本篇是
用DirectX
Audio和DirectShow播放聲音和音樂(1)的續(xù)篇。
開始使用主音頻緩存
讓緩存在程序啟動的時候開始播放可以節(jié)省不少處理器時間。因為內(nèi)存資源是有限的,特別是在硬件設(shè)備中,而你使用的數(shù)據(jù)緩存可能需要任意大小,因此主音頻緩沖區(qū)和輔助緩沖區(qū)使用環(huán)形緩存。
環(huán)形緩沖的示意圖如下:

因為數(shù)據(jù)緩沖是一個一維數(shù)組,所以可以讓這個緩沖區(qū)頭尾相接。這是一個十分強大的技術(shù),利用這個技術(shù)我們可以節(jié)省大量的內(nèi)存。
聲音在進行混音處理后,被送入環(huán)形主音頻緩存。一旦播放位置到達主音頻緩存的終點,聲音又從頭開始播放,這樣聲音就被無間隙地連續(xù)播放。如果想要使用緩存的這種循環(huán)特性,需要指定啟用循環(huán)播放的特性,若不然當播放到緩沖區(qū)終點時,播放就停止了。
為了播放緩存中的音頻數(shù)據(jù)(在開啟循環(huán)選項的情況下播放),需要調(diào)用Play函數(shù)。
The Play method causes the sound
buffer to play, starting at the play cursor.
HRESULT Play(
DWORD dwReserved1,
DWORD dwPriority,
DWORD dwFlags
);
Parameters
- dwReserved1
- Reserved. Must be 0.
- dwPriority
- Priority for the sound,
used by the voice manager when assigning hardware mixing resources. The
lowest priority is 0, and the highest priority is 0xFFFFFFFF. If the buffer
was not created with the DSBCAPS_LOCDEFER flag, this value must be 0.
- dwFlags
- Flags specifying how to
play the buffer. The following flags are defined:
Looping flag
|
Value |
Description |
|
DSBPLAY_LOOPING |
After
the end of the audio buffer is reached, play restarts at the
beginning of the buffer. Play continues until explicitly stopped.
This flag must be set when playing a primary buffer. |
Voice allocation flags
- The voice allocation flags
are valid only for buffers created with the DSBCAPS_LOCDEFER flag. One of
the following flags can be used to force the processing of the sound into
hardware or software. If neither DBSPLAY_LOCHARDWARE nor DBSPLAY_LOCSOFTWARE
is set, the sound is played in either software or hardware, depending on the
availability of resources at the time the method is called. See Remarks.
|
Value |
Description |
|
DSBPLAY_LOCHARDWARE |
Play
this voice in a hardware buffer only. If the hardware has no
available voices and no voice management flags are set, the call to
IDirectSoundBuffer8::Play fails. This flag cannot be combined with
DSBPLAY_LOCSOFTWARE. |
|
DSBPLAY_LOCSOFTWARE |
Play
this voice in a software buffer only. This flag cannot be combined
with DSBPLAY_LOCHARDWARE or any voice management flag. |
Voice management flags
- The voice management flags
are valid only for buffers created with the DSBCAPS_LOCDEFER flag, and are
used for sounds that are to play in hardware. These flags enable hardware
resources that are already in use to be yielded to the current sound. Only
buffers created with the DSBCAPS_LOCDEFER flag are candidates for premature
termination. See Remarks.
|
Value |
Description |
|
DSBPLAY_TERMINATEBY_TIME |
If the
hardware has no available voices, a currently playing nonlooping
buffer will be stopped to make room for the new buffer. The buffer
prematurely terminated is the one with the least time left to play. |
|
DSBPLAY_TERMINATEBY_DISTANCE |
If the
hardware has no available voices, a currently playing buffer will be
stopped to make room for the new buffer. The buffer prematurely
terminated will be selected from buffers that have the buffer's
DSBCAPS_ MUTE3DATMAXDISTANCE flag set and are beyond their maximum
distance. If there are no such buffers, the method fails. |
|
DSBPLAY_TERMINATEBY_PRIORITY |
If the
hardware has no available voices, a currently playing buffer will be
stopped to make room for the new buffer. The buffer prematurely
terminated will be the one with the lowest priority as set by the
dwPriority parameter passed to IDirectSoundBuffer8::Play for the
buffer. |
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the
return value is DS_OK. If the method fails, the return value may be one of the
following error values:
|
Return code |
|
DSERR_BUFFERLOST |
|
DSERR_INVALIDCALL |
|
DSERR_INVALIDPARAM |
|
DSERR_PRIOLEVELNEEDED |
當完成主音頻緩存設(shè)置后(以及整個音響系統(tǒng)),如果想停止它,需要調(diào)用IDirectSoundBuffer::Stop。
The Stop method causes the sound
buffer to stop playing.
HRESULT Stop();
Parameters
None.
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the
return value is DS_OK. If the method fails, the return value may be one of the
following error values:
Remarks
For secondary sound buffers,
IDirectSoundBuffer8::Stop sets the play cursor to the sample that follows the
last sample played. This means that when the Play method is next called on the
buffer, it will continue playing where it left off.
For the primary buffer, if an
application has the DSSCL_WRITEPRIMARY level, this method will stop the buffer
and reset the play cursor to 0 (the beginning of the buffer). This is necessary
because the primary buffers on most sound cards can play only from the beginning
of the buffer.
However, if
IDirectSoundBuffer8::Stop is called on a primary buffer and the application has
a cooperative level other than DSSCL_WRITEPRIMARY, this method simply reverses
the effects of IDirectSoundBuffer8::Play. It configures the primary buffer to
stop if no secondary buffers are playing. If other buffers are playing in this
or other applications, the primary buffer will not actually stop until they are
stopped. This method is useful because playing the primary buffer consumes
processing overhead even if the buffer is playing sound data with the amplitude
of 0 decibels.
使用輔助音頻緩存
想要使用輔助音頻緩存的數(shù)據(jù),需要將輔助音頻緩存中包含的數(shù)據(jù)填充到主音頻緩存,如下圖所示:
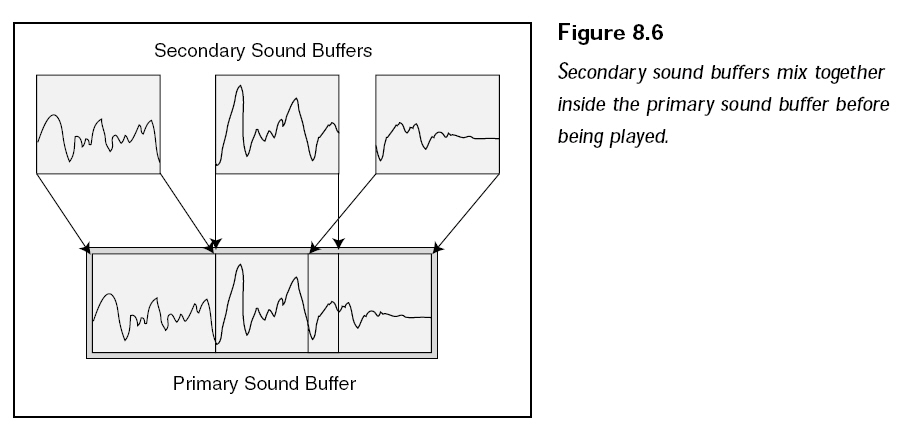
如果在主音頻緩存的同一區(qū)域?qū)懭雰啥我纛l數(shù)據(jù),這兩段聲音就會被同時播放。輔助音頻緩存使用 IDirectSoundBuffer8接口,這個接口和IDirectSoundBuffer十分類似,實際上如果想要創(chuàng)建
IDirectSoundBuffer8接口,必須先創(chuàng)建IDirectSoundBuffer接口,然后通過請求新接口來獲取
IDirectSoundBuffer8接口。
創(chuàng)建輔助音頻緩存和創(chuàng)建主音頻緩存時主要的不同是必須在初始化時設(shè)置回放格式,這意味著緩沖區(qū)只能使用一種格式。如果希望使用另外的格式,必須釋放當前的緩存,重新創(chuàng)建另外一個。
代碼示例:
// initialize and configure directsound
// creates and initializes an object that supports the IDirectSound8 interface
if(FAILED(DirectSoundCreate8(NULL, &g_ds, NULL)))
{
MessageBox(NULL, "Unable to create DirectSound object", "Error", MB_OK);
return 0;
}
// set the cooperative level of the application for this sound device
g_ds->SetCooperativeLevel(g_hwnd, DSSCL_NORMAL);
// create a sound buffer
// setup the WAVEFORMATEX structure
WAVEFORMATEX wave_format;
ZeroMemory(&wave_format, sizeof(WAVEFORMATEX));
wave_format.wFormatTag = WAVE_FORMAT_PCM;
wave_format.nChannels = 1; // mono
wave_format.nSamplesPerSec = 11025;
wave_format.wBitsPerSample = 16;
wave_format.nBlockAlign = (wave_format.wBitsPerSample / 8) * wave_format.nChannels;
wave_format.nAvgBytesPerSec = wave_format.nSamplesPerSec * wave_format.nBlockAlign;
// setup the DSBUFFERDESC structure
DSBUFFERDESC ds_buffer_desc;
// zero out strcutre
ZeroMemory(&ds_buffer_desc, sizeof(DSBUFFERDESC));
ds_buffer_desc.dwSize = sizeof(DSBUFFERDESC);
ds_buffer_desc.dwFlags = DSBCAPS_CTRLVOLUME;
ds_buffer_desc.dwBufferBytes = wave_format.nAvgBytesPerSec * 2; // 2 seconds
ds_buffer_desc.lpwfxFormat = &wave_format;
// create the fist version object
if(FAILED(g_ds->CreateSoundBuffer(&ds_buffer_desc, &ds, NULL)))
{
// error ocuurred
MessageBox(NULL, "Unable to create sound buffer", "Error", MB_OK);
}
else
{
// get the version 8 interface
ds->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundBuffer8, (void**)&g_ds_buffer);
// release the original interface
ds->Release();
}
鎖定和加載 --- 在緩沖區(qū)中加載數(shù)據(jù)
緩存接口有一對處理數(shù)據(jù)加載的函數(shù)。 IDirectSoundBuffer8::Lock函數(shù)鎖定音頻緩沖數(shù)據(jù),并且找回指向緩沖區(qū)數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)據(jù)指針;
IDirectSoundBuffer8::Unlock釋放在鎖定操作中使用的資源。
當鎖定緩存以后,就能對緩沖區(qū)進行寫入操作。先告訴緩沖寫入偏移量的字節(jié)數(shù)、寫入位置、要寫入數(shù)據(jù)的字節(jié)數(shù),寫入完成后返回兩個指向數(shù)據(jù)的指針以及寫入數(shù)據(jù)的字節(jié)數(shù)。為什么會有兩個指針和兩個數(shù)據(jù)大小呢?因為音頻數(shù)據(jù)緩沖區(qū)是環(huán)形的,寫入的數(shù)據(jù)也需要跨過起始位置。返回的第一個指針是請求的位置,第一個值是從請求的位置到結(jié)束所寫入的字節(jié)數(shù),第二個指針通常是緩存區(qū)的起始位置,第二個值是從起點開始寫入的字節(jié)數(shù)。
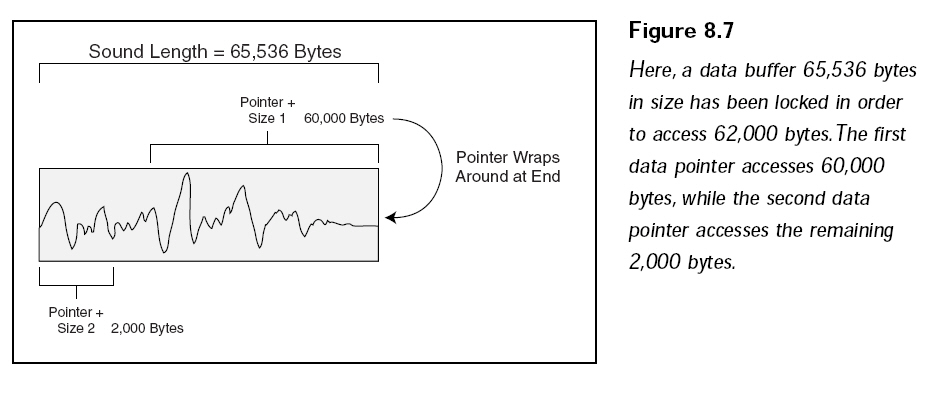
這里有一個長度是
65536字節(jié)大小的緩沖區(qū),這個緩沖區(qū)被鎖定,以便于寫入62000字節(jié)的數(shù)據(jù)。第一個指針處寫入了60000字節(jié),第二個指針處還剩下2000字節(jié),如下圖所示:
Lock函數(shù)使用信息如下:
The Lock method readies all or
part of the buffer for a data write and returns pointers to which data can be
written.
HRESULT Lock(
DWORD dwOffset,
DWORD dwBytes,
LPVOID * ppvAudioPtr1,
LPDWORD pdwAudioBytes1,
LPVOID * ppvAudioPtr2,
LPDWORD pdwAudioBytes2,
DWORD dwFlags
);
Parameters
- dwOffset
- Offset, in bytes, from the
start of the buffer to the point where the lock begins. This parameter is
ignored if DSBLOCK_FROMWRITECURSOR is specified in the dwFlags parameter.
- dwBytes
- Size, in bytes, of the
portion of the buffer to lock. The buffer is conceptually circular, so this
number can exceed the number of bytes between dwOffset and the end of the
buffer.
- ppvAudioPtr1
- Address of a variable that
receives a pointer to the first locked part of the buffer.
- pdwAudioBytes1
- Address of a variable that
receives the number of bytes in the block at ppvAudioPtr1. If this value is
less than dwBytes, the lock has wrapped and ppvAudioPtr2 points to a second
block of data at the beginning of the buffer .
- ppvAudioPtr2
- Address of a variable that
receives a pointer to the second locked part of the capture buffer. If NULL
is returned, the ppvAudioPtr1 parameter points to the entire locked portion
of the capture buffer.
- pdwAudioBytes2
- Address of a variable that
receives the number of bytes in the block at ppvAudioPtr2. If ppvAudioPtr2
is NULL, this value is zero.
- dwFlags
- Flags modifying the lock
event. The following flags are defined:
|
Value |
Description |
|
DSBLOCK_FROMWRITECURSOR |
Start
the lock at the write cursor. The dwOffset parameter is ignored. |
|
DSBLOCK_ENTIREBUFFER |
Lock
the entire buffer. The dwBytes parameter is ignored. |
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the
return value is DS_OK. If the method fails, the return value may be one of the
following error values:
|
Return code |
|
DSERR_BUFFERLOST |
|
DSERR_INVALIDCALL |
|
DSERR_INVALIDPARAM |
|
DSERR_PRIOLEVELNEEDED |
Remarks
This method accepts an offset
and a byte count, and returns two write pointers and their associated sizes. If
the locked portion does not extend to the end of the buffer and wrap to the
beginning, the second pointer, ppvAudioBytes2, receives NULL. If the lock does
wrap, ppvAudioBytes2 points to the beginning of the buffer.
If the application passes NULL
for the ppvAudioPtr2 and pdwAudioBytes2 parameters, the lock extends no further
than the end of the buffer and does not wrap.
After writing data to the
pointers returned by this method, the application must immediately call Unlock
to notify DirectSound that the data is ready for playback. Failure to do so can
cause audio breakup or silence on some sound device configurations.
This method returns write
pointers only. The application should not try to read sound data from this
pointer, because the data might not be valid. For example, if the buffer is
located in on-card memory, the pointer might be an address to a temporary buffer
in system memory. When IDirectSoundBuffer8::Unlock is called, the contents of
this temporary buffer are transferred to the on-card memory.
以下這段代碼鎖定輔助音頻緩沖區(qū),并且填充隨機數(shù)據(jù)。
// lock buffer, fill with random values, and unlock.
char* ptr;
DWORD size;
// readies all or part of the buffer for a data write and returns pointers to which data can be written
if(SUCCEEDED(g_ds_buffer->Lock(0, 0, (void**)&ptr, &size, NULL, 0, DSBLOCK_ENTIREBUFFER)))
{
for(DWORD i = 0; i < size; i++)
ptr[i] = rand() % 256;
}
填充完數(shù)據(jù)后,應(yīng)該給緩沖區(qū)解鎖,調(diào)用IDirectSoundBuffer8::Unlock解鎖。
The Unlock method releases a
locked sound buffer.
HRESULT Unlock(
LPVOID pvAudioPtr1,
DWORD dwAudioBytes1,
LPVOID pvAudioPtr2,
DWORD dwAudioBytes2
);
Parameters
- pvAudioPtr1
- Address of the value
retrieved in the ppvAudioPtr1 parameter of the Lock method.
- dwAudioBytes1
- Number of bytes written to
the portion of the buffer at pvAudioPtr1. See Remarks.
- pvAudioPtr2
- Address of the value
retrieved in the ppvAudioPtr2 parameter of the IDirectSoundBuffer8::Lock
method.
- dwAudioBytes2
- Number of bytes written to
the portion of the buffer at pvAudioPtr2. See Remarks.
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the
return value is DS_OK. If the method fails, the return value may be one of the
following error values:
|
Return code |
|
DSERR_INVALIDCALL |
|
DSERR_INVALIDPARAM |
|
DSERR_PRIOLEVELNEEDED |
Remarks
An application must pass both
pointers, pvAudioPtr1 and pvAudioPtr2, returned by the IDirectSoundBuffer8::Lock
method to ensure the correct pairing of IDirectSoundBuffer8::Lock and
IDirectSoundBuffer8::Unlock. The second pointer is needed even if nothing was
written to the second pointer.
The values in dwAudioBytes1 and
dwAudioBytes2 must specify the number of bytes actually written to each part of
the buffer, which might be less than the size of the lock. DirectSound uses
these values to determine how much data to commit to the device.
以下代碼解鎖剛才鎖定的輔助音頻緩沖區(qū):
// releases a locked sound buffer
g_ds_buffer->Unlock(ptr, size, NULL, 0);
播放緩沖區(qū)中的聲音
在輔助音頻緩沖區(qū)中播放音頻和在主音頻緩沖區(qū)中播放是一樣的,惟一不同的是這次需要設(shè)置播放的起始位置,通過IDirectSoundBuffer8::
SetCurrentPosition來設(shè)置。一般情況下,會選擇從緩沖的開頭播放,需要注意的是,停止播放一段音頻并不會重置播放位置,所以可以通過停止播放來達到暫停的目的,只需要再次調(diào)用播放函數(shù)來恢復播放。
The SetCurrentPosition method
sets the position of the play cursor, which is the point at which the next byte
of data is read from the buffer.
HRESULT SetCurrentPosition(
DWORD dwNewPosition
);
Parameters
- dwNewPosition
- Offset of the play cursor,
in bytes, from the beginning of the buffer.
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the
return value is DS_OK. If the method fails, the return value may be one of the
following error values:
|
Return code |
|
DSERR_INVALIDCALL |
|
DSERR_INVALIDPARAM |
|
DSERR_PRIOLEVELNEEDED |
Remarks
This method cannot be called on
the primary buffer.
If the buffer is playing, the
cursor immediately moves to the new position and play continues from that point.
If it is not playing, playback will begin from the new position the next time
the Play method is called.
改變音量
DirectSound
在播放聲音時按照采樣時的最大音量播放,加之受限于音頻硬件,所以沒有辦法讓音量變得更大,DirectSound只能讓音量變得更小些。這是通過減小聲音級別來完成的,這個級別的單位是百分之一分貝。范圍從0(最大音量)--
10000(無聲),利用這個特性可以在程序中加入“淡入”或“淡出“的效果。
要調(diào)整音量,可以使用 IDirectSoundBuffer8::SetVolume函數(shù)。
The SetVolume method sets the
attenuation of the sound.
HRESULT SetVolume(
LONG lVolume
);
Parameters
- lVolume
- Attenuation, in hundredths
of a decibel (dB).
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the
return value is DS_OK. If the method fails, the return value may be one of the
following error values:
|
Return code |
|
DSERR_CONTROLUNAVAIL |
|
DSERR_GENERIC |
|
DSERR_INVALIDPARAM |
|
DSERR_PRIOLEVELNEEDED |
Remarks
Allowable values are between
DSBVOLUME_MAX (no attenuation) and DSBVOLUME_MIN (silence). These values are
defined in Dsound.h as 0 and ?10,000 respectively. The value DSBVOLUME_MAX
represents the original, unadjusted volume of the stream. The value
DSBVOLUME_MIN indicates an audio volume attenuated by 100 dB, which, for all
practical purposes, is silence. DirectSound does not support amplification.
以下給出一個完整示例來運用剛才學到的知識。
點擊下載源碼和工程
源碼示例:
/***************************************************************************************
PURPOSE:
Lock Load Playing Demo
***************************************************************************************/
#define DIRECTINPUT_VERSION 0x0800
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dsound.h>
#include "resource.h"
#pragma comment(lib, "dxguid.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "dsound.lib")
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#define Safe_Release(p) if((p)) (p)->Release();
// window handles, class and caption text.
HWND g_hwnd;
char g_class_name[] = "LockLoadClass";
IDirectSound8* g_ds; // directsound component
IDirectSoundBuffer8* g_ds_buffer; // sound buffer object
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Window procedure.
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
long WINAPI Window_Proc(HWND hwnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch(msg)
{
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
}
return (long) DefWindowProc(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam);
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Main function, routine entry.
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE inst, HINSTANCE, LPSTR cmd_line, int cmd_show)
{
WNDCLASS win_class;
MSG msg;
IDirectSoundBuffer* ds = NULL;
// create window class and register it
win_class.style = CS_HREDRAW | CS_VREDRAW;
win_class.lpfnWndProc = Window_Proc;
win_class.cbClsExtra = 0;
win_class.cbWndExtra = DLGWINDOWEXTRA;
win_class.hInstance = inst;
win_class.hIcon = LoadIcon(inst, IDI_APPLICATION);
win_class.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW);
win_class.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH) (COLOR_BTNFACE + 1);
win_class.lpszMenuName = NULL;
win_class.lpszClassName = g_class_name;
if(! RegisterClass(&win_class))
return FALSE;
// create the main window
g_hwnd = CreateDialog(inst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_LOCKLOAD), 0, NULL);
ShowWindow(g_hwnd, cmd_show);
UpdateWindow(g_hwnd);
// initialize and configure directsound
// creates and initializes an object that supports the IDirectSound8 interface
if(FAILED(DirectSoundCreate8(NULL, &g_ds, NULL)))
{
MessageBox(NULL, "Unable to create DirectSound object", "Error", MB_OK);
return 0;
}
// set the cooperative level of the application for this sound device
g_ds->SetCooperativeLevel(g_hwnd, DSSCL_NORMAL);
// create a sound buffer
// setup the WAVEFORMATEX structure
WAVEFORMATEX wave_format;
ZeroMemory(&wave_format, sizeof(WAVEFORMATEX));
wave_format.wFormatTag = WAVE_FORMAT_PCM;
wave_format.nChannels = 1; // mono
wave_format.nSamplesPerSec = 11025;
wave_format.wBitsPerSample = 16;
wave_format.nBlockAlign = (wave_format.wBitsPerSample / 8) * wave_format.nChannels;
wave_format.nAvgBytesPerSec = wave_format.nSamplesPerSec * wave_format.nBlockAlign;
// setup the DSBUFFERDESC structure
DSBUFFERDESC ds_buffer_desc;
// zero out strcutre
ZeroMemory(&ds_buffer_desc, sizeof(DSBUFFERDESC));
ds_buffer_desc.dwSize = sizeof(DSBUFFERDESC);
ds_buffer_desc.dwFlags = DSBCAPS_CTRLVOLUME;
ds_buffer_desc.dwBufferBytes = wave_format.nAvgBytesPerSec * 2; // 2 seconds
ds_buffer_desc.lpwfxFormat = &wave_format;
// create the fist version object
if(FAILED(g_ds->CreateSoundBuffer(&ds_buffer_desc, &ds, NULL)))
{
// error ocuurred
MessageBox(NULL, "Unable to create sound buffer", "Error", MB_OK);
}
else
{
// get the version 8 interface
ds->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundBuffer8, (void**)&g_ds_buffer);
// release the original interface
ds->Release();
// lock buffer, fill with random values, and unlock.
char* ptr;
DWORD size;
// readies all or part of the buffer for a data write and returns pointers to which data can be written
if(SUCCEEDED(g_ds_buffer->Lock(0, 0, (void**)&ptr, &size, NULL, 0, DSBLOCK_ENTIREBUFFER)))
{
for(DWORD i = 0; i < size; i++)
ptr[i] = rand() % 256;
}
// releases a locked sound buffer
g_ds_buffer->Unlock(ptr, size, NULL, 0);
// play sound looping
// sets the position of the play cursor,
// which is the point at which the next byte of data is read from the buffer.
g_ds_buffer->SetCurrentPosition(0);
// set the attenuation of the sound
g_ds_buffer->SetVolume(DSBVOLUME_MAX);
// causes the sound buffer to play, starting at the play cursor.
g_ds_buffer->Play(0, 0, DSBPLAY_LOOPING);
}
// start message pump, waiting for signal to quit.
ZeroMemory(&msg, sizeof(MSG));
while(msg.message != WM_QUIT)
{
if(PeekMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
}
// release directsound objects
g_ds->Release();
UnregisterClass(g_class_name, inst);
return (int) msg.wParam;
}
運行截圖:
閱讀下篇:
用DirectX
Audio和DirectShow播放聲音和音樂(3)