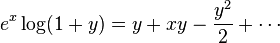http://cn.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/sylvester.html
‘alternating optimization’ or ‘alternative optimization’?
Sue (UTS) comment: ‘Alternating’ means you use this optimization with another optimization, one after the other. ‘Alternative’ means you use this optimization instead of any other.
цчGSM-PAFцхчЈч?/span>‘alternating optimization’
Taylor series in several variables
The Taylor series may also be generalized to functions of more than one variable with
For example, for a function that depends on two variables, x and y, the Taylor series to second order about the point (a, b) is:
where the subscripts denote the respective partial derivatives.
A second-order Taylor series expansion of a scalar-valued function of more than one variable can be written compactly as
where 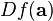 is the gradient of
is the gradient of 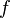 evaluated at
evaluated at 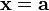 and
and  is the Hessian matrix. Applying the multi-index notation the Taylor series for several variables becomes
is the Hessian matrix. Applying the multi-index notation the Taylor series for several variables becomes
which is to be understood as a still more abbreviated multi-index version of the first equation of this paragraph, again in full analogy to the single variable case.
[edit]Example
Compute a second-order Taylor series expansion around point  of a function
of a function
Firstly, we compute all partial derivatives we need
The Taylor series is
which in this case becomes
Since log(1 + y) is analytic in |y| < 1, we have
for |y| < 1.
If λ1 and λ2 are two arbitrary nonnegative real numbers such that λ1 + λ2 = 1 then convexity of  implies
implies
 [qхАБцЏхИхНцАчхЎфЙ]
[qхАБцЏхИхНцАчхЎфЙ]
This can be easily generalized: if λ1, λ2, ..., λn are nonnegative real numbers such that λ1 + ... + λn = 1, then
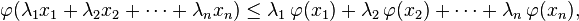
фОхІ-log(x)цЏхИхНцА
http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%9C%80%E9%80%9F%E4%B8%8B%E9%99%8D%E6%B3%95
Gradient descent is based on the observation that if the multivariable function
 is defined and differentiable in a neighborhood of a point
is defined and differentiable in a neighborhood of a point 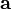 , then
, then  decreases fastest if one goes from
decreases fastest if one goes from 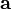 in the direction of the negative gradient of
in the direction of the negative gradient of  at
at 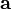 ,
, 
фИКхЅцЅщПшІххяМTianyiчшЇЃщхОхЅНяМхІццЅщПqхЄЇхQхЏшНфЩхОхНцАхщgИхяМц шІххАцЅщП (фИщЂqфИЊхЁцЏхЈОUцИчеdЅНхQчЖхscanч?у?br />Andrew NGчcourseraшЏЁЈMachine learningч?span style="text-align: justify; text-transform: none; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; letter-spacing: normal; display: inline !important; font: 13px/18px Verdana, Helvetica, Arial; white-space: normal; float: none; color: rgb(94,94,94); word-spacing: 0px; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">II. Linear Regression with One Variableч?span style="font-family: 'Calibri','sans-serif'; font-size: 10.5pt; mso-bidi-font-size: 11.0pt; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-fareast-font-family: хЎфН; mso-fareast-theme-font: minor-fareast; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-bidi; mso-ansi-language: EN-US; mso-fareast-language: ZH-CN; mso-bidi-language: AR-SA" lang="EN-US">Gradient descent IntuitionфИчшЇЃщхОхЅНхQцЏхІхЈфИхОхЈхГфОЇччЙяМхцЂЏхКІцЏцЃцАхQ?font size="2" face="Arial">
 цЏшДцЭМхГфЩхНхчaххА
цЏшДцЭМхГфЩхНхчaххА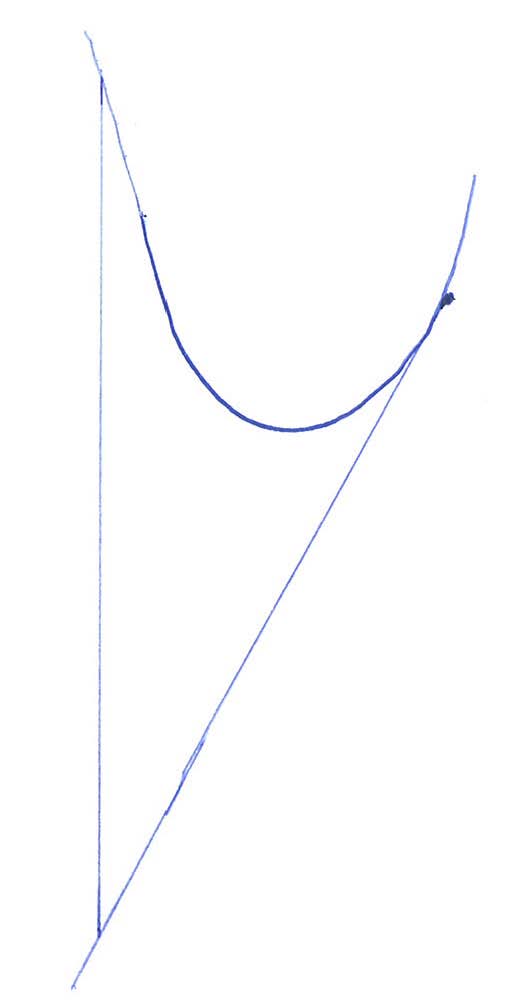
цшЊхЗБщЂхЄчцшяМхІццЏхИхНцАхQхЏЙшЊхщцБххЏМфИ?хQчЖххАшЊхщцБхКцЅфИхАБшЁфКхяМфИКхЅqшІцЂЏхКІфИщхQфИqюCОфКцЏфИшЁчяМх фихЏЙMцБхЏМхфИMц х ГфКухtianyiшЎЈшЎКхQцЃх фицБхЏМфИ? цВЁцшЇЃцшЇЃщчЈцЂЏхКІфИщяМцшЇЃцшЇЃЎоqЛцфК
1. цЂЏхКІфИщцГ?/strong>
цЂЏхКІфИщцГчхчхЏфЛЅхшяМцЏхІМцКхЈхІфЙ чЌЌфИшЎ?/a>у?/span>
цхЎщЊцчЈчцАцЎц?00фИЊфКОlДчЙу?/span>
хІццЂЏхКІфИщНцГфИшНцЃхИИqшЁхQшшфНПчЈцДхАчцЅщ?фЙхАБцЏхІфЙ ч)хQшПщщшІцГЈцфИЄчЙяМ
1хQхЏЙфКшіхЄхАч? шНфПшЏхЈцЏфИцЅщНххАхQ?/span>
2хQфНцЏхІцхЄЊЎяМцЂЏхКІфИщНцГцЖцчфМхОц
ЂхQ?/span>
цШЛхQ?/span>
1хQхІцхЄЊЎяМЎзМцЖцхОц
ЂхQ?/span>
2хQхІцхЄЊхЄЇяМЎзИшНфПшЏцЏфИЦЁшPфЛЃщНххАхQфЙЎзИшНфПшЏцЖцяМ
хІфНщцЉ-ОlщЊчцЙцГяМ
..., 0.001, 0.003, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1...
ОU?хфКхфИфИЊцАу?/span>
matlabцКч хQ?/span>
- function [theta0,theta1]=Gradient_descent(X,Y);
- theta0=0;
- theta1=0;
- t0=0;
- t1=0;
- while(1)
- for i=1:1:100 %100фИЊчЙ
- t0=t0+(theta0+theta1*X(i,1)-Y(i,1))*1;
- t1=t1+(theta0+theta1*X(i,1)-Y(i,1))*X(i,1);
- end
- old_theta0=theta0;
- old_theta1=theta1;
- theta0=theta0-0.000001*t0 %0.000001шЁЈчЄКхІфЙ ч?nbsp;
- theta1=theta1-0.000001*t1
- t0=0;
- t1=0;
- if(sqrt((old_theta0-theta0)^2+(old_theta1-theta1)^2)<0.000001) % qщцЏхЄццЖцчцЁфgхQхНчЖхЏфЛЅцх ЖфЛцвГцЅх
- break;
- end
- end
2. щцКцЂЏхКІфИщцГ?/strong>
щцКцЂЏхКІфИщцГщчЈфКц ЗцЌчЙцАщщхИИхКхЄЇчц хЕяМНцГфНПхОцжMНхчцЂЏхКІфИщхПЋчцЙхфИщу?/span>
matlabцКч хQ?/span>
- function [theta0,theta1]=Gradient_descent_rand(X,Y);
- theta0=0;
- theta1=0;
- t0=theta0;
- t1=theta1;
- for i=1:1:100
- t0=theta0-0.01*(theta0+theta1*X(i,1)-Y(i,1))*1
- t1=theta1-0.01*(theta0+theta1*X(i,1)-Y(i,1))*X(i,1)
- theta0=t0
- theta1=t1
- end
Newton-RaphsonНцГхЈчЛшЎЁфИђqПцГхКчЈфКцБшЇЃMLEчхцюCМАшЎЁу?/p>
хЏЙхКчххщхІфИхОяМ

хЄх хНцАНцГхQ?/p>

ExampleхQяМimplemented in RхQ?/p>
#хЎфЙхНцАf(x)
f=function(x){
1/x+1/(1-x)
}
#хЎфЙf_d1фИоZИщЖхЏМхНцА
f_d1=function(x){
-1/x^2+1/(x-1)^2
}
#хЎфЙf_d2фИоZКщЖхЏМхНцА
f_d2=function(x){
2/x^3-2/(x-1)^3
}
#NRНцГу
NR=function(time,init){
X=NULL
D1=NULL #хЈхXiфИщЖхЏМхНцАх?br />D2=NULL #хЈхXiфКщЖхЏМхНцАх?br /> count=0
X[1]=init
l=seq(0.02,0.98,0.0002)
plot(l,f(l),pch='.')
points(X[1],f(X[1]),pch=2,col=1)
for (i in 2:time){
D1[i-1]=f_d1(X[i-1])
D2[i-1]=f_d2(X[i-1])
X[i]=X[i-1]-1/(D2[i-1])*(D1[i-1]) #NRНцГqфЛЃхМ?br /> if (abs(D1[i-1])<0.05)break
points(X[i],f(X[i]),pch=2,col=i)
count=count+1
}
return(list(x=X,Deriviative_1=D,deriviative2=D2,count))
}
o=NR(30,0.9)
ОlцхІфИхОяМхОфИфИхщЂшВчфИшЇхХшЁЈчЄКiЦЁшPфЛЃфёччфМАшЎЁхМXi

o=NR(30,0.9)
#хІххНцАf(x)
f=function(x){
return(exp(3.5*cos(x))+4*sin(x))
}
f_d1=function(x){
return(-3.5*exp(3.5*cos(x))*sin(x)+4*cos(x))
}
f_d2=function(x){
return(-4*sin(x)+3.5^2*exp(3.5*cos(x))*(sin(x))^2-3.5*exp(3.5*cos(x))*cos(x))
}
хОхАОlцхІфИхQ?/p>

Reference from:
Kevin Quinn
Assistant Professor
Univ Washington
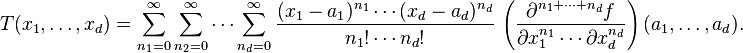
![\begin{align} f(x,y) & \approx f(a,b) +(x-a)\, f_x(a,b) +(y-b)\, f_y(a,b) \\ & {}\quad + \frac{1}{2!}\left[ (x-a)^2\,f_{xx}(a,b) + 2(x-a)(y-b)\,f_{xy}(a,b) +(y-b)^2\, f_{yy}(a,b) \right], \end{align}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/5/5/8/5587e7367ecb9029926201c9747966b2.png)


 around origin.
around origin.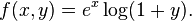
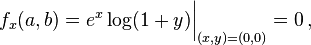

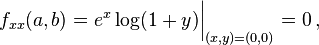


![\begin{align} T(x,y) = f(a,b) & +(x-a)\, f_x(a,b) +(y-b)\, f_y(a,b) \\ &+\frac{1}{2!}\left[ (x-a)^2\,f_{xx}(a,b) + 2(x-a)(y-b)\,f_{xy}(a,b) +(y-b)^2\, f_{yy}(a,b) \right]+ \cdots\,,\end{align}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/d/a/d/dad3055d4695f7e70e10c5e403a92112.png)
![\begin{align}T(x,y) &= 0 + 0(x-0) + 1(y-0) + \frac{1}{2}\Big[ 0(x-0)^2 + 2(x-0)(y-0) + (-1)(y-0)^2 \Big] + \cdots \\ &= y + xy - \frac{y^2}{2} + \cdots. \end{align}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/f/e/2/fe2770b7f29c8d32af5ca24d26b9cd99.png)