
ST算法可以說就是個二維的動態規劃,黑書上有解釋。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_I = 50010;
const int MAX_J = 20;
int nMax[MAX_I][MAX_J];
int nMin[MAX_I][MAX_J];
int nArr[MAX_I];
int nN, nQ;
void InitRmq(int nN)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= nN; ++i)
{
nMax[i][0] = nMin[i][0] = nArr[i];
}
for (int j = 1; (1 << j) <= nN; ++j)
{
for (int i = 1; i + (1 << j) - 1 <= nN; ++i)
{
nMax[i][j] = max(nMax[i][j - 1],
nMax[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
nMin[i][j] = min(nMin[i][j - 1],
nMin[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
}
}
int Query(int nA, int nB)
{
int k = (int)(log(1.0 * nB - nA + 1) / log(2.0));
int nBig = max(nMax[nA][k], nMax[nB - (1 << k) + 1][k]);
int nSml = min(nMin[nA][k], nMin[nB - (1 << k) + 1][k]);
return nBig - nSml;
}
int main()
{
while (scanf("%d%d", &nN, &nQ) == 2)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= nN; ++i)
{
scanf("%d", &nArr[i]);
}
InitRmq(nN);
for (int i = 0; i < nQ; ++i)
{
int nA, nB;
scanf("%d%d", &nA, &nB);
printf("%d\n", Query(nA, nB));
}
}
return 0;
}
該題就是求一個字符串的最長回文子串,就是一個滿足本身是回文的最長的子串。
該題貌似可以用后綴數組和擴展kmp做,但是好像后綴數組貌似會tle,改學了下
一個專門的叫Manacher算法的東西。。。
這又是一個線性改良算法。找到有篇文章寫的不錯,鏈接如下:
http://www.felix021.com/blog/read.php?2040。
該算法說起來也不是太復雜,比較容易看懂的那種,當然是接觸過其它字符串算法
的前提下了。記得以前就看了看,硬是沒看懂,想不到現在這么快就明白了。
該算法需要額外的O(N)空間。說起來是空間換時間吧。
大概的思路是先預處理字符串,使其成為一個長度一定為偶數的串。而且第一個字符
是'$',假設'$'沒有在原串出現過。然后再在原來的每個字符前面加上'#',最后再加個
'#'。比如,abc就變成了$#a#b#c#。現在再對新的字符串進行處理。
開一個新的數組nRad[MAX],nRad[i]表示新串中第i個位置向左邊和向右邊同時擴展
并且保持對稱的最大距離。如果求出了nRad數組后,有一個結論,nRad[i]-1恰好表示原串
對應的位置能夠擴展的回文子串長度。這個的證明,應該比較簡單,因為新串基本上是原串
的2倍了,而且新串每一個有效字符兩側都有插入的#,這個找個例子看下就知道是這樣了。
最重要的是如何求出nRad數組。
求這個數組的算法也主要是利用了一些間接的結論優化了nRad[i]的初始化值。比如我們求
nRad[i]的時候,如果知道了i以前的nRad值,而且知道了前面有一個位置id,能夠最大的向
兩邊擴展距離max。那么有一個結論,nRad[i] 能夠初始化為min(nRad[2*id - i], max - i),
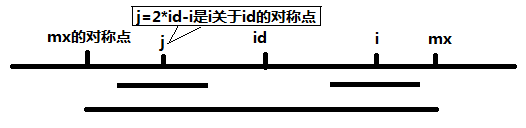
然后再進行遞增。關鍵是如何證明這個,這個的證明,對照圖片就很清楚了。
證明如下:
當 mx - i > P[j] 的時候,以S[j]為中心的回文子串包含在以S[id]為中心的回文子串中,由于 i 和 j 對稱,
以S[i]為中心的回文子串必然包含在以S[id]為中心的回文子串中,所以必有 P[i] = P[j],見下圖。
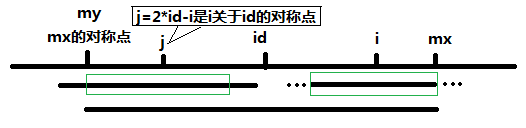
 當 P[j] > mx - i 的時候,以S[j]為中心的回文子串不完全包含于以S[id]為中心的回文子串中,但是基于
當 P[j] > mx - i 的時候,以S[j]為中心的回文子串不完全包含于以S[id]為中心的回文子串中,但是基于
對稱性可知,下圖中兩個綠框所包圍的部分是相同的,也就是說以S[i]為中心的回文子串,其向右至少會
擴張到mx的位置,也就是說 P[i] >= mx - i。至于mx之后的部分是否對稱,就只能老老實實去匹配了。
這個就說明得很清楚了。。。
代碼如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 110010 * 2;
char szIn[MAX];
char szOut[MAX];
int nRad[MAX];
int Proc(char* pszIn, char* pszOut)
{
int nLen = 1;
*pszOut++ = '$';
while (*pszIn)
{
*pszOut++ = '#';
nLen++;
*pszOut++ = *pszIn++;
nLen++;
}
*pszOut++ = '#';
*pszOut = '\0';
return nLen + 1;
}
void Manacher(int* pnRad, char* pszStr, int nN)
{
int nId = 0, nMax = 0;
//pnRad[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nN; ++i)
{
if (nMax > i)
{
pnRad[i] = min(pnRad[2 * nId - i], nMax - i);
}
else pnRad[i] = 1;
while (pszStr[i + pnRad[i]] == pszStr[i - pnRad[i]])
{
++pnRad[i];
}
if (pnRad[i] + i > nMax)
{
nMax = pnRad[i] + i;
nId = i;
}
}
}
int main()
{
while (scanf("%s", szIn) == 1)
{
int nLen = Proc(szIn, szOut);
Manacher(nRad, szOut, nLen);
int nAns = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nLen; ++i)
{
nAns = max(nRad[i], nAns);
}
printf("%d\n", nAns - 1);
}
return 0;
}
此題就是給出N個字符串,然后求一個最長的子串,它至少出現在N/2+1個字符串中,
如果有多個這樣的子串,按字典序輸出,如果沒有這樣的子串,輸出?。
此題是羅穗騫論文里面的例11,他有講述具體的解法。要用后綴數組做這樣的題真不
容易,用后綴數組就感覺是一件非常糾結的事情了。
這個題的解法還是那種模式化的思路。把N個字符串連接成一個,注意中間加不出現在
任何一個字符串中的分隔符,然后建立sa數組和height數組等。
最后二分答案,根據答案,即子串的長度對height數組進行分組,分組的思路還是羅穗
騫論文里面例3的思路,即從到后枚舉height數組,把連續大于等于答案的值放做一組,
一旦小于答案那么就是新的分組。這個題需要找到一些分組,其中的后綴是能夠出現在N個原
串中,這個分組的公共前綴就是sa[i]開始的nMid個字符了(nMid是二分時候獲得的子串長度)。
由于這個題需要按字典序輸出多個滿足要求的子串,所以麻煩了點。需要在Check函數里面
記錄這些子串,而且輸出答案的時候需要排序,再unique,由于是按height數組的順序查找的,
而sa[i]已經排好序了,所以排序答案的過程可以省略,但是必須unique。想下Check函數里面
遍歷height數組的過程就知道可能出現重復的子串。。。
代碼如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 110;
const int MAX_L = 1010;
const int MAX = MAX_N * MAX_L;
int nAns;
char szStr[MAX_L];
char szAns[MAX][MAX_L];
char* pszAns[MAX];
int nNum[MAX];
int nLoc[MAX];
bool bVis[MAX_N];
int sa[MAX], rank[MAX], height[MAX];
int wa[MAX], wb[MAX], wv[MAX], wd[MAX];
bool CmpStr(const char* pszOne, const char* pszTwo)
{
return strcmp(pszOne, pszTwo) < 0;
}
bool EqualStr(const char* pszOne, const char* pszTwo)
{
return strcmp(pszOne, pszTwo) == 0;
}
int cmp(int* r, int a, int b, int l)
{
return r[a] == r[b] && r[a + l] == r[b + l];
}
//倍增算法,r為待匹配數組,n為總長度,m為字符串范圍
void da(int* r, int n, int m)
{
int i, j, p, *x = wa, *y = wb;
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) wd[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) wd[x[i] = r[i]]++;
for (i = 1; i < m; ++i) wd[i] += wd[i - 1];
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) sa[--wd[x[i]]] = i;
for (j = 1, p = 1; p < n; j *= 2, m = p)
{
for (p = 0, i = n - j; i < n; ++i) y[p++] = i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (sa[i] >= j) y[p++] = sa[i] - j;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) wv[i] = x[y[i]];
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) wd[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) wd[wv[i]]++;
for (i = 1; i < m; ++i) wd[i] += wd[i - 1];
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) sa[--wd[wv[i]]] = y[i];
swap(x, y);
for (p = 1, x[sa[0]] = 0, i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
x[sa[i]] = cmp(y, sa[i - 1], sa[i], j)? p - 1 : p++;
}
}
}
//求height數組
void calHeight(int* r, int n)
{
int i, j, k = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) rank[sa[i]] = i;
for (i = 0; i < n; height[rank[i++]] = k)
{
if (k) --k;
for(j = sa[rank[i] - 1]; r[i + k] == r[j + k]; k++);
}
}
bool Check(int nMid, int nN, int nK)
{
int nCnt = 0;
int nNo = 0;
memset(bVis, false, sizeof(bVis));
for (int i = 1; i <= nN; ++i)
{
if (height[i] < nMid)
{
nCnt = 0;
memset(bVis, false, sizeof(bVis));
}
else
{
if (!bVis[nLoc[sa[i - 1]]])
{
++nCnt;
bVis[nLoc[sa[i - 1]]] = true;
}
if (!bVis[nLoc[sa[i]]])
{
++nCnt;
bVis[nLoc[sa[i]]] = true;
}
if (nCnt == nK)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nMid; ++j)
{
szAns[nNo][j] = nNum[sa[i] + j];
}
szAns[nNo][nMid] = 0;
++nNo;
nCnt = 0;
}
}
}
if (nNo > 0) nAns = nNo;
return nNo > 0;
}
int main()
{
int nN;
bool bFirst = true;
while (scanf("%d", &nN), nN)
{
if (bFirst) bFirst = false;
else putchar('\n');
int nEnd = 300;
int nP = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nN; ++i)
{
scanf("%s", szStr);
int nLen = strlen(szStr);
for (int j = 0; j < nLen; ++j)
{
nNum[nP] = szStr[j];
nLoc[nP++] = i;
}
nNum[nP] = nEnd;
nLoc[nP++] = nEnd++;
}
nNum[nP] = 0;
if (nN == 1)
{
printf("%s\n\n", szStr);
continue;
}
da(nNum, nP + 1, 500);//500是估計的字符集大小
calHeight(nNum, nP);
int nLeft = 1, nRight = strlen(szStr);
int nTemp = 0, nMid;
int nK = nN / 2 + 1;
nAns = 0;
while (nLeft <= nRight)
{
nMid = (nLeft + nRight) >> 1;
if (Check(nMid, nP, nK))
{
nTemp = nMid;
nLeft = nMid + 1;
}
else nRight = nMid - 1;
}
if (nTemp == 0)
{
printf("?\n");
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < nAns; ++i)
{
pszAns[i] = szAns[i];
}
//sort(pszAns, pszAns + nAns, CmpStr);
nAns = unique(pszAns, pszAns + nAns, EqualStr) - pszAns;
for (int i = 0; i < nAns; ++i)
{
printf("%s\n", pszAns[i]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
求N個字符串最長的公共子串。這題數據比較水,暴力第一個字符串的子串也可以過。
初學后綴數組,有很多不明白的東西,此題后綴數組的代碼在網上也是一把抓。
說實話我確實還不懂后綴數組,但是后綴數組太強大了,只能硬著頭皮照著葫蘆畫瓢了。
貼下代碼方便以后查閱吧。。。
感覺后綴數組的應用最主要的還是height數組,看懂倍增算法排序后綴已經非常困難了。
然后再理解height數組怎么用也不是一件容易的事情。然后貌似height數組最關鍵的用法是
枚舉某一個長度的子串時候,比如長度為k,能夠用這個k對height數組進行分組,這個羅穗騫
的論文里面有個求不重疊最長重復子串的例子說明了這個height數組分組的思路,不過我現在
還是不怎么理解。。。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 110;
const int MAX_L = MAX_N * MAX_N;
char szStr[MAX_N];
int nNum[MAX_L];
int nLoc[MAX_L];
bool bVisit[MAX_N];
int sa[MAX_L], rank[MAX_L], height[MAX_L];
int wa[MAX_L], wb[MAX_L], wv[MAX_L], wd[MAX_L];
int cmp(int* r, int a, int b, int l)
{
return r[a] == r[b] && r[a + l] == r[b + l];
}
//倍增算法,r為待匹配數組,n為總長度,m為字符串范圍
void da(int* r, int n, int m)
{
int i, j, p, *x = wa, *y = wb;
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) wd[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) wd[x[i] = r[i]]++;
for (i = 1; i < m; ++i) wd[i] += wd[i - 1];
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) sa[--wd[x[i]]] = i;
for (j = 1, p = 1; p < n; j *= 2, m = p)
{
for (p = 0, i = n - j; i < n; ++i) y[p++] = i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (sa[i] >= j) y[p++] = sa[i] - j;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) wv[i] = x[y[i]];
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) wd[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) wd[wv[i]]++;
for (i = 1; i < m; ++i) wd[i] += wd[i - 1];
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) sa[--wd[wv[i]]] = y[i];
swap(x, y);
for (p = 1, x[sa[0]] = 0, i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
x[sa[i]] = cmp(y, sa[i - 1], sa[i], j)? p - 1 : p++;
}
}
}
//求height數組
void calHeight(int* r, int n)
{
int i, j, k = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) rank[sa[i]] = i;
for (i = 0; i < n; height[rank[i++]] = k)
{
if (k) --k;
for(j = sa[rank[i] - 1]; r[i + k] == r[j + k]; k++);
}
}
bool Check(int nMid, int nLen, int nN)
{
int nCnt = 0;
memset(bVisit, false, sizeof(bVisit));
for (int i = 2; i <= nLen; ++i)
{
if (nMid > height[i])
{
nCnt = 0;
memset(bVisit, false, sizeof(bVisit));
continue;
}
if (!bVisit[nLoc[sa[i - 1]]])
{
bVisit[nLoc[sa[i - 1]]] = true;
++nCnt;
}
if (!bVisit[nLoc[sa[i]]])
{
bVisit[nLoc[sa[i]]] = true;
++nCnt;
}
if (nCnt == nN) return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int nT;
scanf("%d", &nT);
while (nT--)
{
int nN;
int nEnd = 300;
int nP = 0;
scanf("%d", &nN);
for (int i = 1; i <= nN; ++i)
{
scanf("%s", szStr);
char* pszStr;
for (pszStr = szStr; *pszStr; ++pszStr)
{
nLoc[nP] = i;
nNum[nP++] = *pszStr;
}
nLoc[nP] = nEnd;
nNum[nP++] = nEnd++;
reverse(szStr, szStr + strlen(szStr));
for (pszStr = szStr; *pszStr; ++pszStr)
{
nLoc[nP] = i;
nNum[nP++] = *pszStr;
}
nLoc[nP] = nEnd;
nNum[nP++] = nEnd++;
}
nNum[nP] = 0;
da(nNum, nP + 1, nEnd);
calHeight(nNum, nP);
int nLeft = 1, nRight = strlen(szStr), nMid;
int nAns = 0;
while (nLeft <= nRight)
{
nMid = (nLeft + nRight) / 2;
if (Check(nMid, nP, nN))
{
nLeft = nMid + 1;
nAns = nMid;
}
else nRight = nMid - 1;
}
printf("%d\n", nAns);
}
return 0;
}
題意是給定一系列模式串。然后給出一個文本串,問至少改變文本串里面多少個字符
可以使文本串不包含任何一個模式串。
還是先建立Trie圖,然后在Trie圖上面進行dp。dp的思路也不是很復雜。dp[i][j]的意思
是長度為i的文本串需要改變dp[i][j]個字符順利到達狀態j。需要注意的是長度為i的時候,
對應的字符串中的第i-1個字符。剛開始一直沒發現這個bug。而且注意中途不能轉移到
匹配成功的狀態上去,多加幾個條件控制即可了。。。
轉移方程,dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][nNext] + szText[i-1] != k),其中nNext
是從狀態j可以轉移到的非匹配成功的狀態,k代表的當前邊的權。
代碼如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 61;
const int MAX_L = 31;
const int MAX_D = 4;
const int INF = 1110;
char chHash[256];
char szPat[MAX_L];
void InitHash()
{
chHash['A'] = 0;
chHash['G'] = 1;
chHash['C'] = 2;
chHash['T'] = 3;
}
struct Trie
{
Trie* fail;
Trie* next[MAX_D];
bool flag;
int no;
};
int nP;
Trie* pRoot;
Trie tries[MAX_N * MAX_L];
Trie* NewNode()
{
memset(&tries[nP], 0, sizeof(Trie));
tries[nP].no = nP;
return &tries[nP++];
}
void InitTrie(Trie*& pRoot)
{
nP = 0;
pRoot = NewNode();
}
void Insert(Trie* pRoot, char* pszPat)
{
Trie* pNode = pRoot;
while (*pszPat)
{
int idx = chHash[*pszPat];
if (pNode->next[idx] == NULL)
{
pNode->next[idx] = NewNode();
}
pNode = pNode->next[idx];
++pszPat;
}
pNode->flag = true;
}
void BuildAC(Trie* pRoot)
{
pRoot->fail = NULL;
queue<Trie*> qt;
qt.push(pRoot);
while (!qt.empty())
{
Trie* front = qt.front();
qt.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_D; ++i)
{
if (front->next[i])
{
Trie* pNode = front->fail;
while (pNode && pNode->next[i] == NULL)
{
pNode = pNode->fail;
}
front->next[i]->fail = pNode? pNode->next[i] : pRoot;
front->next[i]->flag |= front->next[i]->fail->flag;
qt.push(front->next[i]);
}
else
{
front->next[i] = front == pRoot? pRoot : front->fail->next[i];
}
}
}
}
int nChange[INF][INF];
char szText[INF];
int Solve()
{
int nLen = strlen(szText);
for (int i = 0; i <= nLen; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nP; ++j)
{
nChange[i][j] = INF;
}
}
int i, j, k;
nChange[0][0] = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= nLen; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < nP; ++j)
{
if (tries[j].flag) continue;
if (nChange[i - 1][j] == INF) continue;
for (k = 0; k < MAX_D; ++k)
{
int nNext = tries[j].next[k] - tries;
if (tries[nNext].flag) continue;
//trie是邊權樹,所以i是從1到len,而且當前字符是szText[i-1]
int nTemp = nChange[i - 1][j] + (k != chHash[szText[i - 1]]);
nChange[i][nNext] = min(nChange[i][nNext], nTemp);
}
}
}
int nAns = INF;
for (i = 0; i < nP; ++i)
{
if (!tries[i].flag)
nAns = min(nAns, nChange[nLen][i]);
}
return nAns == INF? -1 : nAns;
}
int main()
{
int nN;
int nCase = 1;
InitHash();
while (scanf("%d", &nN), nN)
{
InitTrie(pRoot);
while (nN--)
{
scanf("%s", szPat);
Insert(pRoot, szPat);
}
BuildAC(pRoot);
scanf("%s", szText);
printf("Case %d: %d\n", nCase++, Solve());
}
return 0;
}
這個題與poj2778dna sequence解法基本一致。只是這個題的答案沒有取模,
而且文本串不太長。問題是不取模的話就只能輸出實際的答案了,就只能用大數了。
而且用大數的話,再用矩陣冥可能就會超時之類的。
這類題還可以用除矩陣冥外的另外一種解法,就是直接dp即可。
二維狀態,第一維代表文本串長度,第二維代表在AC自動機中的狀態。
比如dp[i][j]代表長度為i的文本串,轉移到Trie圖中節點j時候滿足不包含任何模式串的答案。
剩下的是如何轉移狀態。轉移的話也是考慮next指針數組,設next = tries[j].next[k],
那么有dp[i+1][next] = dp[i+1][next] + dp[i][j],從0到字母集合大小N枚舉k即可。
這個題有一個易錯的地方,就是字母集合可能是ascii碼在128到256的范圍內。而char
的范圍可能是-128到127或者0到255,這個是根據編譯器不同的。所以,直接用字符串
數組讀入數據后需要再處理下。可以直接將每個字符加128后再處理。
另外,getchar返回的是int,但是與gets之類的函數獲得的值的差別也不是那么確定的了。
我覺得getchar除了對eof之外其余都返回正值。但是,如果char是有符號的話,scanf或者
gets之類得到的char數組里面可能就包含負值了。。。
這個可以生成隨機文件,再用getchar讀入并用%d輸出其返回值驗證下。驗證程序如下:
注釋掉的部分是生成隨機文件的部分。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char ch;
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("in.txt", "w", stdout);
int nNum = 100;
int nCh;
do
{
printf("%d\n", nCh = getchar());
}while (nCh != EOF);
/*while (nNum--)
{
putchar(rand() % 256);
}*/
return 0;
}
該題的代碼如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_D = 256;
const int MAX_N = 51;
const int MAX_M = 51;
const int MAX_P = 11;
struct Trie
{
Trie* fail;
Trie* next[MAX_D];
int no;
bool flag;
};
Trie tries[MAX_P * MAX_P];
int nP;
int nN, nM;
Trie* pRoot;
int nHash[MAX_D];
char szPat[MAX_M];
Trie* NewNode()
{
memset(&tries[nP], 0, sizeof(Trie));
tries[nP].no = nP;
return &tries[nP++];
}
void InitTrie(Trie*& pRoot)
{
nP = 0;
pRoot = NewNode();
}
void Insert(Trie* pRoot, char* pszPat)
{
Trie* pNode = pRoot;
while (*pszPat)
{
int idx = nHash[*pszPat];
if (pNode->next[idx] == NULL)
{
pNode->next[idx] = NewNode();
}
pNode = pNode->next[idx];
++pszPat;
}
pNode->flag = true;
}
void BuildAC(Trie* pRoot)
{
pRoot->fail = NULL;
queue<Trie*> qt;
qt.push(pRoot);
while (!qt.empty())
{
Trie* front = qt.front();
qt.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < nN; ++i)
{
if (front->next[i])
{
Trie* pNode = front;
while (pNode && pNode->next[i] == NULL)
{
pNode = pNode->fail;
}
front->next[i]->fail = pNode? pNode->next[i] : pRoot;
front->next[i]->flag |= front->next[i]->fail->flag;
qt.push(front->next[i]);
}
else
{
front->next[i] = front->fail->next[i];
}
}
}
}
const int MAX_L = 200;
struct BigInt
{
int nD[MAX_L];
BigInt()
{
Clear();
}
void Clear()
{
memset(nD, 0, sizeof(nD));
}
void Print()
{
int i = MAX_L - 1;
while (!nD[i] && i)--i;
while (i >= 0)
{
putchar(nD[i] + '0');
--i;
}
}
int operator[](int idx) const
{
return nD[idx];
}
int& operator[](int idx)
{
return nD[idx];
}
};
BigInt bi[MAX_M][MAX_D];
BigInt operator+(const BigInt& one, const BigInt& two)
{
BigInt ret;
for (int i = 0, nAdd = 0; i < MAX_L; ++i)
{
ret[i] = one[i] + two[i] + nAdd;
nAdd = ret[i] / 10;
ret[i] %= 10;
}
return ret;
}
void Solve()
{
BigInt ans;
for (int i = 0; i <= nM; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nP; ++j)
{
bi[i][j].Clear();
}
}
bi[0][0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= nM; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nP; ++j)
{
if (tries[j].flag) continue;
for (int k = 0; k < nN; ++k)
{
int nNext = tries[j].next[k] - tries;
if (tries[nNext].flag == false)
{
bi[i][nNext] = bi[i][nNext] + bi[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < nP; ++i)
{
ans = ans + bi[nM][i];
}
ans.Print();
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int nT;
while (scanf("%d%d%d%*c", &nN, &nM, &nT) == 3)
{
int nCh;
int nTmp = 0;
memset(nHash, 0, sizeof(nHash));
while (nCh = getchar(), nCh != '\n')
{
if (!nHash[nCh])
{
nHash[nCh] = nTmp++;
}
}
InitTrie(pRoot);
while (nT--)
{
gets(szPat);
Insert(pRoot, szPat);
}
printf("1");
BuildAC(pRoot);
printf("2");
Solve();
}
return 0;
}
赤裸裸的字符串最小表示題。所謂字符串最小表示指的是給定一個字符串,假設其可以循環移
位,問循環左移多少位能夠得到最小的字符串。
算法即是周源的最小表示法,搜索可以找到相關論文和ppt。
該算法其實也不是太復雜,思路可以這樣理解。假設原字符串為s,設s1 = s + s; s2 = s1循
環左移1位;現在處理s1和s2,實際寫程序的時候可以通過下標偏移和取模得到s1和s2,而并不需
要生成。
處理過程是這樣的,設i和j分別指向s1和s2的開頭。我們的目的是找到這樣的i和j,假設k是s的
長度,滿足條件s1[i,i+k-1] = s2[j,j+k-1] 并且s1[i,i+k-1] 是所有滿足條件的字符串中最小的
字符串,如果有多個這樣的s1[i,i+k-1] 那么我們希望i最小。
其實這個算法主要是做了一個優化,從而把時間搞成線性的。比如,對于當前的i和j,我們一直
進行匹配,也就是s1[i,i+k] = s2[j,j+k] 一直滿足,突然到了一個位置s1[i+k] != s2[j+k]了,
現在我們需要改變i和j了。但是,我們不能只是++i或者++j。而是根據s1[i+k]>s2[j+k]的話i =
i + k + 1,否則j = j + k + 1。這樣的瞬移i或者j就能夠保證復雜度是線性的了。
問題是如何證明可以這樣的瞬移。其實,說穿了也很簡單。因為s1[i,i+k - 1] = s2[j,j+k -1]
是滿足的,只是到了s1[i+k]和s2[j+k]才出現問題了。假如s1[i+k]>s2[j+k],那么我們改變i為
區間[i+1,i+k]中任何一個值m都不可能得到我們想要的答案,這是因為我們總可以在s2中找到相應
的比s1[m,m+k-1]小的字符串s2[j+m-i,j+m-i+k-1],因為有s1[i+k]>s2[j+k]。
同樣對于s1[i+k]<s2[j+k]的情況。
文字可能描述的不是很清楚。看PPT能夠根據圖進行分析。
代碼如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int GetMin(string& str)
{
int nSize = str.size();
int i = 0, j = 1, k = 0;
while (i < nSize && j < nSize && k < nSize)
{
char chDif = str[(i + k) % nSize]
- str[(j + k) % nSize];
if (!chDif) ++k;
else
{
if (chDif > 0) i = i + k + 1;
else j = j + k + 1;
if (i == j) ++j;
k = 0;
}
}
return min(i, j);
}
int main()
{
string str;
int nN;
scanf("%d", &nN);
while (nN--)
{
cin >> str;
printf("%d\n", GetMin(str) + 1);
}
return 0;
}
這個題目更奇葩。據說是上一個題的加強版。
題意是給定M個模式串,然后給定長度L,問不超過L的文本至少含有一個模式的情況的總種數。
還是用模式串建立Trie圖,根據Trie圖建立起路徑長度為1的矩陣M。
總情況數目為26^1+26^2+...+26^L。不含模式串的情況總數為矩陣N = M^1+M^2+M^3
+...+M^L的第一行之和。總情況數目減去不含模式串的情況就是答案。
這里用到了矩陣的一些算法,比如快速冥,還有快速冥求和。但是,我用了操作符重載,最悲劇
的是重載后的操作符沒有優先級,而我還當作有優先級的在用,所以悲劇了。。。一直樣例都過不
去。。。唉,最后才發現了這個問題。。。寫了260行左右的代碼,前面的一部分代碼可以當作矩
陣操作的模板了。。。Trie圖的也不錯,過幾天估計得打印下來用了。。。
代碼如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <
string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned
long long INT;
const int MAX_D = 26;
const int MAX_L = 10;
const int MAX_N = 10;
char szPat[MAX_L];
const int MAX_S = 31;
struct Matrix
{
int nSize;
INT nD[MAX_S][MAX_S];
Matrix(
int nS)
{
Clear(nS);
}
Matrix&
operator = (
const Matrix& m)
{
nSize = m.nSize;
for (
int i = 0; i < nSize; ++i)
{
for (
int j = 0; j < nSize; ++j)
{
nD[i][j] = m.nD[i][j];
}
}
return *
this;
}
void Clear(
int nS)
{
nSize = nS;
memset(nD, 0,
sizeof(nD));
}
void Unit()
{
for (
int i = 0; i < nSize; ++i)
{
for (
int j = 0; j < nSize; ++j)
{
nD[i][j] = (i == j ? 1 : 0);
}
}
}
};
Matrix
operator+(
const Matrix& A,
const Matrix& B)
{
Matrix C(A.nSize);
for (
int i = 0; i < A.nSize; ++i)
{
for (
int j = 0; j < A.nSize; ++j)
{
C.nD[i][j] = A.nD[i][j] + B.nD[i][j];
}
}
return C;
}
Matrix
operator*(
const Matrix& nA,
const Matrix& nB)
{
Matrix nC(nB.nSize);
for (
int i = 0; i < nA.nSize; ++i)
{
for (
int j = 0; j < nA.nSize; ++j)
{
for (
int k = 0; k < nA.nSize; ++k)
{
nC.nD[i][j] += nA.nD[i][k] * nB.nD[k][j];
}
}
}
return nC;
}
Matrix
operator^(Matrix B, INT nExp)
{
Matrix ans(B.nSize);
ans.Unit();
while (nExp)
{
if (nExp % 2)
{
ans = ans * B;
}
B = B * B;
nExp >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
//求base^1+base^2+ +base^N
+base^N
Matrix SumPowMatrix(Matrix&
base, INT nN)
{
if (nN == 1)
{
return base;
}
Matrix ans = SumPowMatrix(
base, nN / 2);
ans = ans + ((
base^(nN / 2)) * ans);
//重載運算符保證不了優先級
if (nN % 2)
{
ans = ans + (
base^nN);
//沒優先級啊,必須加括號,查錯2個小時了
}
return ans;
}
struct Trie
{
Trie* next[MAX_D];
Trie* fail;
int no;
bool flag;
};
Trie tries[MAX_L * MAX_N];
int nP;
Trie* pRoot;
Trie* NewNode()
{
memset(&tries[nP], 0,
sizeof(Trie));
tries[nP].no = nP;
return &tries[nP++];
}
void InitTrie(Trie*& pRoot)
{
nP = 0;
pRoot = NewNode();
}
void Insert(Trie* pRoot,
char* pszPat)
{
Trie* pNode = pRoot;
while (*pszPat)
{
int idx = *pszPat - 'a';
if (pNode->next[idx] == NULL)
{
pNode->next[idx] = NewNode();
}
pNode = pNode->next[idx];
++pszPat;
}
pNode->flag =
true;
}
void BuildAC(Trie* pRoot, Matrix& M)
{
pRoot->fail = NULL;
queue<Trie*> qt;
qt.push(pRoot);
M.Clear(nP);
while (!qt.empty())
{
Trie* front = qt.front();
qt.pop();
for (
int i = 0; i < MAX_D; ++i)
{
if (front->next[i])
{
Trie* pNode = front->fail;
while (pNode && pNode->next[i] == NULL)
{
pNode = pNode->fail;
}
front->next[i]->fail = pNode? pNode->next[i] : pRoot;
if (front->next[i]->fail->flag)
{
front->next[i]->flag =
true;
}
qt.push(front->next[i]);
}
else {
front->next[i] = front == pRoot? pRoot : front->fail->next[i];
}
//這里必須要加上front->flag為false的判斷么?加不加會生成不同的矩陣
if (!front->next[i]->flag)
{
++M.nD[front->no][front->next[i]->no];
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int nN;
INT nL;
Matrix M(0);
while (scanf("%d%I64u", &nN, &nL) == 2)
{
InitTrie(pRoot);
while (nN--)
{
scanf("%s", szPat);
Insert(pRoot, szPat);
}
BuildAC(pRoot, M);
Matrix tmp(1);
tmp.nD[0][0] = 26;
tmp = SumPowMatrix(tmp, nL);
INT nAns = tmp.nD[0][0];
Matrix msum = SumPowMatrix(M, nL);
for (
int i = 0; i < msum.nSize; ++i)
{
nAns -= msum.nD[0][i];
}
printf("%I64u\n", nAns);
}
return 0;
}
題意很簡單,假定文本集就是A,C,T,G,給定M個模式串,問你長度為N的文本不出現這些模式
串的可能性到底有多少種。。。
確實非常不直觀的樣子。。。
解法是先學學AC自動機,建立起Trie圖,根據trie圖可以得到長度為1的路徑矩陣,然后再快速
冥得到長度為N的路徑矩陣。
說起來都非常糾結,沒學過AC自動機更加無法理解。學AC自動機之前據說得先學Trie樹和KMP
才好理解。學AC自動機搞Trie圖就花費了近2天了,然后弄懂這個題又是一天,好在基本明白了。
馬上快比賽了,從長春換到金華也不知道是好是壞。。。還是弱菜啊。。。
貼下我的Trie圖+快速冥(直接二分了,沒有寫成數論里面那種算法)...
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long INT;
const int MOD = 100000;
const int MAX_P = 100;
const int MAX_D = 4;
int nIdx[256];
char szPat[MAX_P];
INT nMatrix[MAX_P][MAX_P];
INT B[MAX_P][MAX_P];
INT A[MAX_P][MAX_P];
void InitIdx()
{
nIdx['A'] = 0;
nIdx['C'] = 1;
nIdx['T'] = 2;
nIdx['G'] = 3;
}
struct Trie
{
Trie* fail;
Trie* next[MAX_D];
int no;
bool flag;
Trie()
{
fail = NULL;
memset(next, 0, sizeof(next));
no = 0;
flag = false;
}
};
Trie tries[MAX_D * MAX_P];
int nP;
Trie* pRoot;
Trie* NewNode()
{
memset(&tries[nP], 0, sizeof(Trie));
tries[nP].no = nP;
return &tries[nP++];
}
void InitTrie(Trie*& pRoot)
{
nP = 0;
pRoot = NewNode();
}
void Insert(char* pszPat)
{
Trie* pNode = pRoot;
while (*pszPat)
{
if (pNode->next[nIdx[*pszPat]] == NULL)
{
pNode->next[nIdx[*pszPat]] = NewNode();
}
pNode = pNode->next[nIdx[*pszPat]];
++pszPat;
}
pNode->flag = true;
}
int BuildAC(Trie* pRoot)
{
memset(nMatrix, 0, sizeof(nMatrix));
pRoot->fail = NULL;
queue<Trie*> qt;
qt.push(pRoot);
while (!qt.empty())
{
Trie* front = qt.front();
qt.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_D; ++i)
{
if (front->next[i])
{
Trie* pNode = front->fail;
while (pNode && pNode->next[i] == NULL)
{
pNode = pNode->fail;
}
front->next[i]->fail = pNode? pNode->next[i] : pRoot;
if (front->next[i]->fail->flag == true)
{
front->next[i]->flag = true;
}
qt.push(front->next[i]);
}
else
{
front->next[i] = front == pRoot? pRoot : front->fail->next[i];
}
if (front->next[i]->flag == false)
{
nMatrix[front->no][front->next[i]->no]++;
}
}
}
return nP;//節點總個數
}
void MultyMatrix(INT A[][MAX_P], INT B[][MAX_P], INT C[][MAX_P], int nSize)
{
for (int i = 0; i < nSize; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nSize; ++j)
{
INT nSum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < nSize; ++k)
{
nSum = (nSum + A[i][k] * B[k][j]) % MOD;
}
C[i][j] = nSum;
}
}
}
void CopyMatrix(INT A[][MAX_P], INT B[][MAX_P], int nSize)
{
for (int i = 0; i < nSize; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nSize; ++j)
{
A[i][j] = B[i][j];
}
}
}
void MatrixPower(INT M[][MAX_P], int nSize, INT nP)
{
if (nP == 1)
{
CopyMatrix(A, M, nSize);
return;
}
MatrixPower(M, nSize, nP / 2);
MultyMatrix(A, A, B, nSize);
if (nP % 2)
{
MultyMatrix(B, M, A, nSize);
}
else
{
CopyMatrix(A, B, nSize);
}
}
int main()
{
INT nM, nN;
InitIdx();
while (scanf("%I64d%I64d", &nM, &nN) == 2)
{
InitTrie(pRoot);
while (nM--)
{
scanf("%s", szPat);
Insert(szPat);
}
int nSize = BuildAC(pRoot);
MatrixPower(nMatrix, nSize, nN);
INT nAns = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nSize; ++i)
{
nAns = (nAns + A[0][i]) % MOD;
}
printf("%I64d\n", nAns % MOD);
}
return 0;
}
句子的語法匹配。這個用DFA確實可以很方便做出來,用遞歸判斷之類的應該也可以。
感覺用dfa只需要保證狀態轉換圖對了,基本上就不會出bug了,但是其它的方法去匹配
這種類似正則表達式的字符串就容易出錯多了。
百度百科的DFA定義如下:
英文全稱:Deterministic Finite Automaton, 簡寫:DFA
DFA定義:一個確定的有窮自動機(DFA)M是一個五元組:M=(K,Σ,f,S,Z)其中
① K是一個有窮集,它的每個元素稱為一個狀態;
② Σ是一個有窮字母表,它的每個元素稱為一個輸入符號,所以也稱Σ為輸入符號字母表;
③ f是轉換函數,是K×Σ→K上的映射,即,如 f(ki,a)=kj,(ki∈K,kj∈K)就意味著,
當前狀態為ki,輸入符為a時,將轉換為下一個狀態kj,我們把kj稱作ki的一個后繼狀態;
④ S ∈ K是唯一的一個初態;
⑤ Z⊂K是一個終態集,終態也稱可接受狀態或結束狀態。
該題的狀態轉換圖:
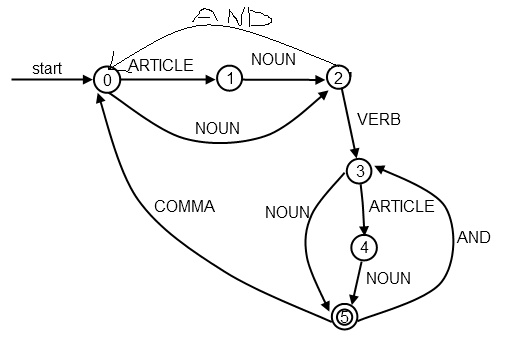
現在再根據狀態轉換圖,寫一個模擬轉換關系的匹配就非常方便了。。。
代碼如下:
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
string strNouns[8] =
{
"tom", "jerry", "goofy", "mickey",
"jimmy", "dog", "cat", "mouse"
};
bool IsNoun(string& str)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
if (str == strNouns[i])
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool IsVerb(string& str)
{
return str == "hate" || str == "love"
|| str == "know" || str == "like"
|| str == "hates" || str == "loves"
|| str == "knows" || str == "likes";
}
bool IsArticle(string& str)
{
return str == "a" || str == "the";
}
bool CheckState(vector<string>& vs)
{
if (vs.empty()) return false;
int nState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vs.size(); ++i)
{
//printf("nState:%d, str:%s\n", nState, vs[i].c_str());
switch (nState)
{
case 0:
if (IsArticle(vs[i]))
{
nState = 1;
break;
}
else if (IsNoun(vs[i]))
{
nState = 2;
break;
}
else
{
return false;
}
case 1:
if (IsNoun(vs[i]))
{
nState = 2;
break;
}
else
{
return false;
}
case 2:
if (vs[i] == "and")
{
nState = 0;
break;
}
else if (IsVerb(vs[i]))
{
nState = 3;
break;
}
else
{
return false;
}
case 3:
if (IsArticle(vs[i]))
{
nState = 4;
break;
}
else if (IsNoun(vs[i]))
{
nState = 5;
break;
}
else
{
return false;
}
case 4:
if (IsNoun(vs[i]))
{
nState = 5;
break;
}
else
{
return false;
}
case 5:
if (vs[i] == "and")
{
nState = 3;
break;
}
else if (vs[i] == ",")
{
nState = 0;
break;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
return nState == 5;
}
int main()
{
int nT;
scanf("%d%*c", &nT);
while (nT--)
{
vector<string> vs;
string line, str;
getline(cin, line);
stringstream ss(line);
while (ss >> str)
{
vs.push_back(str);
}
printf("%s\n", CheckState(vs) ? "YES I WILL" : "NO I WON'T");
}
return 0;
}