新建網頁 1
球和平面的相交性檢測
球和平面的靜態檢測相對容易一些,可以用公式12.14來計算球心到平面的距離。如果距離小于球半徑,那么它們相交。實際上還能作一種更靈活的檢測,這種檢測把相交分為球完全在平面正面,完全在背面,跨平面等三種情況。仔細分析程序清單13.2:
Listing 13.2: Determining which side of a plane a sphere is on
// Given a sphere and plane, determine which side of the plane
// the sphere is on.
//
// Return values:
//
// < 0 Sphere is completely on the back
// > 0 Sphere is completely on the front
// 0 Sphere straddles plane
int classifySpherePlane(
const Vector3 &planeNormal, // must be normalized
float planeD, // p * planeNormal = planeD
const Vector3 &sphereCenter, // center of sphere
float sphereRadius // radius of sphere
)
{
// Compute distance from center of sphere to the plane
float d = planeNormal * sphereCenter – planeD;
// Completely on the front side?
if (d >= sphereRadius)
return +1;
// Completely on the back side?
if (d <= –sphereRadius)
return –1;
// Sphere intersects the plane
return 0;
}
動態檢測要稍微復雜一些。設平面為靜止的,球作所有的相對位移。
平面的定義方式一如既往,用標準形式p . n = d,n為單位向量。球由半徑r和初始球心位置c定義。球的位移,由單位向量d指明方向,L代表位移的距離。t從0變化到L,用直線方程c+td計算球心的運動軌跡。如圖13.13所示:
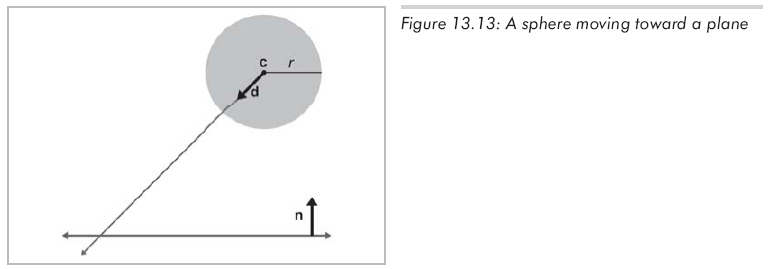
不管在平面上的哪一點上發生相交,在球上的相交點總是固定的,認識到這一點能大大簡化問題。用c-rn來計算交點,如圖13.14所示:
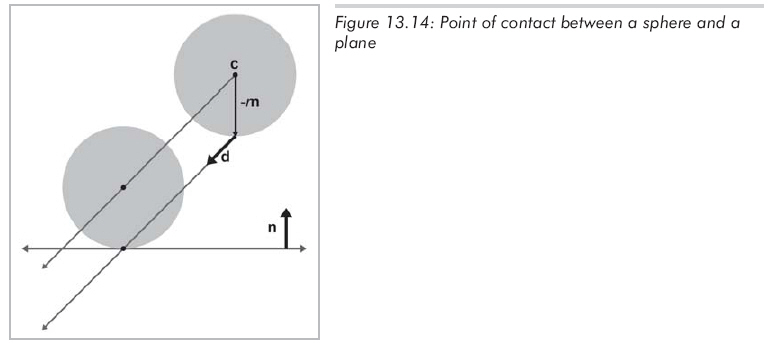
現在我們知道了球上的相交點,就可以利用射線與平面相交性檢測的方法,替換掉公式13.6中的p0,得到公式13.9:
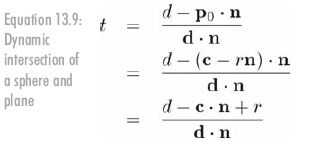
射線和三角形的相交性檢測
在圖形學和計算幾何中射線與三角形的相交性檢測是非常重要的。因為缺乏射線和復雜物體間相交性檢測的方法,我們通常用三角網格代表(或至少是近似代表)物體表面,再作射線和三角網格的相交性檢測。第一步是計算射線和包含該三角形的平面的交點,第二步是通過計算交點的重心坐標,來判斷它是否在三角形中。
為了使測試效率盡可能高,要使用下列技巧:
(1)在檢測中盡可能地返回負值(沒有相交),這稱作"提前結束(early out)"。
(2)盡可能地延遲昂貴的數學運算,如除法。有兩個原因:第一,如果并不需要昂貴運算的結果,比如說遇到了提前結束的情況,那么執行這些運算的時間就白白浪費了。第二,它給了編譯器更多的空間以利用現代處理器的指令管道的優點。在準備除法運算時,它產生執行其他測試的代碼(可能導致提前結束)。所以,在執行期間,如果確實需要除法運算的結果,該結果可能已經被計算出來,或至少已經部分被計算出來了。
(3)只檢測與三角形正面的相交,這幾乎可以節省一半的檢測時間。
// Ray-triangle intersection test.
//
// Algorithm from Didier Badouel, Graphics Gems I, pp 390-393
float rayTriangleIntersect(
const Vector3 &rayOrg, // origin of the ray
const Vector3 &rayDelta, // ray length and direction
const Vector3 &p0, // triangle vertices
const Vector3 &p1, // .
const Vector3 &p2, // .
float minT) // closest intersection found so far. (Start with 1.0)
{
// We'll return this huge number if no intersection is detected
const float kNoIntersection = 1e30f;
// Compute clockwise edge vectors.
Vector3 e1 = p1 – p0;
Vector3 e2 = p2 – p1;
// Compute surface normal. (Unnormalized)
Vector3 n = crossProduct(e1, e2);
// Compute gradient, which tells us how steep of an angle
// we are approaching the *front* side of the triangle
float dot = n * rayDelta;
// Check for a ray that is parallel to the triangle or not pointing toward the front face
// of the triangle.
//
// Note that this also will reject degenerate triangles and rays as well. We code this in a
// very particular way so that NANs will bail here. (This does not behave the same as
// "dot >= 0.0f" when NANs are involved.)
if (!(dot < 0.0f))
return kNoIntersection;
// Compute d value for the plane equation. We will use the plane equation with d on the right side:
//
// Ax + By + Cz = d
float d = n * p0;
// Compute parametric point of intersection with the plane containing the triangle, checking at the
// earliest possible stages for trivial rejection.
float t = d – n * rayOrg;
// Is ray origin on the backside of the polygon? Again, we phrase the check so that NANs will bail.
if (!(t <= 0.0f))
return kNoIntersection;
// Closer intersection already found? (Or does ray not reach the plane?)
//
// since dot < 0:
//
// t/dot > minT
//
// is the same as
//
// t < dot * minT
//
// (And then we invert it for NAN checking )
)
if (!(t >= dot * minT))
return kNoIntersection;
// OK, ray intersects the plane. Compute actual parametric point of intersection.
t /= dot;
assert(t >= 0.0f);
assert(t <= minT);
// Compute 3D point of intersection
Vector3 p = rayOrg + rayDelta * t;
// Find dominant axis to select which plane
// to project onto, and compute u's and v's
float u0, u1, u2;
float v0, v1, v2;
if (fabs(n.x) > fabs(n.y))
{
if (fabs(n.x) > fabs(n.z))
{
u0 = p.y – p0.y;
u1 = p1.y – p0.y;
u2 = p2.y – p0.y;
v0 = p.z – p0.z;
v1 = p1.z – p0.z;
v2 = p2.z – p0.z;
}
else
{
u0 = p.x – p0.x;
u1 = p1.x – p0.x;
u2 = p2.x – p0.x;
v0 = p.y – p0.y;
v1 = p1.y – p0.y;
v2 = p2.y – p0.y;
}
}
else
{
if (fabs(n.y) > fabs(n.z))
{
u0 = p.x – p0.x;
u1 = p1.x – p0.x;
u2 = p2.x – p0.x;
v0 = p.z – p0.z;
v1 = p1.z – p0.z;
v2 = p2.z – p0.z;
}
else
{
u0 = p.x – p0.x;
u1 = p1.x – p0.x;
u2 = p2.x – p0.x;
v0 = p.y – p0.y;
v1 = p1.y – p0.y;
v2 = p2.y – p0.y;
}
}
// Compute denominator, check for invalid.
float temp = u1 * v2 – v1 * u2;
if (!(temp != 0.0f))
return kNoIntersection;
temp = 1.0f / temp;
// Compute barycentric coords, checking for out-of-range at each step
float alpha = (u0 * v2 – v0 * u2) * temp;
if (!(alpha >= 0.0f))
return kNoIntersection;
float beta = (u1 * v0 – v1 * u0) * temp;
if (!(beta >= 0.0f))
return kNoIntersection;
float gamma = 1.0f - alpha - beta;
if (!(gamma >= 0.0f))
return kNoIntersection;
// Return parametric point of intersection
return t;
}
還有一個能優化昂貴計算的策略沒體現在上述代碼中:即預先計算結果。如果像多邊形向量這樣的值預先被計算出來的話,就可以采用更加優化的策略。
射線和AABB的相交性檢測
檢測AABB和射線的相交性非常重要,因為根據檢測的結果可以避免對更復雜物體的測試。(例如,我們要檢測射線與多個由三角網格組成的物體的相交性,可以先計算射線和三角網格的AABB的相交性。有時候可以一次就排除整個物體,而不必去檢測這個物體的所有三角形。)
Woo提出一種方法,先判斷矩形邊界框的哪個面會相交,再檢測射線與包含這個面的平面的相交性。如果交點在盒子中,那么射線與矩形邊界框相交,否則不存在相交。
cAABB3中rayIntersect()就是用Woo的技術來實現的。
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Parametric intersection with a ray. Returns parametric point
// of intsersection in range 0 1 or a really big number (>1) if no
1 or a really big number (>1) if no
// intersection.
//
// From "Fast Ray-Box Intersection," by Woo in Graphics Gems I, page 395.
//
// See 12.9.11
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
float AABB3::rayIntersect(const Vector3& rayOrg, // origin of the ray
const Vector3& rayDelta, // length and direction of the ray
Vector3* returnNormal) const // optionally, the normal is returned
{
// We'll return this huge number if no intersection
const float kNoIntersection = 1e30f;
// Check for point inside box, trivial reject, and determine parametric distance to each front face.
bool inside = true;
float xt, xn;
if (rayOrg.x < min.x)
{
xt = min.x - rayOrg.x;
if (xt > rayDelta.x)
return kNoIntersection;
xt /= rayDelta.x;
inside = false;
xn = -1.0f;
}
else if (rayOrg.x > max.x)
{
xt = max.x - rayOrg.x;
if (xt < rayDelta.x)
return kNoIntersection;
xt /= rayDelta.x;
inside = false;
xn = 1.0f;
}
else
xt = -1.0f;
float yt, yn;
if (rayOrg.y < min.y)
{
yt = min.y - rayOrg.y;
if (yt > rayDelta.y)
return kNoIntersection;
yt /= rayDelta.y;
inside = false;
yn = -1.0f;
}
else if (rayOrg.y > max.y)
{
yt = max.y - rayOrg.y;
if (yt < rayDelta.y)
return kNoIntersection;
yt /= rayDelta.y;
inside = false;
yn = 1.0f;
}
else
yt = -1.0f;
float zt, zn;
if (rayOrg.z < min.z)
{
zt = min.z - rayOrg.z;
if (zt > rayDelta.z)
return kNoIntersection;
zt /= rayDelta.z;
inside = false;
zn = -1.0f;
}
else if (rayOrg.z > max.z)
{
zt = max.z - rayOrg.z;
if (zt < rayDelta.z)
return kNoIntersection;
zt /= rayDelta.z;
inside = false;
zn = 1.0f;
}
else
zt = -1.0f;
// Inside box?
if (inside)
{
if (returnNormal != NULL)
{
*returnNormal = -rayDelta;
returnNormal->normalize();
}
return 0.0f;
}
// Select farthest plane - this is
// the plane of intersection.
int which = 0;
float t = xt;
if (yt > t)
{
which = 1;
t = yt;
}
if (zt > t)
{
which = 2;
t = zt;
}
switch (which)
{
case 0: // intersect with yz plane
{
float y = rayOrg.y + rayDelta.y * t;
if (y < min.y || y > max.y)
return kNoIntersection;
float z = rayOrg.z + rayDelta.z * t;
if (z < min.z || z > max.z)
return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL)
{
returnNormal->x = xn;
returnNormal->y = 0.0f;
returnNormal->z = 0.0f;
}
}
break;
case 1: // intersect with xz plane
{
float x = rayOrg.x + rayDelta.x * t;
if (x < min.x || x > max.x)
return kNoIntersection;
float z = rayOrg.z + rayDelta.z * t;
if (z < min.z || z > max.z)
return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL)
{
returnNormal->x = 0.0f;
returnNormal->y = yn;
returnNormal->z = 0.0f;
}
}
break;
case 2: // intersect with xy plane
{
float x = rayOrg.x + rayDelta.x * t;
if (x < min.x || x > max.x)
return kNoIntersection;
float y = rayOrg.y + rayDelta.y * t;
if (y < min.y || y > max.y)
return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL)
{
returnNormal->x = 0.0f;
returnNormal->y = 0.0f;
returnNormal->z = zn;
}
}
break;
}
// Return parametric point of intersection
return t;
}