Team Them Up!
|
Time Limit: 1000MS
|
|
Memory Limit: 10000K
|
|
Total Submissions: 1440
|
|
Accepted: 358
|
|
Special Judge
|
Description
Your task is to divide a number of persons into two teams, in such a way, that:
everyone belongs to one of the teams;
every team has at least one member;
every person in the team knows every other person in his team;
teams are as close in their sizes as possible.
This task may have many solutions. You are to find and output any solution, or to report that the solution does not exist.
Input
For simplicity, all persons are assigned a unique integer identifier from 1 to N.
The first line in the input file contains a single integer number N (2 <= N <= 100) - the total number of persons to divide into teams, followed by N lines - one line per person in ascending order of their identifiers. Each line contains the list of distinct numbers Aij (1 <= Aij <= N, Aij != i) separated by spaces. The list represents identifiers of persons that ith person knows. The list is terminated by 0.
Output
If the solution to the problem does not exist, then write a single message "No solution" (without quotes) to the output file. Otherwise write a solution on two lines. On the first line of the output file write the number of persons in the first team, followed by the identifiers of persons in the first team, placing one space before each identifier. On the second line describe the second team in the same way. You may write teams and identifiers of persons in a team in any order.
Sample Input
5
2 3 5 0
1 4 5 3 0
1 2 5 0
1 2 3 0
4 3 2 1 0
Sample Output
3 1 3 5
2 2 4
Source
Northeastern Europe 2001
題目大意:把n個人分成2各組,每一個人有他所認識的人。所分的組有四點要求:
1、 每個人都必需屬于一個組。
2、 每個組至少有一個人。
3、 每個組里面的每個人必需互相認識。
4、 兩個組的成員應盡量接近。
首先分析這道題目,題目給出的是一個有向圖,即如果有A認識B,但不一定有B認識A。但是在所分配的組里面,任意兩個人都要互相認識。
1、 先讀入數據建立有向圖,然后對這個有向圖進行處理,如果兩個點之間的邊是單向邊,就認為兩個點之間無邊(因為這兩個人不互相認識),對于兩個點間的雙向邊,即建立一條無向邊(這兩個人互相認識),這樣就可以把一個有向圖轉化為一個無向圖。
2、 將這個無向圖轉化為它的反圖。即有邊的把邊刪去,無邊的添上一條邊。(其實1,2步在程序實現時可以一次完成)。
3、 對轉換后的反圖求極大連通分量。想想就會明白剛才為什么要求反圖,可以看到在這個反圖中的不同的連通分量中的兩個人都是互相認識的!!!接下來很關鍵,那些互不認識的人就在一個連通分量里面。
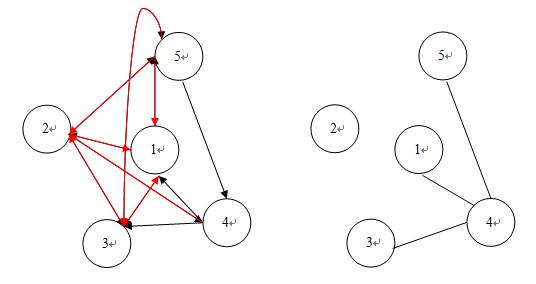
4、 在做DFS求連通分量的時候,同時對連通分量中的點染色(0或1),如果一個點顏色為0,那么所有和它相鄰的點與它的顏色應該不同(標記為1)。這是因為反圖中相鄰的兩個人都是不認識的(回顧剛才反圖的作用)。這樣DFS結束后,就可以根據顏色把連通分量中的點分成兩個組s0和s1,在不同兩個組的人是不可能分到一個team內的。到這里要做一個特判,對于s0或s1組里的任意兩個人p,q如果反圖中存在一條邊(p,q),說明無解,輸出"No solution"。
5、 求出了所有的連通分量,對于第i個連通分量都把其節點分為兩個組s1i和s2i。這時要做的就是把所有的s1i和s2i分配到team1和team2中去,使team1的總和與team2的總和差值最小。就可以用背包DP了。
dp[i][j]表示第i個連通分量達到j的差值,true為可達,false為不可達。
狀態轉移方程:
dp[i][j+si0-si1]=true if dp[i-1][j] == true
dp[i][j-si0+si1]=true if dp[i-1][j] == true
同時記錄轉移路徑,差值j的范圍是-100~+100可以坐標平移。
最后在dp[m][i](m是最后一個連通塊數)中找出值為true的最小i值。輸出答案。


1 #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
#include <string.h>
3
4 int g[205][205],r[205][205],n;
int g[205][205],r[205][205],n;
5 int mark[205],cnt,dp[205][205];
int mark[205],cnt,dp[205][205];
6 char st[205][205][105];
char st[205][205][105];
7 struct P
struct P
8

 {
{
9 int a[2];
int a[2];
10 int s[2][105];
int s[2][105];
11 }p[105];
}p[105];
12
13 void dfs(int v, int color, int num)
void dfs(int v, int color, int num)
14

 {
{
15 int i;
int i;
16 mark[v]=true;
mark[v]=true;
17 p[num].s[color][p[num].a[color]]=v;
p[num].s[color][p[num].a[color]]=v;
18 p[num].a[color]++;
p[num].a[color]++;
19 for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
20

 {
{
21 if(!mark[i] && r[v][i])
if(!mark[i] && r[v][i])
22

 {
{
23 dfs(i,color^1,num);
dfs(i,color^1,num);
24 }
}
25 }
}
26 }
}
27 bool fit()
bool fit()
28

 {
{
29 int i,j,k;
int i,j,k;
30 for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
31

 {
{
32 for(j=0; j<p[i].a[0]; j++)
for(j=0; j<p[i].a[0]; j++)
33

 {
{
34 for(k=j+1; k<p[i].a[0]; k++)
for(k=j+1; k<p[i].a[0]; k++)
35

 {
{
36 if(r[p[i].s[0][j]][p[i].s[0][k]])
if(r[p[i].s[0][j]][p[i].s[0][k]])
37 return false;
return false;
38 }
}
39 }
}
40 for(j=0; j<p[i].a[1]; j++)
for(j=0; j<p[i].a[1]; j++)
41

 {
{
42 for(k=j+1; k<p[i].a[1]; k++)
for(k=j+1; k<p[i].a[1]; k++)
43

 {
{
44 if(r[p[i].s[1][j]][p[i].s[1][k]])
if(r[p[i].s[1][j]][p[i].s[1][k]])
45 return false;
return false;
46 }
}
47 }
}
48 }
}
49 return true;
return true;
50 }
}
51
52 int main()
int main()
53

 {
{
54 int i,j,k,ii,t,flag,ans1[105],ans2[105];
int i,j,k,ii,t,flag,ans1[105],ans2[105];
55 //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
56 scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%d",&n);
57 memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
58 memset(r,0,sizeof(r));
memset(r,0,sizeof(r));
59 for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
60

 {
{
61 while(scanf("%d",&j), j)
while(scanf("%d",&j), j)
62

 {
{
63 g[i][j]=1;
g[i][j]=1;
64 }
}
65 }
}
66 for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
67

 {
{
68 for(j=1; j<=n; j++)
for(j=1; j<=n; j++)
69

 {
{
70 if(!g[i][j] || !g[j][i])
if(!g[i][j] || !g[j][i])
71 r[i][j]=r[j][i]=1;
r[i][j]=r[j][i]=1;
72 }
}
73 }
}
74 memset(mark,0,sizeof(mark));
memset(mark,0,sizeof(mark));
75 cnt=0;
cnt=0;
76 memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
77 for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
78

 {
{
79 if(!mark[i])
if(!mark[i])
80

 {
{
81 dfs(i,0,cnt++);
dfs(i,0,cnt++);
82 }
}
83 }
}
84 if(!fit())
if(!fit())
85

 {
{
86 printf("No solution\n");
printf("No solution\n");
87 return 0;
return 0;
88 }
}
89 memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
90 memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
91 dp[0][100+p[0].a[0]-p[0].a[1]]=1;
dp[0][100+p[0].a[0]-p[0].a[1]]=1;
92 memset(st[0][100+p[0].a[0]-p[0].a[1]],0,sizeof(st[0][100+p[0].a[0]-p[0].a[1]]));
memset(st[0][100+p[0].a[0]-p[0].a[1]],0,sizeof(st[0][100+p[0].a[0]-p[0].a[1]]));
93 for(i=0; i<p[0].a[0]; i++)
for(i=0; i<p[0].a[0]; i++)
94 st[0][100+p[0].a[0]-p[0].a[1]][p[0].s[0][i]]=1;
st[0][100+p[0].a[0]-p[0].a[1]][p[0].s[0][i]]=1;
95 dp[0][100-p[0].a[0]+p[0].a[1]]=1;
dp[0][100-p[0].a[0]+p[0].a[1]]=1;
96 memset(st[0][100-p[0].a[0]+p[0].a[1]],0,sizeof(st[0][100-p[0].a[0]+p[0].a[1]]));
memset(st[0][100-p[0].a[0]+p[0].a[1]],0,sizeof(st[0][100-p[0].a[0]+p[0].a[1]]));
97 for(i=0; i<p[0].a[1]; i++)
for(i=0; i<p[0].a[1]; i++)
98 st[0][100-p[0].a[0]+p[0].a[1]][p[0].s[1][i]]=1;
st[0][100-p[0].a[0]+p[0].a[1]][p[0].s[1][i]]=1;
99 for(i=1; i<cnt; i++)
for(i=1; i<cnt; i++)
100

 {
{
101 for(j=100+n; j>=100-n; j--)
for(j=100+n; j>=100-n; j--)
102

 {
{
103 if(dp[i-1][j])
if(dp[i-1][j])
104

 {
{
105 //for(k=0; k<cnt; k++)
//for(k=0; k<cnt; k++)
106 //{
//{
107 t=j+p[i].a[0]-p[i].a[1];
t=j+p[i].a[0]-p[i].a[1];
108 if(!dp[i][t])
if(!dp[i][t])
109

 {
{
110 dp[i][t]=1;
dp[i][t]=1;
111 memcpy(st[i][t],st[i-1][j],sizeof(st[i-1][j]));
memcpy(st[i][t],st[i-1][j],sizeof(st[i-1][j]));
112 for(ii=0; ii<p[i].a[0]; ii++)
for(ii=0; ii<p[i].a[0]; ii++)
113 st[i][t][p[i].s[0][ii]]=1;
st[i][t][p[i].s[0][ii]]=1;
114
115 }
}
116 t=j-p[i].a[0]+p[i].a[1];
t=j-p[i].a[0]+p[i].a[1];
117 if(!dp[i][t])
if(!dp[i][t])
118

 {
{
119 dp[i][t]=1;
dp[i][t]=1;
120 memcpy(st[i][t],st[i-1][j],sizeof(st[i-1][j]));
memcpy(st[i][t],st[i-1][j],sizeof(st[i-1][j]));
121 for(ii=0; ii<p[i].a[1]; ii++)
for(ii=0; ii<p[i].a[1]; ii++)
122

 {
{
123 st[i][t][p[i].s[1][ii]]=1;
st[i][t][p[i].s[1][ii]]=1;
124 }
}
125 }
}
126 //}
//}
127 }
}
128 }
}
129 }
}
130 flag=0;
flag=0;
131 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
132

 {
{
133 if(dp[cnt-1][100+i])
if(dp[cnt-1][100+i])
134

 {
{
135 t=0;
t=0;
136 k=0;
k=0;
137 for(j=1; j<=n; j++)
for(j=1; j<=n; j++)
138

 {
{
139 if(st[cnt-1][100+i][j])
if(st[cnt-1][100+i][j])
140

 {
{
141 ans1[t++]=j;
ans1[t++]=j;
142 }
}
143 else
else
144 ans2[k++]=j;
ans2[k++]=j;
145 }
}
146 if(t && k)
if(t && k)
147

 {
{
148 flag=1;
flag=1;
149 printf("%d",t);
printf("%d",t);
150 for(j=0; j<t; j++)
for(j=0; j<t; j++)
151 printf(" %d",ans1[j]);
printf(" %d",ans1[j]);
152 printf("\n");
printf("\n");
153 printf("%d",k);
printf("%d",k);
154 for(j=0; j<k; j++)
for(j=0; j<k; j++)
155 printf(" %d",ans2[j]);
printf(" %d",ans2[j]);
156 printf("\n");
printf("\n");
157 break;
break;
158 }
}
159 }
}
160 if(dp[cnt-1][100-i])
if(dp[cnt-1][100-i])
161

 {
{
162 t=0;
t=0;
163 k=0;
k=0;
164 for(j=1; j<=n; j++)
for(j=1; j<=n; j++)
165

 {
{
166 if(st[cnt-1][100-i][j])
if(st[cnt-1][100-i][j])
167

 {
{
168 ans1[t++]=j;
ans1[t++]=j;
169 }
}
170 else
else
171 ans2[k++]=j;
ans2[k++]=j;
172 }
}
173 if(t && k)
if(t && k)
174

 {
{
175 flag=1;
flag=1;
176 printf("%d",t);
printf("%d",t);
177 for(j=0; j<t; j++)
for(j=0; j<t; j++)
178 printf(" %d",ans1[j]);
printf(" %d",ans1[j]);
179 printf("\n");
printf("\n");
180 printf("%d",k);
printf("%d",k);
181 for(j=0; j<k; j++)
for(j=0; j<k; j++)
182 printf(" %d",ans2[j]);
printf(" %d",ans2[j]);
183 printf("\n");
printf("\n");
184 break;
break;
185 }
}
186 }
}
187 }
}
188 if(!flag)
if(!flag)
189 printf("No solution\n");
printf("No solution\n");
190 return 0;
return 0;
191 }
}
192
193
posted on 2008-08-08 00:51
飛飛 閱讀(3489)
評論(2) 編輯 收藏 引用 所屬分類:
ACM/ICPC