNDBUFFER * ppDSBuffer,
LPUNKNOWN pUnkOuter
);
Parameters
- pcDSBufferDesc
- Address of a DSBUFFERDESC
structure that describes the sound buffer to create.
- ppDSBuffer
- Address of a variable that
receives the IDirectSoundBuffer interface of the new buffer object. Use
QueryInterface to obtain IDirectSoundBuffer8. IDirectSoundBuffer8 is not
available for the primary buffer.
- pUnkOuter
- Address of the controlling
object's IUnknown interface for COM aggregation. Must be NULL.
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the
return value is DS_OK, or DS_NO_VIRTUALIZATION if a requested 3D algorithm was
not available and stereo panning was substituted. See the description of the
guid3DAlgorithm member of DSBUFFERDESC. If the method fails,
the return value may be one of the error values shown in the following table.
|
Return code |
|
DSERR_ALLOCATED |
|
DSERR_BADFORMAT
|
|
DSERR_BUFFERTOOSMALL |
|
DSERR_CONTROLUNAVAIL |
|
DSERR_DS8_REQUIRED |
|
DSERR_INVALIDCALL |
|
DSERR_INVALIDPARAM |
|
DSERR_NOAGGREGATION |
|
DSERR_OUTOFMEMORY |
|
DSERR_UNINITIALIZED |
|
DSERR_UNSUPPORTED |
Remarks
DirectSound does not initialize
the contents of the buffer, and the application cannot assume that it contains
silence.
If an attempt is made to create a
buffer with the DSBCAPS_LOCHARDWARE flag on a system where hardware acceleration
is not available, the method fails with either DSERR_CONTROLUNAVAIL or
DSERR_INVALIDCALL, depending on the operating system.
pcDSBufferDesc是一個(gè)指向DSBUFFERDESC結(jié)構(gòu)的指針,保存所創(chuàng)建的緩沖區(qū)的信息。
The DSBUFFERDESC structure
describes the characteristics of a new buffer object. It is used by the
IDirectSound8::CreateSoundBuffer method and by the DirectSoundFullDuplexCreate8
function.
An earlier version of this
structure, DSBUFFERDESC1, is maintained in Dsound.h for compatibility with
DirectX 7 and earlier.
typedef struct DSBUFFERDESC {
DWORD dwSize;
DWORD dwFlags;
DWORD dwBufferBytes;
DWORD dwReserved;
LPWAVEFORMATEX lpwfxFormat;
GUID guid3DAlgorithm;
} DSBUFFERDESC;
Members
- dwSize
- Size of the structure, in
bytes. This member must be initialized before the structure is used.
- dwFlags
- Flags specifying the
capabilities of the buffer. See the dwFlags member of the
DSBCAPS structure for a detailed listing of valid flags.
- dwBufferBytes
- Size of the new buffer, in
bytes. This value must be 0 when creating a buffer with the
DSBCAPS_PRIMARYBUFFER flag. For secondary buffers, the minimum and maximum
sizes allowed are specified by DSBSIZE_MIN and DSBSIZE_MAX, defined in
Dsound.h.
- dwReserved
- Reserved. Must be 0.
- lpwfxFormat
- Address of a WAVEFORMATEX or
WAVEFORMATEXTENSIBLE structure specifying the waveform format for the
buffer. This value must be NULL for primary buffers.
- guid3DAlgorithm
- Unique identifier of the
two-speaker virtualization algorithm to be used by DirectSound3D hardware
emulation. If DSBCAPS_CTRL3D is not set in dwFlags, this member must be
GUID_NULL (DS3DALG_DEFAULT). The following algorithm identifiers are
defined.
|
Value |
Description |
Availability |
|
DS3DALG_DEFAULT |
DirectSound uses the
default algorithm. In most cases this is DS3DALG_NO_VIRTUALIZATION.
On WDM drivers, if the user has selected a surround sound speaker
configuration in Control Panel, the sound is panned among the
available directional speakers. |
Applies to software
mixing only. Available on WDM or Vxd Drivers. |
|
DS3DALG_NO_VIRTUALIZATION |
3D output is mapped onto
normal left and right stereo panning. At 90 degrees to the left, the
sound is coming out of only the left speaker; at 90 degrees to the
right, sound is coming out of only the right speaker. The vertical
axis is ignored except for scaling of volume due to distance.
Doppler shift and volume scaling are still applied, but the 3D
filtering is not performed on this buffer. This is the most
efficient software implementation, but provides no virtual 3D audio
effect. When the DS3DALG_NO_VIRTUALIZATION algorithm is specified,
HRTF processing will not be done. Because DS3DALG_NO_VIRTUALIZATION
uses only normal stereo panning, a buffer created with this
algorithm may be accelerated by a 2D hardware voice if no free 3D
hardware voices are available. |
Applies to software
mixing only. Available on WDM or Vxd Drivers. |
|
DS3DALG_HRTF_FULL |
The 3D API is processed
with the high quality 3D audio algorithm. This algorithm gives the
highest quality 3D audio effect, but uses more CPU cycles. See
Remarks. |
Applies to software
mixing only. Available on Microsoft Windows 98 Second Edition and
later operating systems when using WDM drivers. |
|
DS3DALG_HRTF_LIGHT |
The 3D API is processed
with the efficient 3D audio algorithm. This algorithm gives a good
3D audio effect, but uses fewer CPU cycles than DS3DALG_HRTF_FULL. |
Applies to software
mixing only. Available on Windows 98 Second Edition and later
operating systems when using WDM drivers. |
需要設(shè)置的惟一一個(gè)值是dwFlags,這是一系列標(biāo)志,用于決定緩沖區(qū)性能。
- dwFlags
- Flags that specify
buffer-object capabilities. Use one or more of the values shown in the
following table.
|
Value |
Description |
|
DSBCAPS_CTRL3D |
The buffer has 3D
control capability. |
|
DSBCAPS_CTRLFREQUENCY |
The buffer has frequency
control capability. |
|
DSBCAPS_CTRLFX |
The buffer supports
effects processing. |
|
DSBCAPS_CTRLPAN |
The buffer has pan
control capability. |
|
DSBCAPS_CTRLVOLUME |
The buffer has volume
control capability. |
|
DSBCAPS_CTRLPOSITIONNOTIFY |
The buffer has position
notification capability. See the Remarks for DSCBUFFERDESC. |
|
DSBCAPS_GETCURRENTPOSITION2 |
The buffer uses the new
behavior of the play cursor when
IDirectSoundBuffer8::GetCurrentPosition is called. In the first
version of DirectSound, the play cursor was significantly ahead of
the actual playing sound on emulated sound cards; it was directly
behind the write cursor. Now, if the DSBCAPS_GETCURRENTPOSITION2
flag is specified, the application can get a more accurate play
cursor. If this flag is not specified, the old behavior is preserved
for compatibility. This flag affects only emulated devices; if a
DirectSound driver is present, the play cursor is accurate for
DirectSound in all versions of DirectX. |
|
DSBCAPS_GLOBALFOCUS |
The buffer is a global
sound buffer. With this flag set, an application using DirectSound
can continue to play its buffers if the user switches focus to
another application, even if the new application uses DirectSound.
The one exception is if you switch focus to a DirectSound
application that uses the DSSCL_WRITEPRIMARY flag for its
cooperative level. In this case, the global sounds from other
applications will not be audible. |
|
DSBCAPS_LOCDEFER |
The buffer can be
assigned to a hardware or software resource at play time, or when
IDirectSoundBuffer8::AcquireResources is called. |
|
DSBCAPS_LOCHARDWARE |
The buffer uses hardware
mixing. |
|
DSBCAPS_LOCSOFTWARE |
The buffer is in
software memory and uses software mixing. |
|
DSBCAPS_MUTE3DATMAXDISTANCE |
The sound is reduced to
silence at the maximum distance. The buffer will stop playing when
the maximum distance is exceeded, so that processor time is not
wasted. Applies only to software buffers. |
|
DSBCAPS_PRIMARYBUFFER |
The buffer is a primary
buffer. |
|
DSBCAPS_STATIC |
The buffer is in
on-board hardware memory. |
|
DSBCAPS_STICKYFOCUS |
The buffer has sticky
focus. If the user switches to another application not using
DirectSound, the buffer is still audible. However, if the user
switches to another DirectSound application, the buffer is muted. |
|
DSBCAPS_TRUEPLAYPOSITION |
Force
IDirectSoundBuffer8::GetCurrentPosition to return the buffer's true
play position. This flag is only valid in Windows Vista. |
以下是創(chuàng)建聲音緩沖區(qū)的代碼:
// setup the DSBUFFERDESC structure
DSBUFFERDESC ds_buffer_desc;
// zero out strcutre
ZeroMemory(&ds_buffer_desc, sizeof(DSBUFFERDESC));
ds_buffer_desc.dwSize = sizeof(DSBUFFERDESC);
ds_buffer_desc.dwFlags = DSBCAPS_CTRLVOLUME;
ds_buffer_desc.dwBufferBytes = wave_format.nAvgBytesPerSec * 2; // 2 seconds
ds_buffer_desc.lpwfxFormat = &wave_format;
// create the fist version object
if(FAILED(g_ds->CreateSoundBuffer(&ds_buffer_desc, &ds, NULL)))
{
// error ocuurred
MessageBox(NULL, "Unable to create sound buffer", "Error", MB_OK);
}
設(shè)置格式
對(duì)于格式,有一系列的選擇,但是建議在11025HZ、16位、單通道;22050HZ、16位、單通道中選擇。選擇格式的時(shí)候,不要嘗試使用立體聲,立體聲浪費(fèi)處理時(shí)間,而且效果很難評(píng)估。同樣也不要使用16位以外的采樣精度,因?yàn)檫@會(huì)導(dǎo)致音質(zhì)的大幅下降。對(duì)于采樣頻率來(lái)說(shuō),越高越好,但是也不要設(shè)置超過(guò)
22050HZ,在這個(gè)采樣頻率下,也能表現(xiàn)出CD音質(zhì)的水準(zhǔn)而沒(méi)有太多的損失。
設(shè)置回放格式需要通過(guò)調(diào)用 IDirectSoundBuffer::SetFormat。
The SetFormat method sets the
format of the primary buffer. Whenever this application has the input focus,
DirectSound will set the primary buffer to the specified format.
HRESULT SetFormat(
LPCWAVEFORMATEX pcfxFormat
);
Parameters
- pcfxFormat
- Address of a WAVEFORMATEX
structure that describes the new format for the primary sound buffer.
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the return
value is DS_OK. If the method fails, the return value may be one of the
following error values:
|
Return code |
|
DSERR_BADFORMAT |
|
DSERR_INVALIDCALL |
|
DSERR_INVALIDPARAM |
|
DSERR_OUTOFMEMORY |
|
DSERR_PRIOLEVELNEEDED |
|
DSERR_UNSUPPORTED |
Remarks
The format of the primary buffer
should be set before secondary buffers are created.
The method fails if the
application has the DSSCL_NORMAL cooperative level.
If the application is using
DirectSound at the DSSCL_WRITEPRIMARY cooperative level, and the format is not
supported, the method fails.
If the cooperative level is
DSSCL_PRIORITY, DirectSound stops the primary buffer, changes the format, and
restarts the buffer. The method succeeds even if the hardware does not support
the requested format; DirectSound sets the buffer to the closest supported
format. To determine whether this has happened, an application can call the
GetFormat method for the primary buffer and compare the result with the format
that was requested with the SetFormat method.
This method is not available for
secondary sound buffers. If a new format is required, the application must
create a new DirectSoundBuffer object.
這個(gè)函數(shù)惟一的參數(shù)是指向WAVEFORMATEX結(jié)構(gòu)的指針,該結(jié)構(gòu)保存已設(shè)置的格式信息。
The WAVEFORMATEX structure
defines the format of waveform-audio data. Only format information common to all
waveform-audio data formats is included in this structure. For formats that
require additional information, this structure is included as the first member
in another structure, along with the additional information.
This structure is part of the
Platform SDK and is not declared in Dsound.h. It is documented here for
convenience.
typedef struct WAVEFORMATEX {
WORD wFormatTag;
WORD nChannels;
DWORD nSamplesPerSec;
DWORD nAvgBytesPerSec;
WORD nBlockAlign;
WORD wBitsPerSample;
WORD cbSize;
} WAVEFORMATEX;
Members
- wFormatTag
- Waveform-audio format type.
Format tags are registered with Microsoft Corporation for many compression
algorithms. A complete list of format tags can be found in the Mmreg.h
header file. For one- or two-channel PCM data, this value should be
WAVE_FORMAT_PCM.
- nChannels
- Number of channels in the
waveform-audio data. Monaural data uses one channel and stereo data uses two
channels.
- nSamplesPerSec
- Sample rate, in samples per
second (hertz). If wFormatTag is WAVE_FORMAT_PCM, then common values for
nSamplesPerSec are 8.0 kHz, 11.025 kHz, 22.05 kHz, and 44.1 kHz. For non-PCM
formats, this member must be computed according to the manufacturer's
specification of the format tag.
- nAvgBytesPerSec
- Required average
data-transfer rate, in bytes per second, for the format tag. If wFormatTag
is WAVE_FORMAT_PCM, nAvgBytesPerSec should be equal to the product of
nSamplesPerSec and nBlockAlign. For non-PCM formats, this member must be
computed according to the manufacturer's specification of the format tag.
- nBlockAlign
- Block alignment, in bytes.
The block alignment is the minimum atomic unit of data for the wFormatTag
format type. If wFormatTag is WAVE_FORMAT_PCM or WAVE_FORMAT_EXTENSIBLE, nBlockAlign must be equal to the product of nChannels and wBitsPerSample
divided by 8 (bits per byte). For non-PCM formats, this member must be
computed according to the manufacturer's specification of the format tag.
Software must process a
multiple of nBlockAlign bytes of data at a time. Data written to and read
from a device must always start at the beginning of a block. For example, it
is illegal to start playback of PCM data in the middle of a sample (that is,
on a non-block-aligned boundary).
- wBitsPerSample
- Bits per sample for the
wFormatTag format type. If wFormatTag is WAVE_FORMAT_PCM, then
wBitsPerSample should be equal to 8 or 16. For non-PCM formats, this member
must be set according to the manufacturer's specification of the format tag.
If wFormatTag is WAVE_FORMAT_EXTENSIBLE, this value can be any integer
multiple of 8. Some compression schemes cannot define a value for
wBitsPerSample, so this member can be zero.
- cbSize
- Size, in bytes, of extra
format information appended to the end of the WAVEFORMATEX structure. This
information can be used by non-PCM formats to store extra attributes for the
wFormatTag. If no extra information is required by the wFormatTag, this
member must be set to zero. For WAVE_FORMAT_PCM formats (and only
WAVE_FORMAT_PCM formats), this member is ignored.
以下設(shè)置音頻格式為:11025HZ、單通道、16位。
// setup the WAVEFORMATEX structure
WAVEFORMATEX wave_format;
ZeroMemory(&wave_format, sizeof(WAVEFORMATEX));
wave_format.wFormatTag = WAVE_FORMAT_PCM;
wave_format.nChannels = 1; // mono
wave_format.nSamplesPerSec = 11025;
wave_format.wBitsPerSample = 16;
wave_format.nBlockAlign = (wave_format.wBitsPerSample / 8) * wave_format.nChannels;
wave_format.nAvgBytesPerSec = wave_format.nSamplesPerSec * wave_format.nBlockAlign;
閱讀下篇:
用DirectX
Audio和DirectShow播放聲音和音樂(lè)(2)