Same Side Technique
A common way to check if a point is in a triangle is to find the vectors connecting the point to each of the triangle's three vertices and sum the angles between those vectors. If the sum of the angles is 2*pi then the point is inside the triangle, otherwise it is not. It works, but it is very slow. This text explains a faster and much easier method.
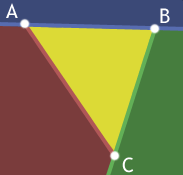 |
First off, forgive the nasty coloring. I'm really sorry about it. Honest.
Okay, A B C forms a triangle and all the points inside it are yellow. Lines AB, BC, and CA each split space in half and one of those halves is entirely outside the triangle. This is what we'll take advantage of.
For a point to be inside the traingle A B C it must be below AB and left of BC and right of AC. If any one of these tests fails we can return early.
|
But, how do we tell if a point is on the correct side of a line? I'm glad you asked.
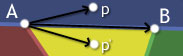
If you take the cross product of [B-A] and [p-A], you'll get a vector pointing out of the screen. On the other hand, if you take the cross product of [B-A] and [p'-A] you'll get a vector pointing into the screen. Ah ha! In fact if you cross [B-A] with the vector from A to any point above the line AB, the resulting vector points out of the screen while using any point below AB yields a vector pointing into the screen. So all we need to do to distinguish which side of a line a point lies on is take a cross product.
The only question remaining is: how do we know what direction the cross product should point in? Because the triangle can be oriented in any way in 3d-space, there isn't some set value we can compare with. Instead what we need is a reference point - a point that we know is on a certain side of the line. For our triangle, this is just the third point C.
So, any point p where [B-A] cross [p-A] does not point in the same direction as [B-A] cross [C-A] isn't inside the triangle. If the cross products do point in the same direction, then we need to test p with the other lines as well. If the point was on the same side of AB as C and is also on the same side of BC as A and on the same side of CA as B, then it is in the triangle.
Implementing this is a breeze. We'll make a function that tells us if two points are on the same side of a line and have the actual point-in-triangle function call this for each edge.
function SameSide(p1,p2, a,b)
cp1 = CrossProduct(b-a, p1-a)
cp2 = CrossProduct(b-a, p2-a)
if DotProduct(cp1, cp2) >= 0 then return true
else return false
function PointInTriangle(p, a,b,c)
if SameSide(p,a, b,c) and SameSide(p,b, a,c)
and SameSide(p,c, a,b) then return true
else return false
|
It's simple, effective and has no square roots, arc cosines, or strange projection axis determination nastiness.
Barycentric Technique
The advantage of the method above is that it's very simple to understand so that once you read it you should be able to remember it forever and code it up at any time without having to refer back to anything. It's just - hey the point has to be on the same side of each line as the triangle point that's not in the line. Cake.
Well, there's another method that is also as easy conceptually but executes faster. The downside is there's a little more math involved, but once you see it worked out it should be no problem.
So remember that the three points of the triangle define a plane in space. Pick one of the points and we can consider all other locations on the plane as relative to that point. Let's go with A -- it'll be our origin on the plane. Now what we need are basis vectors so we can give coordinate values to all the locations on the plane. We'll pick the two edges of the triangle that touch A, (C - A) and (B - A). Now we can get to any point on the plane just by starting at A and walking some distance along (C - A) and then from there walking some more in the direction (B - A).
With that in mind we can now describe any point on the plane as
P = A + u * (C - A) + v * (B - A)
Notice now that if u or v < 0 then we've walked in the wrong direction and must be outside the triangle. Also if u or v > 1 then we've walked too far in a direction and are outside the triangle. Finally if u + v > 1 then we've crossed the edge BC again leaving the triangle.
Given u and v we can easily calculate the point P with the above equation, but how can we go in the reverse direction and calculate u and v from a given point P? Time for some math!
P = A + u * (C - A) + v * (B - A) // Original equation
(P - A) = u * (C - A) + v * (B - A) // Subtract A from both sides
v2 = u * v0 + v * v1 // Substitute v0, v1, v2 for less writing
// We have two unknowns (u and v) so we need two equations to solve
// for them. Dot both sides by v0 to get one and dot both sides by
// v1 to get a second.
(v2) . v0 = (u * v0 + v * v1) . v0
(v2) . v1 = (u * v0 + v * v1) . v1
// Distribute v0 and v1
v2 . v0 = u * (v0 . v0) + v * (v1 . v0)
v2 . v1 = u * (v0 . v1) + v * (v1 . v1)
// Now we have two equations and two unknowns and can solve one
// equation for one variable and substitute into the other. Or
// if you're lazy like me, fire up Mathematica and save yourself
// some handwriting.
Solve[v2.v0 == {u(v0.v0) + v(v1.v0), v2.v1 == u(v0.v1) + v(v1.v1)}, {u, v}]
u = ((v1.v1)(v2.v0)-(v1.v0)(v2.v1)) / ((v0.v0)(v1.v1) - (v0.v1)(v1.v0))
v = ((v0.v0)(v2.v1)-(v0.v1)(v2.v0)) / ((v0.v0)(v1.v1) - (v0.v1)(v1.v0))
Here's an implementation in Flash that you can play with. :)
|
|
// Compute vectors
v0 = C - A
v1 = B - A
v2 = P - A
// Compute dot products
dot00 = dot(v0, v0)
dot01 = dot(v0, v1)
dot02 = dot(v0, v2)
dot11 = dot(v1, v1)
dot12 = dot(v1, v2)
// Compute barycentric coordinates
invDenom = 1 / (dot00 * dot11 - dot01 * dot01)
u = (dot11 * dot02 - dot01 * dot12) * invDenom
v = (dot00 * dot12 - dot01 * dot02) * invDenom
// Check if point is in triangle
return (u > 0) && (v > 0) && (u + v < 1)
|
The algorithm outlined here follows one of the techniques described in Realtime Collision Detection. You can also find more information about Barycentric Coordinates at Wikipedia and MathWorld.