題目描述:
Luck is the key to life. When I have to decide something, I will make my decision by flipping a coin. And then, I have two things to do. First, I have the decision made. Second, I go to the nearest church and donate the coin.
But there are always too many things I have to decide. For example, what should I eat today for lunch? OK, now we are talking about a decision, so let us assume that I have two kinds of food: quick-served noodle A and quick-served noodle B.
I just have bought N bowls of noodle A and N bowls of noodle B. If I have some space to make a decision (i.e. having two kinds of quick-served noodle to choose from), then I will flip a coin to decide which kind of noodle to eat.
My question is, before I eat up all 2 * N bowls of quick-served noodle, what is the mathematical expectation of the number of coins I will have to donate.
Input
Standard input will contain multiple test cases. The first line of the input is a single integer T (1 <= T <= 1000) which is the number of test cases. And it will be followed by T consecutive test cases.
Each test case contains an integer N (1 <= N <= 1000).
Output
Results should be directed to standard output. The output of each test case should be a single real number, which is the mathematical expectation of the number of coins I have to donate. The result should be accurate to two digits after the fractional point.
Sample Input
2
1
2
Sample Output
1.00
2.50
該題目的思路很明確,就是概率題,嘗試了兩種解法,一種是用遞推,另一種是直接利用組合公式
遞推法:
//solution 1
以P[i][j]表示狀態(tài), i代表A種面條剩下的數(shù)量,j代表B種面條的數(shù)量。
P[i][j] = P[i - 1][j] * 0.5 + P[i][j - 1] * 0.5 (i - 1 != 0 && j - 1 != 0, i為0或者j為0則為終結(jié)態(tài))
Result = 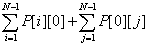
 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
 #include <queue>
#include <queue>
 #include <cmath>
#include <cmath>
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
 #define MAXN 1100
#define MAXN 1100
 double P[MAXN][MAXN];
double P[MAXN][MAXN];





 double dVal;
double dVal;
 double dResult[MAXN + 100];
double dResult[MAXN + 100];

 int main()
int main()


 {
{

 int iCaseTimes;
int iCaseTimes;
 int k, i, j;
int k, i, j;
 double dVal;
double dVal;


 scanf("%d", &iCaseTimes);
scanf("%d", &iCaseTimes);
 for(k = 0; k < iCaseTimes; k++)
for(k = 0; k < iCaseTimes; k++)


 {
{
 scanf("%d", &iNum);
scanf("%d", &iNum);
 dRet = 0;
dRet = 0;
 P[iNum + 1][iNum] = 1;
P[iNum + 1][iNum] = 1;
 P[iNum][iNum + 1] = 1;
P[iNum][iNum + 1] = 1;
 for(i = iNum; i >= 0; i--)
for(i = iNum; i >= 0; i--)


 {
{
 for(j = iNum; j >= 0; j--)
for(j = iNum; j >= 0; j--)


 {
{
 if(i + 1 >= 1 && j >= 1)
if(i + 1 >= 1 && j >= 1)
 P[i][j] += P[i + 1][j] * 0.5;
P[i][j] += P[i + 1][j] * 0.5;
 if(i >= 1 && j + 1 >= 1)
if(i >= 1 && j + 1 >= 1)
 P[i][j] += P[i][j + 1] * 0.5;
P[i][j] += P[i][j + 1] * 0.5;
 if(i == 0 || j == 0)
if(i == 0 || j == 0)


 {
{
 dRet += P[i][j] * (iNum * 2 - i - j);
dRet += P[i][j] * (iNum * 2 - i - j);
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}


 printf("%.2lf\n", dRet);
printf("%.2lf\n", dRet);
 }
}
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
很明顯,算上總的Case數(shù)量,這種方法的時間復雜度為O(n^3), 所以,超時是必然的
這時轉(zhuǎn)換下思路,想想能不能一下子就把1000規(guī)模的打好表呢?在上述表示情況下,打表是不行的,因為每次進行計算的時候,都需要將P[iNum][iNum]
設置為概率1,所以,當直接打好1000的規(guī)模,其子問題仍然沒法計算出來。
//solution 2
換一狀態(tài)表示方法
我們令P[i][j]來代表狀態(tài),其中的i, j代表A類面條吃了i碗,B類面條吃了j碗,這樣我們可以這樣得到答案:
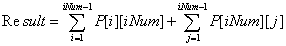
再觀察這時候的子結(jié)構(gòu),假設先計算好規(guī)模為1000的表,此時的輸入為iNum,我們可以看到,到數(shù)量為iNum - 1的結(jié)果都是對的,而數(shù)量為iNum的結(jié)果
是錯誤的,因為1000大于iNum,在1000的規(guī)模下,到iNum時沒有進行終結(jié),而當單類面條吃到iNum碗時,應該是結(jié)束態(tài),所以,我們只能利用到規(guī)模為
iNum - 1數(shù)量的結(jié)果,并利用其推出最后答案。
 //solution 1 O(n^2)
//solution 1 O(n^2)
 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
 #include <cmath>
#include <cmath>
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
 #define MAXN 1100
#define MAXN 1100

 double dRet[MAXN][MAXN];
double dRet[MAXN][MAXN];

 int main()
int main()


 {
{
 int i, j;
int i, j;
 int iNum, iCaseTimes;
int iNum, iCaseTimes;
 double dResult;
double dResult;

 memset(dRet, 0, sizeof(dRet));
memset(dRet, 0, sizeof(dRet));
 dRet[0][0] = 1;
dRet[0][0] = 1;
 for(i = 0; i <= 1000; i++)
for(i = 0; i <= 1000; i++)


 {
{
 for(j = 0; j <= 1000; j++)
for(j = 0; j <= 1000; j++)


 {
{
 if(i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
if(i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
 if(i - 1 >= 0)
if(i - 1 >= 0)
 dRet[i][j] += dRet[i - 1][j] * 0.5;
dRet[i][j] += dRet[i - 1][j] * 0.5;
 if(j - 1 >= 0)
if(j - 1 >= 0)
 dRet[i][j] += dRet[i][j - 1] * 0.5;
dRet[i][j] += dRet[i][j - 1] * 0.5;
 //dRet[i][j] += 1;
//dRet[i][j] += 1;
 }
}
 }
}

 scanf("%d", &iCaseTimes);
scanf("%d", &iCaseTimes);
 while(iCaseTimes--)
while(iCaseTimes--)


 {
{
 scanf("%d", &iNum);
scanf("%d", &iNum);
 dResult = 0;
dResult = 0;

 for(i = 0; i <= iNum - 1; i++)
for(i = 0; i <= iNum - 1; i++)


 {
{
 dResult += dRet[iNum - 1][i] * (iNum + i) * 0.5;
dResult += dRet[iNum - 1][i] * (iNum + i) * 0.5;
 }
}
 dResult *= 2;
dResult *= 2;
 printf("%.2lf\n", dResult);
printf("%.2lf\n", dResult);
 }
}
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
假如直接利用組合公式能否計算呢?
因為該事件發(fā)生的概率不是等可能事件,也就是說,假設有2 * iNum 碗面條,2 ^ (iNum + 1)并不是其樣本空間,因為其中一些序列是不可能發(fā)生的
那么假設拋硬幣事件一定發(fā)生(有點像條件概率,我具體想不明白:( ), 那么,可以得到下面的公式:
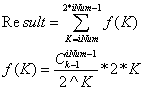
總的樣本空間為2^K,因為拋了K次硬幣,每次兩種選擇;而在這長度為K的串中,最后一碗必定是固定的(肯定為吃完的那種),
所以只要在剩下的K - 1碗中選出iNum - 1個位置便可。乘以二代表有兩類面條吃完的對稱情況,乘以K是轉(zhuǎn)換成期望。
 //solution 2 O(n^2)
//solution 2 O(n^2)
 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
 #define MAXN 2100
#define MAXN 2100

 double C[MAXN][MAXN - 1000];
double C[MAXN][MAXN - 1000];

 int main()
int main()


 {
{
 int i, j;
int i, j;

 memset(C, 0, sizeof(C));
memset(C, 0, sizeof(C));
 C[0][0] = 0.5;
C[0][0] = 0.5;
 C[1][0] = 0.25;
C[1][0] = 0.25;
 C[1][1] = 0.25;
C[1][1] = 0.25;
 for(i = 2; i <= 2000; i++)
for(i = 2; i <= 2000; i++)


 {
{
 C[i][0] = C[i - 1][0] / 2.0;
C[i][0] = C[i - 1][0] / 2.0;
 for(j = 1; j <= 1000; j++)
for(j = 1; j <= 1000; j++)


 {
{
 C[i][j] = (C[i - 1][j] + C[i - 1][j - 1]) / 2.0;
C[i][j] = (C[i - 1][j] + C[i - 1][j - 1]) / 2.0;
 }
}
 }
}

 int iNum;
int iNum;
 int iN;
int iN;
 double dRetVal;
double dRetVal;

 scanf("%d", &iNum);
scanf("%d", &iNum);
 while(iNum--)
while(iNum--)


 {
{
 scanf("%d", &iN);
scanf("%d", &iN);
 dRetVal = 0;
dRetVal = 0;
 for(i = iN; i <= iN * 2 - 1; i++)
for(i = iN; i <= iN * 2 - 1; i++)


 {
{
 dRetVal += C[i - 1][iN - 1] * i;
dRetVal += C[i - 1][iN - 1] * i;
 }
}
 printf("%.2lf\n", dRetVal * 2);
printf("%.2lf\n", dRetVal * 2);
 }
}
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
主要的思路是將組合數(shù)進行打表,更需要注意的是將2^k次也融入到整個組合數(shù)的表中,也就是說,在利用楊輝三角進行遞推的時候就將除二操作加進去。
這里要注意double類型的精度問題,由于題目只要求精確到小數(shù)兩位,所以利用double還是可以滿足的。
對于上述方法,雖然時間復雜度是O(n^2),但是其空間復雜度也為O(n^2),觀察到每兩個f(K)函數(shù)之間也有遞推關(guān)系,我們只要計算出第一個之后,再
乘上一個式子,除以一個式子,就可以得到下一個值,所以,再實現(xiàn)一個空間復雜度更小的O(n^2)的方法:
 //solution 3
//solution 3
 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;

 int main()
int main()


 {
{
 int i, j;
int i, j;

 int iNum;
int iNum;
 int iN;
int iN;
 double dRetVal;
double dRetVal;
 double dPreVal;
double dPreVal;
 double dStartValue;
double dStartValue;

 scanf("%d", &iNum);
scanf("%d", &iNum);
 while(iNum--)
while(iNum--)


 {
{
 scanf("%d", &iN);
scanf("%d", &iN);
 dRetVal = 0;
dRetVal = 0;
 dStartValue = 1;
dStartValue = 1;
 //(iN - 1, iN - 1)
//(iN - 1, iN - 1)
 for(i = iN; i >= 1; i--) dStartValue /= 2.0;
for(i = iN; i >= 1; i--) dStartValue /= 2.0;

 dRetVal = dStartValue * iN;
dRetVal = dStartValue * iN;
 dPreVal = dStartValue;
dPreVal = dStartValue;
 for(i = iN + 1; i <= iN * 2 - 1; i++)
for(i = iN + 1; i <= iN * 2 - 1; i++)


 {
{
 dRetVal += (double) dPreVal * (i - 1) / (i - iN) * i / 2;
dRetVal += (double) dPreVal * (i - 1) / (i - iN) * i / 2;
 dPreVal = dPreVal * (i - 1) / ((i - iN) * 2);
dPreVal = dPreVal * (i - 1) / ((i - iN) * 2);
 }
}
 printf("%.2lf\n", dRetVal * 2);
printf("%.2lf\n", dRetVal * 2);
 }
}
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}

通過對該題的解決,可以看到,概率類的題目基本上兩個方向:1.直接用組合公式解決。但是這種方法容易產(chǎn)生精度問題,而且不一定能夠簡單的推出來
2.用遞推公式解決。這種方法比較容易想清楚方法,但是面臨的問題便是時間與空間的限制。