在MaNGOS-Zero中認證登錄服務器是已獨立的進程存在的,名字叫realmd,這樣命名可能是和游戲client端根目錄下的realmlist.wtf文件相對應。realmd的主要工作是:檢查登錄用戶的合法性,并在合法的情況下完成通信密鑰的交換,最后把游戲邏輯服務器的地址信息列表傳給client端。
realmd認證的基本流程如下:
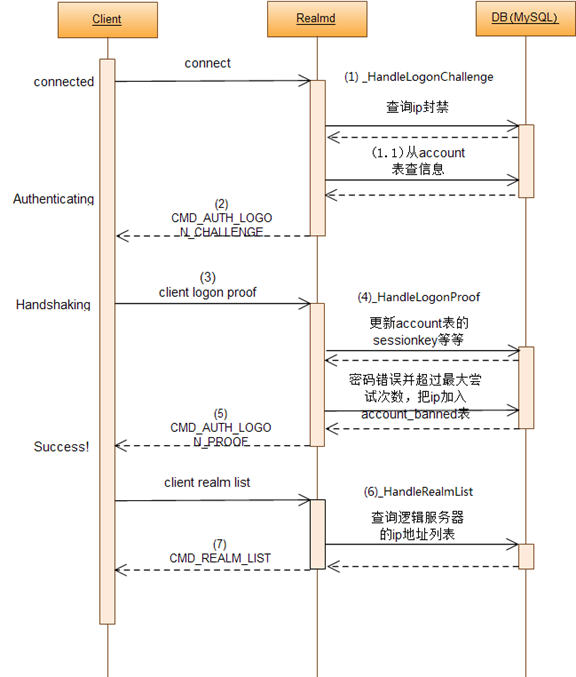
圖中的(1)~(7)詳細過程如下:
(1)Client啟動后立即嘗試連接realmlist.wtf文件中指定的認證服務器,就發送LogonChallenge給認證服務器realmd。協議結構如下:
1: typedef struct AUTH_LOGON_CHALLENGE_C
2: { 3: uint8 cmd; //Cmd is the command/operation code of the packet. Always 0 for this message
4: uint8 error;
5: uint16 size; //Size of the remaining part of the message
6: uint8 gamename[4]; //4 byte C-String, containing the String "WoW\0"
7: uint8 version1; //Major version number of the client ( 1 for 1.12.1 )
8: uint8 version2; //Minor version number of the client ( 12 for 1.12.1 )
9: uint8 version3; //Patchlevel version number of the client ( 1 for 1.12.1 )
10: uint16 build; //Build number of the client. ( 5875 for 1.12.1 )
11: uint8 platform[4]; //Platform the client is running on, reversed C-String ( "68x\0" for x86 )
12: uint8 os[4]; //OS the client is running on, reversed C-String ( "niW\0" for Windows )
13: uint8 country[4]; //Locale of the client, reversed C-String ( "SUne" for enUS )
14: uint32 timezone_bias;
15: uint32 ip; //IP address of the client in binary format
16: uint8 I_len; //Length of the Identity ( user name ) in characters
17: uint8 I[1]; //The Identity string ( user name )
18: } sAuthLogonChallenge_C;
uint8 I[1]是一個unsigned char的變長數組的頭指針,保存user name,服務器端保存的時候要把\0后面的東西去掉,防止SQL injection。(1.1)執行“SELECT sha_pass_hash,id,locked,last_ip,gmlevel,v,s FROM account WHERE username = '%s'”語句從數據庫中讀取數據。
realmd收到sAuthLogonChallenge_C協議后處理步驟如下:
1) 檢查該ip是否被封禁,如果是發送相應的錯誤
2) 查詢數據庫中是否有該賬戶,如果沒有返回相應的錯誤
3) 查看最后一次登錄ip與賬戶是否綁定,如果綁定對比當前ip與last_ip是否一致
4) 檢查該賬號是否被封禁,如果是發送相應的錯誤信息
5) 獲取用戶名密碼,開始SRP6計算,參見本文最下方的附錄《MaNGOS所使用的SRP6算法》
6) _accountSecurityLevel,保存用戶的權限等級,普通用戶、GM、admin等等
7) 本地化:根據_localizationName的名字找對應的.mpq文件所在的位置比如enUS,zhTW,zhCN
(2) realmd向client發送challenge,協議如下:
1: typedef struct
2: { 3: uint8 cmd; //Cmd is the command/operation code of the packet. Always 0 for this message.
4: uint8 error;
5: uint8 unk2; //random value
6: uint8 B[32]; //B is an SRP6 value. It is the server's public value.
7: uint8 g_len; //Length of the SRP6 g value we send the client in bytes. Always 1
8: uint8 g[1]; //The SRP6 g value we send the client. Always 7
9: uint8 N_len; //Lenght of the SRP6 N value we send the client. Always 32
10: uint8 N[32]; //The SRP6 N value we send the client.
11: uint8 s[32]; //The SRP6 s value
12: uint8 unk3[16]; //a randomly generated 16 byte value.
13: uint8 unk4; //a single byte 0.
14: } sAuthLogonChallenge_S;
(3)客戶端的Handshaking階段,client為了回應realmd的challenge消息,證明client的密碼和server上保存的密碼一致,需要計算M1值,并發送給realmd,發送的協議如下:
1: typedef struct AUTH_LOGON_PROOF_C
2: { 3: uint8 cmd; //Cmd is the command/operation code of the packet. Always 1 for this message
4: uint8 A[32]; //The client SRP6 A value ( public client value ).
5: uint8 M1[20]; //The client's SRP6 M value.待比較的最終值
6: uint8 crc_hash[20]; //doesn't seem to be used
7: uint8 number_of_keys; //It also seems to be always 0
8: uint8 securityFlags; // 0x00-0x04
9: } sAuthLogonProof_C;
計算公式如下,各個變量的含義請查看本文最下方的附錄《MaNGOS所使用的SRP6算法》
A = g^a mod N //a為19個字節的隨機數
B = (kv + g^b) mod N
u = H(A, B)
x = H(s, p)
S = (B - kg^x) ^ (a + ux)
K = H(S)
M = H(H(N) xor H(g), H(I), s, A, B, K)
上訴的哈希函數H都使用的是SHA1
(4)realmd收到client發來的Proof協議,(a)開始檢查版本是否允許,(b) 使用SRP6計算M值,與client傳過來的M1做對比,if (!memcmp(M.AsByteArray(), lp.M1, 20)) { } (c) 如果M值相等計算K —— 即sessionkey,并最終保存到數據庫。
(5)驗證成功,realmd向client發送server的logon proof
1: typedef struct AUTH_LOGON_PROOF_S
2: { 3: uint8 cmd;
4: uint8 error;
5: uint8 M2[20]; //The SRP6 M values,M = H(H(N) xor H(g), H(I), s, A, B, K)
6: uint32 unk1; // AccountFlags (trial 0x08, ProPass 0x800000, gm 0x01)
7: uint32 unk2; // SurveyId
8: uint16 unk3; // some flags (AccountMsgAvailable = 0x01)
9: } sAuthLogonProof_S;
(6)_HandleRealmList,查詢realmcharacters表獲得角色和realmid的對應關系,然后可以在RealmList類里通過realmid找到對應的表項,RealmList在初始化的時候再realmlist表里讀取數據放在內存里使用:“SELECT id, name, address, port, icon, realmflags, timezone, allowedSecurityLevel, population, realmbuilds FROM realmlist WHERE (realmflags & 1) = 0 ORDER BY name ” 查詢邏輯服務器。
(7)發送realmlist給客戶端,客戶端選擇對應的服務器后點擊enter world的時,會主動斷開和realmd的連接。
總結:整個登錄認證過程主要干了如下幾件事
(a)使用公鑰算法驗證client的合法性。
(b)client合法的情況下,計算sessionkey并保存在MySQL里,以備后面的邏輯服務器使用。
(c)驗證通過后,把邏輯服務器列表發給client。
其中最為重要的就是在驗證合法性、交換密鑰的過程中,如何在傳遞的協議里隱藏client的密鑰,使其在被截獲的情況下也無法被黑客解析,這就只能依仗密碼學了。WOW所使用的加密算法是SRP6,詳細的介紹如下:
附錄:MaNGOS所使用的SRP6算法
SRP全稱Secure Remote Password(安全遠程密碼).使用SRP的客戶機和服務器不會在網絡上傳送明文密碼,這樣可以消除直接密碼嗅探行為,另外使用高強度的算法保證了不可能使用字典法攻擊嗅探到的數據[1]。SRP協議的描述見 http://srp.stanford.edu/design.html
SRP6名詞解釋:
N - A large safe prime (N = 2q+1, where q is prime) All arithmetic is done modulo N.
g - A generator modulo N
k - Multiplier parameter (k = H(N, g) in SRP-6a, k = 3 for legacy SRP-6)
s - User's salt
I - Username
p - Cleartext Password
H() - One-way hash function
^ - (Modular) Exponentiation
u - Random scrambling parameter
a,b - Secret ephemeral values
A,B - Public ephemeral values
x - Private key (derived from p and s)
v - Password verifier
對應MaNGOS的計算方法和變量含義:
sha_pass_hash:使用這個函數進行Sha1Hash哈希std::string AccountMgr::CalculateShaPassHash(std::string& name, std::string& password)后得到的值。
N: A large safe prime (N = 2q+1, where q is prime), All arithmetic is done modulo N. 在MaNGOS里N被設成N.SetHexStr("894B645E89E1535BBDAD5B8B290650530801B18EBFBF5E8FAB3C82872A3E9BB7");
s: 32個字節的隨機數,算過一次后保存在數據庫里。
x: 計算v值使用到的x,即私鑰是s與數據庫里的sha_pass_hash的倒置的Sha1Hash
v: g^x mod N,驗證密碼時使用Password verifier,算過一次后保存在數據庫里。
g: g = 7
b: 為19個字節的隨機數,每次client連接認證的時候重新生成。
a: 19個字節的隨機數,由客戶端產生。
B: 公鑰, gmod = g^b, N , B = ((v * 3) + gmod) % N
K: 認證通過后最終保存到數據庫里的sessionkey,(1)計算A 客戶端公鑰A = g^a mod N a為19為隨機數,(2)計算x,x = sha(s, I),I = sha(“username : password”); (3)計算u,u = sha(A, B) //(服務公鑰,客戶公鑰);(4)計算S,S = (B - g^x*3)^(a+u*x); (5)計算K,S為32位,K為40位是 sha(s奇部分)20位, sha(s偶部分)20位的奇偶交錯組合。
M: 20個字節的數,用于與client傳過來的最終結果M1進行對比,如果M和M1每個字節都相等則驗證通過。計算方法:t3 = sha(N)[i] ^ sha(g)[i],t4 = sha(username),M = sha(t3,t4,s,A,B,K)
k: k = 3
總結:服務端,客戶端各自計算S的公式個不同,公鑰部分服務端用A,b, 客戶端用B,a 但其計算結果相同………私鑰x被很好的隱藏了,因為想從M獲得x是基本不可能的!基于數學難題基礎上的加密算法確實很給力。
References:
[1]http://blog.csdn.net/lfhfut/article/details/1124768
[2]http://www.arcemu.org/wiki/
[3]http://hi.baidu.com/zyy503950958/blog/item/3addce90a91eda81a877a463.html