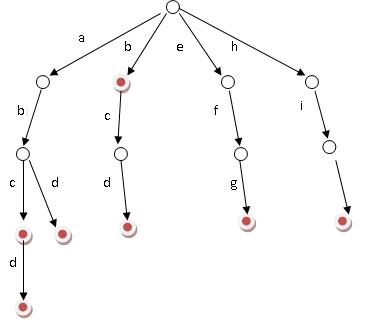
Trie,又稱字典樹、單詞查找樹,是一種樹形結構,用于保存大量的字符串。它的優點是:利用字符串的公共前綴來節約存儲空間。
相對來說,Trie樹是一種比較簡單的數據結構.理解起來比較簡單,正所謂簡單的東西也得付出代價.故Trie樹也有它的缺點,Trie樹的內存消耗非常大.當然,或許用左兒子右兄弟的方法建樹的話,可能會好點.
其基本性質可以歸納為:
1. 根節點不包含字符,除根節點外每一個節點都只包含一個字符。
2. 從根節點到某一節點,路徑上經過的字符連接起來,為該節點對應的字符串。
3. 每個節點的所有子節點包含的字符都不相同。
其基本操作有:查找 插入和刪除,當然刪除操作比較少見.我在這里只是實現了對整個樹的刪除操作,至于單個word的刪除操作也很簡單.
搜索字典項目的方法為:
(1) 從根結點開始一次搜索;
(2) 取得要查找關鍵詞的第一個字母,并根據該字母選擇對應的子樹并轉到該子樹繼續進行檢索;
(3) 在相應的子樹上,取得要查找關鍵詞的第二個字母,并進一步選擇對應的子樹進行檢索。
(4) 迭代過程……
(5) 在某個結點處,關鍵詞的所有字母已被取出,則讀取附在該結點上的信息,即完成查找。
其他操作類似處理.

 /**//*
/**//*
 Name: Trie樹的基本實現
Name: Trie樹的基本實現
 Author: MaiK
Author: MaiK
 Description: Trie樹的基本實現 ,包括查找 插入和刪除操作*/
Description: Trie樹的基本實現 ,包括查找 插入和刪除操作*/
 #include<algorithm>
#include<algorithm>
 #include<iostream>
#include<iostream>
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;

 const int sonnum=26,base='a';
const int sonnum=26,base='a';
 struct Trie
struct Trie


 {
{
 int num;//to remember how many word can reach here,that is to say,prefix
int num;//to remember how many word can reach here,that is to say,prefix
 bool terminal;//If terminal==true ,the current point has no following point
bool terminal;//If terminal==true ,the current point has no following point
 struct Trie *son[sonnum];//the following point
struct Trie *son[sonnum];//the following point
 };
};
 Trie *NewTrie()// create a new node
Trie *NewTrie()// create a new node


 {
{
 Trie *temp=new Trie;
Trie *temp=new Trie;
 temp->num=1;temp->terminal=false;
temp->num=1;temp->terminal=false;
 for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)temp->son[i]=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)temp->son[i]=NULL;
 return temp;
return temp;
 }
}
 void Insert(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)// insert a new word to Trie tree
void Insert(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)// insert a new word to Trie tree


 {
{
 Trie *temp=pnt;
Trie *temp=pnt;
 for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
for(int i=0;i<len;++i)


 {
{
 if(temp->son[s[i]-base]==NULL)temp->son[s[i]-base]=NewTrie();
if(temp->son[s[i]-base]==NULL)temp->son[s[i]-base]=NewTrie();
 else temp->son[s[i]-base]->num++;
else temp->son[s[i]-base]->num++;
 temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
 }
}
 temp->terminal=true;
temp->terminal=true;
 }
}
 void Delete(Trie *pnt)// delete the whole tree
void Delete(Trie *pnt)// delete the whole tree


 {
{
 if(pnt!=NULL)
if(pnt!=NULL)


 {
{
 for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)if(pnt->son[i]!=NULL)Delete(pnt->son[i]);
for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)if(pnt->son[i]!=NULL)Delete(pnt->son[i]);
 delete pnt;
delete pnt;
 pnt=NULL;
pnt=NULL;
 }
}
 }
}
 Trie* Find(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)//trie to find the current word
Trie* Find(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)//trie to find the current word


 {
{
 Trie *temp=pnt;
Trie *temp=pnt;
 for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
 if(temp->son[s[i]-base]!=NULL)temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
if(temp->son[s[i]-base]!=NULL)temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
 else return NULL;
else return NULL;
 return temp;
return temp;
 }
}


轉自:http://hi.baidu.com/luyade1987/blog/item/2667811631106657f2de320a.html