【轉(zhuǎn)帖】《3D數(shù)學(xué)基礎(chǔ):圖形與游戲開發(fā)》讀書筆記1
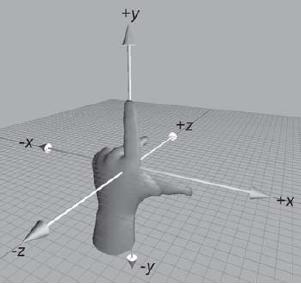
左手坐標(biāo)系的直觀表示:
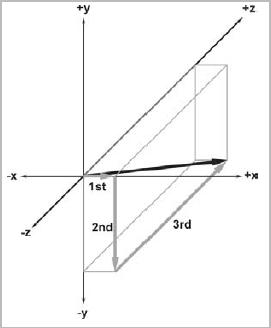
向量的表示(軸對齊包圍盒(AABB(axially aligned bounding box))):
2D向量的長度:||v|| = sqrt(vx*vx + vy*vy)
3D向量的長度:||v|| = sqrt(vx*vx + vy*vy + vz*vz)
標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化向量=此向量/此向量的長度=vx / ||v|| , vy / ||v|| , vz / ||v||
標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化后的向量的頭接觸到圓心在原點的單位圓(單位圓的半徑為1)
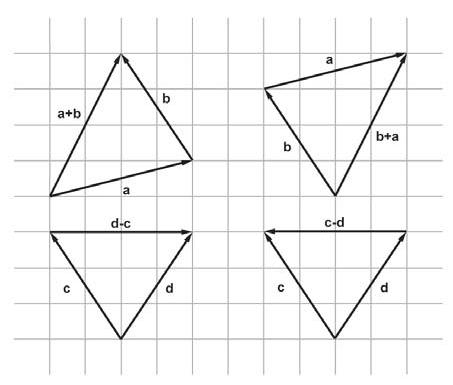
向量加法的幾何意義(三角形法則):
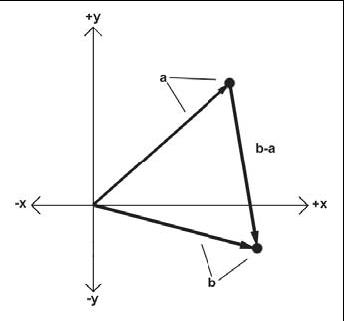
計算一個點到另一個點的位移可以使用三角形法則和向量減法來解決這個問題:
兩點間距離的公式:設(shè)兩點分別為3D向量a和b
則距離(a,b)=||b-a||=sqrt((bx - ax)2 +(by - ay)2 +(bz - az)2 )
向量點乘:點乘等于向量大小與向量夾角的cos值的積,其中c為兩點a和b的夾角:
a點乘b=||a||*||b||*cos(c)
計算向量的夾角:c =acos( (a*b)/(||a|| * ||b||))
如果a和b是單位向量,則c=acos(a*b)
當(dāng)點乘結(jié)果大于0,則夾角小于90度
當(dāng)點乘結(jié)果等于0,則夾角等于90度
當(dāng)點乘結(jié)果小于0,則夾角大于90度
向量差乘:
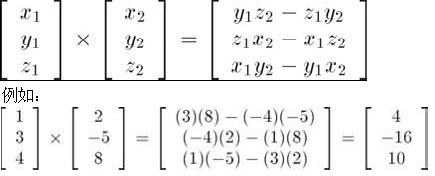
向量的封裝類:

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 //
//
 // 3D Math Primer for Games and Graphics Development
// 3D Math Primer for Games and Graphics Development
 //
//
 // Vector3.h - Declarations for 3D vector class
// Vector3.h - Declarations for 3D vector class
 //
//
 // Visit gamemath.com for the latest version of this file.
// Visit gamemath.com for the latest version of this file.
 //
//
 // For additional comments, see Chapter 6.
// For additional comments, see Chapter 6.
 //
//

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////

 #ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
#ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
 #define __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
#define __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__

 #include <math.h>
#include <math.h>


 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 //
//
 // class Vector3 - a simple 3D vector class
// class Vector3 - a simple 3D vector class
 //
//

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////


 class Vector3
class Vector3  {
{
 public:
public:

 // Public representation: Not many options here.
// Public representation: Not many options here.

 float x,y,z;
float x,y,z;

 // Constructors
// Constructors

 // Default constructor leaves vector in
// Default constructor leaves vector in
 // an indeterminate state
// an indeterminate state


 Vector3()
Vector3()  {}
{}

 // Copy constructor
// Copy constructor


 Vector3(const Vector3 &a) : x(a.x), y(a.y), z(a.z)
Vector3(const Vector3 &a) : x(a.x), y(a.y), z(a.z)  {}
{}

 // Construct given three values
// Construct given three values


 Vector3(float nx, float ny, float nz) : x(nx), y(ny), z(nz)
Vector3(float nx, float ny, float nz) : x(nx), y(ny), z(nz)  {}
{}

 // Standard object maintenance
// Standard object maintenance

 // Assignment. We adhere to C convention and
// Assignment. We adhere to C convention and
 // return reference to the lvalue
// return reference to the lvalue


 Vector3 &operator =(const Vector3 &a)
Vector3 &operator =(const Vector3 &a)  {
{
 x = a.x; y = a.y; z = a.z;
x = a.x; y = a.y; z = a.z;
 return *this;
return *this;
 }
}

 // Check for equality
// Check for equality


 bool operator ==(const Vector3 &a) const
bool operator ==(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{
 return x==a.x && y==a.y && z==a.z;
return x==a.x && y==a.y && z==a.z;
 }
}


 bool operator !=(const Vector3 &a) const
bool operator !=(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{
 return x!=a.x || y!=a.y || z!=a.z;
return x!=a.x || y!=a.y || z!=a.z;
 }
}


 // Vector operations
// Vector operations

 // Set the vector to zero
// Set the vector to zero


 void zero()
void zero()  { x = y = z = 0.0f; }
{ x = y = z = 0.0f; }

 // Unary minus returns the negative of the vector
// Unary minus returns the negative of the vector


 Vector3 operator -() const
Vector3 operator -() const  { return Vector3(-x,-y,-z); }
{ return Vector3(-x,-y,-z); }

 // Binary + and - add and subtract vectors
// Binary + and - add and subtract vectors


 Vector3 operator +(const Vector3 &a) const
Vector3 operator +(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{
 return Vector3(x + a.x, y + a.y, z + a.z);
return Vector3(x + a.x, y + a.y, z + a.z);
 }
}


 Vector3 operator -(const Vector3 &a) const
Vector3 operator -(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{
 return Vector3(x - a.x, y - a.y, z - a.z);
return Vector3(x - a.x, y - a.y, z - a.z);
 }
}

 // Multiplication and division by scalar
// Multiplication and division by scalar


 Vector3 operator *(float a) const
Vector3 operator *(float a) const  {
{
 return Vector3(x*a, y*a, z*a);
return Vector3(x*a, y*a, z*a);
 }
}


 Vector3 operator /(float a) const
Vector3 operator /(float a) const  {
{
 float oneOverA = 1.0f / a; // NOTE: no check for divide by zero here
float oneOverA = 1.0f / a; // NOTE: no check for divide by zero here
 return Vector3(x*oneOverA, y*oneOverA, z*oneOverA);
return Vector3(x*oneOverA, y*oneOverA, z*oneOverA);
 }
}

 // Combined assignment operators to conform to
// Combined assignment operators to conform to
 // C notation convention
// C notation convention


 Vector3 &operator +=(const Vector3 &a)
Vector3 &operator +=(const Vector3 &a)  {
{
 x += a.x; y += a.y; z += a.z;
x += a.x; y += a.y; z += a.z;
 return *this;
return *this;
 }
}


 Vector3 &operator -=(const Vector3 &a)
Vector3 &operator -=(const Vector3 &a)  {
{
 x -= a.x; y -= a.y; z -= a.z;
x -= a.x; y -= a.y; z -= a.z;
 return *this;
return *this;
 }
}


 Vector3 &operator *=(float a)
Vector3 &operator *=(float a)  {
{
 x *= a; y *= a; z *= a;
x *= a; y *= a; z *= a;
 return *this;
return *this;
 }
}


 Vector3 &operator /=(float a)
Vector3 &operator /=(float a)  {
{
 float oneOverA = 1.0f / a;
float oneOverA = 1.0f / a;
 x *= oneOverA; y *= oneOverA; z *= oneOverA;
x *= oneOverA; y *= oneOverA; z *= oneOverA;
 return *this;
return *this;
 }
}

 // Normalize the vector
// Normalize the vector


 void normalize()
void normalize()  {
{
 float magSq = x*x + y*y + z*z;
float magSq = x*x + y*y + z*z;

 if (magSq > 0.0f)
if (magSq > 0.0f)  { // check for divide-by-zero
{ // check for divide-by-zero
 float oneOverMag = 1.0f / sqrt(magSq);
float oneOverMag = 1.0f / sqrt(magSq);
 x *= oneOverMag;
x *= oneOverMag;
 y *= oneOverMag;
y *= oneOverMag;
 z *= oneOverMag;
z *= oneOverMag;
 }
}
 }
}

 // Vector dot product. We overload the standard
// Vector dot product. We overload the standard
 // multiplication symbol to do this
// multiplication symbol to do this


 float operator *(const Vector3 &a) const
float operator *(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{
 return x*a.x + y*a.y + z*a.z;
return x*a.x + y*a.y + z*a.z;
 }
}
 };
};


 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 //
//
 // Nonmember functions
// Nonmember functions
 //
//

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////

 // Compute the magnitude of a vector
// Compute the magnitude of a vector


 inline float vectorMag(const Vector3 &a)
inline float vectorMag(const Vector3 &a)  {
{
 return sqrt(a.x*a.x + a.y*a.y + a.z*a.z);
return sqrt(a.x*a.x + a.y*a.y + a.z*a.z);
 }
}

 // Compute the cross product of two vectors
// Compute the cross product of two vectors


 inline Vector3 crossProduct(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)
inline Vector3 crossProduct(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)  {
{
 return Vector3(
return Vector3(
 a.y*b.z - a.z*b.y,
a.y*b.z - a.z*b.y,
 a.z*b.x - a.x*b.z,
a.z*b.x - a.x*b.z,
 a.x*b.y - a.y*b.x
a.x*b.y - a.y*b.x
 );
);
 }
}

 // Scalar on the left multiplication, for symmetry
// Scalar on the left multiplication, for symmetry


 inline Vector3 operator *(float k, const Vector3 &v)
inline Vector3 operator *(float k, const Vector3 &v)  {
{
 return Vector3(k*v.x, k*v.y, k*v.z);
return Vector3(k*v.x, k*v.y, k*v.z);
 }
}

 // Compute the distance between two points
// Compute the distance between two points


 inline float distance(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)
inline float distance(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)  {
{
 float dx = a.x - b.x;
float dx = a.x - b.x;
 float dy = a.y - b.y;
float dy = a.y - b.y;
 float dz = a.z - b.z;
float dz = a.z - b.z;
 return sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz);
return sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz);
 }
}

 // Compute the distance between two points, squared. Often useful
// Compute the distance between two points, squared. Often useful
 // when comparing distances, since the square root is slow
// when comparing distances, since the square root is slow


 inline float distanceSquared(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)
inline float distanceSquared(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)  {
{
 float dx = a.x - b.x;
float dx = a.x - b.x;
 float dy = a.y - b.y;
float dy = a.y - b.y;
 float dz = a.z - b.z;
float dz = a.z - b.z;
 return dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz;
return dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz;
 }
}


 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 //
//
 // Global variables
// Global variables
 //
//

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////

 // We provide a global zero vector constant
// We provide a global zero vector constant

 extern const Vector3 kZeroVector;
extern const Vector3 kZeroVector;


 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 #endif // #ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
#endif // #ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__

向量的表示(軸對齊包圍盒(AABB(axially aligned bounding box))):

2D向量的長度:||v|| = sqrt(vx*vx + vy*vy)
3D向量的長度:||v|| = sqrt(vx*vx + vy*vy + vz*vz)
標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化向量=此向量/此向量的長度=vx / ||v|| , vy / ||v|| , vz / ||v||
標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化后的向量的頭接觸到圓心在原點的單位圓(單位圓的半徑為1)
向量加法的幾何意義(三角形法則):

計算一個點到另一個點的位移可以使用三角形法則和向量減法來解決這個問題:

兩點間距離的公式:設(shè)兩點分別為3D向量a和b
則距離(a,b)=||b-a||=sqrt((bx - ax)2 +(by - ay)2 +(bz - az)2 )
向量點乘:點乘等于向量大小與向量夾角的cos值的積,其中c為兩點a和b的夾角:
a點乘b=||a||*||b||*cos(c)
計算向量的夾角:c =acos( (a*b)/(||a|| * ||b||))
如果a和b是單位向量,則c=acos(a*b)
當(dāng)點乘結(jié)果大于0,則夾角小于90度
當(dāng)點乘結(jié)果等于0,則夾角等于90度
當(dāng)點乘結(jié)果小于0,則夾角大于90度
向量差乘:
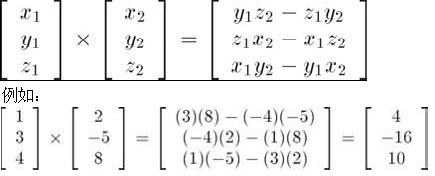
向量的封裝類:

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //
// // 3D Math Primer for Games and Graphics Development
// 3D Math Primer for Games and Graphics Development //
// // Vector3.h - Declarations for 3D vector class
// Vector3.h - Declarations for 3D vector class //
// // Visit gamemath.com for the latest version of this file.
// Visit gamemath.com for the latest version of this file. //
// // For additional comments, see Chapter 6.
// For additional comments, see Chapter 6. //
//
 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 #ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
#ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__ #define __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
#define __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
 #include <math.h>
#include <math.h>

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //
// // class Vector3 - a simple 3D vector class
// class Vector3 - a simple 3D vector class //
//
 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////

 class Vector3
class Vector3  {
{ public:
public:
 // Public representation: Not many options here.
// Public representation: Not many options here.
 float x,y,z;
float x,y,z;
 // Constructors
// Constructors
 // Default constructor leaves vector in
// Default constructor leaves vector in // an indeterminate state
// an indeterminate state

 Vector3()
Vector3()  {}
{}
 // Copy constructor
// Copy constructor

 Vector3(const Vector3 &a) : x(a.x), y(a.y), z(a.z)
Vector3(const Vector3 &a) : x(a.x), y(a.y), z(a.z)  {}
{}
 // Construct given three values
// Construct given three values

 Vector3(float nx, float ny, float nz) : x(nx), y(ny), z(nz)
Vector3(float nx, float ny, float nz) : x(nx), y(ny), z(nz)  {}
{}
 // Standard object maintenance
// Standard object maintenance
 // Assignment. We adhere to C convention and
// Assignment. We adhere to C convention and // return reference to the lvalue
// return reference to the lvalue

 Vector3 &operator =(const Vector3 &a)
Vector3 &operator =(const Vector3 &a)  {
{ x = a.x; y = a.y; z = a.z;
x = a.x; y = a.y; z = a.z; return *this;
return *this; }
}
 // Check for equality
// Check for equality

 bool operator ==(const Vector3 &a) const
bool operator ==(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{ return x==a.x && y==a.y && z==a.z;
return x==a.x && y==a.y && z==a.z; }
}

 bool operator !=(const Vector3 &a) const
bool operator !=(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{ return x!=a.x || y!=a.y || z!=a.z;
return x!=a.x || y!=a.y || z!=a.z; }
}

 // Vector operations
// Vector operations
 // Set the vector to zero
// Set the vector to zero

 void zero()
void zero()  { x = y = z = 0.0f; }
{ x = y = z = 0.0f; }
 // Unary minus returns the negative of the vector
// Unary minus returns the negative of the vector

 Vector3 operator -() const
Vector3 operator -() const  { return Vector3(-x,-y,-z); }
{ return Vector3(-x,-y,-z); }
 // Binary + and - add and subtract vectors
// Binary + and - add and subtract vectors

 Vector3 operator +(const Vector3 &a) const
Vector3 operator +(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{ return Vector3(x + a.x, y + a.y, z + a.z);
return Vector3(x + a.x, y + a.y, z + a.z); }
}

 Vector3 operator -(const Vector3 &a) const
Vector3 operator -(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{ return Vector3(x - a.x, y - a.y, z - a.z);
return Vector3(x - a.x, y - a.y, z - a.z); }
}
 // Multiplication and division by scalar
// Multiplication and division by scalar

 Vector3 operator *(float a) const
Vector3 operator *(float a) const  {
{ return Vector3(x*a, y*a, z*a);
return Vector3(x*a, y*a, z*a); }
}

 Vector3 operator /(float a) const
Vector3 operator /(float a) const  {
{ float oneOverA = 1.0f / a; // NOTE: no check for divide by zero here
float oneOverA = 1.0f / a; // NOTE: no check for divide by zero here return Vector3(x*oneOverA, y*oneOverA, z*oneOverA);
return Vector3(x*oneOverA, y*oneOverA, z*oneOverA); }
}
 // Combined assignment operators to conform to
// Combined assignment operators to conform to // C notation convention
// C notation convention

 Vector3 &operator +=(const Vector3 &a)
Vector3 &operator +=(const Vector3 &a)  {
{ x += a.x; y += a.y; z += a.z;
x += a.x; y += a.y; z += a.z; return *this;
return *this; }
}

 Vector3 &operator -=(const Vector3 &a)
Vector3 &operator -=(const Vector3 &a)  {
{ x -= a.x; y -= a.y; z -= a.z;
x -= a.x; y -= a.y; z -= a.z; return *this;
return *this; }
}

 Vector3 &operator *=(float a)
Vector3 &operator *=(float a)  {
{ x *= a; y *= a; z *= a;
x *= a; y *= a; z *= a; return *this;
return *this; }
}

 Vector3 &operator /=(float a)
Vector3 &operator /=(float a)  {
{ float oneOverA = 1.0f / a;
float oneOverA = 1.0f / a; x *= oneOverA; y *= oneOverA; z *= oneOverA;
x *= oneOverA; y *= oneOverA; z *= oneOverA; return *this;
return *this; }
}
 // Normalize the vector
// Normalize the vector

 void normalize()
void normalize()  {
{ float magSq = x*x + y*y + z*z;
float magSq = x*x + y*y + z*z;
 if (magSq > 0.0f)
if (magSq > 0.0f)  { // check for divide-by-zero
{ // check for divide-by-zero float oneOverMag = 1.0f / sqrt(magSq);
float oneOverMag = 1.0f / sqrt(magSq); x *= oneOverMag;
x *= oneOverMag; y *= oneOverMag;
y *= oneOverMag; z *= oneOverMag;
z *= oneOverMag; }
} }
}
 // Vector dot product. We overload the standard
// Vector dot product. We overload the standard // multiplication symbol to do this
// multiplication symbol to do this

 float operator *(const Vector3 &a) const
float operator *(const Vector3 &a) const  {
{ return x*a.x + y*a.y + z*a.z;
return x*a.x + y*a.y + z*a.z; }
} };
};

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //
// // Nonmember functions
// Nonmember functions //
//
 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 // Compute the magnitude of a vector
// Compute the magnitude of a vector

 inline float vectorMag(const Vector3 &a)
inline float vectorMag(const Vector3 &a)  {
{ return sqrt(a.x*a.x + a.y*a.y + a.z*a.z);
return sqrt(a.x*a.x + a.y*a.y + a.z*a.z); }
}
 // Compute the cross product of two vectors
// Compute the cross product of two vectors

 inline Vector3 crossProduct(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)
inline Vector3 crossProduct(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)  {
{ return Vector3(
return Vector3( a.y*b.z - a.z*b.y,
a.y*b.z - a.z*b.y, a.z*b.x - a.x*b.z,
a.z*b.x - a.x*b.z, a.x*b.y - a.y*b.x
a.x*b.y - a.y*b.x );
); }
}
 // Scalar on the left multiplication, for symmetry
// Scalar on the left multiplication, for symmetry

 inline Vector3 operator *(float k, const Vector3 &v)
inline Vector3 operator *(float k, const Vector3 &v)  {
{ return Vector3(k*v.x, k*v.y, k*v.z);
return Vector3(k*v.x, k*v.y, k*v.z); }
}
 // Compute the distance between two points
// Compute the distance between two points

 inline float distance(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)
inline float distance(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)  {
{ float dx = a.x - b.x;
float dx = a.x - b.x; float dy = a.y - b.y;
float dy = a.y - b.y; float dz = a.z - b.z;
float dz = a.z - b.z; return sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz);
return sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz); }
}
 // Compute the distance between two points, squared. Often useful
// Compute the distance between two points, squared. Often useful // when comparing distances, since the square root is slow
// when comparing distances, since the square root is slow

 inline float distanceSquared(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)
inline float distanceSquared(const Vector3 &a, const Vector3 &b)  {
{ float dx = a.x - b.x;
float dx = a.x - b.x; float dy = a.y - b.y;
float dy = a.y - b.y; float dz = a.z - b.z;
float dz = a.z - b.z; return dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz;
return dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz; }
}

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //
// // Global variables
// Global variables //
//
 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 // We provide a global zero vector constant
// We provide a global zero vector constant
 extern const Vector3 kZeroVector;
extern const Vector3 kZeroVector;

 /**//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #endif // #ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
#endif // #ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__posted on 2010-02-23 21:11 Code Knight 閱讀(377) 評論(0) 編輯 收藏 引用 所屬分類: 一起學(xué)數(shù)學(xué)


