設(shè)計模式的分類:
·創(chuàng)建型
·結(jié)構(gòu)型
·行為型
1.創(chuàng)建型模式
·簡單工廠模式 (Simple Factory)
·工廠方法模式 (Factory Method)
·抽象工廠模式 (Abstract Factory)
·建造者模式 (Builder)
·原型模式 (Prototype)
·單例模式 (Singleton)
2.結(jié)構(gòu)型模式
·外觀模式 (Facade)
·適配器模式 (Adapter)
·代理模式 (Proxy)
·裝飾模式 (Decorator)
·橋接模式 (Bridge)
·組合模式 (Composite)
·享元模式 (Flyweight)
3.行為型模式
·模板方法模式 (Template Method)
·觀察者模式 (Observer)
·狀態(tài)模式 (State)
·策略模式 (Strategy)
·職責鏈模式 (Chain of Responsibility)
·命令模式 (Command)
·訪問者模式 (Visitor)
·調(diào)停者模式 (Mediator)
·備忘錄模式 (Memento)
·迭代器模式 (Iterator)
·解釋器模式 (Interpreter)
posted @
2011-05-01 18:55 unixfy 閱讀(195) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏搜索引擎會通過日志文件把用戶每次檢索使用的所有檢索串都記錄下來,每個查詢串的長度為1-255字節(jié)。
假設(shè)目前有一千萬個記錄(這些查詢串的重復(fù)度比較高,雖然總數(shù)是1千萬,但如果除去重復(fù)后,不超過3百萬個。一個查詢串的重復(fù)度越高,說明查詢它的用戶越多,也就是越熱門。請你統(tǒng)計最熱門的10個查詢串,要求使用的內(nèi)存不能超過1G。
先統(tǒng)計所有查詢的次數(shù),所有查詢有 300 萬個,255 * 300 * 10000B = 765 MB,可以存入內(nèi)存。這里使用 STL 中的 map。所得時間復(fù)雜度為 O(NlogM),N 為所有的查詢,包括重復(fù)的,M 為不重復(fù)的查詢。更好的方法是用散列。
然后遍歷 map,維護一個大小為 10 的集合,在遍歷 map 時,比較當前查詢的出現(xiàn)次數(shù)與集合中出現(xiàn)次數(shù)最小的查詢的出現(xiàn)此時比較,如果大于,將當前查詢替換到集合中。
這里的集合還是用的 map,時間復(fù)雜度為 O(MlogK),這里 K = 10。
總的時間復(fù)雜度為 O(NlogM) + O(MlogK)
也可以將這個過程合二為一。即每次在統(tǒng)計的過程中,查詢大小為 K 的集合。如果符合條件,則將當前查詢替換到集合中。但是還要考慮實時更新集合中的元素。
這種方法的時間復(fù)雜度為 O(N(logM + logK + K))。
由于第二種方法還得考慮實時更新。效率遠沒有第一種方案高。
實現(xiàn):
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <fstream>
3 #include <map>
4 #include <string>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 void statistics(map<string, int>& data, const string& query)
8 {
9 ++data[query];
10 }
11
12 void findTopK(multimap<int, string>& topK, int k, const map<string, int>& data)
13 {
14 topK.clear();
15 for (map<string, int>::const_iterator cit = data.begin(); cit != data.end(); ++cit)
16 {
17 if (topK.size() < k)
18 {
19 topK.insert(make_pair(cit->second, cit->first));
20 }
21 else
22 {
23 if (cit->second > topK.begin()->first)
24 {
25 topK.erase(topK.begin());
26 topK.insert(make_pair(cit->second, cit->first));
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 }
31
32 int main()
33 {
34 ifstream fin("queryfile.txt");
35 map<string, int> data;
36 multimap<int, string> top10;
37 string query;
38 while (getline(fin, query))
39 {
40 statistics(data, query);
41 }
42
43 //for (map<string, int>::const_iterator cit = data.begin(); cit != data.end(); ++cit)
44 //{
45 // cout << cit->first << '\t' << cit->second << endl;
46 //}
47
48 //cout << endl;
49 findTopK(top10, 10, data);
50
51 for (multimap<int, string>::const_reverse_iterator cit = top10.rbegin(); cit != top10.rend(); ++cit)
52 {
53 cout << cit->second << '\t' << cit->first << endl;
54 }
55
56 return 0;
57 }
http://blog.donews.com/jiji262/2011/03/baidu_top_k_interview/http://blog.redfox66.com/post/2010/09/23/top-k-algoriyhm-analysis.aspxhttp://blog.csdn.net/jasonblog/archive/2010/08/19/5825026.aspx
posted @
2011-04-30 18:06 unixfy 閱讀(216) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏來自于《大話設(shè)計模式》
訪問者模式(Visitor):
表示一個作用于某對象結(jié)構(gòu)中的個元素的操作。它是你可以在不改變各元素的類的前提下定義作用于這些元素的新操作。
行為型
UML 類圖:
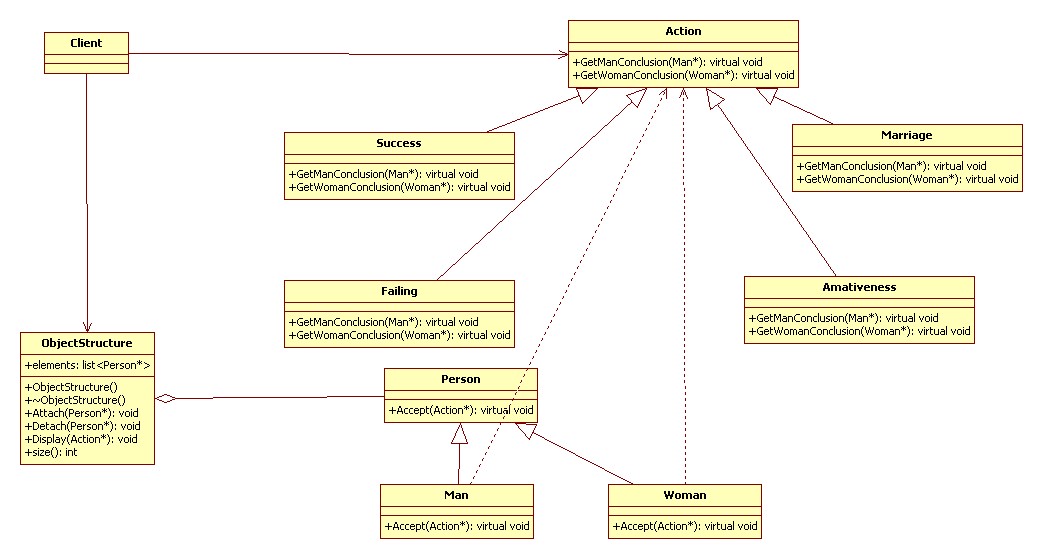
代碼實現(xiàn) C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <string>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 class Action;
8
9 class Person
10 {
11 protected:
12 string name;
13 public:
14 Person(const string& s = "Person") : name(s) {}
15 virtual void Accept(Action* visitor) = 0;
16 virtual string getName()
17 {
18 return name;
19 }
20 };
21
22 class Man;
23 class Woman;
24
25 class Action
26 {
27 protected:
28 string name;
29 public:
30 Action(const string& s = "Action") : name(s) {}
31 virtual void GetManConclusion(Man* m) = 0;
32 virtual void GetWomanConclusion(Woman* w) = 0;
33 };
34
35 class Man : public Person
36 {
37 public:
38 Man(const string& s = "Man") : Person(s) {}
39 virtual void Accept(Action* visitor)
40 {
41 visitor->GetManConclusion(this);
42 }
43 };
44
45 class Woman : public Person
46 {
47 public:
48 Woman(const string& s = "Woman") : Person(s) {}
49 virtual void Accept(Action* visitor)
50 {
51 visitor->GetWomanConclusion(this);
52 }
53 };
54
55 class Success : public Action
56 {
57 public:
58 Success(const string& s = "Success") : Action(s) {}
59 virtual void GetManConclusion(Man* m)
60 {
61 cout << name << endl;
62 cout << m->getName() << endl;
63 cout << "1" << endl;
64 }
65 virtual void GetWomanConclusion(Woman* w)
66 {
67 cout << name << endl;
68 cout << w->getName() << endl;
69 cout << "2" << endl;
70 }
71 };
72
73 class Failing : public Action
74 {
75 public:
76 Failing(const string& s = "Failing") : Action(s) {}
77 virtual void GetManConclusion(Man* m)
78 {
79 cout << name << endl;
80 cout << m->getName() << endl;
81 cout << "3" << endl;
82 }
83 virtual void GetWomanConclusion(Woman* w)
84 {
85 cout << name << endl;
86 cout << w->getName() << endl;
87 cout << "4" << endl;
88 }
89 };
90
91 class Amativeness : public Action
92 {
93 public:
94 Amativeness(const string& s = "Amativeness") : Action(s) {}
95 virtual void GetManConclusion(Man* m)
96 {
97 cout << name << endl;
98 cout << m->getName() << endl;
99 cout << "5" << endl;
100 }
101 virtual void GetWomanConclusion(Woman* w)
102 {
103 cout << name << endl;
104 cout << w->getName() << endl;
105 cout << "6" << endl;
106 }
107 };
108
109 class Marriage : public Action
110 {
111 public:
112 Marriage(const string& s = "Marriage") : Action(s) {}
113 virtual void GetManConclusion(Man* m)
114 {
115 cout << name << endl;
116 cout << m->getName() << endl;
117 cout << "7" << endl;
118 }
119 virtual void GetWomanConclusion(Woman* w)
120 {
121 cout << name << endl;
122 cout << w->getName() << endl;
123 cout << "8" << endl;
124 }
125 };
126
127 class ObjectStructure
128 {
129 private:
130 list<Person*> elements;
131 public:
132 ObjectStructure() {}
133 ~ObjectStructure()
134 {
135 for (list<Person*>::iterator iter = elements.begin(); iter != elements.end(); ++iter)
136 {
137 delete (*iter);
138 }
139 }
140 void Attach(Person* element)
141 {
142 elements.push_back(element);
143 }
144 void Detach(Person* element)
145 {
146 list<Person*>::iterator iter = find(elements.begin(), elements.end(), element);
147 if (iter != elements.end())
148 {
149 elements.erase(iter);
150 }
151 }
152 void Display(Action* visitor)
153 {
154 for (list<Person*>::iterator iter = elements.begin(); iter != elements.end(); ++iter)
155 {
156 (*iter)->Accept(visitor);
157 }
158 }
159 int size()
160 {
161 return elements.size();
162 }
163 };
164
165 int main()
166 {
167 ObjectStructure o;
168 o.Attach(new Man);
169 o.Attach(new Woman);
170
171 cout << o.size() << endl;
172
173 Success* v1 = new Success;
174 o.Display(v1);
175 Failing* v2 = new Failing;
176 o.Display(v2);
177 Amativeness* v3 = new Amativeness;
178 o.Display(v3);
179 Marriage* v4 = new Marriage;
180 o.Display(v4);
181
182 delete v4;
183 delete v3;
184 delete v2;
185 delete v1;
186
187 return 0;
188 }
posted @
2011-04-30 15:21 unixfy 閱讀(468) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏來自于《大話設(shè)計模式》
解釋器模式(Interpreter):
給定一個語言,定義它的文法的一種表示,并定義一個解釋器,這個解釋器使用該表示來解釋語言中的句子。
行為型
UML 類圖:
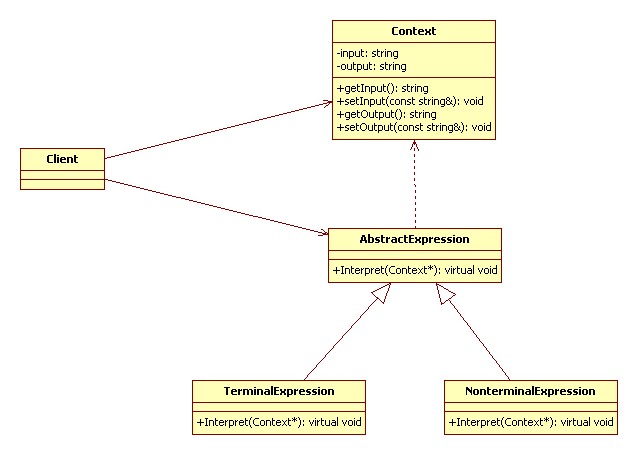
代碼實現(xiàn) C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 #include <list>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 class Context
7 {
8 private:
9 string input;
10 string output;
11 public:
12 string getInput()
13 {
14 return input;
15 }
16 void setInput(const string& s)
17 {
18 input = s;
19 }
20 string getOutput()
21 {
22 return output;
23 }
24 void setOutput(const string& s)
25 {
26 output = s;
27 }
28 };
29
30 class AbstractExpression
31 {
32 public:
33 virtual void Interpret(Context* context) = 0;
34 };
35
36 class TerminalExpression : public AbstractExpression
37 {
38 public:
39 virtual void Interpret(Context* context)
40 {
41 context->setOutput("終端解釋器:" + context->getInput());
42 cout << context->getOutput() << endl;
43 }
44 };
45
46 class NonterminalExpression : public AbstractExpression
47 {
48 public:
49 virtual void Interpret(Context* context)
50 {
51 context->setOutput("非終端解釋器:" + context->getInput());
52 cout << context->getOutput() << endl;
53 }
54 };
55
56 int main()
57 {
58 Context* context = new Context;
59 context->setInput("abc");
60 list<AbstractExpression*> lae;
61
62 lae.push_back(new TerminalExpression);
63 lae.push_back(new NonterminalExpression);
64 lae.push_back(new TerminalExpression);
65 lae.push_back(new TerminalExpression);
66
67 for (list<AbstractExpression*>::iterator iter = lae.begin(); iter != lae.end(); ++iter)
68 {
69 (*iter)->Interpret(context);
70 }
71
72 for (list<AbstractExpression*>::iterator iter = lae.begin(); iter != lae.end(); ++iter)
73 {
74 delete (*iter);
75 }
76 delete context;
77
78 return 0;
79 }
posted @
2011-04-30 14:32 unixfy 閱讀(964) |
評論 (2) |
編輯 收藏來自于《大話設(shè)計模式》
享元模式(Flyweight):
運用共享技術(shù)有效地支持大量細粒度的對象。
結(jié)構(gòu)型
UML 類圖:
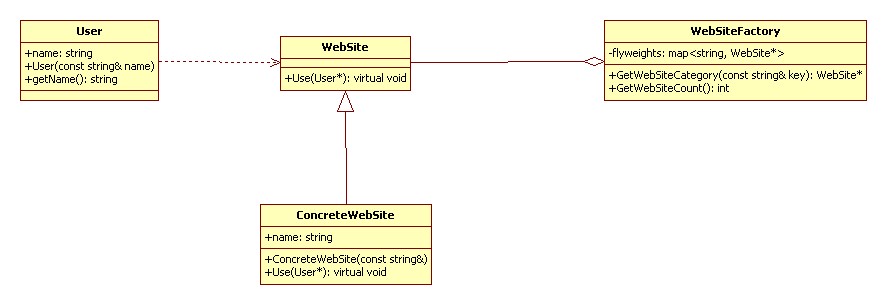
代碼實現(xiàn) C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <map>
3 #include <string>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 class User
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 public:
11 User(const string& s) : name(s) {}
12 string getName()
13 {
14 return name;
15 }
16 };
17
18 class WebSite
19 {
20 public:
21 WebSite() {}
22 virtual ~WebSite() {}
23 virtual void Use(User* user) = 0;
24 };
25
26 class ConcreteWebSite : public WebSite
27 {
28 private:
29 string name;
30 public:
31 ConcreteWebSite() {}
32 virtual ~ConcreteWebSite() {}
33 ConcreteWebSite(const string& s) : name(s){}
34 virtual void Use(User* user)
35 {
36 cout << "網(wǎng)站分類:" << name << " 用戶:" << user->getName() << endl;
37 }
38 };
39
40 class WebSiteFactory
41 {
42 private:
43 map<string, WebSite*> flyweights;
44 public:
45 ~WebSiteFactory()
46 {
47 for (map<string, WebSite*>::iterator iter = flyweights.begin(); iter != flyweights.end(); ++iter)
48 {
49 delete iter->second;
50 }
51 }
52 WebSite* GetWebSiteCategory(const string& key)
53 {
54 map<string, WebSite*>::iterator iter = flyweights.find(key);
55 if (iter != flyweights.end())
56 {
57 return iter->second;
58 }
59 else
60 {
61 flyweights.insert(make_pair(key, new ConcreteWebSite(key)));
62 return flyweights[key];
63 }
64 }
65 int GetWebSiteCount()
66 {
67 return flyweights.size();
68 }
69 };
70
71 int main()
72 {
73 WebSiteFactory* f = new WebSiteFactory;
74 cout << f->GetWebSiteCount() << endl;
75 WebSite* fx = f->GetWebSiteCategory("產(chǎn)品展示");
76 cout << f->GetWebSiteCount() << endl;
77 User* user = new User("小菜");
78 fx->Use(user);
79 delete user;
80
81 WebSite* fy = f->GetWebSiteCategory("產(chǎn)品展示");
82 cout << f->GetWebSiteCount() << endl;
83 user = new User("大鳥");
84 fy->Use(user);
85 delete user;
86
87 WebSite* fz = f->GetWebSiteCategory("產(chǎn)品展示");
88 cout << f->GetWebSiteCount() << endl;
89 user = new User("嬌嬌");
90 fz->Use(user);
91 delete user;
92
93 WebSite* fl = f->GetWebSiteCategory("博客");
94 cout << f->GetWebSiteCount() << endl;
95 user = new User("老頑童");
96 fl->Use(user);
97 delete user;
98
99 WebSite* fm = f->GetWebSiteCategory("博客");
100 cout << f->GetWebSiteCount() << endl;
101 user = new User("桃谷六仙");
102 fm->Use(user);
103 delete user;
104
105 WebSite* fn = f->GetWebSiteCategory("博客");
106 cout << f->GetWebSiteCount() << endl;
107 user = new User("南海鱷神");
108 fn->Use(user);
109 delete user;
110
111 cout << "網(wǎng)站分類總數(shù)為:" << f->GetWebSiteCount() << endl;
112 delete f;
113 return 0;
114 }
posted @
2011-04-30 14:09 unixfy 閱讀(248) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏來自于《大話設(shè)計模式》
終結(jié)者模式(Mediator):
用一個中介對象來封裝一系列的對象交互。中介者使各對象不需要顯式地相互作用,從而使其耦合松散,而且可以獨立地改變他們之間的交互。
行為型
UML 類圖:
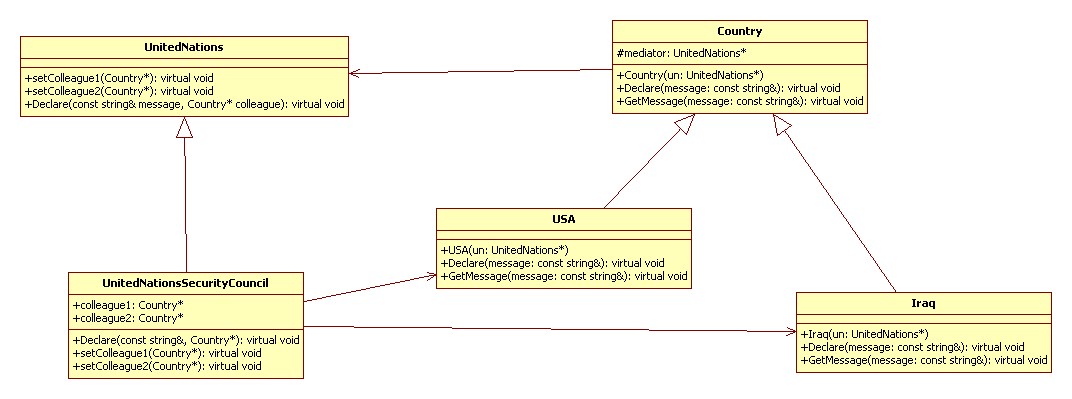
代碼實現(xiàn) C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class Country;
6
7 class UnitedNations
8 {
9 public:
10 virtual void Declare(const string& message, Country* colleague) = 0;
11 virtual void setColleague1(Country* c1) = 0;
12 virtual void setColleague2(Country* c2) = 0;
13 };
14
15 class Country
16 {
17 protected:
18 UnitedNations* mediator;
19 public:
20 Country(UnitedNations* un) : mediator(un) {}
21 virtual void Declare(const string& message) = 0;
22 virtual void GetMessage(const string& message) = 0;
23 };
24
25 class USA : public Country
26 {
27 public:
28 USA(UnitedNations* un) : Country(un) {}
29 void Declare(const string& message)
30 {
31 mediator->Declare(message, this);
32 }
33 void GetMessage(const string& message)
34 {
35 cout << "美國獲得對方信息:" << message << endl;
36 }
37 };
38
39 class Iraq : public Country
40 {
41 public:
42 Iraq(UnitedNations* un) : Country(un) {}
43 void Declare(const string& message)
44 {
45 mediator->Declare(message, this);
46 }
47 void GetMessage(const string& message)
48 {
49 cout << "伊拉克獲得對方信息:" << message << endl;
50 }
51 };
52
53 class UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil : public UnitedNations
54 {
55 private:
56 Country* colleague1;
57 Country* colleague2;
58 public:
59 void setColleague1(Country* u)
60 {
61 colleague1 = u;
62 }
63 void setColleague2(Country* i)
64 {
65 colleague2 = i;
66 }
67 virtual void Declare(const string& message, Country* colleague)
68 {
69 if (colleague == colleague1)
70 {
71 colleague2->GetMessage(message);
72 }
73 else
74 {
75 colleague1->GetMessage(message);
76 }
77 }
78 };
79
80 int main()
81 {
82 UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil* UNSC = new UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil;
83 USA* c1 = new USA(UNSC);
84 Iraq* c2 = new Iraq(UNSC);
85
86 UNSC->setColleague1(c1);
87 UNSC->setColleague2(c2);
88
89 c1->Declare("不準研制核武器,否則要發(fā)動戰(zhàn)爭!");
90 c2->Declare("我們沒有核武器,也不怕侵略!");
91
92 delete c2;
93 delete c1;
94 delete UNSC;
95
96 return 0;
97 }
posted @
2011-04-30 12:02 unixfy 閱讀(524) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏職責鏈模式(Chain of Responsibility):
使多個對象都有機會處理請求,從而避免請求的發(fā)送者和接受者之間的耦合關(guān)系。將這個對象連成一條鏈,并沿著這條鏈傳遞該請求,直到有一個對象處理它為止。
行為型
UML 類圖:
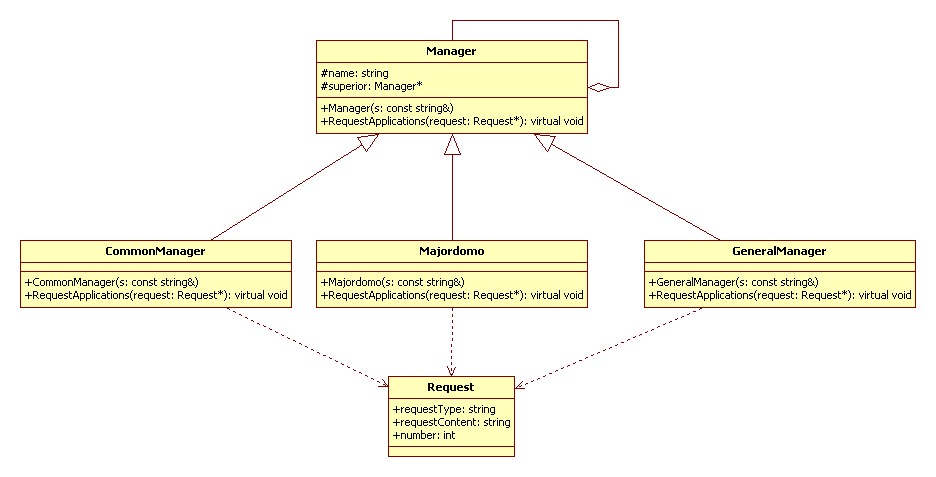
代碼實現(xiàn) C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class Request
6 {
7 public:
8 string requestType;
9 string requestContent;
10 int number;
11 };
12
13 class Manager
14 {
15 protected:
16 string name;
17 Manager* superior;
18 public:
19 Manager(const string& s) : name(s), superior(0) {}
20 void SetSuperior(Manager* m)
21 {
22 superior = m;
23 }
24 virtual void RequestApplications(Request* request) = 0;
25 };
26
27 class CommonManager : public Manager
28 {
29 public:
30 CommonManager(const string& s) : Manager(s) {}
31 virtual void RequestApplications(Request* request)
32 {
33 if (request->requestType == "請假" && request->number <= 2)
34 {
35 cout << name << ": " << request->requestContent << " 數(shù)量 " << request->number << " 被批準!" << endl;
36 }
37 else if (superior != 0)
38 {
39 superior->RequestApplications(request);
40 }
41 else
42 {
43 cout << "不能得到處理!" << endl;
44 }
45 }
46 };
47
48 class Majordomo : public Manager
49 {
50 public:
51 Majordomo(const string& s) : Manager(s) {}
52 virtual void RequestApplications(Request* request)
53 {
54 if (request->requestType == "請假" && request->number <= 5)
55 {
56 cout << name << ": " << request->requestContent << " 數(shù)量 " << request->number << " 被批準!" << endl;
57 }
58 else if (superior != 0)
59 {
60 superior->RequestApplications(request);
61 }
62 else
63 {
64 cout << "不能得到處理!" << endl;
65 }
66 }
67 };
68
69 class GeneralManager : public Manager
70 {
71 public:
72 GeneralManager(const string& s) : Manager(s) {}
73 virtual void RequestApplications(Request* request)
74 {
75 if (request->requestType == "請假")
76 {
77 cout << name << ": " << request->requestContent << " 數(shù)量 " << request->number << " 被批準!" << endl;
78 }
79 else if (request->requestType == "加薪" && request->number <= 500)
80 {
81 cout << name << ": " << request->requestContent << " 數(shù)量 " << request->number << " 被批準!" << endl;
82 }
83 else if (request->requestType == "加薪" && request->number > 500)
84 {
85 cout << name << ": " << request->requestContent << " 數(shù)量 " << request->number << " 再說吧!" << endl;
86 }
87 else if (superior != 0)
88 {
89 superior->RequestApplications(request);
90 }
91 else
92 {
93 cout << "不能得到處理!" << endl;
94 }
95 }
96 };
97
98 int main()
99 {
100 CommonManager* jinli = new CommonManager("金利");
101 Majordomo* zongjian = new Majordomo("宗劍");
102 GeneralManager* zhongjingli = new GeneralManager("鐘精勵");
103
104 jinli->SetSuperior(zongjian);
105 zongjian->SetSuperior(zhongjingli);
106
107 Request* request = new Request;
108 request->requestType = "請假";
109 request->requestContent = "小菜請假";
110 request->number = 1;
111 jinli->RequestApplications(request);
112
113 Request* request2 = new Request;
114 request2->requestType = "請假";
115 request2->requestContent = "小菜請假";
116 request2->number = 4;
117 jinli->RequestApplications(request2);
118
119 Request* request3 = new Request;
120 request3->requestType = "加薪";
121 request3->requestContent = "小菜請求加薪";
122 request3->number = 500;
123 jinli->RequestApplications(request3);
124
125 Request* request4 = new Request;
126 request4->requestType = "加薪";
127 request4->requestContent = "小菜請求加薪";
128 request4->number = 1000;
129 jinli->RequestApplications(request4);
130
131 return 0;
132 }
posted @
2011-04-30 11:07 unixfy 閱讀(210) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏來自于《大話設(shè)計模式》
命令模式(Command):將一個請求封裝為一個對象,從而使你可用不同的請求對客戶進行參數(shù)化;對請求排隊或記錄請求日志,以及支持可撤銷的操作。
行為型
UML 類圖:
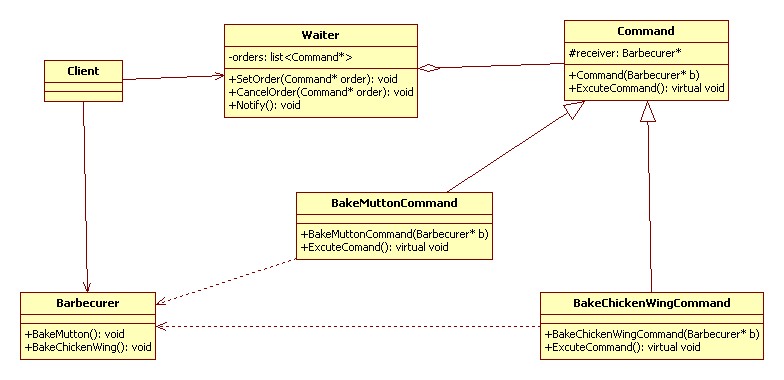
代碼實現(xiàn) C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 class Barbecurer
7 {
8 public:
9 void BakeMutton()
10 {
11 cout << "烤羊肉串!" << endl;
12 }
13 void BakeChickenWing()
14 {
15 cout << "烤雞翅!" << endl;
16 }
17 };
18
19 class Command
20 {
21 protected:
22 Barbecurer* receiver;
23 public:
24 Command(Barbecurer* b)
25 {
26 receiver = b;
27 }
28 virtual void ExcuteCommand() = 0;
29 };
30
31 class BakeMuttonCommand : public Command
32 {
33 public:
34 BakeMuttonCommand(Barbecurer* b) : Command(b) {}
35 virtual void ExcuteCommand()
36 {
37 receiver->BakeMutton();
38 }
39 };
40
41 class BakeChickenWingCommand : public Command
42 {
43 public:
44 BakeChickenWingCommand(Barbecurer* b) : Command(b) {}
45 virtual void ExcuteCommand()
46 {
47 receiver->BakeChickenWing();
48 }
49 };
50
51 class Waiter
52 {
53 private:
54 list<Command*> orders;
55 public:
56 void SetOrder(Command* order)
57 {
58 cout << "增加訂單!" << endl;
59 orders.push_back(order);
60 }
61 void CancelOrder(Command* order)
62 {
63 list<Command*>::iterator iter = find(orders.begin(), orders.end(), order);
64 if (iter != orders.end())
65 {
66 cout << "取消訂單!" << endl;
67 orders.erase(iter);
68 }
69 }
70 void Notify()
71 {
72 for (list<Command*>::iterator iter = orders.begin(); iter != orders.end(); ++iter)
73 {
74 (*iter)->ExcuteCommand();
75 }
76 }
77 };
78
79 int main()
80 {
81 Barbecurer* boy = new Barbecurer;
82
83 Command* bakeMuttonCommand1 = new BakeMuttonCommand(boy);
84 Command* bakeMuttonCommand2 = new BakeMuttonCommand(boy);
85 Command* bakeChickenWingCommand1 = new BakeChickenWingCommand(boy);
86
87 Waiter* girl = new Waiter;
88
89 girl->SetOrder(bakeMuttonCommand1);
90 girl->SetOrder(bakeMuttonCommand2);
91 girl->SetOrder(bakeChickenWingCommand1);
92
93 girl->Notify();
94
95
96 girl->CancelOrder(bakeMuttonCommand2);
97 girl->Notify();
98
99 return 0;
100 }
posted @
2011-04-29 21:15 unixfy 閱讀(385) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏來自于《大話設(shè)計模式》
橋接模式(Bridge):將抽象部分與它的實現(xiàn)部分分離,使它們都可以獨立地變化。
結(jié)構(gòu)型
UML 類圖:
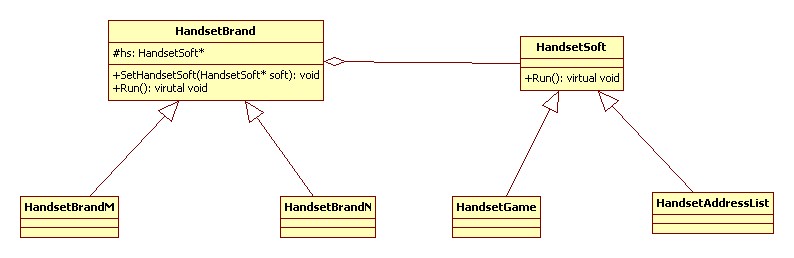
代碼實現(xiàn) C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class HandsetSoft
5 {
6 public:
7 virtual void Run() = 0;
8 };
9
10 class HandsetGame : public HandsetSoft
11 {
12 public:
13 virtual void Run()
14 {
15 cout << "運行手機游戲!" << endl;
16 }
17 };
18
19 class HandsetAddressList : public HandsetSoft
20 {
21 public:
22 virtual void Run()
23 {
24 cout << "運行手機通訊錄!" << endl;
25 }
26 };
27
28 class HandsetBrand
29 {
30 protected:
31 HandsetSoft* hs;
32 public:
33 HandsetBrand() : hs(0) {}
34 virtual ~HandsetBrand()
35 {
36 delete hs;
37 }
38 void SetHandsetSoft(HandsetSoft* soft)
39 {
40 delete hs;
41 hs = soft;
42 }
43 virtual void Run() = 0;
44 };
45
46 class HandsetBrandN : public HandsetBrand
47 {
48 public:
49 virtual void Run()
50 {
51 hs->Run();
52 }
53 };
54
55 class HandsetBrandM : public HandsetBrand
56 {
57 public:
58 virtual void Run()
59 {
60 hs->Run();
61 }
62 };
63
64 int main()
65 {
66 HandsetBrand* ab = new HandsetBrandN;
67
68 ab->SetHandsetSoft(new HandsetGame);
69 ab->Run();
70
71 ab->SetHandsetSoft(new HandsetAddressList);
72 ab->Run();
73
74 delete ab;
75
76 ab = new HandsetBrandM;
77
78 ab->SetHandsetSoft(new HandsetGame);
79 ab->Run();
80
81 ab->SetHandsetSoft(new HandsetAddressList);
82 ab->Run();
83
84 delete ab;
85
86 return 0;
87 }
posted @
2011-04-29 20:42 unixfy 閱讀(342) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏
來自于《大話設(shè)計模式》
單例模式(Singleton):保證一個類僅有一個實例,并提供訪問它的全局訪問點。類的實例化有類本身管理。
UML 類圖:

代碼實現(xiàn) C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class Singleton
5 {
6 private:
7 static Singleton* instance;
8 Singleton() {}
9 public:
10 static Singleton* GetInstance()
11 {
12 if (instance == 0)
13 {
14 instance = new Singleton;
15 }
16 return instance;
17 }
18 ~Singleton()
19 {
20 delete instance;
21 }
22 };
23
24 Singleton* Singleton::instance = 0;
25
26 int main()
27 {
28 Singleton* s1 = Singleton::GetInstance();
29 Singleton* s2 = Singleton::GetInstance();
30
31 cout << s1 << endl;
32 cout << s2 << endl;
33
34 return 0;
35 }
posted @
2011-04-29 17:09 unixfy 閱讀(240) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏