just do it
+ - * / += -= *= /= >> <<
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class Complex
5 {
6 private:
7 double real;
8 double image;
9 public:
10 Complex(double r = 0.0, double i = 0.0) : real(r), image(i) {}
11 Complex(const Complex& c)
12 {
13 real = c.real;
14 image = c.image;
15 }
16 ~Complex() {}
17 Complex& operator=(const Complex& c)
18 {
19 if (this != &c)
20 {
21 real = c.real;
22 image = c.image;
23 }
24 return *this;
25 }
26 Complex& operator+=(const Complex& c)
27 {
28 real += c.real;
29 image += c.image;
30 return *this;
31 }
32 Complex& operator-=(const Complex& c)
33 {
34 real -= c.real;
35 image -= c.image;
36 return *this;
37 }
38 Complex& operator*=(const Complex& c)
39 {
40 double r2 = real, i2 = image;
41 real = r2 * c.real - i2 * c.image;
42 image = r2 * c.image + i2 * c.real;
43 return *this;
44 }
45 Complex& operator/=(const Complex& c)
46 {
47 double r2 = real, i2 = image;
48 real = (r2 * c.real + i2 * c.image) / (c.real * c.real + c.image * c.image);
49 image = (i2 * c.real - r2 * c.image) / (c.real * c.real + c.image * c.image);
50 return *this;
51 }
52 friend Complex operator+(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);
53 friend Complex operator-(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);
54 friend Complex operator*(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);
55 friend Complex operator/(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);
56 friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Complex& c);
57 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Complex& c);
58 };
59
60 Complex operator+(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
61 {
62 Complex t(c1);
63 return t += c2;
64 }
65
66 Complex operator-(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
67 {
68 Complex t(c1);
69 return t -= c2;
70 }
71
72 Complex operator*(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
73 {
74 Complex t(c1);
75 return t *= c2;
76 }
77
78 Complex operator/(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
79 {
80 Complex t(c1);
81 return t /= c2;
82 }
83
84 istream& operator>>(istream& in, Complex& c)
85 {
86 in >> c.real >> c.image;
87 if (!in)
88 {
89 cerr << "Input error!" << endl;
90 exit(1);
91 }
92 return in;
93 }
94
95 ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Complex& c)
96 {
97 out << c.real << '+' << c.image << 'i';
98 return out;
99 }
100
101 int main()
102 {
103 Complex c1(1.0, 2.0), c2(3.0, 4.0);
104 cout << c1 << endl;
105 cout << c2 << endl;
106 cout << c1 + c2 << endl;
107 cout << c1 - c2 << endl;
108 cout << c1 * c2 << endl;
109 cout << c1 / c2 << endl;
110
111 Complex c3(5.0, 6.0), c4(7.0, 8.0);
112 c1 += c2 += c3 += c4;
113 cout << c1 << endl;
114 cout << c2 << endl;
115 cout << c3 << endl;
116 cout << c4 << endl;
117 return 0;
118 }
如果需要添加其他操作,需要
·添加一個操作類
·修改 OperationFactory
·修改客戶代碼以使用這個操作
UML 類圖如下:
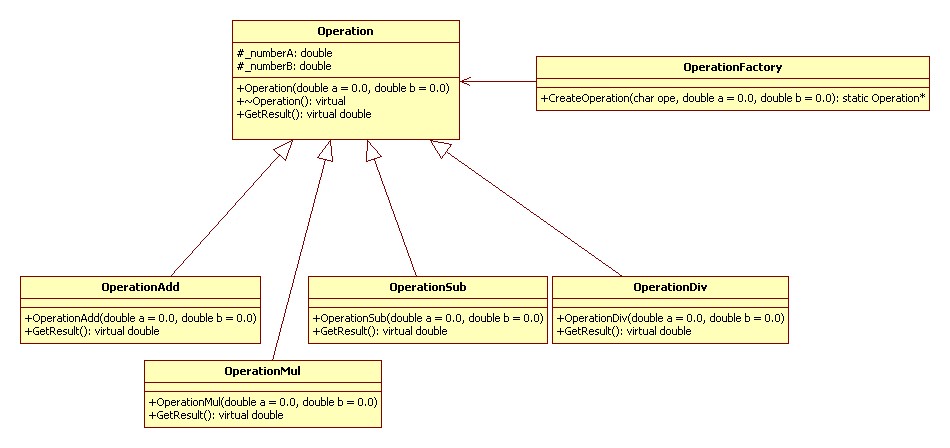
實例代碼 C++:
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class Operation
5 {
6 protected:
7 double _numberA;
8 double _numberB;
9 public:
10 Operation(double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0) : _numberA(a), _numberB(b) {}
11 virtual ~Operation() {}
12 virtual double GetResult()
13 {
14 double result = 0.0;
15 return result;
16 }
17 };
18
19 class OperationAdd : public Operation
20 {
21 public:
22 OperationAdd(double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0) : Operation(a, b) {}
23 virtual double GetResult()
24 {
25 return _numberA + _numberB;
26 }
27 };
28
29 class OperationSub : public Operation
30 {
31 public:
32 OperationSub(double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0) : Operation(a, b) {}
33 virtual double GetResult()
34 {
35 return _numberA - _numberB;
36 }
37 };
38
39 class OperationMul : public Operation
40 {
41 public:
42 OperationMul(double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0) : Operation(a, b) {}
43 virtual double GetResult()
44 {
45 return _numberA * _numberB;
46 }
47 };
48
49 class OperationDiv : public Operation
50 {
51 public:
52 OperationDiv(double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0) : Operation(a, b) {}
53 virtual double GetResult()
54 {
55 if (_numberB == 0.0)
56 {
57 throw runtime_error("Denominator is 0!");
58 }
59 return _numberA / _numberB;
60 }
61 };
62
63 class OperationFactory
64 {
65 public:
66 static Operation* CreateOperation(char ope, double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0)
67 {
68 Operation* ret = 0;
69 switch (ope)
70 {
71 case '+':
72 ret = new OperationAdd(a, b);
73 break;
74 case '-':
75 ret = new OperationSub(a, b);
76 break;
77 case '*':
78 ret = new OperationMul(a, b);
79 break;
80 case '/':
81 ret = new OperationDiv(a, b);
82 break;
83 default:
84 break;
85 }
86 return ret;
87 }
88 };
89
90 int main()
91 {
92 try
93 {
94 Operation* p_ope;
95 p_ope = OperationFactory::CreateOperation('+', 3.0, 5.0);
96 if (p_ope != 0)
97 {
98 cout << p_ope->GetResult() << endl;
99 delete p_ope;
100 p_ope = 0;
101 }
102
103 p_ope = OperationFactory::CreateOperation('-', 3.0, 5.0);
104 if (p_ope != 0)
105 {
106 cout << p_ope->GetResult() << endl;
107 delete p_ope;
108 p_ope = 0;
109 }
110
111 p_ope = OperationFactory::CreateOperation('*', 3.0, 5.0);
112 if (p_ope != 0)
113 {
114 cout << p_ope->GetResult() << endl;
115 delete p_ope;
116 p_ope = 0;
117 }
118
119 p_ope = OperationFactory::CreateOperation('/', 3.0, 5.0);
120 if (p_ope != 0)
121 {
122 cout << p_ope->GetResult() << endl;
123 delete p_ope;
124 p_ope = 0;
125 }
126
127 p_ope = OperationFactory::CreateOperation('/', 3.0, 0.0);
128 if (p_ope != 0)
129 {
130 cout << p_ope->GetResult() << endl;
131 delete p_ope;
132 p_ope = 0;
133 }
134 }
135 catch (const exception& e)
136 {
137 cerr << e.what() << endl;
138 }
139 return 0;
140 }
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #define N 10000
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int i, j, t;
9 char a[N], p[N];
10 scanf("%s %s", a, p);
11
12 for (i = 0; a[i] != 0; ++i)
13 {
14 for (j = 0; p[j] != 0; ++j)
15 {
16 if (a[i + j] != p[j])
17 {
18 break;
19 }
20 }
21 if (p[j] == 0)
22 {
23 printf("%d ", i);
24 }
25 }
26 printf("\n");
27 return 0;
28 }
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #include <stdlib.h>
5
6 typedef struct node* link;
7
8 struct node
9 {
10 int item;
11 link next;
12 };
13
14 int main()
15 {
16 int i, N, M;
17 link p;
18 scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
19 link t = (link)malloc(sizeof (*t)), x = t;
20 t->item = 1;
21 t->next = t;
22 for (i = 2; i <= N; ++i)
23 {
24 /*x = x->next = (link)malloc(sizeof (*x));
25 x->item = i;
26 x->next = t;*/
27 p = (link)malloc(sizeof (*x));
28 p->item = i;
29 x->next = p;
30 x = x->next;
31 x->next = t;
32 }
33
34 while (x != x->next)
35 {
36 for (i = 1; i < M; ++i)
37 {
38 x = x->next;
39 }
40 // x->next = x->next->next;
41 t = x->next;
42 x->next = x->next ->next;
43 free(t);
44 --N;
45 }
46 printf("%d\n", x->item);
47 free(x);
48 return 0;
49 }
2 // 埃拉托色尼篩法
3
4 #include <stdio.h>
5 #define N 10000
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 int i, j, a[N];
10 for (i = 2; i < N; ++i)
11 {
12 a[i] = 1;
13 }
14 for (i = 2; i * i <= N; ++i)
15 {
16 if (a[i] == 1)
17 {
18 for (j = i; i * j < N; ++j)
19 {
20 a[i * j] = 0;
21 }
22 }
23 }
24 for (i = 2; i < N; ++i)
25 {
26 if (a[i] == 1)
27 {
28 printf("%4d ", i);
29 }
30 }
31 printf("\n");
32 return 0;
33 }
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4
5 int search(int a[], int v, int l, int r)
6 {
7 int i;
8 for (i = l; i <= r; ++i)
9 {
10 if (v == a[i])
11 {
12 return i;
13 }
14 }
15 return -1;
16 }
17
18 int main()
19 {
20 int a[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
21 int i, pos;
22 for (i = 10; i >= -1; --i)
23 {
24 printf("%d\n", search(a, i, 0, 9));
25 }
26 return 0;
27 }
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4
5 int search(int a[], int v, int l, int r)
6 {
7 int m;
8 while (r >= l)
9 {
10 m = (l + r) / 2;
11 if (v == a[m])
12 {
13 return m;
14 }
15 if (v > a[m])
16 {
17 l = m + 1;
18 }
19 else
20 {
21 r = m - 1;
22 }
23 }
24 return -1;
25 }
26
27 int main()
28 {
29 int a[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
30 int i, pos;
31 for (i = 10; i >= -1; --i)
32 {
33 printf("%d\n", search(a, i, 0, 9));
34 }
35 return 0;
36 }
來自于《算法:C 語言實現》
1.
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #define N 10000
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int i, p, q, t, id[N];
9 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
10 {
11 id[i] = i;
12 }
13 while (scanf("%d %d", &p, &q) == 2)
14 {
15 if (id[p] == id[q])
16 {
17 continue;
18 }
19 for (t = id[p], i = 0; i < N; ++i)
20 {
21 if (id[i] == t)
22 {
23 id[i] = id[q];
24 }
25 }
26 printf(" %d %d\n", p, q);
27 }
28 }
2.
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #define N 10000
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int i, j, p, q, id[N];
9 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
10 {
11 id[i] = i;
12 }
13 while (scanf("%d %d", &p, &q) == 2)
14 {
15 for (i = p; i != id[i]; i = id[i]);
16 for (j = q; j != id[j]; j = id[j]);
17 if (i == j)
18 {
19 continue;
20 }
21 id[i] = j;
22 printf(" %d %d\n", p, q);
23 }
24 }
3.
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #define N 10000
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int i, j, p, q, id[N], sz[N];
9 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
10 {
11 id[i] = i;
12 sz[i] = 1;
13 }
14 while (scanf("%d %d", &p, &q) == 2)
15 {
16 for (i = p; i != id[i]; i = id[i]);
17 for (j = q; j != id[j]; j = id[j]);
18 if (i == j)
19 {
20 continue;
21 }
22 if (sz[i] < sz[j])
23 {
24 id[i] = j;
25 sz[j] += sz[i];
26 }
27 else
28 {
29 id[j] = i;
30 sz[i] += sz[j];
31 }
32 printf(" %d %d\n", p, q);
33 }
34 }
4.
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #define N 10000
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int i, j, p, q, id[N], sz[N];
9 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
10 {
11 id[i] = i;
12 sz[i] = 1;
13 }
14 while (scanf("%d %d", &p, &q) == 2)
15 {
16 for (i = p; i != id[i]; i = id[i])
17 {
18 id[i] = id[id[i]];
19 }
20 for (j = q; j != id[j]; j = id[j])
21 {
22 id[j] = id[id[j]];
23 }
24 if (i == j)
25 {
26 continue;
27 }
28 if (sz[i] < sz[j])
29 {
30 id[i] = j;
31 sz[j] += sz[i];
32 }
33 else
34 {
35 id[j] = i;
36 sz[i] += sz[j];
37 }
38 printf(" %d %d\n", p, q);
39 }
40 }
TinyXML
TinyXML 是一個簡單的、小的、可以容易地集成到其他程序中的 C++ 解析器。
1. 它可以做些什么
簡單地講,TinyXML 可以分析 XML 文檔并從一個可以被讀取、修改和存儲的文檔對象模型(Document Object Model, DOM)。
XML 是 eXtensible Markup Language 的簡稱。它允許你建立自己的文檔標記。HTML 可以很好地為瀏覽器標記文檔,XML 允許你定義任何文檔標記,比如一個描述為組織應用的 “to do” 列表的文檔。XML 是一種非常結構化和方便的格式。所有那些用來存儲應用數據的穩健格式都可以用 XML 來代替。這樣的解析器對一切適用。
你可以到 http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-xml-20040204 尋找完整、正確的說明書。你也可以到 http://skew.org/xml/tutorial 來看一下 XML 的簡介。
有不懂的方法來讀取和交互 XML 數據。TinyXML 使用一個文檔對象模型(DOM),XML 數據被解析為一個可以瀏覽、操作和寫到硬盤或其他輸出流的 C++ 對象。你也可以從 C++ 對象建立一個 XML 文檔,并將其寫到硬盤或其他的輸出流中。
TinyXML 被設計成容易和快速地學習。它有兩個頭文件和四個 cpp 文件。你可以很簡單地將其添加到你的工程中。這里有一個例子文件 xmltest.cpp,你可以從這里開始。
TinyXML 是在 ZLib 協議下發布的,你可以將其應用于開源項目中或者商業代碼中。這個協議的細節位于每個源文件的最上端。
TinyXML 嘗試成為一個靈活的解析器,正確的和順從于 XML 輸出。
TinyXML 應該可以在任何合適的 C++ 系統中編譯。它不依賴于異常機制和運行時類型識別(RTTI)。在有或無 STL 支持的環境下,它都可以編譯。TinyXML 完全支持 UTF-8 編碼,和最前面的 64k 的字符實體。
2。它不可以做什么
TinyXML 不能解析或使用 DTDs(Document Type Definitions)或者 XSLs(eXtensible Stylesheet Language)。有其他的解析器(http://www.sourceforge.org, 搜索 XML)可以做其上的工作。但是這些解析器更大,需要更長的時間以建立在你的工程中,更高的學習曲線并且有更多的限制協議。如果你需要為一個瀏覽器工作或者有更完全的 XML 需求,TinyXML 并不適合你。
下面的 DTD 語法在 TinyXML 中無法解析:
@verbatim
<!DOCTYPE Archiv [
<!ELEMENT Comment (#PCDATA)>
]>
@endverbatim
TinyXML 視 !DOCTYPE 節點非法嵌入一個 !ELEMENT 節點。將來這個問題可能被解決。
3。教程
對于急切的人,這里有個教程可以幫助你入門。非常好的入門方法,但是把這個手冊讀完是值得的。
4。代碼狀況
TinyXML 是一個成熟的、被測試過的代碼。它非常穩定。如果你發現了 bugs,請在 sourceforge (http://www.sourceforge.net/projects/tinyxml)上寫一份 bug 報告。我們將盡快將其校正。
有一些需要改進的方面,如果你對 TinyXML 有興趣,請加入檢查 sourceforge。
5. 相關的工程
TinyXML 工程,你可能發現它非常有用。
TinyXPath:http://tinyxpath.sourceforge.net ,一個小的 XPath 語法解碼器,C++ 實現。
TinyXML++:http://code.google.com/p/ticpp ,一個相對 TinyXML 更新接口的 XML 解析器。它利用了許多 C++ 的功能,比如模板、異常處理機制和許多更好的錯誤處理。
6。特征
6。1 使用 STL
TinyXML 在有或無 STL 的環境下都可以被編譯。當使用 STL 時,TinyXML 使用 std::string 類,支持 std::istream, std::ostream, operator<<, 和 operator>>。許多 API 有 'const char*' 和 'const std::strign&' 兩種形式。
當 STL 支持被編譯出時,非 STL 文件不管怎么被包含。所有的 string 類是有 TinyXML 自身實現的。API 都使用 'const char*' 形式來支持輸入。
使用編譯時 #define:
TIXML_USE_STL
來編譯一個版本或其他版本。可以通過編譯期傳遞或者放在 "tinyxml.h" 文件的第一行中。
注意:如果在 Linux 中編譯測試代碼,設置環境變量 TINYXML_USE_STL=YES/NO 來控制編譯。在 Windows 工程文件中,STL 和 non STL 目標都是被支持的。在你的工程中,在 tinyxml.h 的文件的第一行中添加 #define TIXML_USE_STL 是非常容易的。
6。2 UTF-8
TinyXML 支持允許以任何語言操作 XML 文件的 UTF-8 編碼方式。TinyXML 也支持合法模式(legacy mode),其實一種被用于 UTF-8 之前的編碼方式,可以被描述成“擴展的ASCII”(extended ASCII).
一般地,TinyXML 試著檢測正確的編碼方式并使用它。但是,可以通過在頭文件中設置 TIXML_DEFAULT_ENCODING 的值來強制使用某一種編碼方式。
TinyXML 將要假設一種合法模式,直到一下的其中之一發生:
1)。如果不是標準的,但是 UTF-8 帶頭字節(UTF-8 lead bytes)出現在文件或數據流的頭部,TinyXML 將按照 UTF-8 的編碼方式讀取。
2)。如果聲明的標簽被讀取,并且它有個 encoding="UTF-8",則按照 UTF-8 編碼方式讀取。
3)。如果聲明的標簽被讀取,它沒有特殊的編碼,則按照 UTF-8 編碼。
4)。如果聲明表中是 encoding="something else",TinyXML 將其讀作為合法模式(legacy mode)。在合法模式中,TinyXML 和以前工作一樣。不清楚具體是哪種模式,老的內容應該保持工作。
5)。直到上面的一種準則滿足,TinyXML 按照合法模式執行。
如果編碼是不正確的,或者被檢測出來將要發生什么?TinyXML 將其看做不合適的編碼。你可能得到的是不正確的結果或亂碼。你可能想強制 TinyXML 變為正確的模式。
這一通過 LoadFile( TIXML_ENCODING_LEGACY ) 或者 LoadFile( filename, TIXML_ENCODING_LEGACY ) 的方式強制 TinyXML 設置為合法模式。你可以設置 TIXML_DEFAULT_ENCODING = TIXML_ENCODING_LEGACY 來一直使用合法模式。同樣地,你也可以使用同樣的技術將其設置為 TIXML_ENCODING_UTF8。
對于英語用戶,使用英文的 XML,UTF-8 與 low-ASCII 是一樣的,你不需要檢測 UTF-8 或者改變你的代碼。可以將 UTF-8 看做 ASCII 的一個超集。
UTF-8 不是雙字節格式,但是它是 Unicode 的標準編碼。
TinyXML 不使用和直接同時支持 wchar, TCHAR, 或者 微軟的 _UNICODE。
用 Unicode 指代 UTF-16 是不合適的,UTF-16 是 Unicode 的一種寬字節編碼方式。這引起了混亂。
對于 high-ascii 語言,TinyXML 可以處理所有的語言,同時,只要 XML 被編碼成 UTF-8。這樣有些滑稽,老的程序員和操作系統趨向于使用 default 和 traditional 的代碼頁。許多應用可以輸出 UTF-8,但是老或者頑固的應用是以默認的代碼頁輸出文本的。
例如,日文系統傳統上使用 SHIFT-JIS 編碼方式。TinyXML 不能讀取 SHIFT-JIS 編碼的文本。一個好的編輯器可以打開 SHIFT-JIS 的文件并將其保存為 UTF-8 的編碼方式。
http://skew.org/xml/tutorial 對轉換編碼做了很好的介紹。
utf8test.xml 是一個包含英語、西班牙語、俄語和簡體中文的 XML 文件。utf8test.gif 是一個在 IE 中渲染的 XML 文件的屏幕截圖。注意如果你的電腦里沒有正確的字體,你不能看到輸出的 GIF 文件,即便你正確地將其解析。也要主要終端的西方代碼頁輸出,以至于 Print() 或者 printf() 不能正確地顯示文件。這不是 TinyXML 的 bug,而是操作系統的問題。沒有數據丟失或者被 TinyXML 破壞。終端不能渲染 UTF-8。
6。3 實體(Entities)
TinyXML 組織預定義的字符實體,即特殊字符。也就是:
& &
< <
> >
" "
' '
當 XML 文檔被讀取和轉換成 UTF-8 等同物時,這些字符被辨識。比如這樣的 XML 文本:
Far & Away
當從 TiXMLText 對象中使用 Value() 查詢 “Far & Away”。作為 & 符號寫回到 XML 流/文件。老的 TinyXML 版本保留字符實體,但是新版本將它們轉換為字符。
另外,任何字符都可以用它的 Unicode 指定:" " 或 " " 都可以指代非中斷空白字符。
6.4 打印(Printing)
TinyXML 可以以許多不同的方式打印輸出,這些方式既有優勢也有限制。
1)。Print( FILE* ). 標準 C 流,包括 C 文件和編制輸出。
漂亮的輸出,但是你不能對輸出選擇進行控制。
輸出被指向 FILE 對象,所以在 TinyXML 代碼中沒有預先的內存。
Print() 和 SaveFile()
2)。opeartor<<。輸出到 C++ 流。
繼承標準 C++ 輸入輸出流
網絡打印,便于網絡傳輸和在 C++ 對象間傳遞 XML,但是難以閱讀。
3)。TiXmlPrinter。輸出到 std::string 或者 內存緩沖區。
API 不簡潔
將來的打印選擇將被添加
將來的版本中,隨著打印被重定義和擴展,打印可能改變。
6。5 流(Streams)
有 TIXML_USE_STL 的 TinyXML 支持 C++ 流(operator <<,>>),像 C(FILE*) 流似的。有一些你需要注意的不同。
1)。C 風格輸出
以 FILE* 為基礎
Print(), SaveFile()
產生格式化輸出,伴隨大量的空白鍵,看可能便于閱讀。非常快速,容忍格式不好的 XML 文檔。例如,一個含有兩個根元素和兩個聲明的 XML 文檔仍然可以被打印。
2)。C 風格輸入
建立在 FILE* 基礎上
Parse(), LoadFile()
快速的,格式任意。在你不需要 C++ 流時使用。
3)。C++ 風格輸出
建立在 std::ostream 基礎上
operator<<
生成壓縮輸出,便于網絡傳輸而不是易于閱讀。依賴于你系統中的輸出流類的實現,可能很很慢。XML 文檔必須有很好的格式:一個文檔應該包含一個正確的根元素。額外的根層元素不能被流輸出。
4)。C++ 風格輸入
建立在 std::istream 基礎上
operator>>
從流中讀取 XML,使它利于網絡傳輸。XML 文檔虛實完整的。TinyXML 假設 XML 數據時完整的,當其讀取了根元素。其他的有多個根元素的錯誤構造不能被正確讀取。operator<< 比 Parse 慢,這與 STL 的實現和 TinyXML 的限制有關。
6。6 空白符(White space)
空白字符被保持還是被壓縮在不同的條件下并不統一。例如,用 '_' 代表一個空白符,對于 “Hello____world”。HTML 和一些 XML 解析器中,其被翻譯成 “Hello_world”。一些 XML 解析器將其保持不變“Hello___world”。另一些將 __Hello___world__ 轉換成 Hello___world。
這個問題還沒有被解決的令我滿意。TinyXML 支持前兩種方法。TiXmlBase::SetCondenseWhiteSpace( bool ) 設置期望的操作。默認的是壓縮空白符。
如果你改變默認的方式,你應該在費用解析 XML 數據的調用之前調用 TiXmlBase::SetCondenseWhiteSpace( bool )。我不推薦當他已被建立了還去改變它。
6。7 處理(Handles)
用穩定的方式瀏覽一個 XML 文檔,檢測函數調用的返回值是不是 null 很重要。一個錯誤安全的實現產生的代碼像這樣一樣:
TiXmlElement* root = document.FirstChildElement( "Document" );
if ( root )
{
TiXmlElement* element = root->FirstChildElement( "Element" );
if ( element )
{
TiXmlElement* child = element->FirstChildElement( "Child" );
if ( child )
{
TiXmlElement* child2 = child->NextSiblingElement( "Child" );
if ( child2 )
{
// Finally do something useful.
Handles 可以把這些代碼清除。使用 TiXmlHandle 類,前面的這些代碼可以縮減為:
TiXmlHandle docHandle( &document );
TiXmlElement* child2 = docHandle.FirstChild( "Document" ).FirstChild( "Element" ).Child( "Child", 1 ).ToElement();
if ( child2 )
{
// do something useful
這種方式更容易處理。可以查看 TiXmlHandle 來獲取更多的信息。
6。8 行和列追蹤(Row and Column tracking)
能夠追蹤節點和屬性在源文件中的原始位置對于一些應用是非常重要的。另外,知道解析錯誤發生在哪里可以及時地保存。
TinyXML 可以追蹤所有節點和屬性在文本文件中的行和列。TiXmlBase::Row() 和 TiXmlBase::Column() 函數返回節點在源文本文件中的位置。正確的制表符可以在 TiXmlDocument::SetTabSize() 中配置。
7。使用和安裝
編譯和運行 xmltest
這里提供了 Linux 的 Makefile 文件和 Windows Visual C++ 下的 .dsw 文件。正常的編譯和運行。它將要向你的硬盤寫入 demotest.xml 文件和向屏幕產生輸出。它還測試沿著 DOM 用不同的技術打印已發現的節點的數目。
Linux makefile 非常通用,可以在許多系統中運行,它已經在 mingw 和 MacOSX 中測試。你不需要運行 'make depend'。這種依賴已經被硬編碼。
7。1 Windows VC6 工程文件
tinyxml: tinyxml library, non-STL
tinyxmlSTL: tinyxml library, STL
tinyXmlTest: test app, non-STL
tinyXmlTestSTL: test app, STL
7。2 Makefile
在 makefile 文件中,你可以設置:
PROFILE, DEBUG 和 TINYXML_USE_STL。細節在 makefile 中。
在 tinyxml 文件夾中,鍵入 'make clean' 和 'make'。可執行文件 'xmltest' 將被產生。
7。3 在應用中使用
將 tinyxml.cpp, tinyxml.h, tinyxmlerror.cpp, tinyxmlparser.cpp, tinystr.cpp 和 tinystr.h 添加到你的工程文件或 makefile 中。就是這樣!它應該可以在任何相容的 C++ 系統中得到編譯。你不需要異常處理機制或運行時類型識別(RTTI)。
8。TinyXML 怎樣工作(How TinyXML works)
一個來自可能是最好的開始方法。例如:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone=no>
<!-- Our to do list data -->
<ToDo>
<Item priority="1"> Go to the <bold>Toy store!</bold></Item>
<Item priority="2"> Do bills</Item>
</ToDo>
它不是一個 To Do 列表,但是它將要這么做。讀取這個文件(demo.xml)你可以產生一個文檔,并解析它:
TiXmlDocument doc( "demo.xml" );
doc.LoadFile();
這樣就可以工作了。現在讓我們觀察一些行,并且他們是怎樣與 DOM 相關聯的。
<?xml version="1.0" standalone=no>
第一行是一個聲明,轉向 TiXmlDeclaration 類。它是這個文檔節點的第一個孩子。
這是 TinyXML 解析的唯一的直接/特殊的標簽。一樣直接標簽被存在 TiXmlUnknown 類中。這樣當存儲到硬盤中時命令不會丟失。
<!-- Our to do list data -->
這是一個注釋。這個將生成一個 TiXmlComment 對象。
<ToDo>
"ToDo" 標簽定義一個 TiXmlElement 對象。這個對象沒有任何屬性,但是它包含兩個元素。
<Item priority="1">
生成另一個 TiXmlElement 對象,它是 "ToDo" 元素的孩子。這個元素有一個屬性,屬性名是 "priority",屬性值為 "1".
Go to the
這是一個 TiXmlText 對象。這是一個葉子節點,不能包含任何其他的節點。它是 "Item" TiXmlElement 對象的孩子。
<bold>
另一個 TiXmlElement 對象,這是 "Item" 元素的孩子。
等。
觀察整個對象樹,你可以得到:
TiXmlDocument "demo.xml"
TiXmlDeclaration "version='1.0'" "standalone=no"
TiXmlComment " Our to do list data"
TiXmlElement "ToDo"
TiXmlElement "Item" Attribtutes: priority = 1
TiXmlText "Go to the "
TiXmlElement "bold"
TiXmlText "Toy store!"
TiXmlElement "Item" Attributes: priority=2
TiXmlText "Do bills"
9。文檔(Documentation)
文檔用 Doxygen 建立,使用的 'dox' 配置文件。
10。協議
TinyXML 是在 zlib 協議下發布的。
這個軟件提供了 "as-is",沒有任何明確的或隱含的保證。作者不詳任何的有本軟件產生的損害負責。
任何人可以使用本軟件已達到任何目的,包括商業應用,可以修改它并重新發布,但是要服從一下的限制:
1)。這個軟件的起源不能被誤傳;你不能聲稱是你寫的這個最初軟件。如果你使用這個軟件在你的產品中,應該在產品的文檔的文檔中有對這個軟件的感謝,但這不是必須的。
2)。修改源代碼必須明白的標注清楚,不可以將其誤傳為原來的代碼。
3)。這個通知可以從任何源代碼的發布中不被刪除或修改。
11。參考資料(References)
World Wide Web 協會是 XML 的定義標注主體,他們的網頁中包含了大量的信息。
定義說明書可以在 http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-xml-20040204 找到。
我也推薦 Robert Eckstein 寫的 XML Pocket Reference 這本書,由 O'Reilly 出版社出版,你這個在這本書獲得全部入門的東西。
12。貢獻者,聯系,一個簡短的歷史(Contributors, Contacts, and a Brief History)
非常感謝每一位提出建議、錯誤、想法和鼓勵的人。它幫助并使得這個工程有趣。特別感謝那些在網頁上保持它一直充滿活力的貢獻者們。
太多的人攻陷發現的錯誤和想法,以至于我們在 changes.txt 文件中列出應得的感謝。
TinyXML 最初是由 Lee Thomason 寫的。(文檔中的“我”。)Lee 在 Yves Berquin、Andraw Ellerton 和 TinyXML 社區的幫助下審查改動和發布最新的版本。
我們感謝你的建議,并非常想知道你是否使用 TinyXML。希望你喜歡它并且發現它很有用。
歡迎提出問題,發表評論和程序錯誤。你也可以聯系我們:
http://www.sourceforge.net/projects/tinyxml
Lee Thomason, Yves Berquin, Andrew Ellerton
摘要: 最初想法來自于《編程珠璣》,下午實現了一下不多說了,直接看代碼吧 1 // 2 // HashTable 3 // 4 // goonyangxiaofang(AT)163(D... 閱讀全文來自于《編程珠璣》
計算球面的距離,輸入是球面上點的經度和緯度,得到一個原始點集,再得到另一個測量點集,輸出測量點集中的每個點到原始點集中的每個點的距離,這里的距離是兩個點的集合距離,即使在笛卡爾坐標系中的歐氏距離,根據經度和緯度,轉換為點在笛卡爾積中的 x, y, z 坐標
測試數據:
5
E23 N35
E150 N80
W50 N20
W175 N55
E20 S35
3
E105 S70
W40 S50
W160 S85
2 // goonyangxiaofang(at)163(dot)com
3 // QQ: 五九一二四七八七六
4 //
5
6 #include <iostream>
7 #include <string>
8 #include <vector>
9 #include <cmath>
10
11 class PointSet
12 {
13 public:
14 struct Point
15 {
16 std::string longitude;
17 std::string latitude;
18 double longi;
19 double lati;
20 double x, y, z;
21 private:
22 void ajust()
23 {
24 if (longitude[0] == 'E')
25 {
26 longi = atof(longitude.c_str() + 1);
27 }
28 else if (longitude[0] == 'W')
29 {
30 longi = 360.0 - atof(longitude.c_str() + 1);
31 }
32 if (latitude[0] == 'N')
33 {
34 lati = atof(latitude.c_str() + 1);
35 }
36 else if (latitude[0] == 'S')
37 {
38 lati = -atof(latitude.c_str() + 1);
39 }
40 x = R * cos(lati * PI / 180.0) * cos(longi * PI / 180.0);
41 y = R * cos(lati * PI / 180.0) * sin(longi * PI / 180.0);
42 z = R * sin(lati * PI / 180.0);
43 }
44 public:
45 Point() : longitude(""), latitude(""), longi(0.0), lati(0.0), x(0.0), y(0.0), z(0.0) {}
46 Point(const std::string& s1, const std::string& s2) : longitude(s1), latitude(s2)
47 {
48 ajust();
49 }
50 Point(const Point& p) : longitude(p.longitude), latitude(p.latitude), longi(p.longi), lati(p.lati), x(p.x), y(p.y), z(p.z) {};
51 Point& operator=(const Point& p)
52 {
53 longitude = p.longitude;
54 latitude = p.latitude;
55 longi = p.longi;
56 lati = p.lati;
57 x = p.x;
58 y = p.y;
59 z = p.z;
60 return *this;
61 }
62 bool operator==(const Point& p) const
63 {
64 return longitude == p.longitude && latitude == p.latitude;
65 }
66 double distance(const Point& p)
67 {
68 return sqrt((x - p.x) * (x - p.x) + (y - p.y) * (y - p.y) + (z - p.z) * (z - p.z));
69 }
70 friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, Point& p);
71 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Point& p);
72 };
73 private:
74 std::vector<Point> m_set;
75 static const double R;
76 static const double PI;
77 public:
78 void insert(const std::string& s1, const std::string& s2)
79 {
80 Point p(s1, s2);
81 m_set.push_back(p);
82 }
83 void insert(const Point& p)
84 {
85 m_set.push_back(p);
86 }
87 void print()
88 {
89 for (std::size_t i = 0; i < m_set.size(); ++i)
90 {
91 std::cout << "Point " << i + 1 << ": ";
92 std::cout << m_set[i];
93 }
94 }
95 std::size_t size()
96 {
97 return m_set.size();
98 }
99 Point& operator[](std::size_t i)
100 {
101 return m_set[i];
102 }
103 const Point& operator[](std::size_t i) const
104 {
105 return m_set[i];
106 }
107 };
108
109 std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, PointSet::Point& p)
110 {
111 std::string s1, s2;
112 in >> s1 >> s2;
113 PointSet::Point p2(s1, s2);
114 p = p2;
115 return in;
116 }
117
118 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const PointSet::Point& p)
119 {
120 out << p.longitude << ' ';
121 out << p.latitude << ' ';
122 out << p.longi << ' ';
123 out << p.lati << ' ';
124 out << p.x << ' ';
125 out << p.y << ' ';
126 out << p.z << ' ';
127 out << std::endl;
128 return out;
129 }
130
131 const double PointSet::R = 6400.0;
132 const double PointSet::PI = 3.1415926;
133
134 int main()
135 {
136 PointSet ps;
137 PointSet::Point p;
138 long n;
139 std::cin >> n;
140 for (long i = 0; i < n; ++i)
141 {
142 std::cin >> p;
143 ps.insert(p);
144 }
145 ps.print();
146
147 PointSet measure_ps;
148 std::cin >> n;
149 for (long i = 0; i < n; ++i)
150 {
151 std::cin >> p;
152 measure_ps.insert(p);
153 }
154 measure_ps.print();
155 for (std::size_t i = 0; i < measure_ps.size(); ++i)
156 {
157 for (std::size_t j = 0; j < ps.size(); ++j)
158 {
159 std::cout << "From " << i + 1 << " to " << j + 1 << ": " << ps[j].distance(measure_ps[i]) << std::endl;
160 }
161 }
162 return 0;
163 }
164


