要求:
高級操作系統與分布式系統作業
ps和top命令列出了unix中當前所有進程的相關信息�,作業要求在linux中增加兩個系統調用�,功能如下:
hide():執行此系統調用后�,隱藏當前進程�,即當前進程不能夠被ps和top命令查看到。
unhide():執行此系統調用后�,取消隱藏當前進程,即當前進程恢復正常�,能夠被ps和top命令查看到。
解題思路:
Ps命令和top命令從/proc文件系統中讀取進程信息并顯示出來�。因此,如果一個進程的進程號沒有在/proc文件系統中反映出來�,則這個進程被“隱藏”了�����,“隱藏”進程在ps或top命令的輸出不出現�����。
2。修改linux的進程控制塊task_struts���,在進程控制塊中增加一個字段:
int hide;
hide的值為1時,表示該進程被隱藏���;為0時,表示該進程不被隱藏�。
3�����。修改創建進程的相關代碼,在進程創建時�����,置hide為0;即進程在初始創建時(默認)不被隱藏�。
4�����。在系統中增加系統調用hide()���,其功能為:
1)將進程控制塊中的hide置1�;
2)刪除/proc文件系統中該進程的相關目錄項;
5�。在系統中增加系統調用unhide()�,其功能為:
1)將進程控制塊中的hide清0���;
2)增加/proc文件系統中該進程的相關目錄項
具體做法:(實驗內核版本2.6.28,)
跟蹤內核可知�,proc目錄下進程號目錄是動態生成的,是在每次readdir,getdents時動態生成�����,所以從某種意義上說增加或刪除/proc文件系統中該進程的相關目錄項這種說法是不正確的�。proc目錄內容的填充函數是proc_pid_readdir(fs/proc/base.c)
int proc_pid_readdir(struct file * filp, void * dirent, filldir_t filldir) //內核源碼,修改前
{
unsigned int nr = filp->f_pos - FIRST_PROCESS_ENTRY;
struct task_struct *reaper = get_proc_task(filp->f_path.dentry->d_inode);
struct tgid_iter iter;
struct pid_namespace *ns;
if (!reaper)
goto out_no_task;
for (; nr < ARRAY_SIZE(proc_base_stuff); filp->f_pos++, nr++) { //這個for�����,填充self目錄
const struct pid_entry *p = &proc_base_stuff[nr];
if (proc_base_fill_cache(filp, dirent, filldir, reaper, p) < 0)
goto out;
}
ns = filp->f_dentry->d_sb->s_fs_info;
iter.task = NULL;
iter.tgid = filp->f_pos - TGID_OFFSET;
for (iter = next_tgid(ns, iter);
iter.task;
iter.tgid += 1, iter = next_tgid(ns, iter)) { //這個for,根據系統內進程動態添加子進程號目錄�,也正是我們需要修改的函數
filp->f_pos = iter.tgid + TGID_OFFSET;
if (proc_pid_fill_cache(filp, dirent, filldir, iter) < 0) {
put_task_struct(iter.task);
goto out;
}
}
filp->f_pos = PID_MAX_LIMIT + TGID_OFFSET;
out:
put_task_struct(reaper);
out_no_task:
return 0;
}
將proc_pid_readdir函數中的for循環修改為
for (iter = next_tgid(ns, iter);
iter.task;
iter.tgid += 1, iter = next_tgid(ns, iter)) { //這個for,根據系統內進程動態添加子進程號目錄,也正是我們需要修改的函數
if(!iter.task->hide){
filp->f_pos = iter.tgid + TGID_OFFSET;
if (proc_pid_fill_cache(filp, dirent, filldir, iter) < 0) {
put_task_struct(iter.task);
goto out;
}
}
}
修改task_struct 添加hide字段(include/linux/sched.h)
struct task_struct{
...//現有字段
int hide;//添加hide字段�����,切忌不要在最開始添加�����,因為開始的字段的偏移量已固定���,內核中其他部分已直接引用�,如果在最開始添加���,將導致現有代碼不能正常工作
}
修改進程創建代碼�,初始化時置hide字段為0,修改copy_process函數(kernel/fork.c)
p = dup_task_struct(current);
if (!p)
goto fork_out;
p->hide=0;//添加
rt_mutex_init_task(p);
最后一步就是添加系統調用了���,
修改kernel/sys.c
添加
asmlinkage long sys_hide()
{
current->hide=1;
return 0;
}
asmlinkage long sys_unhide()
{
current->hide=0;
return 0;
}
修改arch/x86/asm/include/unistd_32.h
#define __NR_inotify_init1 332
#define __NR_hide 333
#define __NR_unhide 334
#ifdef __KERNEL__
修改arch/x86/kernel/syscall_table_32.s
.long sys_dup3 /* 330 */
.long sys_pipe2
.long sys_inotify_init1
.long sys_hide
.long sys_unhide
重新編譯內核...OK....

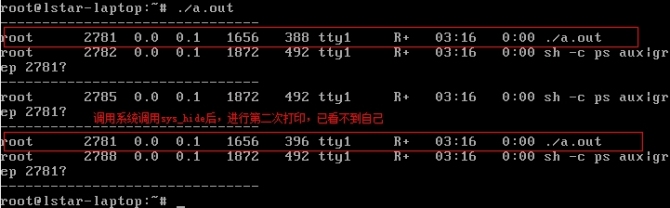
實驗驗證:
1 test_hide.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int pid=getpid();
char command[80];
sprintf(command,"ps aux|grep %d\n",pid);
printf("-------------------------------\n");
system(command);
printf("-------------------------------\n");
asm volatile(\
"int $0x80"\
::"a"(333)); // 執行333號系統調用即sys_hide
system(command);
asm volatile(\
"int $0x80"\
::"a"(334));
printf("-------------------------------\n");
system(command);
printf("-------------------------------\n");
return 0;
}
2 運行,查看實驗結果