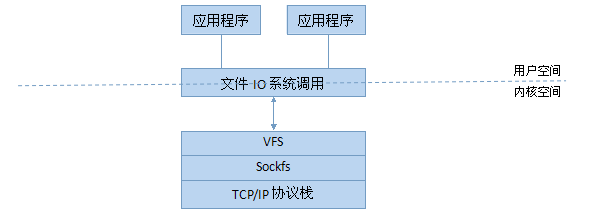
在Unix的世界里,萬物皆文件,通過虛擬文件系統VFS,程序可以用標準的Unix系統調用對不同的文件系統,甚至不同介質上的文件系統進行讀寫操作。對于網絡套接字socket也是如此,除了專屬的Berkeley Sockets API,還支持一些標準的文件IO系統調用如read(v)、write(v)和close等。那么為什么socket也支持文件IO系統調用呢?在Linux上,這是通過套接口偽文件系統sockfs來實現的,因為sockfs實現了VFS中的4種主要對象:超級塊super block、索引節點inode、目錄項對象dentry和文件對象file,當執行文件IO系統調用時,VFS就將請求轉發給sockfs,而sockfs就調用特定的協議實現,層次結構如下圖:
初始化
在內核引導時初始化網絡子系統,進而調用sock_init,該函數主要步驟如下:創建inode緩存,注冊和裝載sockfs,定義在net/socket.c中。
1 static int __init sock_init(void)
static int __init sock_init(void)
2 {
{
3

4 init_inodecache();
init_inodecache();
5 register_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);
register_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);
6 sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);
sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);
7

8 }
}
 static int __init sock_init(void)
static int __init sock_init(void)2
 {
{3


4
 init_inodecache();
init_inodecache();5
 register_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);
register_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);6
 sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);
sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);7


8
 }
}創建inode緩存
init_inodecache為socket_alloc對象創建SLAB緩存,名稱為sock_inode_cachep,socket_alloc定義在include/net/sock.h中。
1 struct socket_alloc {
struct socket_alloc {
2 struct socket socket;
struct socket socket;
3 struct inode vfs_inode;
struct inode vfs_inode;
4 };
};
 struct socket_alloc {
struct socket_alloc {2
 struct socket socket;
struct socket socket;3
 struct inode vfs_inode;
struct inode vfs_inode;4
 };
}; socket_alloc由socket和inode結構2部分組成,這樣就方便了在套接字與inode對象間雙向定位。
注冊sockfs
調用VFS的函數register_filesystem實現注冊,sock_fs_type定義在net/socket.c中。
注冊sockfs
調用VFS的函數register_filesystem實現注冊,sock_fs_type定義在net/socket.c中。
1 static struct file_system_type sock_fs_type = {
static struct file_system_type sock_fs_type = {
2 .name = "sockfs",
.name = "sockfs",
3 .get_sb = sockfs_get_sb,
.get_sb = sockfs_get_sb,
4 .kill_sb = kill_anon_super,
.kill_sb = kill_anon_super,
5 };
};
 static struct file_system_type sock_fs_type = {
static struct file_system_type sock_fs_type = {2
 .name = "sockfs",
.name = "sockfs",3
 .get_sb = sockfs_get_sb,
.get_sb = sockfs_get_sb,4
 .kill_sb = kill_anon_super,
.kill_sb = kill_anon_super,5
 };
};1 static int sockfs_get_sb(struct file_system_type *fs_type,int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,struct vfsmount *mnt)
static int sockfs_get_sb(struct file_system_type *fs_type,int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,struct vfsmount *mnt)
2 {
{
3 return get_sb_pseudo(fs_type, "socket:", &sockfs_ops, SOCKFS_MAGIC, mnt);
return get_sb_pseudo(fs_type, "socket:", &sockfs_ops, SOCKFS_MAGIC, mnt);
4 }
}
 static int sockfs_get_sb(struct file_system_type *fs_type,int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,struct vfsmount *mnt)
static int sockfs_get_sb(struct file_system_type *fs_type,int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,struct vfsmount *mnt)2
 {
{3
 return get_sb_pseudo(fs_type, "socket:", &sockfs_ops, SOCKFS_MAGIC, mnt);
return get_sb_pseudo(fs_type, "socket:", &sockfs_ops, SOCKFS_MAGIC, mnt);4
 }
}sockfs_ops定義在net/socket.c中。
1 static const struct super_operations sockfs_ops = {
static const struct super_operations sockfs_ops = {
2 .alloc_inode = sock_alloc_inode,
.alloc_inode = sock_alloc_inode,
3 .destroy_inode = sock_destroy_inode,
.destroy_inode = sock_destroy_inode,
4 .statfs = simple_statfs,
.statfs = simple_statfs,
5 };
};
 static const struct super_operations sockfs_ops = {
static const struct super_operations sockfs_ops = {2
 .alloc_inode = sock_alloc_inode,
.alloc_inode = sock_alloc_inode,3
 .destroy_inode = sock_destroy_inode,
.destroy_inode = sock_destroy_inode,4
 .statfs = simple_statfs,
.statfs = simple_statfs,5
 };
};裝載sockfs
由kern_mount函數實現裝載一個偽文件系統(當然,它沒有裝載點),返回一個static vfsmount對象sock_mnt。
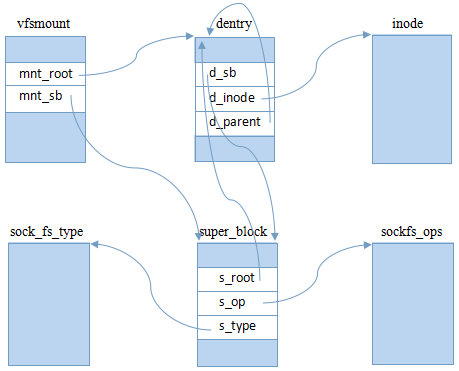
經過以上步驟后,所創建的VFS對象關系如下圖:
對于根目錄項,不用進行路徑轉換,因此dentry的d_op為空(未畫出);對于偽文件系統,操作索引對象沒有意義,所以inode的i_op為空(未畫出)。
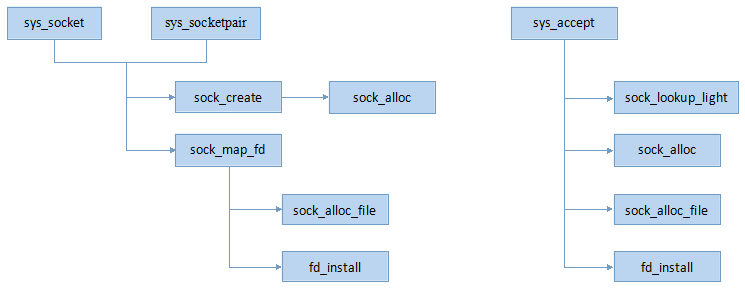
Socket創建
系統調用socket、accept和socketpair是用戶空間創建socket的幾種方法,其核心調用鏈如下圖:
構造inode
由sock_alloc函數實現,定義在net/socket.c中。
1 static struct socket *sock_alloc(void)
static struct socket *sock_alloc(void)
2 {
{
3 struct inode *inode;
struct inode *inode;
4 struct socket *sock;
struct socket *sock;
5
6 inode = new_inode(sock_mnt->mnt_sb);
inode = new_inode(sock_mnt->mnt_sb);
7

8 sock = SOCKET_I(inode);
sock = SOCKET_I(inode);
9

10 inode->i_mode = S_IFSOCK | S_IRWXUGO;
inode->i_mode = S_IFSOCK | S_IRWXUGO;
11 inode->i_uid = current_fsuid();
inode->i_uid = current_fsuid();
12 inode->i_gid = current_fsgid();
inode->i_gid = current_fsgid();
13

14 return sock;
return sock;
15 }
}
 static struct socket *sock_alloc(void)
static struct socket *sock_alloc(void)2
 {
{3
 struct inode *inode;
struct inode *inode;4
 struct socket *sock;
struct socket *sock;5

6
 inode = new_inode(sock_mnt->mnt_sb);
inode = new_inode(sock_mnt->mnt_sb);7


8
 sock = SOCKET_I(inode);
sock = SOCKET_I(inode);9


10
 inode->i_mode = S_IFSOCK | S_IRWXUGO;
inode->i_mode = S_IFSOCK | S_IRWXUGO;11
 inode->i_uid = current_fsuid();
inode->i_uid = current_fsuid();12
 inode->i_gid = current_fsgid();
inode->i_gid = current_fsgid();13


14
 return sock;
return sock;15
 }
}構造file
有了inode對象后,接下來就要構造對應的file對象了,由sock_alloc_file實現,定義在net/socket.c中。
1 static int sock_alloc_file(struct socket *sock, struct file **f, int flags)
static int sock_alloc_file(struct socket *sock, struct file **f, int flags)
2 {
{
3 struct qstr name = { .name = "" };
struct qstr name = { .name = "" };
4 struct path path;
struct path path;
5 struct file *file;
struct file *file;
6 int fd;
int fd;
7
8 fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
9

10 path.dentry = d_alloc(sock_mnt->mnt_sb->s_root, &name);
path.dentry = d_alloc(sock_mnt->mnt_sb->s_root, &name);
11

12 path.mnt = mntget(sock_mnt);
path.mnt = mntget(sock_mnt);
13
14 path.dentry->d_op = &sockfs_dentry_operations;
path.dentry->d_op = &sockfs_dentry_operations;
15 d_instantiate(path.dentry, SOCK_INODE(sock));
d_instantiate(path.dentry, SOCK_INODE(sock));
16 SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_fop = &socket_file_ops;
SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_fop = &socket_file_ops;
17
18 file = alloc_file(&path, FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE, &socket_file_ops);
file = alloc_file(&path, FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE, &socket_file_ops);
19

20 sock->file = file;
sock->file = file;
21 file->f_flags = O_RDWR | (flags & O_NONBLOCK);
file->f_flags = O_RDWR | (flags & O_NONBLOCK);
22 file->f_pos = 0;
file->f_pos = 0;
23 file->private_data = sock;
file->private_data = sock;
24
25 *f = file;
*f = file;
26 return fd;
return fd;
27 }
}
 static int sock_alloc_file(struct socket *sock, struct file **f, int flags)
static int sock_alloc_file(struct socket *sock, struct file **f, int flags)2
 {
{3
 struct qstr name = { .name = "" };
struct qstr name = { .name = "" };4
 struct path path;
struct path path;5
 struct file *file;
struct file *file;6
 int fd;
int fd;7

8
 fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);9


10
 path.dentry = d_alloc(sock_mnt->mnt_sb->s_root, &name);
path.dentry = d_alloc(sock_mnt->mnt_sb->s_root, &name);11


12
 path.mnt = mntget(sock_mnt);
path.mnt = mntget(sock_mnt);13

14
 path.dentry->d_op = &sockfs_dentry_operations;
path.dentry->d_op = &sockfs_dentry_operations;15
 d_instantiate(path.dentry, SOCK_INODE(sock));
d_instantiate(path.dentry, SOCK_INODE(sock));16
 SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_fop = &socket_file_ops;
SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_fop = &socket_file_ops;17

18
 file = alloc_file(&path, FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE, &socket_file_ops);
file = alloc_file(&path, FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE, &socket_file_ops);19


20
 sock->file = file;
sock->file = file;21
 file->f_flags = O_RDWR | (flags & O_NONBLOCK);
file->f_flags = O_RDWR | (flags & O_NONBLOCK);22
 file->f_pos = 0;
file->f_pos = 0;23
 file->private_data = sock;
file->private_data = sock;24

25
 *f = file;
*f = file;26
 return fd;
return fd;27
 }
}1)得到空閑的文件描述符fd,實際上就是fd數組的索引,準備作為返回值。
2)先初始化路徑path:其目錄項的父目錄項為超級塊對應的根目錄,名稱為空,操作對象為sockfs_dentry_operations,對應的索引節點對象為sock套接字關聯的索引節點對象,即SOCK_INODE(sock);裝載點為sock_mnt。
sockfs_dentry_operations定義在net/socket.c中。
1 static const struct dentry_operations sockfs_dentry_operations = {
static const struct dentry_operations sockfs_dentry_operations = {
2 .d_dname = sockfs_dname,
.d_dname = sockfs_dname,
3 };
};
 static const struct dentry_operations sockfs_dentry_operations = {
static const struct dentry_operations sockfs_dentry_operations = {2
 .d_dname = sockfs_dname,
.d_dname = sockfs_dname,3
 };
};3)設置索引節點的文件操作對象為socket_file_ops,定義在net/socket.c中。
1 static const struct file_operations socket_file_ops = {
static const struct file_operations socket_file_ops = {
2

3 .aio_read = sock_aio_read,
.aio_read = sock_aio_read,
4 .aio_write = sock_aio_write,
.aio_write = sock_aio_write,
5

6 .open = sock_no_open, /* special open code to disallow open via /proc */
.open = sock_no_open, /* special open code to disallow open via /proc */
7 .release = sock_close,
.release = sock_close,
8

9 };
};
 static const struct file_operations socket_file_ops = {
static const struct file_operations socket_file_ops = {2


3
 .aio_read = sock_aio_read,
.aio_read = sock_aio_read,4
 .aio_write = sock_aio_write,
.aio_write = sock_aio_write,5


6
 .open = sock_no_open, /* special open code to disallow open via /proc */
.open = sock_no_open, /* special open code to disallow open via /proc */7
 .release = sock_close,
.release = sock_close,8


9
 };
};5)建立file與socket的一一映射關系。
安裝file
由fd_install實現,定義在fs/open.c中。
1 void fd_install(unsigned int fd, struct file *file)
void fd_install(unsigned int fd, struct file *file)
2 {
{
3 struct files_struct *files = current->files;
struct files_struct *files = current->files;
4 struct fdtable *fdt;
struct fdtable *fdt;
5 spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
6 fdt = files_fdtable(files);
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
7 BUG_ON(fdt->fd[fd] != NULL);
BUG_ON(fdt->fd[fd] != NULL);
8 rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file);
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file);
9 spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
10 }
}
 void fd_install(unsigned int fd, struct file *file)
void fd_install(unsigned int fd, struct file *file)2
 {
{3
 struct files_struct *files = current->files;
struct files_struct *files = current->files;4
 struct fdtable *fdt;
struct fdtable *fdt;5
 spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);6
 fdt = files_fdtable(files);
fdt = files_fdtable(files);7
 BUG_ON(fdt->fd[fd] != NULL);
BUG_ON(fdt->fd[fd] != NULL);8
 rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file);
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file);9
 spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);10
 }
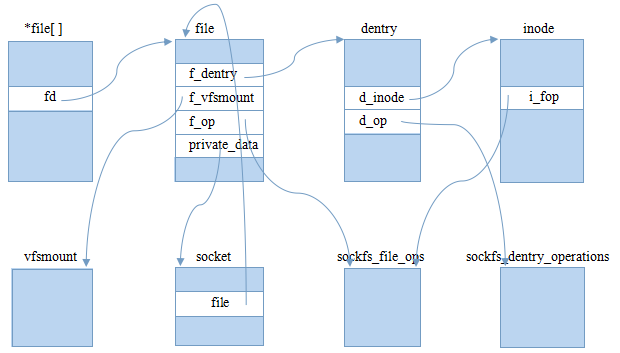
}經過以上過程后,所創建的VFS對象關系圖如下




 .open
.open 

