本文簡(jiǎn)單簡(jiǎn)介二叉樹的概念�����,并給出平衡一顆二叉樹的方法
關(guān)于二叉樹
現(xiàn)在有N個(gè)元素的數(shù)組或者鏈表���,要查找一個(gè)元素必須遍歷數(shù)組直到找到元素�。假如元素在是數(shù)組中最后一個(gè)或者數(shù)組中不存在這樣的元素,那么很不幸���,我們要遍歷整個(gè)數(shù)組。如果N非常大�,那將是非常痛苦的一件事情�����。
用二叉樹情況就好多了:
1. 更快的查找
2. 增加元素時(shí),元素被自動(dòng)排列
原理:
在鏈表或數(shù)組中�,元素一個(gè)接著一個(gè)�����,如圖
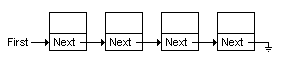
在二叉樹中情況不太一樣了
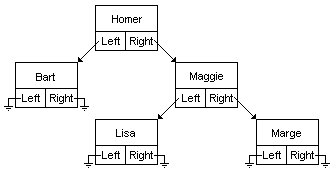
每個(gè)元素連著兩個(gè)元素,左孩子和右孩子�����。他們存儲(chǔ)的值的關(guān)系有如下規(guī)定
Value(left)<Value(middle)<=Value(right)
排序:
在二叉樹中利用遞歸你能很方便的排序
前序遍歷
 PrintElement(pTopMostElement)
PrintElement(pTopMostElement)
 .
.
 .
.
 void PrintElement(TreeElement* pElement)
void PrintElement(TreeElement* pElement)


 {
{
 if (pElement)
if (pElement)


 {
{
 PrintElement(pElement->LeftChild)
PrintElement(pElement->LeftChild)
 pElement->PrintMe()
pElement->PrintMe()
 PrintElement(pElement->RightChild)
PrintElement(pElement->RightChild)
 }
}
 }
}

后序遍歷:
 PrintElementReversed(pTopMostElement)
PrintElementReversed(pTopMostElement)
 .
.
 .
.
 void PrintElementReversed(TreeElement* pElement)
void PrintElementReversed(TreeElement* pElement)


 {
{
 if (pElement)
if (pElement)


 {
{
 PrintElementReversed(pElement->RightChild)
PrintElementReversed(pElement->RightChild)
 pElement->PrintMe()
pElement->PrintMe()
 PrintElementReversed(pElement->LeftChild)
PrintElementReversed(pElement->LeftChild)
 }
}
 }
}

如何使二叉樹平衡�����?
添加元素的順序?qū)⒂绊懚鏄涞男螒B(tài)���,以3,6,4,8,1,9,2,7,5的順序得到
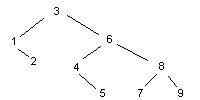
以1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9將得到
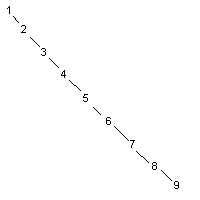
有以下方法可以考慮:
1. 以非排序的元素插入元素�����,不能要求給出的元素是高度不排序的
2. 以一組隨機(jī)元素構(gòu)造二叉樹�����,然后替換這些元素���,然后通過(guò)旋轉(zhuǎn)得到平衡的樹�����。參考隨機(jī)樹�。
3. 重構(gòu)這稞樹
重構(gòu)整稞樹
1. 把元素拷貝到數(shù)組中�����,以升序排序
2. 清空這棵樹
3. 從數(shù)組中高度不排序的選取元素插入樹中可以這樣完成第三步:
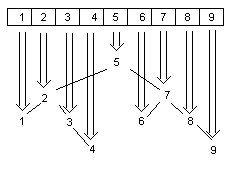
可以遞歸的實(shí)現(xiàn):
 // Assuming array ranges from [0..arraySize-1]
// Assuming array ranges from [0..arraySize-1]
 GetFromOrderedArray(0,arraySize-1)
GetFromOrderedArray(0,arraySize-1)
 .
.
 .
.
 void GetFromOrderedArray(int lowBound,int highBound)
void GetFromOrderedArray(int lowBound,int highBound)


 {
{
 if (hi < low) return;
if (hi < low) return;
 middlePos = lowBound+(highBound-lowBound)/2
middlePos = lowBound+(highBound-lowBound)/2
 // middlePos is now at the element in the middle
// middlePos is now at the element in the middle
 // between lowBound and highBound, so we just add
// between lowBound and highBound, so we just add
 // it to the tree
// it to the tree

 AddElement ( theOrderedArray[middlePos] )
AddElement ( theOrderedArray[middlePos] )

 // Pick the middle one "to the left"
// Pick the middle one "to the left"
 AddFromOrderedArray(lowBound,middlePos-1)
AddFromOrderedArray(lowBound,middlePos-1)

 // Pick the middle one "to the right"
// Pick the middle one "to the right"
 AddFromOrderedArray(middlePos+1,highBound)
AddFromOrderedArray(middlePos+1,highBound)
 }
}

刪除一個(gè)元素
首先要找到要?jiǎng)h除的元素E�����,有兩種方法:
1. 通過(guò)遍歷找到這個(gè)元素E
2. 給每個(gè)元素一個(gè)指向雙親的指針
接下來(lái)就是刪除的過(guò)程了:
1. 剪斷E與他雙親的連接
2. 將左右孩子所在的子樹同其他元素一樣加到樹中
3. 刪除E
 void RemoveElement(TreeElement* theOneToRemove)
void RemoveElement(TreeElement* theOneToRemove)


 {
{
 TreeElement* pParent = theOneToRemove->GetParent();
TreeElement* pParent = theOneToRemove->GetParent();

 // Ok, so it has a parent, then we'll simply just disconnect it.
// Ok, so it has a parent, then we'll simply just disconnect it.
 if (pParent)
if (pParent)


 {
{
 if (pParent->GetLeftChild() == theOneToRemove)
if (pParent->GetLeftChild() == theOneToRemove)


 {
{
 pParent->SetLeftChild(NULL);
pParent->SetLeftChild(NULL);
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 ASSERT(pParent->GetRightChild() == theOneToRemove);
ASSERT(pParent->GetRightChild() == theOneToRemove);
 pParent->SetRightChild(NULL);
pParent->SetRightChild(NULL);
 }
}
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 // No parent? Then we're removing the root element.
// No parent? Then we're removing the root element.
 theTopMostElement = NULL;
theTopMostElement = NULL;
 }
}

 // Disconnected, now we reconnect its children (if any)
// Disconnected, now we reconnect its children (if any)
 // just by adding them as we add any other node.
// just by adding them as we add any other node.
 if (theOneToRemove->GetLeftChild())
if (theOneToRemove->GetLeftChild())
 AddElement(theOneToRemove->GetLeftChild());
AddElement(theOneToRemove->GetLeftChild());
 if (theOneToRemove->GetRightChild())
if (theOneToRemove->GetRightChild())
 AddElement(theOneToRemove->GetRightChild());
AddElement(theOneToRemove->GetRightChild());

 //Zap the element (if that's what you want to do)
//Zap the element (if that's what you want to do)
 delete theOneToRemove;
delete theOneToRemove;

 }
}

注解:
通過(guò)函數(shù)回調(diào) 遍歷二叉樹
注:函數(shù)回調(diào)例如AddElement(theOneToRemove->GetRightChild());
簡(jiǎn)而言之,回調(diào)函數(shù)就是一個(gè)通過(guò)函數(shù)指針調(diào)用的函數(shù)。如果你把函數(shù)的指針(地址)作為參數(shù)傳遞給另一個(gè)函數(shù),當(dāng)這個(gè)指針被用為調(diào)用它所指向的函數(shù)時(shí)���,我們就說(shuō)這是回調(diào)函數(shù)。
可以把調(diào)用者與被調(diào)用者分開�。調(diào)用者不關(guān)心誰(shuí)是被調(diào)用者�,所有它需知道的�����,只是存在一個(gè)具有某種特定原型���、某些限制條件(如返回值為int)的被調(diào)用函數(shù)�。
#內(nèi)容選自CodeGuru
若理解錯(cuò)誤���,歡迎指正�����!