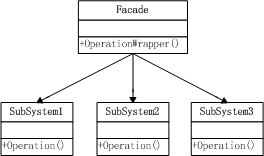
外觀模式(Facade)的定義是:為子系統(tǒng)中的一組接口提供一個(gè)一致的界面,F(xiàn)acade模式定義了一個(gè)高層接口,這個(gè)接口使得這一子系統(tǒng)更加容易使用。結(jié)構(gòu)圖如下:
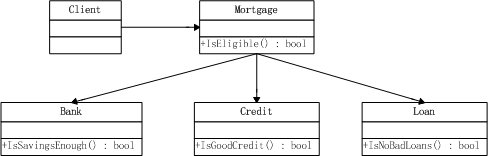
假設(shè)有一個(gè)抵押系統(tǒng),存在三個(gè)子系統(tǒng),銀行子系統(tǒng)(查詢是否有足夠多的存款)、信用子系統(tǒng)(查詢是否有良好的信用)以及貸款子系統(tǒng)(查詢有無貸款劣跡),只有這三個(gè)子系統(tǒng)都通過時(shí)才可進(jìn)行抵押。
當(dāng)客戶申請(qǐng)抵押貸款時(shí),他需要分別去這三個(gè)子系統(tǒng)辦理相關(guān)手續(xù),此時(shí)若使用外觀模式為三個(gè)子系統(tǒng)中的接口提供一個(gè)統(tǒng)一的服務(wù),這時(shí),客戶再辦理手續(xù)就只需要去一個(gè)地方了,結(jié)構(gòu)圖如下:
實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼:
//Bank.h
class Bank
{
public:
Bank();
virtual ~Bank();
bool IsSavingsEnought();
};
//Bank.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Mortgage.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Mortgage* pMortgage = new Mortgage;
pMortgage->IsEligible();
return 0;
}
//Credit.h
class Credit
{
public:
Credit();
virtual ~Credit();
bool IsGoodCredit();
};
//Credit.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Credit.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Credit::Credit()
{
}
Credit::~Credit()
{
}
bool Credit::IsGoodCredit()
{
cout << "信用系統(tǒng)檢查是否有良好的信用" << endl;
return true;
}
//Loan.h
class Loan
{
public:
Loan();
virtual ~Loan();
bool IsNoBadLoans();
};
//Loan.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Loan.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Loan::Loan()
{
}
Loan::~Loan()
{
}
bool Loan::IsNoBadLoans()
{
cout << "貸款系統(tǒng)檢查是否沒有貸款劣跡" << endl;
return true;
}
//Mortgage.h
class Mortgage
{
public:
Mortgage();
virtual ~Mortgage();
bool IsEligible();
};
//Mortgage.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Mortgage.h"
#include "Bank.h"
#include "Credit.h"
#include "Loan.h"
Mortgage::Mortgage()
{
}
Mortgage::~Mortgage()
{
}
bool Mortgage::IsEligible()
{
Bank* pBank = new Bank;
Credit* pCredit = new Credit;
Loan* pLoan = new Loan;
return pBank->IsSavingsEnought() && pCredit->IsGoodCredit() && pLoan->IsNoBadLoans();
}
//main.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Mortgage.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Mortgage* pMortgage = new Mortgage;
pMortgage->IsEligible();
return 0;
}
最后輸出為:
銀行系統(tǒng)檢查是否有足夠的存款
信用系統(tǒng)檢查是否有良好的信用
貸款系統(tǒng)檢查是否沒有貸款劣跡