DirectPlay Messages to Game
Messages
As I’ve mentioned before, the
server needs to convert the DirectPlay network messages
into the game-related messages you’ve just read about. You accomplish this by
processing incoming player connection, disconnection, and receive data messages
from
DirectPlay and converting those messages into game messages.
To accomplish this conversion
of messages, you derive a class from cNetworkServer
and override the create_player, destroy_player, and receive functions:
class cServer : public cNetworkServer
{
protected:
virtual bool create_player(const DPNMSG_CREATE_PLAYER* msg);
virtual bool destroy_player(const DPNMSG_DESTROY_PLAYER* msg);
virtual bool receive(const DPNMSG_RECEIVE* msg);
};
Because I’m using the System Core
to handle application processing, a problem
quickly arises when dealing with the network. The network component and
application
component are two separate entities, which means that neither component is
allowed to modify the other's private data.
As Figure 19.11 illustrates, the
network component needs a way to siphon incoming
messages into the application, which by chance is handled by creating three
public
functions that match the network class’s functions.
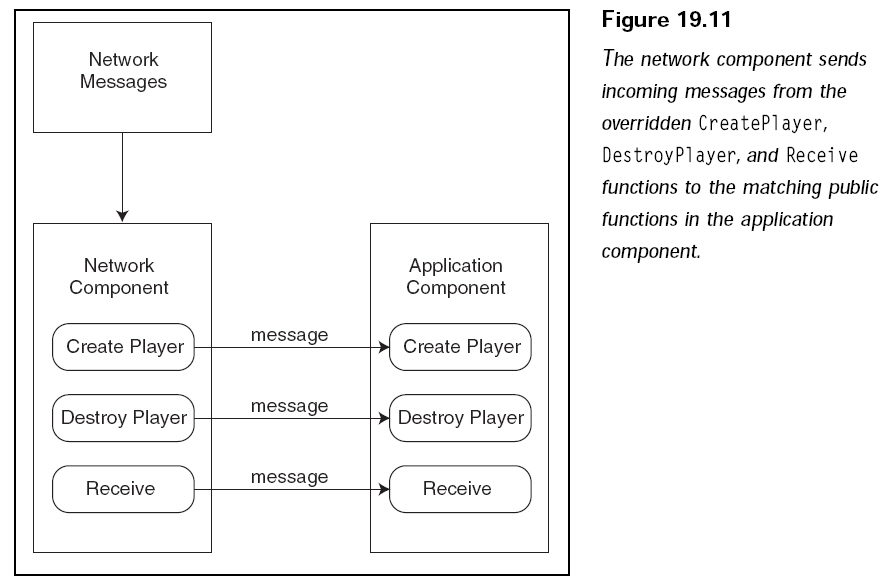
To use the three message
functions in the application component, you construct a
derived cFramework class that contains the three public functions as follows:
class cApp : public cFramework
{
private:
HWND m_controls[3];
CRITICAL_SECTION m_msg_cs;
cMesh m_level_mesh;
GUID* m_adapter_guid;
cNetworkAdapter m_adapter;
cServer m_server;
long m_connected_player_num;
sPlayer* m_players;
sMsg* m_msgs;
long m_msg_head;
long m_msg_tail;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public:
void set_adapter_guid(GUID* adapter_guid)
{
m_adapter_guid = adapter_guid;
}
public:
cApp();
virtual bool init();
virtual bool frame();
virtual void shutdown();
void create_player(const DPNMSG_CREATE_PLAYER* msg);
void destroy_player(const DPNMSG_DESTROY_PLAYER* msg);
void receive(const DPNMSG_RECEIVE* msg);
private:
bool select_adapter();
void setup_app_window();
bool init_game();
bool host_game();
void list_players();
void process_queue_msg();
void update_players();
void update_network();
void update_latency();
bool send_player_info(const sMsg* msg, DPNID to);
bool queue_msg(const void* msg);
bool add_player(const sMsg* msg);
void remove_player(const sMsg* msg);
bool player_state_change(const sMsg* msg);
bool send_network_msg(void* msg, long send_flags, int to);
bool check_intersect(cMesh* mesh,
float x_start, float y_start, float z_start,
float x_end, float y_end, float z_end);
};
To start sending DirectPlay
messages to the application class, you code the overridden
cServer functions to call upon the matching application functions. In order for
the
server to know which application class instance to send messages to, you need to
declare a global variable that points to the current application class instance
in use:
cApp* g_app;
cNetworkAdapter* g_adapter;
Inside the derived application
class’s constructor, you then point the global
g_app variable to the application class instance:
cApp::cApp()
{
m_adapter_guid = NULL;
m_msgs = NULL;
m_msg_head = 0;
m_msg_tail = 0;
m_connected_player_num = 0;
m_players = NULL;
g_app = this;
g_adapter = &m_adapter;
InitializeCriticalSection(&m_msg_cs);
}
Now, you can code the network
server component to send incoming messages to
the application object defined by the global g_app pointer:
bool cServer::create_player(const DPNMSG_CREATE_PLAYER* msg)
{
g_app->create_player(msg);
return true;
}
bool cServer::destroy_player(const DPNMSG_DESTROY_PLAYER* msg)
{
g_app->destroy_player(msg);
return true;
}
bool cServer::receive(const DPNMSG_RECEIVE* msg)
{
g_app->receive(msg);
return true;
}
The server component is now
complete and is forwarding network messages to the
application class. To convert those network messages to game-related messages,
the application class must contain the following public functions:
void cApp::create_player(const DPNMSG_CREATE_PLAYER* msg)
{
sCreatePlayerMsg create_msg;
create_msg.header.type = MSG_CREATE_PLAYER;
create_msg.header.size = sizeof(sCreatePlayerMsg);
create_msg.header.player_id = msg->dpnidPlayer;
queue_msg(&create_msg);
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void cApp::destroy_player(const DPNMSG_DESTROY_PLAYER* msg)
{
sDestroyPlayerMsg destroy_msg;
destroy_msg.header.type = MSG_DESTROY_PLAYER;
destroy_msg.header.size = sizeof(sDestroyPlayerMsg);
destroy_msg.header.player_id = msg->dpnidPlayer;
queue_msg(&destroy_msg);
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void cApp::receive(const DPNMSG_RECEIVE* msg)
{
sMsgHeader* header = (sMsgHeader*) msg->pReceiveData;
// make sure it is a valid message type and queue it
switch(header->type)
{
case MSG_SEND_PLAYER_INFO:
case MSG_STATE_CHANGE:
queue_msg(msg->pReceiveData);
break;
}
}
You can see that in each of the
three functions, I’m constructing a game-related
message using the data from the DirectPlay messages provided. When a player
tries
to connect to the server, a create-player message is created that stores the
connecting
player’s DirectPlayer identification number (along with the message type and
size).
That create-player message is then queued.
As for players disconnecting from
the game, a disconnect-player message is constructed
and queued. Last, whenever data (other than a system message) is
received from a client, the cApp::receive function checks it to see whether it’s
a valid
message type, and if so, the message is queued.
I keep mentioning the message
queue and how the previously shown function adds
messages to the queue. Next, you find out what the queue is and how it works.