1. 解決的問題:
假如現在要編寫一個天氣預報的公布欄, 公布欄有兩種顯示方式, 一種是圖像方式顯示, 一種是表格形式顯示.
2. 問題分析:
應該根據數據與現實分離的原則將天氣預報數據和現實形式分別封裝起來,
今后可能增加其他的顯示形式;
天氣預報數據發生變化后,需要對所有的顯示形式進行更新.
3. UML圖與代碼實現:
1)用Push的方式更新Observer數據, 通過Subject對Observer進行注冊:
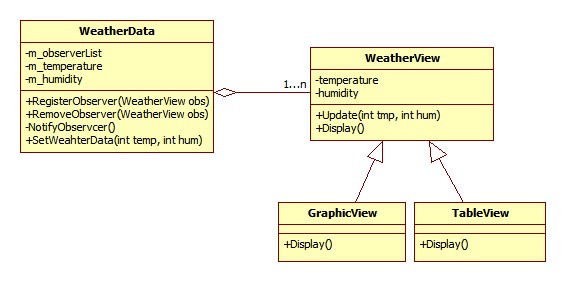
- //這個例子中WeatherData就是Subject, 而WeatherView則是Observer,
- //這里WeatherView中沒有包含到WeatherData的引用,
- //因此這里是Subject用push的方法向Observer發送數據;
- //并且注冊和反注冊Observer的時候都是由Subject(WeatherData)執行的
-
- #include <iostream>
- #include <vector>
- #include <algorithm>
-
- using namespace std;
-
- class WeatherData;
-
- class WeatherView
- {
- public:
- void Update(int temp, int hum)
- {
- temperature = temp;
- humidity = hum;
- };
- virtual void Display()
- {
- cout << "temperature = " << temperature << ", humidity = " << humidity << endl;
- }
-
- private:
-
- int temperature;
- int humidity;
- };
-
- class GraphicView: public WeatherView
- {
- public:
- void Display()
- {
- cout << "====--Weather Report With Graphic Format--===="<< endl;
- WeatherView::Display();
- }
- };
-
- class TableView: public WeatherView
- {
- public:
- void Display()
- {
- cout << "====--Weather Report With Table Format--===="<< endl;
- WeatherView::Display();
- }
- };
-
- class WeatherData
- {
- public:
- void SetWeahterData(int temp, int hum)
- {
- temperature = temp;
- humidity = hum;
- NotifyObservcer();
- }
-
- void RegisterObserver(WeatherView* obs)
- {
- obsList.push_back(obs);
- }
-
- void RemoveObserver(WeatherView* obs)
- {
- vector<WeatherView*>::iterator it;
- it = find(obsList.begin(), obsList.end(), obs);
- if (it != obsList.end())
- obsList.erase(it);
- }
-
- private:
- vector<WeatherView*> obsList;
- int temperature;
- int humidity;
- void NotifyObservcer()
- {
- vector<WeatherView*>::iterator it;
- for(it = obsList.begin(); it < obsList.end(); it++)
- {
- (*it)->Update(temperature, humidity);
- }
- }
- };
-
-
- int main()
- {
- WeatherData *wd = new WeatherData();
- GraphicView *gv = new GraphicView();
- TableView *tv = new TableView();
-
- wd->RegisterObserver(gv);
- wd->RegisterObserver(tv);
- wd->SetWeahterData(23,45);
- gv->Display();
- tv->Display();
-
- wd->RemoveObserver(gv);
- wd->SetWeahterData(67,89);
- gv->Display();
- tv->Display();
-
- return 0;
- }
2)用Pull的方式更新Observer數據, Observer自己進行注冊:
- #ifndef WEATHERDATA_HPP_INCLUDED
- #define WEATHERDATA_HPP_INCLUDED
- #include <iostream>
- #include <vector>
-
- #include "WeatherView.hpp"
-
- class WeatherData
- {
- public:
- void SetWeahterData(int temp, int hum)
- {
- temperature = temp;
- humidity = hum;
- NotifyObservcer();
- }
-
- int GetTemperature()
- {
- return temperature;
- }
-
- int GetHumidty()
- {
- return humidity;
- }
-
- void RegisterObserver(WeatherView* obs);
- void RemoveObserver(WeatherView* obs);
-
- private:
- vector<WeatherView*> obsList;
- int temperature;
- int humidity;
- void NotifyObservcer();
- };
-
- #endif
- #ifndef WEATHERVIEW_HPP_INCLUDED
- #define WEATHERVIEW_HPP_INCLUDED
-
- #include <iostream>
- #include <vector>
- #include <algorithm>
-
-
- class WeatherData;
-
- using namespace std;
-
- class WeatherView
- {
- public:
- WeatherView(WeatherData* wd);
-
- void Update();
- void Register();
- void Unregister();
-
- virtual void Display()
- {
- cout << "temperature = " << temperature << ", humidity = " << humidity << endl;
- }
-
- private:
- WeatherData* wd;
- int temperature;
- int humidity;
- };
-
- class GraphicView: public WeatherView
- {
- public:
- GraphicView(WeatherData* wd);
- void Display()
- {
- cout << "====--Weather Report With Graphic Format--===="<< endl;
- WeatherView::Display();
- }
- };
-
- class TableView: public WeatherView
- {
- public:
- TableView(WeatherData* wd);
- void Display()
- {
- cout << "====--Weather Report With Table Format--===="<< endl;
- WeatherView::Display();
- }
- };
-
- #endif
- //這個例子中WeatherData就是Subject, 而WeatherView則是Observer,
- //這里WeatherView中有一個包含到WeatherData的指針,
- //因此這里是Observer用pull的方法主動向Observer索取數據;
- //并且注冊和反注冊都是Observer自己執行的
- #include <iostream>
- #include <vector>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include "WeatherView.hpp"
- #include "WeatherData.hpp"
-
- void WeatherData::RegisterObserver(WeatherView* obs)
- {
- obsList.push_back(obs);
- }
-
- void WeatherData::RemoveObserver(WeatherView* obs)
- {
- vector<WeatherView*>::iterator it;
- it = find(obsList.begin(), obsList.end(), obs);
- if (it != obsList.end())
- obsList.erase(it);
- }
-
- void WeatherData::NotifyObservcer()
- {
- vector<WeatherView*>::iterator it;
- for(it = obsList.begin(); it < obsList.end(); it++)
- {
- (*it)->Update();
- }
- }
-
-
- WeatherView::WeatherView(WeatherData* pwd)
- {
- wd = pwd;
- }
-
- void WeatherView::Update()
- {
- temperature = wd->GetTemperature();
- humidity = wd->GetHumidty();
- };
-
- void WeatherView::Register()
- {
- wd->RegisterObserver(this);
- };
-
- void WeatherView::Unregister()
- {
- wd->RemoveObserver(this);
- };
-
- GraphicView::GraphicView(WeatherData* pwd) : WeatherView(pwd)
- {
-
- }
-
- TableView::TableView(WeatherData* pwd) : WeatherView(pwd)
- {
-
- }
- int main()
- {
- WeatherData *wd = new WeatherData();
- GraphicView *gv = new GraphicView(wd);
- gv->Register();
- TableView *tv = new TableView(wd);
- tv->Register();
-
- wd->SetWeahterData(23,45);
- gv->Display();
- tv->Display();
-
- gv->Unregister();
- wd->SetWeahterData(67,89);
- gv->Display();
- tv->Display();
-
- return 0;
- }
上面兩種實現的執行結果如下:
- ====--Weather Report With Graphic Format--====
- temperature = 23, humidity = 45
- ====--Weather Report With Table Format--====
- temperature = 23, humidity = 45
- ====--Weather Report With Graphic Format--====
- temperature = 23, humidity = 45
- ====--Weather Report With Table Format--====
- temperature = 67, humidity = 89
4. Push還是Pull?
對于上面的例子, Observer中的數據是從Subject中一次性全部更新的(temperature 和 humidity), 這種更新數據的方式便是push;然而如果WeatherData中的數據量非常大, 而有些Observer并不需要所有的數據, 比如現在要新增兩個顯示方式,一個是只顯示溫度,而另一個則只顯示濕度, 這樣的話就沒有必要讓所有的Observer都得到所有的數據. 最好的方式是Observer能根據自己的需要從Subject中去取得數據,這種更新數據的方式便是Pull. Observer模式中Push和Pull兩種設計方法體現在具體的程序中就是Observer中的Update()接口參數不同, 對于Push模式, Update()接口的參數通常就是需要Push的那些數據,比如這里的溫度和濕度; 對于Pull模式, Update()的參數是Subject的一個引用, 然后Subject提供一些數據接口,由Observer通過這些接口自己取得所需要的數據.
5. 總結:
1. Strategy 模式定義:
定義對象間的一種一對多的依賴關系,當一個對象的狀態發生改變時,所有依賴于它的對象都得到通知并被自動更新.
2. 體現的設計原則:
- 將數據與現實分別封裝;
- 多使用組合,少使用繼承;
- 面向接口編程,而不面向實現編程;
3. UML圖:
4. 要點:
- Strategy 基類需要定義出可供Client使用的一些算法接口;
- 可以隨時根據需要增加 Strategy 而不會影響到Client;
- Client 里面需要包含對 Strategy 的引用;
- Client 可以隨時更換 Strategy;
6. 理解:
- Observer模式是解決對象之間數據傳遞問題的一種模式;
- Observer的注冊可以由Subject執行也可以由Observer自己執行;
- 和Strategy模式的比較:
1) Observer模式中Observer 中定義了 Update()接口供 Subject調用; 而Strategy模式中,Strategy定義了AlgrithmInterface()供Client調用;
2) Observer模式中Subject和Observer是一對多的關系, 因此Subject是一次調用n個Observer的Update()接口;而Strategy模式中Client與Strategy之間是一對一的關系, Client 就是調用指定的那個Strategy的AlgrithmInterface();
3) 也正因為這種對應關系的不同, 在Observer模式中, Subject可以Register或者Remove某個Observer, 而Strategy模式中通常只是set某個Strategy
轉自:http://blog.csdn.net/minico/article/details/5471100
posted on 2012-10-30 17:16
老馬驛站 閱讀(400)
評論(0) 編輯 收藏 引用 所屬分類:
Design pattern