一
Visual Studio 調(diào)試器和 C 運行時 (CRT) 庫為我們提供了檢測和識別內(nèi)存泄漏的有效方法。主要使用函數(shù):_CrtDumpMemoryLeaks();
二 實例
 #define _CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC //輸出更詳細的report
#define _CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC //輸出更詳細的report
 #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
 #include <crtdbg.h>
#include <crtdbg.h>
 //以上的內(nèi)容必須放在其他include的前面
//以上的內(nèi)容必須放在其他include的前面

 #include <vector>
#include <vector>

 class MyClass
class MyClass


 {
{
 private:
private:
 int *p;
int *p;
 public:
public:
 MyClass()
MyClass()


 {
{
 if(p != NULL)
if(p != NULL)


 {
{
 p = new int(0);
p = new int(0);
 }
}
 }
}
 ~MyClass()
~MyClass()


 {
{
 if(p != NULL)
if(p != NULL)


 {
{
 delete p;
delete p;
 p = NULL;
p = NULL;
 }
}
 }
}
 };
};

 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])


 {
{
 int *i = NULL; // better for read
int *i = NULL; // better for read
 i = new int(0);
i = new int(0);
 int *&y = i; // pointer's reference
int *&y = i; // pointer's reference

 MyClass *pMyClass = new MyClass();
MyClass *pMyClass = new MyClass();

 std::vector<MyClass*> myClasses;
std::vector<MyClass*> myClasses;
 myClasses.push_back(new MyClass());
myClasses.push_back(new MyClass());
 myClasses.push_back(new MyClass());
myClasses.push_back(new MyClass());

 _CrtDumpMemoryLeaks();
_CrtDumpMemoryLeaks();
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}三說明
1)只對debug模有用,可以在程序運行后在vs的ide的output的最后看到泄露的檢測結(jié)果。
2)可以檢測系統(tǒng)類型,自定義類型和stl 容器。
3)#define _CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC //包含該宏定義輸出更詳細的report
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <crtdbg.h>
//以上的內(nèi)容必須放在其他include的前面,否則可能使上面定義的宏失效。
4)如果程序有統(tǒng)一的退出口,則在退出時調(diào)用_CrtDumpMemoryLeaks();
5)如果程序有多個出口,則可以在程序開始處包含下面的調(diào)用:_CrtSetDbgFlag ( _CRTDBG_ALLOC_MEM_DF | _CRTDBG_LEAK_CHECK_DF );這條語句無論程序在什么地方退出都會自動調(diào)用 _CrtDumpMemoryLeaks。
四 更多(更多的API和demo的下載)
http://msdn2.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/fxszt639(VS.80).aspx五 其他同類文章
http://www.shnenglu.com/zhouhuishine/archive/2008/01/22/41609.html
使用MFC提供的功能來檢測內(nèi)存泄露。
使用方法:
1)工程是MFC工程,或是工程的設(shè)置中有Use MFC in a Shared DLL,
2)很多地方說是要定義以下宏
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define new DEBUG_NEW
#endif
但是我發(fā)現(xiàn)只要include <afx.h> 即可。(大家可以檢測一下)
3)可以在F5運行程序后,在output窗口中看到如下的內(nèi)存泄露的顯示。(只在debug下有用哦)
4)如果有泄露,則顯示如下:
Detected memory leaks!
Dumping objects ->
{214} normal block at 0x00D91618, 4 bytes long.
Data: < > 00 00 00 00
{208} normal block at 0x00D914D0, 4 bytes long.
Data: < > 00 00 00 00
{207} normal block at 0x00D91490, 4 bytes long.
Data: < > D0 14 D9 00
{205} normal block at 0x00D91410, 4 bytes long.
Data: < > 00 00 00 00
{204} normal block at 0x003AFFD8, 4 bytes long.
Data: < > 10 14 D9 00
{203} normal block at 0x003AFF98, 4 bytes long.
Data: < > 00 00 00 00
{202} normal block at 0x003AFF58, 4 bytes long.
Data: < : > 98 FF 3A 00
{200} normal block at 0x003AFF18, 4 bytes long.
Data: < > 00 00 00 00
Object dump complete.
一 簡單的對內(nèi)存的分配和釋放跟蹤,并將結(jié)果輸出到console,它也是一般C++內(nèi)存泄露的檢測原理,來自C++編程思想:
(比較簡單,大家都可以看的明白的哦)實現(xiàn)如下:
MemCheck.h
 //: C02:MemCheck.h
//: C02:MemCheck.h
 #ifndef MEMCHECK_H
#ifndef MEMCHECK_H
 #define MEMCHECK_H
#define MEMCHECK_H
 #include <cstddef> // for size_t
#include <cstddef> // for size_t

 // Hijack the new operator (both scalar and array versions)
// Hijack the new operator (both scalar and array versions)
 void* operator new(std::size_t, const char*, long);
void* operator new(std::size_t, const char*, long);
 void* operator new[](std::size_t, const char*, long);
void* operator new[](std::size_t, const char*, long);
 #define new new (__FILE__, __LINE__)
#define new new (__FILE__, __LINE__)

 extern bool traceFlag;
extern bool traceFlag;
 #define TRACE_ON() traceFlag = true
#define TRACE_ON() traceFlag = true
 #define TRACE_OFF() traceFlag = false
#define TRACE_OFF() traceFlag = false

 extern bool activeFlag;
extern bool activeFlag;
 #define MEM_ON() activeFlag = true
#define MEM_ON() activeFlag = true
 #define MEM_OFF() activeFlag = false
#define MEM_OFF() activeFlag = false

 #endif
#endif

 /**////:~
/**////:~

MemCheck.cpp
 //: C02:MemCheck.cpp {O}
//: C02:MemCheck.cpp {O}
 #include <cstdio>
#include <cstdio>
 #include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdlib>
 #include <cassert>
#include <cassert>
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
 #undef new
#undef new

 // Global flags set by macros in MemCheck.h
// Global flags set by macros in MemCheck.h
 bool traceFlag = true;
bool traceFlag = true;
 bool activeFlag = false;
bool activeFlag = false;


 namespace
namespace  {
{

 // Memory map entry type
// Memory map entry type

 struct Info
struct Info  {
{
 void* ptr;
void* ptr;
 const char* file;
const char* file;
 long line;
long line;
 };
};

 // Memory map data
// Memory map data
 const size_t MAXPTRS = 10000u;
const size_t MAXPTRS = 10000u;
 Info memMap[MAXPTRS];
Info memMap[MAXPTRS];
 size_t nptrs = 0;
size_t nptrs = 0;

 // Searches the map for an address
// Searches the map for an address
 int findPtr(void* p)
int findPtr(void* p)


 {
{
 for (int i = 0; i < nptrs; ++i)
for (int i = 0; i < nptrs; ++i)
 if (memMap[i].ptr == p)
if (memMap[i].ptr == p)
 return i;
return i;
 return -1;
return -1;
 }
}

 void delPtr(void* p)
void delPtr(void* p)


 {
{
 int pos = findPtr(p);
int pos = findPtr(p);
 assert(p >= 0);
assert(p >= 0);
 // Remove pointer from map
// Remove pointer from map
 for (size_t i = pos; i < nptrs-1; ++i)
for (size_t i = pos; i < nptrs-1; ++i)
 memMap[i] = memMap[i+1];
memMap[i] = memMap[i+1];
 --nptrs;
--nptrs;
 }
}

 // Dummy type for static destructor
// Dummy type for static destructor
 struct Sentinel
struct Sentinel


 {
{
 ~Sentinel()
~Sentinel()


 {
{
 if (nptrs > 0)
if (nptrs > 0)


 {
{
 printf("Leaked memory at:\n");
printf("Leaked memory at:\n");
 for (size_t i = 0; i < nptrs; ++i)
for (size_t i = 0; i < nptrs; ++i)
 printf("\t%p (file: %s, line %ld)\n",
printf("\t%p (file: %s, line %ld)\n",
 memMap[i].ptr, memMap[i].file, memMap[i].line);
memMap[i].ptr, memMap[i].file, memMap[i].line);
 }
}
 else
else
 printf("No user memory leaks!\n");
printf("No user memory leaks!\n");
 }
}
 };
};

 // Static dummy object
// Static dummy object
 Sentinel s;
Sentinel s;

 } // End anonymous namespace
} // End anonymous namespace

 // Overload scalar new
// Overload scalar new
 void* operator new(size_t siz, const char* file,
void* operator new(size_t siz, const char* file,

 long line)
long line)  {
{
 void* p = malloc(siz);
void* p = malloc(siz);
 if (activeFlag)
if (activeFlag)


 {
{
 if (nptrs == MAXPTRS)
if (nptrs == MAXPTRS)


 {
{
 printf("memory map too small (increase MAXPTRS)\n");
printf("memory map too small (increase MAXPTRS)\n");
 exit(1);
exit(1);
 }
}
 memMap[nptrs].ptr = p;
memMap[nptrs].ptr = p;
 memMap[nptrs].file = file;
memMap[nptrs].file = file;
 memMap[nptrs].line = line;
memMap[nptrs].line = line;
 ++nptrs;
++nptrs;
 }
}
 if (traceFlag)
if (traceFlag)


 {
{
 printf("Allocated %u bytes at address %p ", siz, p);
printf("Allocated %u bytes at address %p ", siz, p);
 printf("(file: %s, line: %ld)\n", file, line);
printf("(file: %s, line: %ld)\n", file, line);
 }
}
 return p;
return p;
 }
}

 // Overload array new
// Overload array new
 void* operator new[](size_t siz, const char* file,
void* operator new[](size_t siz, const char* file,

 long line)
long line)  {
{
 return operator new(siz, file, line);
return operator new(siz, file, line);
 }
}

 // Override scalar delete
// Override scalar delete
 void operator delete(void* p)
void operator delete(void* p)


 {
{
 if (findPtr(p) >= 0)
if (findPtr(p) >= 0)


 {
{
 free(p);
free(p);
 assert(nptrs > 0);
assert(nptrs > 0);
 delPtr(p);
delPtr(p);
 if (traceFlag)
if (traceFlag)
 printf("Deleted memory at address %p\n", p);
printf("Deleted memory at address %p\n", p);
 }
}
 else if (!p && activeFlag)
else if (!p && activeFlag)
 printf("Attempt to delete unknown pointer: %p\n", p);
printf("Attempt to delete unknown pointer: %p\n", p);
 }
}

 // Override array delete
// Override array delete

 void operator delete[](void* p)
void operator delete[](void* p)  {
{
 operator delete(p);
operator delete(p);

 } /**////:~
} /**////:~

二 說明:
1)通過重載new和delete來實現(xiàn)
2)使用時需要在工程中加入MemCheck.h和MemCheck.cpp,在需要檢測的文件的前面include “MemCheck.h”,但是必須在所有的include的最后。
3)MEM_ON(),MEM_OFF()用來打開或關(guān)閉檢測
4)TRACE_ON(),和TRACE_OFF()用來打開或關(guān)閉檢測結(jié)果的輸出
5)可以檢測代碼中使用了流,標(biāo)準(zhǔn)容器,以及某個類的構(gòu)造函數(shù)分配了空間
三 使用實例:
console 的project中加入下面的file:
 // MemoryLeak3.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
// MemoryLeak3.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
 //
//

 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
 #include <cstring>
#include <cstring>

 #include "MemCheck.h" // Must appear last!
#include "MemCheck.h" // Must appear last!
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;

 void Test()
void Test()


 {
{
 int *i = new int(0);
int *i = new int(0);
 }
}

 class MyClass
class MyClass


 {
{
 private:
private:
 int *p;
int *p;
 public:
public:
 MyClass()
MyClass()


 {
{
 if(p != NULL)
if(p != NULL)


 {
{
 p = new int(0);
p = new int(0);
 }
}
 }
}
 ~MyClass()
~MyClass()


 {
{
 if(p != NULL)
if(p != NULL)


 {
{
 delete p;
delete p;
 p = NULL;
p = NULL;
 }
}
 }
}
 };
};

 void Test2()
void Test2()


 {
{
 int *i = NULL; // better for read
int *i = NULL; // better for read
 i = new int(0);
i = new int(0);
 int *&y = i; // pointer's reference
int *&y = i; // pointer's reference
 delete i;
delete i;

 MyClass *pMyClass = new MyClass();
MyClass *pMyClass = new MyClass();

 std::vector<MyClass*> myClasses;
std::vector<MyClass*> myClasses;
 myClasses.push_back(new MyClass());
myClasses.push_back(new MyClass());
 myClasses.push_back(new MyClass());
myClasses.push_back(new MyClass());

 std::vector<void*> myVector;
std::vector<void*> myVector;
 myVector.push_back(new MyClass());
myVector.push_back(new MyClass());
 myVector.push_back(new MyClass());
myVector.push_back(new MyClass());
 delete (MyClass *)(myVector.at(0));
delete (MyClass *)(myVector.at(0));
 delete myVector.at(1); // memory leak
delete myVector.at(1); // memory leak
 }
}

 class Foo
class Foo


 {
{
 char* s;
char* s;
 public:
public:
 Foo(const char*s )
Foo(const char*s )


 {
{
 this->s = new char[strlen(s) + 1];
this->s = new char[strlen(s) + 1];
 strcpy(this->s, s);
strcpy(this->s, s);
 }
}
 ~Foo()
~Foo()


 {
{
 delete [] s;
delete [] s;
 }
}
 };
};
 void Test3()
void Test3()


 {
{
 cout << "hello\n";
cout << "hello\n";
 int* p = new int;
int* p = new int;
 delete p;
delete p;
 int* q = new int[3];
int* q = new int[3];
 delete [] q;
delete [] q;
 int* r;
int* r;

 /**//*delete r;*/
/**//*delete r;*/
 vector<int> v;
vector<int> v;
 v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(1);
 Foo s("goodbye");
Foo s("goodbye");
 }
}
 int main()
int main()


 {
{
 TRACE_OFF();
TRACE_OFF();
 MEM_ON();
MEM_ON();
 Test();
Test();
 Test2();
Test2();
 Test3();
Test3();
 MEM_OFF();
MEM_OFF();

 } /**////:~
} /**////:~

四 測試結(jié)果如下:
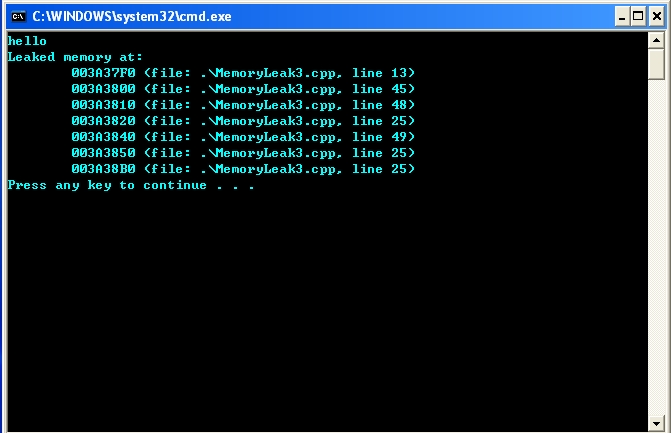
一 使用各種工具,一般都是收費的,但是可以申請試用。
二 工具收集
1)BoundsChecker :(
http://www.compuware.com/)(首選BoundsChecker)
應(yīng)該說是功能最強,使用只需要open需要測試的exe,然后start就可以了,可以通過檢測結(jié)果定位到源代碼中有內(nèi)存泄露的代碼行。
2)Purifyplus (
http://www.ibm.com)
3)Memory Validator(
http://www.softwareverify.com/index.html)
應(yīng)該說是功能也比較強,使用只需要start application wizard的start exe就可以了,可以通過檢測結(jié)果定位到源代碼中有內(nèi)存泄露的代碼行。
4)其實以上工具還可以進行其他的各種檢測,提高代碼的健壯性!
三
工具只能幫助我們更好的發(fā)現(xiàn)泄露,但是并不能解決所有的問題,比如說我們的項目非常的復(fù)雜或是使用了多個第三方的lib,這樣的話,有可能使用以上的工具就檢測不到。
豐富的編程經(jīng)驗和良好的編程習(xí)慣才能夠徹底的杜絕內(nèi)存的泄露。
本文轉(zhuǎn)自:
http://www.shnenglu.com/mzty/archive/2007/08/13/29922.htmlposted on 2012-10-24 13:17
王海光 閱讀(596)
評論(0) 編輯 收藏 引用 所屬分類:
C++