本篇是
用DirectX
Audio和DirectShow播放聲音和音樂(4)的續(xù)篇。
使用DirectMusic
在DirectAudio 中,DirectSound負(fù)責(zé)數(shù)字音頻方面的處理,而DirectMusic則負(fù)責(zé)Midi文件(Musical Instrument
Data
Interface,數(shù)字音樂格式,.mid作為文件擴(kuò)展名),DirectMusic固有音樂文件(.sgt文件)和數(shù)字錄音設(shè)備錄制的波形格式文件(.wav文件)等文件的播放操作。
能體現(xiàn)DirectMusic的強(qiáng)大之處是DirectMusic固有文件格式,一首用
DirectMusic固有文件格式制作的音樂包括數(shù)個(gè)小音樂格式,這些樣式還能用不同的樂器組合一個(gè)接一個(gè)地播放。隨機(jī)的樣式和樂器的選取創(chuàng)造出了隨時(shí)都在改變的音樂,再加上節(jié)拍變化,就形成了一個(gè)魅力無窮的音樂系統(tǒng)。DirectMusic的另一個(gè)特性是可以使用“基調(diào)”,就是在正在播放的音樂片段上疊加一段其他音樂,新加入的音樂可以很平滑的融入到原有的音樂中。這在很多時(shí)候都有用,比如一個(gè)玩家完成了一個(gè)目標(biāo),可以馬上播放一段“獲得榮譽(yù)”的音樂提示他。
除了傳統(tǒng)的音符之外,Midi音樂中可以包含數(shù)字音頻作為音符,比如槍聲、猴子的尖叫、也或者是其他各種各樣你覺得奇怪的東西。比如可以在游戲中使用曾經(jīng)夢(mèng)想到的最令你心驚膽顫的音樂,而這些MIDI音樂都能完成。使用數(shù)字樂譜還有一個(gè)巨大的好處,即音樂在所有的計(jì)算機(jī)上可以發(fā)出一致的聲音,這點(diǎn)是通過使用統(tǒng)一的DirectSound合成器完成的,當(dāng)然DirectMusic允許使用
DirectSound接口或者是個(gè)人創(chuàng)建的接口。音樂數(shù)據(jù)使用的合成器通道稱為音頻通道(Audio
Path),你可以獲取這個(gè)通道,并在普通的DirectSound音頻緩沖中播放。
使用Midi文件和
DirectMusic固有文件有共同的好處,那就是可以修改播放的節(jié)拍,這也是很有用的特性。有了這個(gè)特性,就可以設(shè)計(jì)隨著屏幕動(dòng)作而加速或者減速的背景音樂。如果游戲進(jìn)入緊張的時(shí)期,就加速節(jié)拍,使音樂具有緊張感,如果高潮的活動(dòng)結(jié)束,可以放慢節(jié)拍。數(shù)字錄音設(shè)備所錄制下來的音樂也是非常豐富多彩的,盡管這種音樂可以擁有非常高的音樂質(zhì)量,但是這種歌曲不能被修改以便匹配游戲活動(dòng),也就是說這些音樂只能保持最開始錄制的那個(gè)樣子,不能有更多的變化,也不能減少里面的元素。
開始使用DirectMusic
使用 DirectMusic的第一步是創(chuàng)建一個(gè)主對(duì)象,我們把這個(gè)對(duì)象叫做演奏器對(duì)象(performance
object),它表現(xiàn)整個(gè)音樂系統(tǒng),第二步創(chuàng)建一個(gè)叫加載器(loader object)的對(duì)象,加載器加載所有原始的音樂文件。
它們之間的交互過程如下所示:
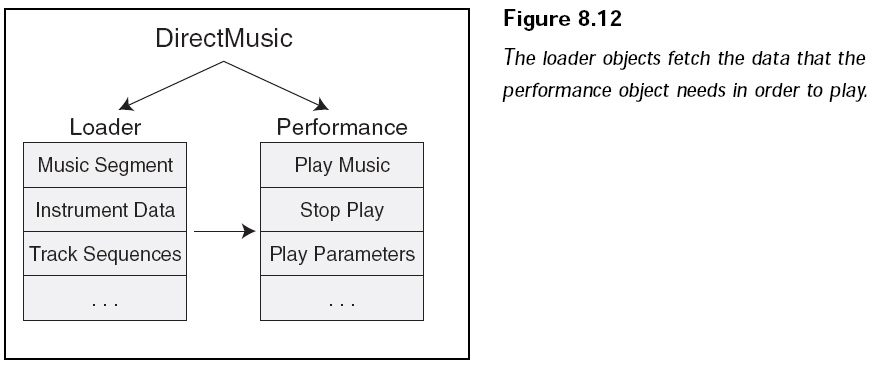
最后必須加載音樂小節(jié)到音樂片段對(duì)象(segment object)中,多個(gè)小節(jié)可以被同時(shí)加載,并一個(gè)接一個(gè)地播放,這可以讓我們創(chuàng)建更具動(dòng)態(tài)效果的音樂。
DirectMusic并沒有提供函數(shù)幫助創(chuàng)建或初始化DirectMusic主接口,所以需要自行初始化COM接口,初始化COM接口所調(diào)用的第一個(gè)函數(shù)是CoInitialize。
Initializes the COM library on the current thread and identifies the
concurrency model as single-thread apartment (STA). Applications must initialize
the COM library before they can call COM library functions other than
CoGetMalloc and memory allocation functions.
New applications should call CoInitializeEx instead of CoInitialize.
HRESULT CoInitialize(
LPVOID pvReserved //Reserved; must be NULL
);
Parameter
- pvReserved
- [in] Reserved; must be NULL.
Return Values
This function supports the standard return values E_INVALIDARG,
E_OUTOFMEMORY, and E_UNEXPECTED, as well as the following:
- S_OK
- The COM library was initialized successfully on this thread.
- S_FALSE
- The COM library is already initialized on this thread.
- RPC_E_CHANGED_MODE
- A previous call to CoInitializeEx specified the
concurrency model for this thread as multithread apartment (MTA).
Remarks
CoInitializeEx provides the same functionality as CoInitialize
and also provides a parameter to explicitly specify the thread's concurrency
model. CoInitialize calls CoInitializeEx and
specifies the concurrency model as single-thread apartment. Applications
developed today should call CoInitializeEx rather than
CoInitialize.
You need to initialize the COM library on a thread before you call any of the
library functions except CoGetMalloc, to get a pointer to the standard
allocator, and the memory allocation functions.
Once the concurrency model for a thread is set, it cannot be changed. A call
to CoInitialize on an apartment that was previously initialized
as multithreaded will fail and return RPC_E_CHANGED_MODE.
Typically, the COM library is initialized on a thread only once. Subsequent
calls to CoInitialize or CoInitializeEx on the
same thread will succeed, as long as they do not attempt to change the
concurrency model, but will return S_FALSE. To close the COM library gracefully,
each successful call to CoInitialize or CoInitializeEx,
including those that return S_FALSE, must be balanced by a corresponding call to
CoUninitialize. However, the first thread in the application
that calls CoInitialize(0) or
CoInitializeEx(COINIT_APARTMENTTHREADED) must be the last thread to
call CoUninitialize(). If the call sequence is not in this
order, then subsequent calls to CoInitialize on the STA will
fail and the application will not work.
Because there is no way to control the order in which in-process servers are
loaded or unloaded, it is not safe to call CoInitialize,
CoInitializeEx, or CoUninitialize from the
DllMain function.
在開始使用DirectMusic的時(shí)候調(diào)用這個(gè)函數(shù),因?yàn)樵摵瘮?shù)有一個(gè)內(nèi)部的計(jì)數(shù)器,顯示被調(diào)用的次數(shù),每調(diào)用一次這個(gè)初始化函數(shù),就必須調(diào)用一次關(guān)閉COM的函數(shù)CoUninitialize。
Closes the COM library on the current thread, unloads all DLLs loaded by the
thread, frees any other resources that the thread maintains, and forces all RPC
connections on the thread to close.
void CoUninitialize( );
Remarks
A thread must call CoUninitialize once for each successful
call it has made to CoInitialize or CoInitializeEx. Only the
CoUninitialize call corresponding to the CoInitialize
or CoInitializeEx call that initialized the library can close
it.
Calls to OleInitialize must be balanced by calls to OleUninitialize. The
OleUninitialize function calls CoUninitialize
internally, so applications that call OleUninitialize do not
also need to call CoUninitialize.
CoUninitialize should be called on application shutdown, as
the last call made to the COM library after the application hides its main
windows and falls through its main message loop. If there are open conversations
remaining, CoUninitialize starts a modal message loop and
dispatches any pending messages from the containers or server for this COM
application. By dispatching the messages, CoUninitialize
ensures that the application does not quit before receiving all of its pending
messages. Non-COM messages are discarded.
Because there is no way to control the order in which in-process servers are
loaded or unloaded, it is not safe to call CoInitialize,
CoInitializeEx, or CoUninitialize from the
DllMain function.
CoUninitialize函數(shù)減少COM接口的使用計(jì)數(shù)器,如果這個(gè)計(jì)數(shù)器減少到0,COM接口就會(huì)從系統(tǒng)釋放內(nèi)存,這樣做可以提高內(nèi)存的使用效率,所有的COM對(duì)象都遵循這個(gè)使用原則。
創(chuàng)建演奏器對(duì)象
演奏器對(duì)象是最主要的對(duì)象,可以創(chuàng)建多個(gè)演奏器對(duì)象,但是建議只使用一個(gè)演奏器。要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建演奏器,首先要聲明一個(gè)IDirectMusicPerformance8對(duì)象,然后調(diào)用
CoCreateInstance初始化。
Creates a single uninitialized object of the class associated with a
specified CLSID. Call CoCreateInstance when you want to create
only one object on the local system. To create a single object on a remote
system, call CoCreateInstanceEx. To create multiple objects based on a single
CLSID, refer to the CoGetClassObject function.
STDAPI CoCreateInstance(
REFCLSID rclsid, //Class identifier (CLSID) of the object
LPUNKNOWN pUnkOuter, //Pointer to controlling IUnknown
DWORD dwClsContext, //Context for running executable code
REFIID riid, //Reference to the identifier of the interface
LPVOID * ppv //Address of output variable that receives
// the interface pointer requested in riid
);
Parameters
- rclsid
- [in] CLSID associated with the data and code that will be used to create
the object.
- pUnkOuter
- [in] If NULL, indicates that the object is not being
created as part of an aggregate. If non-NULL, pointer to
the aggregate object's IUnknown interface (the controlling
IUnknown).
- dwClsContext
- [in] Context in which the code that manages the newly created object
will run. The values are taken from the enumeration CLSCTX.
- riid
- [in] Reference to the identifier of the interface to be used to
communicate with the object.
- ppv
- [out] Address of pointer variable that receives the interface pointer
requested in riid. Upon successful return, *ppv contains
the requested interface pointer.
Return Values
- S_OK
- An instance of the specified object class was successfully created.
- REGDB_E_CLASSNOTREG
- A specified class is not registered in the registration database. Also
can indicate that the type of server you requested in the CLSCTX
enumeration is not registered or the values for the server types in the
registry are corrupt.
- CLASS_E_NOAGGREGATION
- This class cannot be created as part of an aggregate.
- E_NOINTERFACE
- The specified class does not implement the requested interface, or the
controlling IUnknown does not expose the requested
interface.
Remarks
The CoCreateInstance helper function provides a convenient
shortcut by connecting to the class object associated with the specified CLSID,
creating an uninitialized instance, and releasing the class object. As such, it
encapsulates the following functionality:
CoGetClassObject(rclsid, dwClsContext, NULL, IID_IClassFactory, &pCF);
hresult = pCF->CreateInstance(pUnkOuter, riid, ppvObj)
pCF->Release();
It is convenient to use CoCreateInstance when you need to
create only a single instance of an object on the local machine. If you are
creating an instance on remote machine, call CoCreateInstanceEx. When you are
creating multiple instances, it is more efficient to obtain a pointer to the
class object's IClassFactory interface and use its methods as
needed. In the latter case, you should use the CoGetClassObject function.
In the CLSCTX enumeration, you can specify the type of server used to manage
the object. The constants can be CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER, CLSCTX_INPROC_HANDLER,
CLSCTX_LOCAL_SERVER, or any combination of these values. The constant CLSCTX_ALL
is defined as the combination of all three. For more information about the use
of one or a combination of these constants, refer to CLSCTX.
以下代碼演示了如何創(chuàng)建演奏器對(duì)象:
IDirectMusicPerformance8* g_dm_performance; // directmusic performance
// create the DirectMusic performance object
//
// creates a single uninitialized object of the class associated with a specified CLSID.
CoCreateInstance(CLSID_DirectMusicPerformance, NULL, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_IDirectMusicPerformance8,
(void**)&g_dm_performance);
演奏器需要被初始化后才能工作,初始化的過程需要首先創(chuàng)建DirectMusic和DirectSound對(duì)象,然后由這兩個(gè)對(duì)象創(chuàng)建音頻緩沖區(qū)并且設(shè)置播放特性,還需要設(shè)置的內(nèi)容是播放音樂所用的音頻通道,一般情況的設(shè)置使用128種樂器(128樂器通道)并且擁有立體聲和混音(回音)效果,可以調(diào)用
InitAudio來初始化。
The InitAudio method initializes the performance and
optionally sets up a default audiopath. This method must be called before the
performance can play using audiopaths.
This method should be used in most cases instead of
IDirectMusicPerformance8::Init.
Syntax
HRESULT InitAudio(
IDirectMusic** ppDirectMusic,
IDirectSound** ppDirectSound,
HWND hWnd,
DWORD dwDefaultPathType,
DWORD dwPChannelCount,
DWORD dwFlags,
DMUS_AUDIOPARAMS *pParams
);
Parameters
ppDirectMusic
Address of a variable that specifies or receives an interface
pointer to a DirectMusic object.
If the variable pointed to by ppDirectMusic contains
a valid IDirectMusic or IDirectMusic8
interface pointer, the existing object is assigned to the performance. The
reference count of the interface is incremented.
If the variable pointed to by ppDirectMusic contains
NULL, a DirectMusic object is created and the IDirectMusic
interface pointer is returned. Use QueryInterface to obtain
IDirectMusic8.
If ppDirectMusic is NULL, a DirectMusic object is
created and used internally by the performance.
See Remarks.
ppDirectSound
Address of a variable that specifies or receives an
IDirectSound interface pointer for a DirectSound device object to use
by default for waveform output. If this parameter contains a NULL pointer,
DirectMusic creates a private DirectSound device object. If the variable pointed
to contains NULL, DirectMusic creates a DirectSound device object and returns
the interface pointer. See Remarks.
hWnd
Window handle to use for the creation of DirectSound. This
parameter can be NULL, in which case the foreground window is used. See Remarks.
This parameter is ignored if an IDirectSound
interface pointer is passed to the method in ppDirectSound. In that
case the application is responsible for setting the window handle by using
IDirectSound8::SetCooperativeLevel.
dwDefaultPathType
Value that specifies the default audiopath type. Can be zero
if no default path type is wanted. For a list of defined values, see
IDirectMusicPerformance8::CreateStandardAudioPath.
dwPChannelCount
Value that specifies the number of performance
channels to allocate to the path, if dwDefaultPathType is
not zero.
dwFlags
Flags that specify requested features. If pParams is
not NULL, this value is ignored and the requested features are specified in the
dwFeatures member of the DMUS_AUDIOPARAMS
structure. The values listed in the following table are defined for use in this
parameter.
|
Value |
Description |
|
DMUS_AUDIOF_3D |
3-D
buffers. This flag is not implemented. Buffers in 3-D audiopaths always
have 3-D capabilities. |
|
DMUS_AUDIOF_ALL |
All
features. |
|
DMUS_AUDIOF_BUFFERS |
Multiple
buffers. |
|
DMUS_AUDIOF_DMOS |
Additional
DMOs. This flag is not implemented. |
|
DMUS_AUDIOF_ENVIRON |
Environmental modeling. This flag is not implemented. |
|
DMUS_AUDIOF_EAX |
Support for
Environmental Audio Extensions (EAX). This flag is not implemented. |
|
DMUS_AUDIOF_STREAMING |
Support for
streaming waveforms. |
pParams
Address of a DMUS_AUDIOPARAMS structure that
specifies parameters for the synthesizer and receives information about what
parameters were set. Can be NULL if the default parameters are wanted.
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the return value is S_OK.
If it fails, the method can return one of the error values shown in the
following table.
|
Return code |
|
DMUS_E_ALREADY_INITED |
|
DSERR_BUFFERLOST |
|
DSERR_PRIOLEVELNEEDED |
|
DSERR_UNINITIALIZED |
|
E_NOINTERFACE |
|
E_OUTOFMEMORY |
|
E_POINTER |
Remarks
This method can be called only once. It cannot be used to retrieve an
existing IDirectMusic8 interface.
A DirectMusic object can be associated with the performance in the following
ways.
- The application allows the performance to create the DirectMusic object
and needs a pointer to that object. In this case, *ppDirectMusic is
NULL on entry and contains the IDirectMusic pointer on
exit.
- The application allows the performance to initialize itself and does not
need a DirectMusic object pointer. In this case, ppDirectMusic is
NULL.
- The application creates its own DirectMusic object and gives it to the
performance by passing the address of the IDirectMusic8
pointer in ppDirectMusic. Most applications do not use this
technique.
If you specify an interface pointer in ppDirectSound, it must be an
interface to an object of class CLSID_DirectSound8. Objects of this class
support both IDirectSound and IDirectSound8,
but the IDirectSound interface must be passed. The DirectSound
device object must be fully initialized before being passed to InitAudio.
If the object was created by using CoCreateInstance, call
IDirectSound8::Initialize. Set the cooperative level to
DSSCL_PRIORITY by using IDirectSound8::SetCooperativeLevel.
You can pass NULL in the hWnd parameter to pass the current
foreground window handle to DirectSound. However, do not assume that the
application window will be in the foreground during initialization. It is best
to pass the top-level application window handle.
The parameters set in dwFlags and pParams apply to the
default audiopath and any audiopaths created subsequently.
The method fails with DSERR_BUFFERLOST if a value other than zero is passed
in dwDefaultPathType and any application has initialized DirectSound
with the write-primary cooperative level.
The performance must be terminated by using the
IDirectMusicPerformance8::CloseDown method before being released.
來看看dwDefaultPathType具體可以指定的類型:
Type of the path. The following values are defined.
|
Value |
Description |
|
DMUS_APATH_DYNAMIC_3D |
One bus to a 3-D buffer. Does not send to environmental
reverb. |
|
DMUS_APATH_DYNAMIC_MONO |
One bus to a mono buffer. |
|
DMUS_APATH_DYNAMIC_STEREO |
Two buses to a stereo buffer. |
|
DMUS_APATH_SHARED_STEREOPLUSREVERB |
Ordinary music setup with stereo outs and reverb. |
DMUS_APATH_DYNAMIC_3D
This standard audiopath sets up a nonshared buffer of type 3-D Dry.
Applications can obtain an interface to the 3-D Dry buffer by calling one of
the GetObjectInPath methods with dwStage set to DMUS_PATH_BUFFER
and dwBuffer set to 0.
The buffer uses the DS3DALG_NO_VIRTUALIZATION algorithm for 3-D effects, and
this property cannot be changed by the application. Other algorithms can be
applied to custom buffers in audiopaths that have been authored in DirectMusic
Producer. For information on 3-D algorithms, see DSBUFFERDESC in the DirectX
documentation.
DMUS_APATH_DYNAMIC_MONO
This standard audiopath sets up a nonshared buffer of type Mono that has no
3-D parameters or special effects.
Applications can obtain an interface to the buffer by calling one of the
GetObjectInPath methods with dwStage set to DMUS_PATH_BUFFER and
dwBuffer set to 0.
DMUS_APATH_DYNAMIC_STEREO
This standard audiopath sets up a nonshared buffer of type Stereo. This
audiopath is intended for sound effects on stereo buffers. No reverberation is
available.
Applications can obtain an interface to the buffer by calling one of the
GetObjectInPath methods with dwStage set to DMUS_PATH_BUFFER and
dwBuffer set to 0.
DMUS_APATH_SHARED_STEREOPLUSREVERB
This standard audiopath sets up buffers of type Reverb and Stereo.
The Stereo buffer is shared among multiple audiopaths. It is a sink-in
buffer, meaning that it accepts data directly from the synthesizer, not from
other buffers.
Applications can obtain an interface to the Stereo buffer by calling one of
the GetObjectInPath methods with dwStage set to DMUS_PATH_BUFFER
and dwBuffer set to 0.
The Reverb buffer is also a shared sink-in buffer. Unlike the Stereo buffer,
it accepts a mono input from the synthesizer and converts the data to stereo
format.
Applications can obtain an interface to the Reverb buffer by calling one of
the GetObjectInPath methods with dwStage set to DMUS_PATH_BUFFER
and dwBuffer set to 1.
The following example function retrieves an IDirectSoundFXWavesReverb8
interface to the
in the Reverb buffer on a default
DMUS_APATH_SHARED_STEREOPLUSREVERB audiopath:
HRESULT GetDMO(IDirectMusicPerformance8* pPerf,IDirectSoundFXWavesReverb8** ppEffectDMO)
{
IDirectMusicAudioPath8 * pAudioPath;
HRESULT hr;
hr = pPerf->GetDefaultAudioPath(&pAudioPath);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
HRESULT hr = pAudioPath->GetObjectInPath(DMUS_PCHANNEL_ALL,
DMUS_PATH_BUFFER_DMO, 1,
GUID_All_Objects, 0, IID_IDirectSoundFXWavesReverb8,
(LPVOID*) ppEffectDMO);
}
return hr;
}
以下代碼演示了如何使用InitAudio來初始化演奏器對(duì)象:
// initialize the performance with the standard audio path.
// this initialize both directmusic and directsound and sets up the synthesizer.
g_dm_performance->InitAudio(NULL, NULL, g_hwnd, DMUS_APATH_SHARED_STEREOPLUSREVERB, 128, DMUS_AUDIOF_ALL, NULL);
演奏器使用完后需要關(guān)閉來釋放資源,這通過IDirectMusicPerformance8::CloseDown來實(shí)現(xiàn)。
The CloseDown method closes down the performance object. An
application that created the performance object and called
IDirectMusicPerformance8::Init or
IDirectMusicPerformance8::InitAudio on it must call CloseDown
before the performance is released.
Syntax
HRESULT CloseDown();
Parameters
This method returns no parameters.
Return Values
The method returns S_OK.
Remarks
Failure to call CloseDown can cause memory leaks or program
failures.
CloseDown handles the release of the IDirectMusic8
interface if this reference was created by
IDirectMusicPerformance8::Init or
IDirectMusicPerformance8::InitAudio. If the application explicitly
created the DirectMusic object, the application is responsible for releasing the
reference.
If the DirectSound device object was created in the call to Init
or InitAudio but no reference was returned to the application,
CloseDown also releases the DirectSound device and all
DirectSound buffers. If your application has obtained any interfaces to
DirectSound buffers, it should release them before calling Closedown.
If the application created the DirectSound device object explicitly, or
obtained a reference form Init or InitAudio,
it is responsible for releasing the DirectSound device.
The method releases any downloaded instruments that have not been unloaded.
創(chuàng)建加載器對(duì)象
創(chuàng)建加載器是使用DirectMusic 的第二步,這個(gè)對(duì)象其實(shí)是一個(gè)緩沖系統(tǒng),用于加速數(shù)據(jù)加載和歌曲支持文件(比如樂器庫)的加載。
IDirectMusicLoader8表示加載器對(duì)象,以下代碼可以創(chuàng)建一個(gè)加載器:
// create the DirectMusic loader object
CoCreateInstance(CLSID_DirectMusicLoader, NULL, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_IDirectMusicLoader8, (void**)&g_dm_loader);
請(qǐng)確定在程序中只有一個(gè)加載器對(duì)象,這樣可以幫助系統(tǒng)控制緩存和經(jīng)常使用的數(shù)據(jù)資源。
使用加載器的下一步是告訴加載器在哪些目錄搜索文件,一般情況下我們把這個(gè)路徑叫做默認(rèn)搜索路徑(default search
directory)。對(duì)于加載單獨(dú)的MIDI文件,不需要設(shè)置默認(rèn)的搜索路徑,但是對(duì)于加載DirectMusic固有文件,必須設(shè)置搜索路徑,以便讓
DirectMusic能順利找到支持文件。
可以通過調(diào)用IDirectMusicLoader8:: SetSearchDirectory函數(shù)來設(shè)置工作路徑。
The SetSearchDirectory method sets a search path for finding
object files. The search path can be set for one object file type or for all
files.
Syntax
HRESULT SetSearchDirectory(
REFGUID rguidClass,
WCHAR* pwszPath,
BOOL fClear
);
Parameters
rguidClass
Reference to (C++) or address of (C) the identifier of the
class of objects that the call pertains to. GUID_DirectMusicAllTypes specifies
all objects. For a list of standard loadable classes, see
IDirectMusicLoader8.
pwszPath
File path for directory. Must be a valid directory and must be
less than MAX_PATH in length. The path, if not fully qualified, is relative to
the current directory when IDirectMusicLoader8::ScanDirectory
is called.
fClear
If TRUE, clears all information about objects before setting
the directory. This prevents the loader from accessing objects in a previous
directory when those objects have the same name. However, objects are not
removed from the cache.
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the return value is S_OK, or S_FALSE if the search
directory is already set to pwszPath.
If it fails, the method can return one of the error values shown in the
following table.
|
Return code |
|
DMUS_E_LOADER_BADPATH |
|
E_OUTOFMEMORY |
|
E_POINTER |
Remarks
After a search path is set, the loader does not need a full path every time
it is given an object to load by file name. This enables objects that refer to
other objects to find them by file name without knowing the full path.
When this method has been called, the loader expects the wszFileName
member of the DMUS_OBJECTDESC structure to contain only a file
name or a path relative to the search directory, unless the DMUS_OBJ_FULLPATH
flag is set in the dwValidData member.
該函數(shù)接收的是寬字符串,使用時(shí)需要把字符串轉(zhuǎn)換為WCHAR數(shù)據(jù)類型,可以通過mbstowcs來轉(zhuǎn)換。
Converts a sequence of multibyte characters to a corresponding sequence of
wide characters.
size_t mbstowcs(
wchar_t *wcstr,
const char *mbstr,
size_t count
);
Parameters
- [out] wcstr
- The address of a sequence of wide characters.
- [in] mbstr
- The address of a sequence of null terminated multibyte characters.
- [in] count
- The maximum number of multibyte characters to convert.
Return Value
If
mbstowcs successfully converts the source string, it
returns the number of converted multibyte characters. If the
wcstr argument is
NULL, the
function returns the required size (in wide characters) of the destination
string. If
mbstowcs encounters an invalid multibyte
character, it returns –1. If the return value is
count, the wide-character string is not null-terminated.
Security Note
Ensure that wcstr and
mbstr do not overlap, and that
count correctly reflects the number of
multibyte characters to convert.
以下代碼演示了如何設(shè)置搜索路徑:
// tell directmusic where the default search path is
char path[MAX_PATH];
WCHAR search_path[MAX_PATH];
GetCurrentDirectory(MAX_PATH, path);
// maps a character string to a wide-character (Unicode) string
MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, path, -1, search_path, MAX_PATH);
// set a search path for finding object files
g_dm_loader->SetSearchDirectory(GUID_DirectMusicAllTypes, search_path, FALSE);
使用音樂片段
通過以上步驟,系統(tǒng)已經(jīng)被初始化,加載器也已經(jīng)準(zhǔn)備就緒,現(xiàn)在該加載歌曲然后播放它們了。完成這個(gè)操作是IDirectMusicSegment8對(duì)象的工作,DirectMusic加載器的職責(zé)是加載音樂和樂器庫,并且創(chuàng)建IDirectMusicSegment8對(duì)象,如下圖所示:
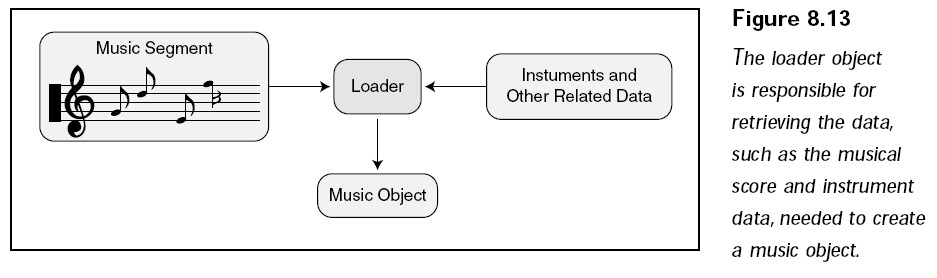
整個(gè)加載過程有2個(gè)步驟,第一個(gè)步驟是加載包含所需播放音樂的音樂片段。
加載音樂片段
加載音樂片段的第一步是設(shè)置一個(gè)對(duì)象描述結(jié)構(gòu),這個(gè)結(jié)構(gòu)被稱為DMUS_OBJECTDESC,它描述了要加載的信息。
The DMUS_OBJECTDESC structure is used to describe a loadable
object. This structure is passed to the IDirectMusicLoader8::GetObject
method to identify the object that the loader should retrieve from storage.
Information about an object is retrieved in this structure by the
IDirectMusicLoader8::EnumObject and
IDirectMusicObject8::GetDescriptor methods.
Syntax
typedef struct _DMUS_OBJECTDESC {
DWORD dwSize;
DWORD dwValidData;
GUID guidObject;
GUID guidClass;
FILETIME ftDate;
DMUS_VERSION vVersion;
WCHAR wszName[DMUS_MAX_NAME];
WCHAR wszCategory[DMUS_MAX_CATEGORY];
WCHAR wszFileName[DMUS_MAX_FILENAME];
LONGLONG llMemLength;
LPBYTE pbMemData;
IStream* pStream
} DMUS_OBJECTDESC, *LPDMUS_OBJECTDESC;
Members
dwSize
Size of the structure, in bytes. This member must be
initialized to sizeof(DMUS_OBJECTDESC) before the structure is
passed to any method.
dwValidData
Flags describing which members are valid and giving further
information about some members. The following values are defined:
|
Flag |
Description |
|
DMUS_OBJ_CATEGORY |
The
wszCategory member is valid. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_CLASS |
The
guidClass member is valid. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_DATE |
The
ftDate member is valid. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_FILENAME |
The
wszFileName member is valid. The presence of this flag is
assumed if DMUS_OBJ_FULLPATH is set. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_FULLPATH |
The
wszFileName member contains either the full path of a file or a
path relative to the application directory. The directory set by
IDirectMusicLoader8::SetSearchDirectory is not searched. If
this flag is not set, wszFilename is always assumed to
be relative to the application directory, or to the search directory if
SetSearchDirectory has been called for this object
type. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_LOADED |
The object
is currently loaded in memory. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_MEMORY |
The object
is in memory, and llMemLength and pbMemData
are valid. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_NAME |
The
wszName member is valid. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_OBJECT |
The
guidObject member is valid. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_STREAM |
The
pStream member contains a pointer to the data stream. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_URL |
The
wszFileName member contains a URL. URLs are not currently
supported by the DirectMusic loader. |
|
DMUS_OBJ_VERSION |
The
vVersion member is valid. |
guidObject
Unique identifier for this object.
guidClass
Unique identifier for the class of object. See DirectMusic
Component GUIDs.
ftDate
Date that the object was last edited.
vVersion
DMUS_VERSION structure containing version
information.
wszName
Name of the object.
wszCategory
Category for the object.
wszFileName
File path. If DMUS_OBJ_FULLPATH is set, this is the full path;
otherwise, it is the file name. If the
IDirectMusicLoader8::SetSearchDirectory method has been called, this
member must contain only a file name.
llMemLength
Size of data in memory.
pbMemData
Pointer to data in memory. Do not use this value except when
loading from a resource contained in the executable file.
pStream
Address of the IStream interface of a custom
stream that can be used to load the object into memory. In most cases this value
should be NULL.See Remarks.
Remarks
At least one of wszName, guidObject, and
wszFileName must contain valid data to retrieve the object by
using the IDirectMusicLoader8::GetObject method.
The name and category strings use 16-bit characters in the WCHAR
format, not 8-bit ANSI characters. Be sure to convert as appropriate. You can
use the C library mbstowcs function to convert from multibyte
to Unicode and the wcstombs function to convert from Unicode
back to multibyte.
Instead of passing on object descriptor to
IDirectMusicLoader8::GetObject or
IDirectMusicLoader8::SetObject with a filename or memory pointer, an
application can pass a stream. This is done by setting the DMUS_OBJ_STREAM flag
in dwValidData and a pointer to the stream in pStream.
When the application calls GetObject, the loader saves the
stream's current location, reads the object from the stream, and then restores
the saved location. The application can continue reading from the stream without
being affected by the call to GetObject.
When SetObject is called with a stream, the loader makes a
clone of the stream object, and this clone is used if the object is later
loaded. Thus an application can release a stream or continue to read from it
after passing it to the loader by using SetObject. The actual
data of the stream is not copied, so the application should not change or delete
the data.
DMUS_OBJECTDESC結(jié)構(gòu)作為參數(shù)被傳遞到IDirectMusicLoader8::GetObject函數(shù)中,這個(gè)函數(shù)確定所有的數(shù)據(jù)被加載并且被鏈接到片段對(duì)象中。
The GetObject method retrieves an object from a file or
resource and returns the specified interface.
Syntax
HRESULT GetObject(
LPDMUS_OBJECTDESC pDesc,
REFIID riid,
LPVOID FAR * ppv
);
Parameters
pDesc
Address of a DMUS_OBJECTDESC structure
describing the object.
riid
Unique identifier of the interface. See DirectMusic Interface
GUIDs.
ppv
Address of a variable that receives a pointer to the desired
interface of the object.
Return Values
If the method succeeds, the return value is S_OK or DMUS_S_PARTIALLOAD.
DMUS_S_PARTIALLOAD is returned if any referenced object cannot be found, such
as a style referenced in a segment. The loader might fail to
find the style if it is referenced by name but
IDirectMusicLoader8::ScanDirectory has not been called for styles.
DMUS_S_PARTIALLOAD might also mean that the default instrument collection file,
Gm.dls, is not available.
If it fails, the method can return one of the error values shown in the
following table.
|
Return code |
|
DMUS_E_LOADER_FAILEDCREATE |
|
DMUS_E_LOADER_FAILEDOPEN |
|
DMUS_E_LOADER_FORMATNOTSUPPORTED |
|
DMUS_E_LOADER_NOCLASSID |
|
E_FAIL |
|
E_INVALIDARG |
|
E_OUTOFMEMORY |
|
E_POINTER |
|
REGDB_E_CLASSNOTREG |
Remarks
For file objects, it is simpler to use the
IDirectMusicLoader8::LoadObjectFromFile method.
DirectMusic does not support loading from URLs. If the dwValidData
member of the DMUS_OBJECTDESC structure contains DMUS_OBJ_URL,
the method returns DMUS_E_LOADER_FORMATNOTSUPPORTED.
The method does not require that all valid members of the
DMUS_OBJECTDESC structure match before retrieving an object. The
dwValidData flags are evaluated in the following order:
- DMUS_OBJ_OBJECT
- DMUS_OBJ_STREAM
- DMUS_OBJ_MEMORY
- DMUS_OBJ_FILENAME and DMUS_OBJ_FULLPATH
- DMUS_OBJ_NAME and DMUS_OBJ_CATEGORY
- DMUS_OBJ_NAME
- DMUS_OBJ_FILENAME
In other words, the highest priority goes to a unique GUID, followed by a
stream pointer, followed by a resource, followed by the full file path name,
followed by an internal name plus category, followed by an internal name,
followed by a local file name.
Do not load data from untrusted sources. Loading DirectMusic data files
causes objects to be constructed, with the possibility that excessive demand on
resources will lead to degradation of performance or system failure.
以下代碼演示了如何加載音樂片段:
DMUS_OBJECTDESC dm_obj_desc;
// get the object
ZeroMemory(&dm_obj_desc, sizeof(DMUS_OBJECTDESC));
dm_obj_desc.dwSize = sizeof(DMUS_OBJECTDESC);
dm_obj_desc.guidClass = CLSID_DirectMusicSegment;
dm_obj_desc.dwValidData = DMUS_OBJ_CLASS | DMUS_OBJ_FILENAME | DMUS_OBJ_FULLPATH;
// Converts a sequence of multibyte characters to a corresponding sequence of wide characters
mbstowcs(dm_obj_desc.wszFileName, filename, MAX_PATH);
// retrieves an object from a file or resource and returns the speficied interface
if(FAILED(g_dm_loader->GetObject(&dm_obj_desc, IID_IDirectMusicSegment8, (LPVOID*)&g_dm_segment)))
return FALSE;
閱讀下篇:
用DirectX Audio和DirectShow播放聲音和音樂(6)