|
|
|
發新文章 |
|
 | |

http://bbs.sciencenet.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=484653&do=blog&id=442300產生式模型(Generative Model)與判別式模型(Discrimitive Model)是分類器常遇到的概念,它們的區別在于: 對于輸入x,類別標簽y: 產生式模型估計它們的聯合概率分布P(x,y) 判別式模型估計條件概率分布P(y|x) 產生式模型可以根據貝葉斯公式得到判別式模型,但反過來不行。 Andrew Ng在NIPS2001年有一篇專門比較判別模型和產生式模型的文章: On Discrimitive vs. Generative classifiers: A comparision of logistic regression and naive Bayes ( http://robotics.stanford.edu/~ang/papers/nips01-discriminativegenerative.pdf) http://blog.sciencenet.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=248173&do=blog&id=227964
【摘要】
- 生成模型:無窮樣本==》概率密度模型 = 產生模型==》預測
- 判別模型:有限樣本==》判別函數 = 預測模型==》預測
【簡介】
簡單的說,假設o是觀察值,q是模型。
如果對P(o|q)建模,就是Generative模型。其基本思想是首先建立樣本的概率密度模型,再利用模型進行推理預測。要求已知樣本無窮或盡可能的大限制。
這種方法一般建立在統計力學和bayes理論的基礎之上。
如果對條件概率(后驗概率) P(q|o)建模,就是Discrminative模型。基本思想是有限樣本條件下建立判別函數,不考慮樣本的產生模型,直接研究預測模型。代表性理論為統計學習理論。
這兩種方法目前交叉較多。
【判別模型Discriminative Model】——inter-class probabilistic description
又可以稱為條件模型,或條件概率模型。估計的是條件概率分布(conditional distribution), p(class|context)。
利用正負例和分類標簽,focus在判別模型的邊緣分布。目標函數直接對應于分類準確率。
- 主要特點:
尋找不同類別之間的最優分類面,反映的是異類數據之間的差異。
- 優點:
分類邊界更靈活,比使用純概率方法或生產模型得到的更高級。
能清晰的分辨出多類或某一類與其他類之間的差異特征
在聚類、viewpoint changes, partial occlusion and scale variations中的效果較好
適用于較多類別的識別
判別模型的性能比生成模型要簡單,比較容易學習
- 缺點:
不能反映訓練數據本身的特性。能力有限,可以告訴你的是1還是2,但沒有辦法把整個場景描述出來。
Lack elegance of generative: Priors, 結構, 不確定性
Alternative notions of penalty functions, regularization, 核函數
黑盒操作: 變量間的關系不清楚,不可視
- 常見的主要有:
logistic regression
SVMs
traditional neural networks
Nearest neighbor
Conditional random fields(CRF): 目前最新提出的熱門模型,從NLP領域產生的,正在向ASR和CV上發展。
- 主要應用:
Image and document classification
Biosequence analysis
Time series prediction
【生成模型Generative Model】——intra-class probabilistic description
又叫產生式模型。估計的是聯合概率分布(joint probability distribution),p(class, context)=p(class|context)*p(context)。
用于隨機生成的觀察值建模,特別是在給定某些隱藏參數情況下。在機器學習中,或用于直接對數據建模(用概率密度函數對觀察到的draw建模),或作為生成條件概率密度函數的中間步驟。通過使用貝葉斯rule可以從生成模型中得到條件分布。
如果觀察到的數據是完全由生成模型所生成的,那么就可以fitting生成模型的參數,從而僅可能的增加數據相似度。但數據很少能由生成模型完全得到,所以比較準確的方式是直接對條件密度函數建模,即使用分類或回歸分析。
與描述模型的不同是,描述模型中所有變量都是直接測量得到。
- 主要特點:
一般主要是對后驗概率建模,從統計的角度表示數據的分布情況,能夠反映同類數據本身的相似度。
只關注自己的inclass本身(即點左下角區域內的概率),不關心到底 decision boundary在哪。
- 優點:
實際上帶的信息要比判別模型豐富,
研究單類問題比判別模型靈活性強
模型可以通過增量學習得到
能用于數據不完整(missing data)情況
modular construction of composed solutions to complex problems
prior knowledge can be easily taken into account
robust to partial occlusion and viewpoint changes
can tolerate significant intra-class variation of object appearance
- 缺點:
tend to produce a significant number of false positives. This is particularly true for object classes which share a high visual similarity such as horses and cows
學習和計算過程比較復雜
- 常見的主要有:
Gaussians, Naive Bayes, Mixtures of multinomials
Mixtures of Gaussians, Mixtures of experts, HMMs
Sigmoidal belief networks, Bayesian networks
Markov random fields
所列舉的Generative model也可以用disriminative方法來訓練,比如GMM或HMM,訓練的方法有EBW(Extended Baum Welch),或最近Fei Sha提出的Large Margin方法。
- 主要應用:
NLP:
Traditional rule-based or Boolean logic systems (Dialog and Lexis-Nexis) are giving way to statistical approaches (Markov models and stochastic context grammars)
Medical Diagnosis:
QMR knowledge base, initially a heuristic expert systems for reasoning about diseases and symptoms been augmented with decision theoretic formulation Genomics and Bioinformatics
Sequences represented as generative HMMs
【兩者之間的關系】
由生成模型可以得到判別模型,但由判別模型得不到生成模型。
Can performance of SVMs be combined elegantly with flexible Bayesian statistics?
Maximum Entropy Discrimination marries both methods: Solve over a distribution of parameters (a distribution over solutions)
【參考網址】
http://prfans.com/forum/viewthread.php?tid=80
http://hi.baidu.com/cat_ng/blog/item/5e59c3cea730270593457e1d.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generative_model
http://blog.csdn.net/yangleecool/archive/2009/04/05/4051029.aspx
==================
比較三種模型:HMMs and MRF and CRF
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4cdaefce010082rm.html
HMMs(隱馬爾科夫模型):
狀態序列不能直接被觀測到(hidden);
每一個觀測被認為是狀態序列的隨機函數;
狀態轉移矩陣是隨機函數,根據轉移概率矩陣來改變狀態。
HMMs與MRF的區別是只包含標號場變量,不包括觀測場變量。
MRF(馬爾科夫隨機場)
將圖像模擬成一個隨機變量組成的網格。
其中的每一個變量具有明確的對由其自身之外的隨機變量組成的近鄰的依賴性(馬爾科夫性)。
CRF(條件隨機場),又稱為馬爾可夫隨機域
一種用于標注和切分有序數據的條件概率模型。
從形式上來說CRF可以看做是一種無向圖模型,考察給定輸入序列的標注序列的條件概率。
在視覺問題的應用:
HMMs:圖像去噪、圖像紋理分割、模糊圖像復原、紋理圖像檢索、自動目標識別等
MRF: 圖像恢復、圖像分割、邊緣檢測、紋理分析、目標匹配和識別等
CRF: 目標檢測、識別、序列圖像中的目標分割
P.S.
標號場為隱隨機場,它描述像素的局部相關屬性,采用的模型應根據人們對圖像的結構與特征的認識程度,具有相當大的靈活性。
空域標號場的先驗模型主要有非因果馬爾可夫模型和因果馬爾可夫模型。
| 夏季用氣注意三關一開 |
| | 信息來源:合肥日報 日期:2011-8-3 | 本報訊 (胡娟 王倩) 記者從合肥燃氣集團了解到,近日,有市民反映燃氣灶接口處的軟管變形問題,對此燃氣集團工作人員及時上門幫助其更換了軟管。天氣炎熱,燃氣集團提醒市民注 意夏季用氣安全,使用燃氣時,人不要遠離,防止鍋中液體溢出,將火焰撲滅造成安全隱患。一旦發現險情,請及時撥打合肥燃氣集團藍焰熱線。
夏季炎熱的氣溫容易導致膠皮管老化,從接口脫落,造成漏氣,燃氣集團工作人員提醒市民最好每兩年更換一次膠管。天然氣膠管連接著灶具和燃氣管道,用戶一定要使用專用的橡膠燃氣膠管,不能用其他軟管替代。
同時,保持廚房通風十分重要。夏季居民開空調時,都習慣將窗戶關嚴實,一旦發生燃氣泄漏會很危險。“居民最好將廚房的窗戶打開,然后關上廚房的門,這樣既 可以起到室內密封的效果,又可以使廚房的空氣流通。”除此之外,平時使用完燃氣后,要注意“三關一開”,即關閉灶具開關、灶前閥和廚房門,打開廚房窗戶。 用戶還應該經常檢查天然氣器具和管道周圍有無堆放易燃、易爆物品。
此外,夏季也是裝修旺季,有些用戶為了美觀,在裝修時會選擇將燃氣立管包裹住,這樣既不能保證通風,出現問題也不便維修,用戶應該選擇能通風或者可拆卸的 方式進行處理。同時,根據《城鎮燃氣管理條例》規定,用戶不得擅自安裝、改裝、拆卸室內管道燃氣設施或者進行危害室內管道燃氣設施安全的裝飾、裝修等活 動。 |
原來看的子空間學習論文均是PCA/LDA+NN,即最近鄰,其實分類器也能用SVM。即PCA/LDA+SVM,見馬毅論文SRC的Fig 8(d),PCA/LDA屬于模式識別系統的特征抽取步驟,SVM屬于分類步驟,兩者是獨立開來的,可以任意組合。
調研記錄
Feiping Nie and Shiming Xiang(20130903),將他們的論文2009-2013的標題都看了,不必再調研。最新的論文分別是 Efficient Image Classification via Multiple Rank Regression
和Nonparametric Illumination Correction have seen, no need to see again
Robust Classification via Structured Sparse Representation (CVPR 2011) Patch alignment need to see:
非傳統人臉識別
Coupled Discriminant Analysis for Heterogeneous Face Recognition Discriminative Multimanifold Analysis for Face Recognition from a Single Training Sample per Person (TPAMI 2013 Feature article)
A General Iterative Shrinkage and Thresholding Algorithm for(ICML 13,有code) Similarity Component Analysis Unsupervised and Semi-Supervised Learning via ℓ1-Norm Graph (Feiping Nie,有code) Local Structure-based Image Decomposition for Feature Extraction with Applications to Face Recognition (TIP) Sparse representation classifier steered discriminant projections (TNNLS 2013) Tumor Classi?cation Based on Non-Negative Matrix(chunhou zheng) L-2,1-Norm Regularized Discriminative Feature Selection for Unsupervised Learning(IJCAI,有code) Towards structural sparsity An explicit l2 l0 approach (主要看下該文Lipchitz輔助函數怎么用的,Chris Ding的講稿"sparseBeijing_Christ Ding"第28頁ppt提到了) Manifold Adaptive Experimental Design for Text Categorization Deng Cai(TKDE 2012,有code) Sparse concept coding for visual analysis (CVPR 2011,有code) A nove lSVM+NDA (Pattern recognition)
ICDM 2010 L2/L0-norm,包括Chris Ding的講稿 (2011) R. Jenatton, J.-Y. Audibert and F. Bach. Structured Variable Selection with Sparsity-Inducing Norms. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12(Oct):2777-2824. ( 20120312開始的一周
和libing 計劃將這篇論文看完)Robust Sparse Coding for Face Recognition (discuss with libing, he said he has understood totally) Feature selection Linear Discriminant Dimensionality Reduction(ECML 2011) Generalized Fisher Score for Feature Selection(UAI 2011) 有空再看的論文:Extreme Learning Machine for Regression and Multiclass Classi?cation(TSMCB 2012) gains:
1、know how to derive formula (13) in SRC (Sparse representation classifier(稀疏表示分類器), Yi Ma, TPAMI 2009); know how to derive formula (14) in “Efficient and Robust Feature Selection via Joint L2,1-Norms Minimization (NIPS 2010)”. The key points are formulas (16) and (17).
2、know how to derive from formulas (10) to (12) in "R1-PCA Rotational invariant L1-norm principal component analysis for robust subspace factorization (ICML 2006)"
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/cc9b4308bb68a98271fefa6f.html (Matlab北航教程) CH 7.6 函數句柄
函數句柄是matlab的一個數據類型,保存函數的路徑、視野、函數名及重載方式等。
使用函數句柄的優點
1.使一些泛函指令工作更可靠
2.使函數調用象變量引用一樣方便
3.可獲得同名重載函數的信息
4.可在更大范圍內調用各種函數,提高軟件的重用性
5.提高函數調用速度。 一、函數句柄的創建與觀察
1.創建
handlef=@fname;
handlef=str2func(‘fname’)
例如:fhandle = @sin;
sin是matlab中自帶的正弦函數,得到的輸出變量fhandle為sin函數的句柄。可以利用fhandle來調用sin函數,例如下面的代碼:
fhandle(0)
上面語句得到的輸出代碼如下:
ans = 0
實際上,該程序中的語句fhandle(0)相當于語句sin(0)。
二、函數句柄的應用
[out1,ou2,…]=fname(in1,in2,…)
也可通過函數句柄來完成函數運算:
[out1,ou2,…]= handlef(in1,in2,…)
[out1,ou2,…]=feval(handlef,in1,in2,…) http://www.ilovematlab.cn/thread-23048-1-1.html matlab 函數句柄@的介紹_什么是函數句柄 覺得自己很少用函數句柄,但是經常遇到,所以在這里總結一下。
函數句柄:是包含了函數的路徑、函數名、類型以及可能存在的重載方法。
函數句柄必須通過專門的定義創建的,而一般的圖像的句柄是自動建立的。
創建函數句柄使用@或者str2func命令創建
執行sin函數 feval
feval('sin',pi/2) %查matlab幫助 feval 既可以,可以不必關心這個函數的使用
ans =
1
那么使用函數句柄有什么好處呢?
1、提高運行速度。因為matlab對函數的調用每次都是要搜索所有的路徑,從set path中我們可以看到,路徑是非常的多的,所以如果一個函數在你的程序中需要經常用到的話,使用函數句柄,對你的速度會有提高的。
2、使用可以與變量一樣方便。比如說,我再這個目錄運行后,創建了本目錄的一個函數句柄,當我轉到其他的目錄下的時候,創建的函數句柄還是可以直接調用的,而不需要把那個函數文件拷貝過來。因為你創建的function handles中,已經包含了路徑,比如說我創建了一個fun
h_fun=str2func('rei');
可以用functions來查看這個function,結果果然已經包括了路徑。
functions(h_fun)
ans =
function: 'rei'
type: 'simple'
file: 'G:\program\serial232\rei.m'
Past conference | Conference | Deadline of Paper Submission | Notation Acceptance | | CVPR 2012 | Nov. 21, 2011 | March 2, 2012 | | ICML 2012 | February 24, 2012 | April 30, 2012 | | IJCAI 2011 (once two years) | | | | AAAI 2012 | | March 28, 2012 | | | | | | ICPR 2012 | Mar. 31, 2012 | Jun. 15, 2012 | | ECML 2012 | Abstract deadline: Thu 19 April 2012; Paper deadline: Mon 23 April 2012 | Early author: Mon 28 May 2012; Author notification: Fri 15 June 2012 | | NIPS 2012 | June 1, 2012 | | Recent conference | Conference | Deadline of Paper Submission | Notation Acceptance | | NIPS 2013 | | | | IJCAI 2013 (once two years) | Abstract submission: January 26, 2013 (11:59PM, UTC-12). Paper submission: January 31, 2013 (11:59PM, UTC-12). | | | AAAI 2013 (once a year) | - December 3, 2012 – January 19, 2013: Authors register on the AAAI web site
- January 19, 2013 (11:59 PM PST): Electronic abstracts due
- January 22, 2013 (11:59 PM PST): Electronic papers due
| | | ICML 2013 | | | | CVPR 2013 | November 15, 2012 | | Some Website: NIPS 2012: https://cmt.research.microsoft.com/NIPS2012/
------------------------------------https://sites.google.com/site/feipingnie/resource ------------------------------------
focus jounals: TPAMI, TNN, TIP, TKDE, TCSVT, TMM, TSMC, TIFS, JMLR, Neural Computation, IJCV, PR, PRL, Neurocomputing focus conferences: NIPS, ICML, AIStat, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV, IJCAI, AAAI, KDD, SIGIR, ACMMM, ECML, ICDM, SDM, CIKM, ICIP, ICPR, ACCV conferences Conf. deadline NIPS June 8, 2007 SIGMM June 2, 2007 ICDM June 1, 2007 ACCV April 27, 2007 ICCV April 10, 2007 KDD February 28th, 2007 ICML February 9, 2007 AAAI February 6, 2007 IJCNN January 31, 2007 SIGIR January 28, 2007 ICIP January 19, 2007 ICME January 5, 2007 CVPR December 3, 2006
(1) 2011年CVPR Longuet-Higgins Prize(獎勵在CVPR領域經典的文章):
- Paul A. Viola and Michael J. Jones, "Rapid Object Detection using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features", CVPR 2001.[該文在google sholar已經引用5187次 ]
Code of feature selection: http://featureselection.asu.edu/software.php; Rongxiang Hu采用的是孫即祥老師模式識別教材P235的"增添特征法",他感覺效果比較不錯。他的判據:分類準確率;第一個特征可以隨機選擇,他的選擇方法:選擇單獨最好的那個特征. 基于score的方法應該都屬于Filter方法,比如Fisher Score和Laplacian Score,因為這些方法都是對每個特征直接計算一個分數,沒有依賴于特定的學習方法。
http://www.postech.ac.kr/~seungjin/submitted.html
Recenlty Done
-
Minje Kim, Jiho Yoo, Kyeongok Kang, and Seungjin Choi (2010),
"Nonnegative matrix partial co-factorization for spectral and temporal drum source separation,"
submitted to IEEE JSTSP, September 30, 2010.
( "major revision in 4 weeks," December 21, 2010 )
( "revised," February 3, 2011 )
( "accepted," May 12, 2011 )
(ETRI=1/2, CMEST=1/2, WCU)
- Shounan An, Jiho Yoo, and Seungjin Choi (2010),
"Manifold-respecting discriminant nonnegative matrix factorization,"
submitted to Pattern Recognition Letters, April 10, 2010.
( "major revision in 4 months," October 13, 2010 )
( "revised," January 10, 2011 )
( "accepted," January 20, 2011 )
(MTF=1/4, CMEST=1/4, VIEW=1/4, CoSDEC=1/4, WCU)
- Yongsoo Kim, Taek-Kyun Kim, Yungu Kim, Jiho Yoo, Sung Yong Yoo,
Seungjin Choi, and Daehee Hwang (2010),
"Principal network analysis: Identification of subnetworks representing
major dynamics using gene expression data,"
submitted to Bioinformatics, September 8, 2010.
( "major revision in 4 months," October 5, 2010 )
( "revised," November 12, 2010 )
( "accepted," December 1, 2010 )
(NCRC=1/4, CORE=1/4, WCU)
- Jong Kyoung Kim and Seungjin Choi (2009),
"Probabilistic models for semi-supervised discriminative motif discovery in DNA sequences,"
submitted to IEEE/ACM TCBB, July 15, 2009.
( "major revision in 3 months," October 4, 2009 )
( "revised," October 30, 2009 )
( "minor revision by March 20, 2010," December 22, 2009 )
( "revised," January 2, 2010 )
( "accepted," January 29, 2010 )
(NCRC=1, WCU)
- Jiho Yoo and Seungjin Choi (2008),
"Orthogonal nonnegative matrix tri-factorization for co-clustering:
Multiplicative updates on Stiefel manifolds,"
submitted to Information Processing and Management, September 15, 2008.
( "major revision, " June 18, 2009 )
( "revised," August 20, 2009 )
( "accept with minor revisions," December 9, 2009 )
( "revised," December 21, 2009 )
( "accepted," December 27, 2009 )
(MTF=1/2, CMEST=1/2, WCU, MSRA)
- Hyekyoung Lee, Jiho Yoo, and Seungjin Choi (2009),
"Semi-supervised nonnegative matrix factorization,"
submitted to IEEE Signal Processing Letters, April 28, 2009
( "accept with mandatory minor revisions," June 9, 2009 )
( "revised," June 13, 2009 )
( "accepted," June 16, 2009 )
(MTF=1/3, CMEST=1/3, VIEW=1/3, WCU, MSRA)
- Young Min Oh, Jong Kyoung Kim, Yongwook Choi, Seungjin Choi, and Joo-Yeon Yoo (2008),
"Prediction and experimental validation of novel STAT3 target genes in human cancer cells,"
submitted to PLoS ONE, April 3, 2009.
( "revised," July 4, 2009 )
( "minor-revised," July 20, 2009 )
( "accepted," August 4, 2009 )
(NCRC=1, WCU)
- Hyohyeong Kang, Yunjun Nam, and Seungjin Choi (2009),
"Composite common spatial pattern for subject-to-subject transfer,"
submitted to IEEE Signal Processing Letters, February 20, 2009.
( "accept with mandatory minor revisions," March 18, 2009 )
( "revised," April 9, 2009 )
( "accepted," Apirl 11, 2009 )
(NCRC=1, WCU)
- Hyekyoung Lee, Andrzej Cichocki, and Seungjin Choi (2008),
"Kernel nonnegative matrix factorization for spectral EEG feature extraction,"
submitted to Neurocomputing, June 25, 2008.
( "accept with minor revision," February 7, 2009 )
( "revised," February 18, 2009 )
( "accepted," March 8, 2009 )
(SAFE=1/2, NCRC=1/2)
- Hyekyoung Lee and Seungjin Choi (2008),
"Group nonnegative matrix factorization for EEG classification,"
submitted to AISTATS-2009, November 1, 2008.
(Notification of acceptance, January 9, 2009)
( "accepted for poster presentation," January 9, 2009 )
(NCRC=1/2, SAFE=1/2)
- Seunghak Lee and Seungjin Choi (2008),
"Landmark MDS ensemble,"
submitted to Pattern Recognition, March 30, 2008.
("reconsider, if revised," by September 14 )
("revised," August 5, 2008 )
( "reconsider, if revised," by October 24 )
( "2nd-revised," October 21, 2008 )
( "accept if revised," by December 20, 2008 )
( "3rd-revised," November 24, 2008 )
( "accepted," November 26, 2008 )
(CMEST=1/2, SAFE=1/2)
|



 是任何維的一般旋轉矩陣:
是任何維的一般旋轉矩陣: 

 這里的
這里的 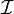 是單位矩陣。
是單位矩陣。 的一個
的一個