Circular Buffer
轉載自:http://www.vias.org/cppcourse/chap20_05.htmlAnother common implementation of a queue is a circular buffer. "Buffer" is a general name for a temporary storage location, although it often refers to an array, as it does in this case. What it means to say a buffer is "circular" should become clear in a minute.
The implementation of a circular buffer is similar to the array implementation of a stack, as in Section 19.7. The queue items are stored in an array, and we use indices to keep track of where we are in the array. In the stack implementation, there was a single index that pointed to the next available space. In the queue implementation, there are two indices:first points to the space in the array that contains the first customer in line and next points to the next available space.
The following figure shows a queue with two items (represented by dots).
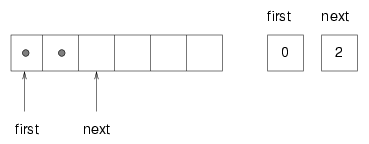
There are two ways to think of the variables first and last. Literally, they are integers, and their values are shown in boxes on the right. Abstractly, though, they are indices of the array, and so they are often drawn as arrows pointing to locations in the array. The arrow representation is convenient, but you should remember that the indices are not references; they are just integers.
Here is an incomplete array implementation of a queue:
class Queue {public:
pvector<Node> array;
int first, next;
Queue () {
array.resize (128);
first = 0;
next = 0;
}
bool empty () {
return first == next;
}
The instance variables and the constructor are straightforward, although again we have the problem that we have to choose an arbitrary size for the array. Later we will solve that problem, as we did with the stack, by resizing the array if it gets full.
The implementation of empty is a little surprising. You might have thought that first == 0 would indicate an empty queue, but that neglects the fact that the head of the queue is not necessarily at the beginning of the array. Instead, we know that the queue is empty if head equals next, in which case there are no items left. Once we see the implementation of insert and remove, that situation will more more sense.
void insert (Node node) {array[next] = node;
next++;
}
Node remove () {
first++;
return array[first-1];
}
insert looks very much like push in Section 19.7; it puts the new item in the next available space and then increments the index.
remove is similar. It takes the first item from the queue and then increments first so it refers to the new head of the queue. The following figure shows what the queue looks like after both items have been removed.
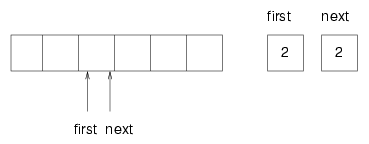
It is always true that next points to an available space. If first catches up with next and points to the same space, thenfirst is referring to an "empty" location, and the queue is empty. I put "empty" in quotation marks because it is possible that the location that first points to actually contains a value (we do nothing to ensure that empty locations contain null); on the other hand, since we know the queue is empty, we will never read this location, so we can think of it, abstractly, as empty.
As an exercise, fix remove so that it returns null if the queue is empty.
The next problem with this implementation is that eventually it will run out of space. When we add an item we incrementnext and when we remove an item we increment first, but we never decrement either. What happens when we get to the end of the array?
The following figure shows the queue after we add four more items:
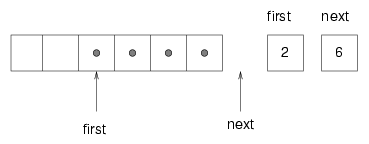
The array is now full. There is no "next available space," so there is nowhere for next to point. One possibility is that we could resize the array, as we did with the stack implementation. But in that case the array would keep getting bigger regardless of how many items were actually in queue. A better solution is to wrap around to the beginning of the array and reuse the spaces there. This "wrap around" is the reason this implementation is called a circular buffer.
One way to wrap the index around is to add a special case whenever we increment an index:
next++;if (next == array.length()) next = 0;
A fancy alternative is to use the modulus operator:
next = (next + 1) % array.length();Either way, we have one last problem to solve. How do we know if the queue is really full, meaning that we cannot insert another item? The following figure shows what the queue looks like when it is "full."
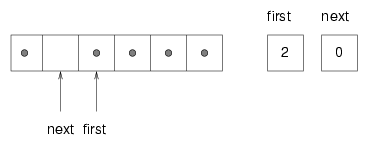
There is still one empty space in the array, but the queue is full because if we insert another item, then we have to increment next such that next == first, and in that case it would appear that the queue was empty!
To avoid that, we sacrifice one space in the array. So how can we tell if the queue is full?
if ((next + 1) % array.length == first)And what should we do if the array is full? In that case resizing the array is probably the only option.
As an exercise, put together all the code from this section and write an implementation of a queue using a circular buffer that resizes itself when necessary.


