問題
1 按順時針方向構建一個m * n的螺旋矩陣(或按順時針方向螺旋訪問一個m * n的矩陣):
2 在不構造螺旋矩陣的情況下,給定坐標i、j值求其對應的值f(i, j)。
比如對11 * 7矩陣, f(6, 0) = 27 f(6, 1) = 52 f(6, 3) = 76 f(6, 4) = 63
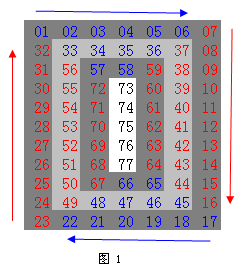
構建螺旋矩陣
對m * n 矩陣,最先訪問最外層的m * n的矩形上的元素,接著再訪問里面一層的 (m - 2) * (n - 2) 矩形上的元素…… 最后可能會剩下一些元素,組成一個點或一條線(見圖1)。
對第i個矩形(i=0, 1, 2 …),4個頂點的坐標為:
(i, i) ----------------------------------------- (i, n–1-i)
| |
| |
| |
(m-1-i, i) ----------------------------------------- (m-1-i, n-1-i)
要訪問該矩形上的所有元素,只須用4個for循環,每個循環訪問一個點和一邊條邊上的元素即可(見圖1)。另外,要注意對最終可能剩下的1 * k 或 k * 1矩陣再做個特殊處理。
代碼:
inline void act(int t) { printf("%3d ", t); }
const int small = col < row ? col : row;
const int count = small / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const int C = col - 1 - i;
const int R = row - 1 - i;
for (int j = i; j < C; ++j) act(arr[i][j]);
for (int j = i; j < R; ++j) act(arr[j][C]);
for (int j = C; j > i; --j) act(arr[R][j]);
for (int j = R; j > i; --j) act(arr[j][i]);
}
if (small & 1) {
const int i = count;
if (row <= col) for (int j = i; j < col - i; ++j) act(arr[i][j]);
else for (int j = i; j < row - i; ++j) act(arr[j][i]);
}
如果只是構建螺旋矩陣的話,稍微修改可以實現4個for循環獨立:
const int small = col < row ? col : row;
const int count = small / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const int C = col - 1 - i;
const int R = row - 1 - i;
const int cc = C - i;
const int rr = R - i;
const int s = 2 * i * (row + col - 2 * i) + 1;
for (int j = i, k = s; j < C; ++j) arr[i][j] = k++;
for (int j = i, k = s + cc; j < R; ++j) arr[j][C] = k++;
for (int j = C, k = s + cc + rr; j > i; --j) arr[R][j] = k++;
for (int j = R, k = s + cc * 2 + rr; j > i; --j) arr[j][i] = k++;
}
if (small & 1) {
const int i = count;
int k = 2 * i * (row + col - 2 * i) + 1;
if (row <= col) for (int j = i; j < col - i; ++j) arr[i][j] = k++;
else for (int j = i; j < row - i; ++j) arr[j][i] = k++;
}
關于s的初始值取 2 * i * (row + col - 2 * i) + 1請參考下一節。
由于C++的二維數組是通過一維數組實現的。二維數組的實現一般有下面三種:
靜態分配足夠大的數組;
動態分配一個長為m*n的一維數組;
動態分配m個長為n的一維數組,并將它們的指針存在一個長為m的一維數組。
二維數組的不同實現方法,對函數接口有很大影響。
給定坐標直接求值f(x, y)
如前面所述,對第i個矩形(i=0, 1, 2 …),4個頂點的坐標為:
(i, i) ----------------------------------------- (i, n–1-i)
| |
| |
| |
(m-1-i, i) ----------------------------------------- (m-1-i, n-1-i)
對給定的坐標(x,y),如果它落在某個這類矩形上,顯然其所在的矩形編號為:
k = min{x, y, m-1-x, n-1-y}
m*n矩陣刪除訪問第k個矩形前所訪問的所有元素后,可得到(m-2*k)*(n-2*k)矩陣,因此已訪問的元素個數為:m*n-(m-2*k)*(n-2*k)=2*k*(m+n-2*k),因而 (k,k)對應的值為:
T(k) = 2*k*(m+n-2*k)+ 1
對某個矩形,設點(x, y)到起始點(k,k)的距離d = x-k + y-k = x+y-2*k
① 向右和向下都只是橫坐標或縱坐標增加1,這兩條邊上的點滿足f(x, y) = T(k) + d
② 向左和向下都只是橫坐標或縱坐標減少1,這兩條邊上的點滿足f(x, y) = T(k+1) - d
如果給定坐標的點(x, y),不在任何矩形上,則它在一條線上,仍滿足f(x, y) = T(k) + d
int getv(int row, int col, int max_row, int max_col) // row < max_row, col < max_col
{
int level = min(min(row, max_row - 1 - row), min(col, max_col - 1 - col));
int distance = row + col - level * 2;
int start_value = 2 * level * (max_row + max_col - 2 * level) + 1;
if (row == level || col == max_col - 1 - level ||
(max_col < max_row && level * 2 + 1 == max_col))
return start_value + distance;
int next_value = start_value + (max_row + max_col - 4 * level - 2) * 2;
return next_value - distance;
}
特別說明
上面的討論都是基于m*n矩陣的,對于特例n*n矩陣,可以做更多的優化。比如構建螺旋矩陣,如果n為奇數,則矩陣可以拆分為幾個矩形加上一個點。前面的條件判斷可以優化為:
if (small & 1) act[count][count];
甚至可以調整4個for循環的遍歷元素個數(前面代碼,每個for循環遍歷n-1-2*i個元素,可以調整為:n-2*i,n-1-2*i, n-1-2*i,n-2-2*i)從而達到省略if判斷。
測試代碼
代碼1:
//螺旋矩陣,給定坐標直接求值 by flyinghearts
//www.cnblogs.com/flyinghearts
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using std::min;
using std::cout;
/*
int getv2(int row, int col, int max_row, int max_col) // row < max_row, col < max_col
{
int level = min(min(row, max_row - 1 - row), min(col, max_col - 1 - col));
int distance = row + col - level * 2;
int start_value = 2 * level * (max_row + max_col - 2 * level) + 1;
if (row == level || col == max_col - 1 - level) return start_value + distance;
//++level; int next_value = 2 * level * (max_row + max_col - 2 * level) + 1;
int next_value = start_value + (max_row + max_col - 4 * level - 2) * 2;
if (next_value > max_col * max_row) return start_value + distance;
return next_value - distance;
}
*/
int getv(int row, int col, int max_row, int max_col) // row < max_row, col < max_col
{
int level = min(min(row, max_row - 1 - row), min(col, max_col - 1 - col));
int distance = row + col - level * 2;
int start_value = 2 * level * (max_row + max_col - 2 * level) + 1;
if (row == level || col == max_col - 1 - level || (max_col < max_row && level * 2 + 1 == max_col))
return start_value + distance;
//++level; int next_value = 2 * level * (max_row + max_col - 2 * level) + 1;
int next_value = start_value + (max_row + max_col - 4 * level - 2) * 2;
return next_value - distance;
}
int main()
{
int test[][2] = {{5, 5}, {5, 7}, {7, 5}, {4, 4}, {4, 6}, {6, 4}};
const int sz = sizeof(test) / sizeof(test[0]);
for (int k = 0; k < sz; ++k) {
int M = test[k][0];
int N = test[k][1];
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
cout.width(4), cout << getv(i, j, M, N) << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
代碼2:
//螺旋矩陣 by flyinghearts#qq.com
//www.cnblogs.com/flyinghearts
#include<iostream>
int counter = 0;
inline void act(int& t)
{
//std::cout.width(3), std::cout << t;
t = ++::counter;
}
void act_arr(int *arr, int row, int col, int max_col) //col < max_col
{
const int small = col < row ? col : row;
const int count = small / 2;
int *p = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const int C = col - 1 - 2 * i;
const int R = row - 1 - 2 * i;
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j) act(*p++);
for (int j = 0; j < R; ++j) act(*p), p += max_col;
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j) act(*p--);
for (int j = 0; j < R; ++j) act(*p), p -= max_col;
p += max_col + 1;
}
if (small & 1) {
const int i = count;
if (row <= col) for (int j = 0; j < col - 2 * i; ++j) act(*p++);
else for (int j = 0; j < row - 2 * i; ++j) act(*p), p += max_col;
}
}
void act_arr(int* arr[], int row, int col)
{
const int small = col < row ? col : row;
const int count = small / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const int C = col - 1 - i;
const int R = row - 1 - i;
for (int j = i; j < C; ++j) act(arr[i][j]);
for (int j = i; j < R; ++j) act(arr[j][C]);
for (int j = C; j > i; --j) act(arr[R][j]);
for (int j = R; j > i; --j) act(arr[j][i]);
}
if (small & 1) {
const int i = count;
if (row <= col) for (int j = i; j < col - i; ++j) act(arr[i][j]);
else for (int j = i; j < row - i; ++j) act(arr[j][i]);
}
}
void act_arr_2(int* arr[], int row, int col)
{
const int small = col < row ? col : row;
const int count = small / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const int C = col - 1 - i;
const int R = row - 1 - i;
const int cc = C - i;
const int rr = R - i;
const int s = 2 * i * (row + col - 2 * i) + 1;
for (int j = i, k = s; j < C; ++j) arr[i][j] = k++;
for (int j = i, k = s + cc; j < R; ++j) arr[j][C] = k++;
for (int j = C, k = s + cc + rr; j > i; --j) arr[R][j] = k++;
for (int j = R, k = s + cc * 2 + rr; j > i; --j) arr[j][i] = k++;
}
if (small & 1) {
const int i = count;
int k = 2 * i * (row + col - 2 * i) + 1;
if (row <= col) for (int j = i; j < col - i; ++j) arr[i][j] = k++;
else for (int j = i; j < row - i; ++j) arr[j][i] = k++;
}
}
void print_arr(int *arr, int row, int col, int max_col) //col < max_col
{
for (int i = 0, *q = arr; i < row; ++i, q += max_col) {
for (int *p = q; p < q + col; ++p)
std::cout.width(4), std::cout << *p;
std::cout << "\n";
}
std::cout << "\n";
}
void print_arr(int* a[], int row, int col) //col < max_col
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
std::cout.width(4), std::cout << a[i][j];
std::cout << "\n";
}
std::cout << "\n";
}
void test_1()
{
const int M = 25;
const int N = 25;
int a[M][N];
int test[][2] = {{5, 5}, {5, 7}, {7, 5}, {4, 4}, {4, 6}, {6, 4}};
const int sz = sizeof(test) / sizeof(test[0]);
std::cout << "Test 1:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
int row = test[i][0];
int col = test[i][1];
if (row < 0 || row > M) row = 3;
if (col < 0 || col > N) col = 3;
::counter = 0;
act_arr(&a[0][0], row, col, N);
print_arr(&a[0][0], row, col, N);
}
}
void test_2()
{
int test[][2] = {{5, 5}, {5, 7}, {7, 5}, {4, 4}, {4, 6}, {6, 4}};
const int sz = sizeof(test) / sizeof(test[0]);
std::cout << "Test 2:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
int row = test[i][0];
int col = test[i][1];
int **arr = new int*[row];
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) arr[i] = new int[col];
::counter = 0;
act_arr(arr, row, col);
print_arr(arr, row, col);
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) delete[] arr[i];
delete[] arr;
}
}
int main()
{
test_1();
test_2();
}