向量的運算已超了傳統(tǒng)意義上的數(shù)的運算,因為向量并不是一般的數(shù)字。這意味著一切可用符號表示出來的事物,都可以對其進行各種關系運算,而不必關心事物的本身。這種符號運算的觀點,推動了近代數(shù)學對一般的集合元素進行的抽象代數(shù)方面的研究。
在線性方程組的求解上,變元較少的方程組(如僅有兩個未知數(shù)x和y的方程組)的解很容易表達出來,但是推廣到較為復雜的更多變元的情形,如何推測方程組的解以及如何用確定的式子表達出來,引發(fā)了對行列式的提出和研究。行列式實質上是方陣數(shù)據(jù)的一種運算,由此自然地想到,可對一般行列數(shù)據(jù)定義代數(shù)運算,就像對向量定義運算一樣,這就是矩陣運算的產生歷史。
由于DirectX三維游戲的開發(fā)僅需要應用4x4矩陣的計算,因此,DirectX 9在d3dx9math.h文件中定義了對應于4x4矩陣的D3DMATRIX結構體和一個提供了4X4矩陣的各種運算處理的D3DXMATRIX類。
typedef struct _D3DMATRIX {
union {
struct {
float _11, _12, _13, _14;
float _21, _22, _23, _24;
float _31, _32, _33, _34;
float _41, _42, _43, _44;
};
float m[4][4];
};
} D3DMATRIX;
typedef struct D3DXMATRIX : public D3DMATRIX
{
public:
D3DXMATRIX() {};
D3DXMATRIX( CONST FLOAT * );
D3DXMATRIX( CONST D3DMATRIX& );
D3DXMATRIX( CONST D3DXFLOAT16 * );
D3DXMATRIX( FLOAT _11, FLOAT _12, FLOAT _13, FLOAT _14,
FLOAT _21, FLOAT _22, FLOAT _23, FLOAT _24,
FLOAT _31, FLOAT _32, FLOAT _33, FLOAT _34,
FLOAT _41, FLOAT _42, FLOAT _43, FLOAT _44 );
// access grants
FLOAT& operator () ( UINT Row, UINT Col );
FLOAT operator () ( UINT Row, UINT Col ) const;
// casting operators
operator FLOAT* ();
operator CONST FLOAT* () const;
// assignment operators
D3DXMATRIX& operator *= ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& );
D3DXMATRIX& operator += ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& );
D3DXMATRIX& operator -= ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& );
D3DXMATRIX& operator *= ( FLOAT );
D3DXMATRIX& operator /= ( FLOAT );
// unary operators
D3DXMATRIX operator + () const;
D3DXMATRIX operator - () const;
// binary operators
D3DXMATRIX operator * ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& ) const;
D3DXMATRIX operator + ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& ) const;
D3DXMATRIX operator - ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& ) const;
D3DXMATRIX operator * ( FLOAT ) const;
D3DXMATRIX operator / ( FLOAT ) const;
friend D3DXMATRIX operator * ( FLOAT, CONST D3DXMATRIX& );
BOOL operator == ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& ) const;
BOOL operator != ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& ) const;
} D3DXMATRIX, *LPD3DXMATRIX;
要正確運行以下的示例程序,需要在工程中包含d3dx9.lib,或者在main函數(shù)前加入
#pragma comment(lib, "d3dx9.lib")
以指示編譯器鏈接d3dx9.lib。
矩陣的基本運算:包括加,減,乘。函數(shù)原型:
D3DXMATRIX operator * ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& ) const; D3DXMATRIX operator + ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& ) const; D3DXMATRIX operator - ( CONST D3DXMATRIX& ) const; D3DXMATRIX operator * ( FLOAT ) const; D3DXMATRIX operator / ( FLOAT ) const;代碼示例:
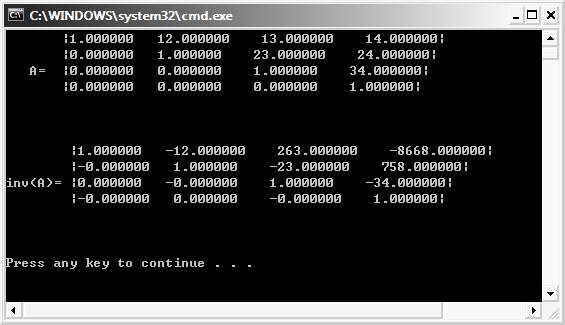
#include <stdio.h>
#include <D3DX9Math.h>
#pragma warning(disable : 4305)
int main()
{
// initialize and print matrix A
D3DXMATRIX A(11.0, 12.0, 13.0, 14.0,
21.0, 22.0, 23.0, 24.0,
31.0, 32.0, 33.0, 34.0,
41.0, 42.0, 43.0, 44.0);
printf("\n");
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", A._11,A._12,A._13,A._14);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", A._21,A._22,A._23,A._24);
printf(" A= |%f %f %f %f|\n", A._31,A._32,A._33,A._34);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", A._41,A._42,A._43,A._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
// initialize and print matrix B
D3DXMATRIX B(-10.0, -12.0, -13.0, -14.0,
-21.0, -21.0, -23.0, -24.0,
-31.0, -32.0, -32.0, -34.0,
-41.0, -42.0, -43.0, -43.0);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", B._11,B._12,B._13,B._14);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", B._21,B._22,B._23,B._24);
printf(" B= |%f %f %f %f|\n", B._31,B._32,B._33,B._34);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", B._41,B._42,B._43,B._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
// calculate A+B
D3DXMATRIX C = A + B;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
if(i != 2)
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", C(i,0), C(i,1), C(i,2), C(i,3));
else
printf(" A+B=|%f %f %f %f|\n", C(i,0), C(i,1), C(i,2), C(i,3));
}
printf("\n\n\n");
// calculate A * B
C = A * B;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
if(i != 2)
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", C(i,0), C(i,1), C(i,2), C(i,3));
else
printf(" AB=|%f %f %f %f|\n", C(i,0), C(i,1), C(i,2), C(i,3));
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
輸出:
 矩陣求逆:
矩陣求逆:// Calculate inverse of matrix. Inversion my fail, in which case NULL will
// be returned. The determinant of pM is also returned it pfDeterminant
// is non-NULL.
D3DXMATRIX* WINAPI D3DXMatrixInverse ( D3DXMATRIX *pOut, FLOAT *pDeterminant, CONST D3DXMATRIX *pM );
代碼示例:
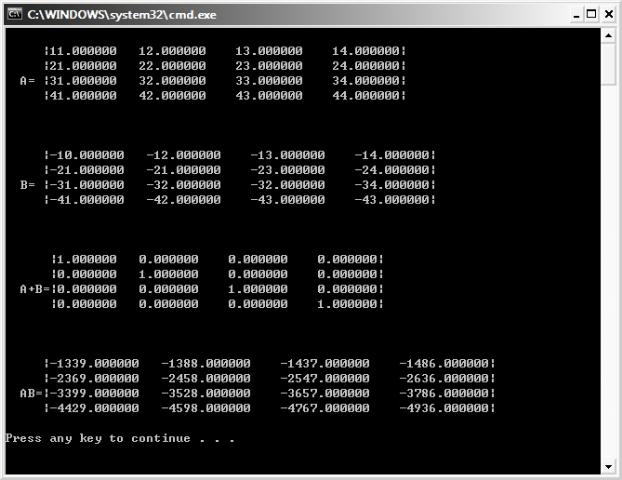
#include <stdio.h>
#include <D3DX9Math.h>
#pragma warning(disable : 4305)
int main()
{
// initialize and print matrix A
D3DXMATRIX A(1.0, 12.0, 13.0, 14.0,
0.0, 1.0, 23.0, 24.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 34.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
printf(" |%-4.6f %-4.6f %-4.6f %-4.6f|\n", A._11, A._12, A._13, A._14);
printf(" |%04.6f %04.6f %04.6f %04.6f|\n", A._21, A._22, A._23, A._24);
printf(" A= |%04.6f %04.6f %04.6f %04.6f|\n", A._31, A._32, A._33, A._34);
printf(" |%04.6f %04.6f %04.6f %04.6f|\n", A._41, A._42, A._43, A._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
// calculate inverse matrix for A
D3DXMATRIX B;
D3DXMatrixInverse(&B, NULL, &A);
printf(" |%04.6f %04.6f %04.6f %04.6f|\n", B._11, B._12, B._13, B._14);
printf(" |%04.6f %04.6f %04.6f %04.6f|\n", B._21, B._22, B._23, B._24);
printf("inv(A)= |%04.6f %04.6f %04.6f %04.6f|\n", B._31, B._32, B._33, B._34);
printf(" |%04.6f %04.6f %04.6f %04.6f|\n", B._41, B._42, B._43, B._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
return 0;
}
輸出:
 矩陣轉置:D3DXMATRIX* WINAPI D3DXMatrixTranspose ( D3DXMATRIX *pOut, CONST D3DXMATRIX *pM );
矩陣轉置:D3DXMATRIX* WINAPI D3DXMatrixTranspose ( D3DXMATRIX *pOut, CONST D3DXMATRIX *pM );
代碼示例:
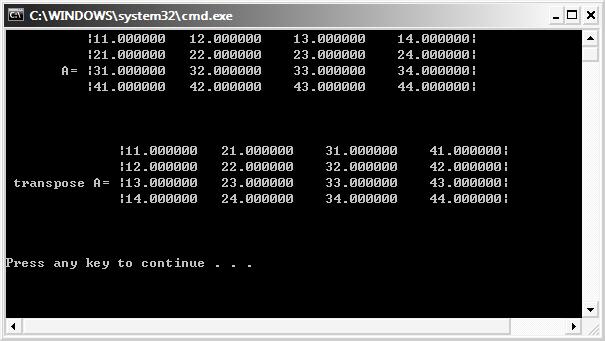
#include <stdio.h>
#include <D3DX9Math.h>
#pragma warning(disable : 4305)
int main()
{
// initialize and print matrix
D3DXMATRIX A(11.0f, 12.0f, 13.0f, 14.0f,
21.0f, 22.0f, 23.0f, 24.0f,
31.0f, 32.0f, 33.0f, 34.0f,
41.0f, 42.0f, 43.0f, 44.0f);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", A._11, A._12, A._13, A._14);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", A._21, A._22, A._23, A._24);
printf(" A= |%f %f %f %f|\n", A._31, A._32, A._33, A._34);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", A._41, A._42, A._43, A._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
// calculate matrix transpose
D3DXMATRIX C;
D3DXMatrixTranspose(&C, &A);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", C._11, C._12, C._13, C._14);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", C._21, C._22, C._23, C._24);
printf(" transpose A= |%f %f %f %f|\n", C._31, C._32, C._33, C._34);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", C._41, C._42, C._43, C._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
return 0;
}
輸出:
 坐標平移變換:
坐標平移變換:1) Builds a matrix using the specified offsets.
D3DXMATRIX *WINAPI D3DXMatrixTranslation(D3DXMATRIX *pOut, FLOAT x, FLOAT y, FLOAT z);2) Transforms a 3-D vector by a given matrix, projecting the result back into w = 1.
D3DXVECTOR3 *WINAPI D3DXVec3TransformCoord(D3DXVECTOR3 *pOut, CONST D3DXVECTOR3 *pV, CONST D3DXMATRIX *pM);This function transforms the vector, pV (x, y, z, 1), by the matrix, pM, projecting the result back into w=1.
3) Transforms the 3-D vector normal by the given matrix.
D3DXVECTOR3 *WINAPI D3DXVec3TransformNormal(D3DXVECTOR3 *pOut, CONST D3DXVECTOR3 *pV, CONST D3DXMATRIX *pM);This function transforms the vector normal (x, y, z, 0) of the vector, pV, by the matrix, pM.
If you transform a normal by a non-affine matrix, the matrix you pass to this function should be the transpose of the inverse of the matrix you would use to transform a coordinate.
D3DXVec3TransformNormal這個函數(shù)似乎執(zhí)行與 D3DXVec3TransformCoord相反的運算,沒搞懂。
代碼示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <D3DX9Math.h>
#pragma warning(disable : 4305)
int main()
{
D3DXVECTOR3 v(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
D3DXMATRIX M;
D3DXMatrixTranslation(&M, v.x, v.y, v.z);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._11, M._12, M._13, M._14);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._21, M._22, M._23, M._24);
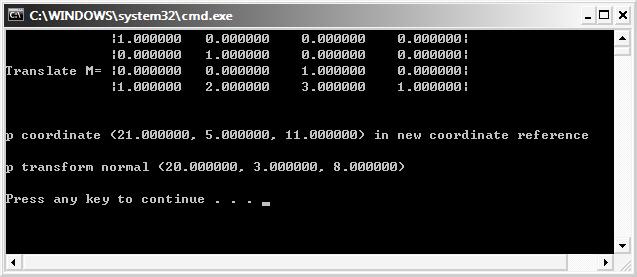
printf("Translate M= |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._31, M._32, M._33, M._34);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._41, M._42, M._43, M._44);
printf("\n\n");
D3DXVECTOR3 P(20.0, 3.0, 8.0);
D3DXVECTOR3 new_P;
D3DXVec3TransformCoord(&new_P, &P, &M);
printf("p coordinate (%f, %f, %f) in new coordinate reference\n\n", new_P.x, new_P.y, new_P.z);
D3DXVec3TransformNormal(&new_P, &P, &M);
printf("p transform normal (%f, %f, %f)\n\n", new_P.x, new_P.y, new_P.z);
return 0;
}
輸出:
 坐標的放大縮小變換:
坐標的放大縮小變換:
Builds a matrix that scales along the x-axis, the y-axis, and the z-axis.
D3DXMATRIX * D3DXMatrixScaling(
D3DXMATRIX *pOut,
FLOAT sx,
FLOAT sy,
FLOAT sz
);
- pOut
- [in, out] Pointer to the D3DXMATRIX structure that is the result of the operation.
- sx
- [in] Scaling factor that is applied along the x-axis.
- sy
- [in] Scaling factor that is applied along the y-axis.
- sz
- [in] Scaling factor that is applied along the z-axis.
代碼示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <D3DX9Math.h>
#pragma warning(disable : 4305)
int main()
{
D3DXMATRIX M;
D3DXMatrixScaling(&M, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._11, M._12, M._13, M._14);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._21, M._22, M._23, M._24);
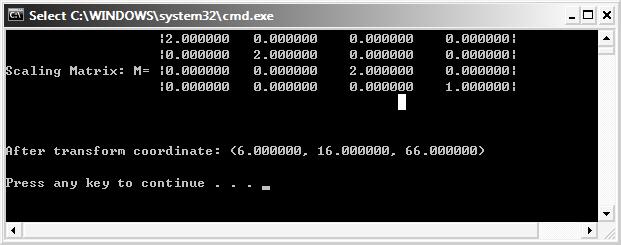
printf("Scaling Matrix: M= |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._31, M._32, M._33, M._34);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._41, M._42, M._43 ,M._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
D3DXVECTOR3 P(3.0, 8.0, 33.0);
D3DXVECTOR3 new_P;
D3DXVec3TransformCoord(&new_P, &P, &M);
printf("After transform coordinate: (%f, %f, %f)\n\n", new_P.x, new_P.y, new_P.z);
return 0;
}
輸出:
 旋轉變換:
旋轉變換:對于旋轉變換的矩陣計算,DirectX提供了 D3DXMatrixRotationX,D3DXMatrixRotationY, D3DXMatrixRotationZ和D3DXMatrixRotationAxis等函數(shù)來計算沿x,y,z軸以及任意軸線的旋轉變換矩陣,這4個函數(shù)的旋轉角都采用弧度作為計量單位.
// Build a matrix which rotates around the X axis
D3DXMATRIX* WINAPI D3DXMatrixRotationX ( D3DXMATRIX *pOut, FLOAT Angle );// Build a matrix which rotates around the Y axis
D3DXMATRIX* WINAPI D3DXMatrixRotationY ( D3DXMATRIX *pOut, FLOAT Angle );// Build a matrix which rotates around the Z axis
D3DXMATRIX* WINAPI D3DXMatrixRotationZ ( D3DXMATRIX *pOut, FLOAT Angle );// Build a matrix which rotates around an arbitrary axis
D3DXMATRIX* WINAPI D3DXMatrixRotationAxis ( D3DXMATRIX *pOut, CONST D3DXVECTOR3 *pV, FLOAT Angle );
代碼示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <D3DX9Math.h>
#pragma warning(disable : 4305)
int main()
{
D3DXMATRIX M;
D3DXVECTOR3 vec_rotate(5.0, 5.0, 5.0);
float angle = D3DX_PI;
D3DXMatrixRotationAxis(&M, &vec_rotate, angle);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._11, M._12, M._13, M._14);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._21, M._22, M._23, M._24);
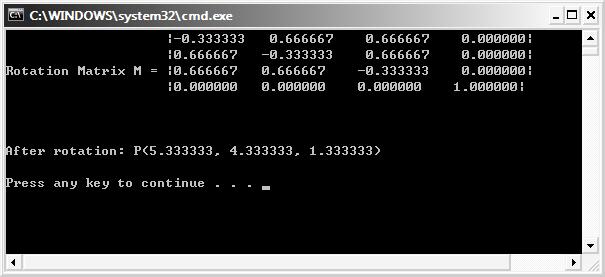
printf("Rotation Matrix M = |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._31, M._32, M._33, M._34);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._41, M._42, M._43, M._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
D3DXVECTOR3 P(2.0, 3.0, 6.0);
D3DXVec3TransformCoord(&P, &P, &M);
printf("After rotation: P(%f, %f, %f)\n\n", P.x, P.y, P.z);
return 0;
}
輸出:
還有一個函數(shù)
D3DXMatrixRotationYawPitchRoll,可以直接計算沿x,y,z軸旋轉的變換矩陣。
Builds a matrix with a specified yaw, pitch, and roll.
D3DXMATRIX * D3DXMatrixRotationYawPitchRoll(
D3DXMATRIX *pOut,
FLOAT Yaw,
FLOAT Pitch,
FLOAT Roll
);
Parameters
- pOut
- [in, out] Pointer to the D3DXMATRIX structure that is the result of the operation.
- Yaw
- [in] Yaw around the y-axis, in radians.
- Pitch
- [in] Pitch around the x-axis, in radians.
- Roll
- [in] Roll around the z-axis, in radians.
Return Values
Pointer to a D3DXMATRIX structure with the specified yaw, pitch, and roll.
Remarks
The return value for this function is the same value returned in the pOut parameter. In this way, the D3DXMatrixRotationYawPitchRoll function can be used as a parameter for another function.
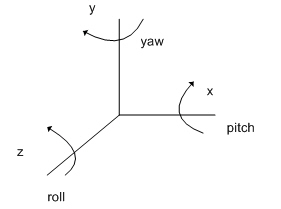
The order of transformations is roll first, then pitch, then yaw. Relative to the object's local coordinate axis, this is equivalent to rotation around the z-axis, followed by rotation around the x-axis, followed by rotation around the y-axis.
Figure 1. Roll, pitch, yaw diagram
代碼示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <D3DX9Math.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "d3dx9.lib")
#pragma warning(disable : 4305)
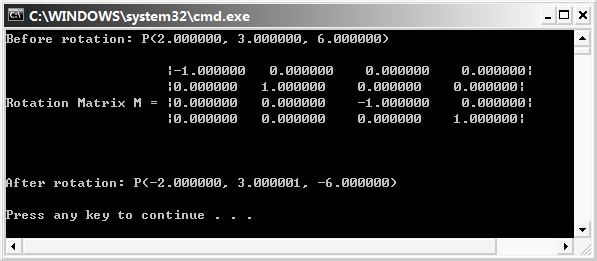
int main()
{
D3DXMATRIX M;
D3DXVECTOR3 P(2.0, 3.0, 6.0);
printf("Before rotation: P(%f, %f, %f)\n\n", P.x, P.y, P.z);
// Rotate around y-axis with 0 degree, around x-axis with PI degree, around z-axis with PI degree.
D3DXMatrixRotationYawPitchRoll(&M, 0, D3DX_PI, D3DX_PI);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._11, M._12, M._13, M._14);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._21, M._22, M._23, M._24);
printf("Rotation Matrix M = |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._31, M._32, M._33, M._34);
printf(" |%f %f %f %f|\n", M._41, M._42, M._43, M._44);
printf("\n\n\n");
D3DXVec3TransformCoord(&P, &P, &M);
printf("After rotation: P(%f, %f, %f)\n\n", P.x, P.y, P.z);
return 0;
}
運行截圖: