D3D中的光照(2)
5.4光源
Direct3D支持三種類型的光源。
點光源——這種光源在世界坐標中有一個位置且向所有方向上都照射光線。
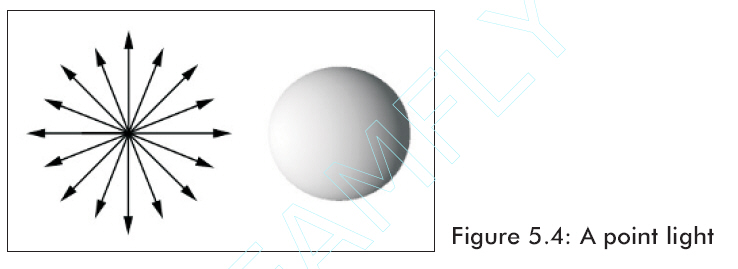
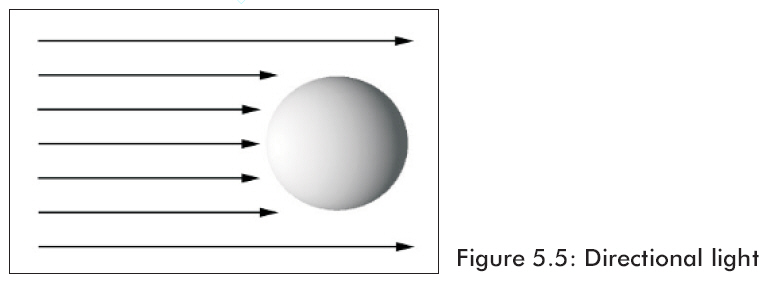
方向光源——這種光源沒有位置但是向指定方向發出平行光線。
聚光燈——這種類型的光源和手電筒的光類似;它有位置并且發出的光在指定方向上按照圓錐形照射。這個圓錐形有兩個角度,θ和φ。角度θ描述內圓錐,φ描述外圓錐。

在代碼中一個燈光資源是通過D3DLIGHT9結構來表現的。
D3DLIGHTTYPE Type;
D3DCOLORVALUE Diffuse;
D3DCOLORVALUE Specular;
D3DCOLORVALUE Ambient;
D3DVECTOR Position;
D3DVECTOR Direction;
float Range;
float Falloff;
float Attenuation0;
float Attenuation1;
float Attenuation2;
float Theta;
float Phi;
} D3DLIGHT9;
Type——定義燈光類型,我們能夠使用下面三種類型之一:D3DLIGHT_POINT, D3DLIGHT_SPOT, D3DLIGHT_DIRECTIONAL
Diffuse——此光源發出的漫射光顏色。
Specular——此光源發出的鏡面光顏色。
Ambient——此光源發出的環境光顏色。
Position——用一個向量來描述的光源世界坐標位置。這個值對于燈光的方向是無意義的。
Direction——用一個向量來描述的光源世界坐標照射方向。這個值不能用在點光源上。
Range——燈光能夠傳播的最大范圍。這個值不能比![]() 大。且不能用于方向光源。
大。且不能用于方向光源。
Attenuation0, Attenuation1, Attenuation2——這些衰減變量被用來定義燈光強度的傳播距離衰減。它們只被用于點光源和聚光燈上。Attenuation0定義恒定衰減,Attenuation1定義線性衰減,Attenuation2定義二次衰減。適當的使用這個公式,D是代表到光源的距離,A0,A1,A2與Attenuation0,1,2相匹配。
attenuation = 1/(A0 + A1D + A2D2)
Theta——只用于聚光燈;指定內圓錐的角度,單位是弧度。
Phi——只用于聚光燈;指定外圓錐的角度,單位是弧度。
現在只是演示怎樣使用InitDirectionalLight。其他的也很類似:
創建一個方向光源,它沿著x軸正方向照射白色燈光。我們按照下面的方法來做:
|
D3DXVECTOR3 dir(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); D3DXCOLOR c = d3d::WHITE; D3DLIGHT9 dirLight = d3d::InitDirectionalLight(&dir, &c); |
在把D3DLIGHT9初始化好以后,我們需要用Direct3D內在支持的燈光來注冊。就象這樣做:
|
Device->SetLight( 0, // element in the light list to set, range is 0-maxlights &light);// address of the D3DLIGHT9 structure to set |
一旦燈光注冊了,我們就能使用下面的列舉的例子來開或關燈光了:
|
Device->LightEnable( 0, // the element in the light list to enable/disable true); // true = enable, false = disable |
5.5實例程序:燈光
這一章的例子是創建如圖5.7所顯示的場景。它示范了怎樣指定頂點法線,怎樣創建材質,以及怎樣創建和使用一個方向燈光。注意在這個示例程序中我們不會使用在文件d3dUtility.h/cpp中的材質和燈光函數。因為我們想展示怎樣手動來做這些設置。
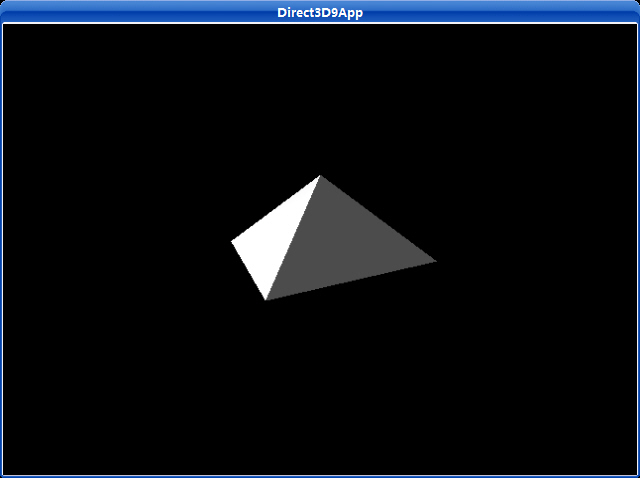
圖5.7
給場景增加燈光的步驟是:
1、 允許使用燈光。
2、 為每個物體創建材質并且在渲染相應物體前應將材質附予物體。
3、 創建一個或多個光源,設置它們,把它們設為可用。
4、 將其他附加光源設為可用,比如鏡面高光。
Renders a light pyramid. Demonstrates how to specify the vertex normals, how to create
and set a material, and how to create and set a directional light.
**************************************************************************************/
#include "d3dUtility.h"
#pragma warning(disable : 4100)
class cLightVertex
{
public:
float m_x, m_y, m_z;
float m_nx, m_ny, m_nz;
cLightVertex() {}
cLightVertex(float x, float y, float z, float nx, float ny, float nz)
{
m_x = x; m_y = y; m_z = z;
m_nx = nx; m_ny = ny; m_nz = nz;
}
};
const DWORD LIGHT_VERTEX_FVF = D3DFVF_XYZ | D3DFVF_NORMAL;
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const int WIDTH = 640;
const int HEIGHT = 480;
IDirect3DDevice9* g_d3d_device = NULL;
IDirect3DVertexBuffer9* g_pyramid_vb = NULL;
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
bool setup()
{
// turn on lighting
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_LIGHTING, TRUE);
g_d3d_device->CreateVertexBuffer(12 * sizeof(cLightVertex), D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY, LIGHT_VERTEX_FVF,
D3DPOOL_MANAGED, &g_pyramid_vb, NULL);
// fill the buffers with the triangle data
cLightVertex* vertices;
g_pyramid_vb->Lock(0, 0, (void**)&vertices, 0);
// front face
vertices[0] = cLightVertex(-1.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.707f, -0.707f);
vertices[1] = cLightVertex( 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.707f, -0.707f);
vertices[2] = cLightVertex( 1.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.707f, -0.707f);
// left face
vertices[3] = cLightVertex(-1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, -0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f);
vertices[4] = cLightVertex( 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, -0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f);
vertices[5] = cLightVertex(-1.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, -0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f);
// right face
vertices[6] = cLightVertex( 1.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f);
vertices[7] = cLightVertex( 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f);
vertices[8] = cLightVertex( 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f);
// back face
vertices[9] = cLightVertex( 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.707f, 0.707f);
vertices[10] = cLightVertex( 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.707f, 0.707f);
vertices[11] = cLightVertex(-1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.707f, 0.707f);
g_pyramid_vb->Unlock();
// create and set the material
D3DMATERIAL9 material;
material.Ambient = WHITE;
material.Diffuse = WHITE;
material.Specular = WHITE;
material.Emissive = BLACK;
material.Power = 5.0f;
g_d3d_device->SetMaterial(&material);
// setup a directional light
D3DLIGHT9 dir_light;
ZeroMemory(&dir_light, sizeof(dir_light));
dir_light.Type = D3DLIGHT_DIRECTIONAL;
dir_light.Diffuse = WHITE;
dir_light.Specular = WHITE * 0.3f;
dir_light.Ambient = WHITE * 0.3f;
dir_light.Direction = D3DXVECTOR3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// set and enable the light
g_d3d_device->SetLight(0, &dir_light);
g_d3d_device->LightEnable(0, TRUE);
// turn on specular lighting and instruct Direct3D to renormalize normals
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_NORMALIZENORMALS, TRUE);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_SPECULARENABLE, TRUE);
// position and aim the camera
D3DXMATRIX view_matrix;
D3DXVECTOR3 pos(0.0f, 1.0f, -3.0f);
D3DXVECTOR3 target(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
D3DXVECTOR3 up(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
D3DXMatrixLookAtLH(&view_matrix, &pos, &target, &up);
g_d3d_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_VIEW, &view_matrix);
// set the projection matrix
D3DXMATRIX proj;
D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH(&proj, D3DX_PI * 0.5f, (float)WIDTH/HEIGHT, 1.0f, 1000.0f);
g_d3d_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_PROJECTION, &proj);
return true;
}
void cleanup()
{
safe_release<IDirect3DVertexBuffer9*>(g_pyramid_vb);
}
bool display(float time_delta)
{
// update the scene: rotate the pyramid
D3DXMATRIX y_rot;
static float y = 0.0f;
D3DXMatrixRotationY(&y_rot, y);
y += time_delta;
if(y >= 6.28f)
y = 0.0f;
g_d3d_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, &y_rot);
// draw the scene
g_d3d_device->Clear(0, NULL, D3DCLEAR_TARGET | D3DCLEAR_ZBUFFER, 0x00000000, 1.0f, 0);
g_d3d_device->BeginScene();
g_d3d_device->SetStreamSource(0, g_pyramid_vb, 0, sizeof(cLightVertex));
g_d3d_device->SetFVF(LIGHT_VERTEX_FVF);
g_d3d_device->DrawPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST, 0, 4);
g_d3d_device->EndScene();
g_d3d_device->Present(NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
return true;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK wnd_proc(HWND hwnd, UINT msg, WPARAM word_param, LPARAM long_param)
{
switch(msg)
{
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
case WM_KEYDOWN:
if(word_param == VK_ESCAPE)
DestroyWindow(hwnd);
break;
}
return DefWindowProc(hwnd, msg, word_param, long_param);
}
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE inst, HINSTANCE, PSTR cmd_line, int cmd_show)
{
if(! init_d3d(inst, WIDTH, HEIGHT, true, D3DDEVTYPE_HAL, &g_d3d_device))
{
MessageBox(NULL, "init_d3d() - failed.", 0, MB_OK);
return 0;
}
if(! setup())
{
MessageBox(NULL, "Steup() - failed.", 0, MB_OK);
return 0;
}
enter_msg_loop(display);
cleanup();
g_d3d_device->Release();
return 0;
}
Setup函數給場景加入燈光。首先允許使用燈光,當然這不是必須的因為默認設置就是允許使用燈光的。
下一步,我們創建頂點緩存,鎖定,并且把“金字塔”的三角形頂點放入其中。頂點法線是利用5.3節中的運算法則預先計算好的。注意三角形共享頂點,但它們的法線不能共享;因此對這個物體使用索引列表并不是最有利的。例如,所有三角形都共享頂點(0,1,0);然而,對每個三角形,它們的頂點法線是不相同的。
為物體產生了頂點數據以后,我們描述利用燈光表現各自材質的物體間是怎樣相互影響的。在這個例子中,“金字塔”反射出白光,自身不發光,且會產生一些高光。
接著,我們創建一個方向光并將其設為可用。方向光是沿著x軸的正方向照射的。燈光照射最強的白色漫射光(dir.Diffuse = WHITE),較弱的白色鏡面光(dir.Specular = WHITE * 0.3f)以及一個中等強度的白色環境光(dir.Ambient = WHITE *0.6f)。
最后,我們設置狀態使法線重新單位化且把鏡面高光設置為可用。



