新建網頁 1
13.2.1 計算頂點
在圖13.4中���,計算三角形網格上的頂點���,我們只是在開始產生頂點的地方���,一行一行的生成頂點數據���,直到結束為止���。單元格的頂點與頂點之間有一塊空白區域���,這會讓我們取得x���、z坐標���,但y坐標是什么呢���?得到y坐標很容易���,當讀取高度圖數據結構時會找到對應的入口���。
注意:這個操作使用一個巨大的頂點緩存去保存所有地形上的所有頂點���。這可能會引起硬件局限性的問題���。例如:3D設備都預設了最大圖元數和最大頂點索引值���。檢查D3DCAPS9結構的MaxPrimitiveCount和MaxVertexlndex成員來獲得你的設備的限定值���。
計算紋理坐標���,看圖13.5���,給我們一個簡單的設定���,允許我們用(u, v)紋理坐標去對應地形頂點坐標���。
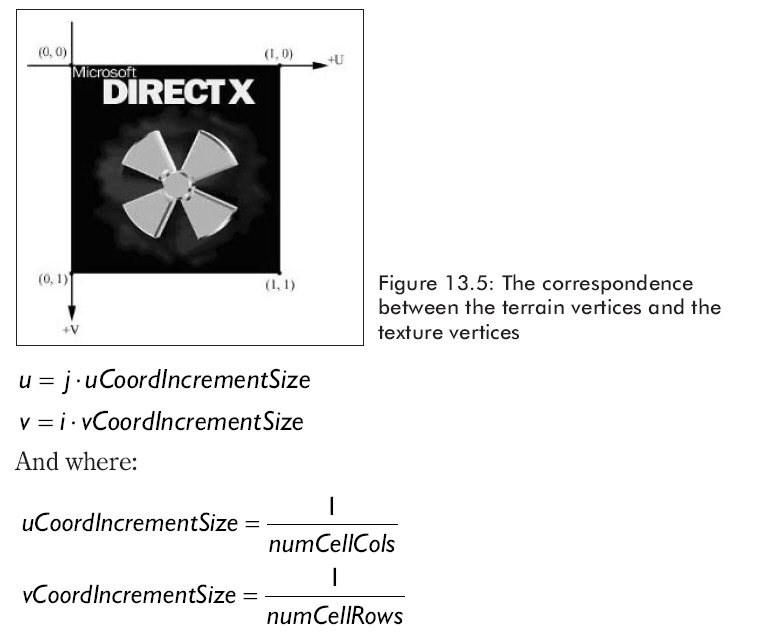
最后���,用代碼生成頂點:
bool cTerrain::generate_vertices()
{
if(FAILED(m_device->CreateVertexBuffer(m_num_vertices * sizeof(cTerrainVertex), D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY,
TERRAIN_VERTEX_FVF, D3DPOOL_MANAGED, &m_vertex_buffer, NULL)))
{
return false;
}
// coordinates to start generating vertices at
int start_x = -m_width / 2;
int start_z = m_depth / 2;
// coordinates to end generating vertices at
int end_x = m_width / 2;
int end_z = -m_depth / 2;
// compute the increment size of the texture coordinates from one vertex to the next
float u_coord_increment_size = 1.0f / m_num_cells_per_row;
float v_coord_increment_size = 1.0f / m_num_cells_per_col;
cTerrainVertex* v;
m_vertex_buffer->Lock(0, 0, (void**)&v, 0);
int row = 0;
for(int z = start_z; z >= end_z; z -= m_cell_spacing)
{
int column = 0;
for(int x = start_x; x <= end_x; x += m_cell_spacing)
{
int index = row * m_num_verts_per_row + column;
v[index] = cTerrainVertex(x, m_height_map[index], z,
column * u_coord_increment_size, row * v_coord_increment_size);
column++;
}
row++;
}
m_vertex_buffer->Unlock();
return true;
}
13.2.2 計算索引-定義三角形
計算三角形網格的索引���,只需要循環訪問每一個格子���,從左上到右下���,如圖13.4���,并且計算組成格子的2個三角形���。
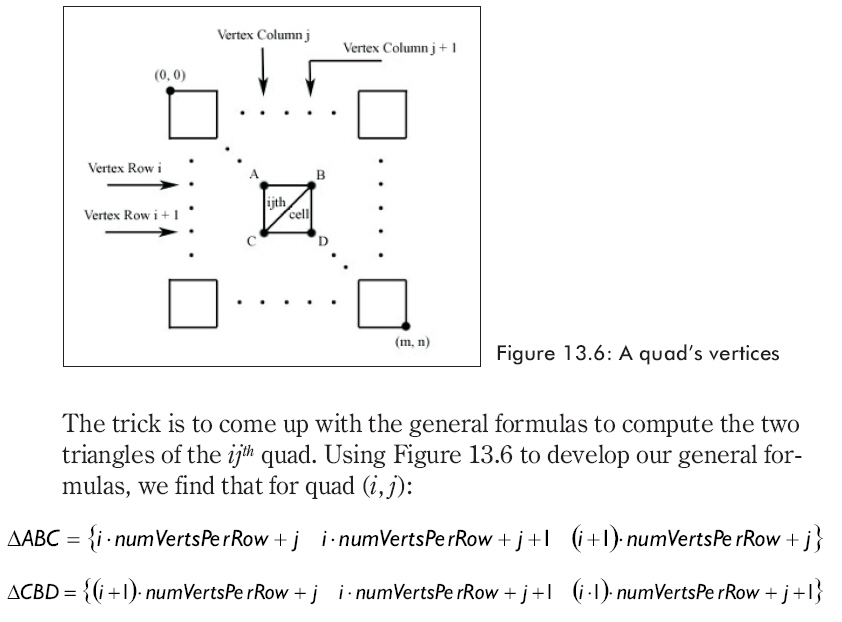
代碼生成索引:
bool cTerrain::generate_indices()
{
if(FAILED(m_device->CreateIndexBuffer(
m_num_triangles * 3 * sizeof(WORD), // 3 indices per triangle
D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY, D3DFMT_INDEX16, D3DPOOL_MANAGED, &m_index_buffer, NULL)))
{
return false;
}
WORD* indices;
m_index_buffer->Lock(0, 0, (void**)&indices, 0);
// index to start of a group of 6 indices that describe the two triangles that make up a quad
int base_index = 0;
// loop through and compute the triangles of each quad
for(int row = 0; row < m_num_cells_per_col; row++)
{
for(int col = 0; col < m_num_cells_per_row; col++)
{
indices[base_index] = row * m_num_verts_per_row + col;
indices[base_index + 1] = row * m_num_verts_per_row + (col+1);
indices[base_index + 2] = (row+1) * m_num_verts_per_row + col;
indices[base_index + 3] = (row+1) * m_num_verts_per_row + col;
indices[base_index + 4] = row * m_num_verts_per_row + (col+1);
indices[base_index + 5] = (row+1) * m_num_verts_per_row + (col+1);
base_index += 6; // next quad
}
}
m_index_buffer->Unlock();
return true;
}
cTerrain類提供2個方法去處理地形的紋理���。最簡單的方法是讀取一個已經制作好的紋理文件并使用它:
bool cTerrain::load_texture(const string& filename)
{
if(FAILED(D3DXCreateTextureFromFile(m_device, filename.c_str(), &m_texture)))
return false;
return true;
}
13.3.1 程序上的處理方法
一個可選擇的方法是用程序計算地形的紋理���,就是說���,我們創建一個空紋理���,根據定義的參數用代碼計算每一個部分的顏色���,在例子中,參數是地形的高度���。
我們用cTerrain::generate_texture方法去生成紋理,首先用D3DXCreateTexture方法創建一個空的紋理���,鎖定高度級別(top level,紋理圖的一個成員,有多個級別),不斷的循環每一個texel(圖素)并給它上色,texel的顏色取決于與方格對應的高度(近似高度)���。我們的想法是:地形中較低的地方是沙灘色,中間的地方像是綠色的小山丘,較高的地方顏色好像雪山���。我們定義的高度是方格中左上角的近似高度。
一旦每個texel都有了顏色,我們想讓每一個texel變暗或是變亮,這基于光打在格子中對應的texel上的角度���,由Terrain::lightTerrain方法實現。
bool cTerrain::generate_texture(D3DXVECTOR3* dir_to_light)
{
// Method fills the top surface of a texture procedurally, then lights the top surface.
// Finally, it fills the other mipmap surfaces based on the top surface data using D3DXFilterTexture.
// texel for each quad cell
int texture_width = m_num_cells_per_row;
int texture_height = m_num_cells_per_col;
// create an empty texture with a complete mipmap chain
if(FAILED(D3DXCreateTexture(m_device, texture_width, texture_height, 0, 0, D3DFMT_X8R8G8B8,
D3DPOOL_MANAGED, &m_texture)))
{
return false;
}
D3DSURFACE_DESC texture_desc;
m_texture->GetLevelDesc(0, &texture_desc);
// make sure we got the requested format because our code that fills the texture is
// hard coded to a 32 bit pixel depth.
if(texture_desc.Format != D3DFMT_X8R8G8B8)
return false;
// lock top entire texture surface
D3DLOCKED_RECT locked_rect;
m_texture->LockRect(0, &locked_rect, NULL, 0);
DWORD* image_data = (DWORD*) locked_rect.pBits;
for(int row = 0; row < texture_height; row++)
{
for(int col = 0; col < texture_width; col++)
{
D3DXCOLOR color;
// get height of upper left vertex of quad
float height = get_height_map_entry(row, col) / m_height_scale;
if(height < 42.5f) color = BEACH_SAND;
else if(height < 85.0f) color = LIGHT_YELLOW_GREEN;
else if(height < 127.5f) color = PUREGREEN;
else if(height < 170.0f) color = DARK_YELLOW_GREEN;
else if(height < 212.5f) color = DARKBROWN;
else color = WHITE;
// fill locked data, note we divide the pitch by four because the pitch is given in bytes
// and there are 4 bytes per DWORD.
image_data[row * (locked_rect.Pitch / 4) + col] = (D3DCOLOR) color;
}
}
m_texture->UnlockRect(0);
if(! light_terrain(dir_to_light))
{
MessageBox(NULL, "light_terrain() - FAILED", "ERROR", MB_OK);
return false;
}
if(FAILED(D3DXFilterTexture(m_texture, NULL, 0, D3DX_DEFAULT)))
{
MessageBox(NULL, "D3DXFilterTexture() - FAILED", "ERROR", MB_OK);
return false;
}
return true;
}