
轉自:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/98913/showart_2004280.html我們通常把一些公用函數制作成函數庫,供其它程序使用。函數庫分為靜態庫和動態庫兩
種。靜態庫在程序編譯時會被連接到目標代碼中,程序運行時將不再需要該靜態庫。動態
庫在程序編譯時并不會被連接到目標代碼中,而是在程序運行是才被載入,因此在程序運
行時還需要動態庫存在。本文主要通過舉例來說明在Linux中如何創建靜態庫和動態庫,以
及使用它們。
在創建函數庫前,我們先來準備舉例用的源程序,并將函數庫的源程序編譯成.o文件。
第1步:編輯得到舉例的程序--hello.h、hello.c和main.c;
hello.c(見程序2)是函數庫的源程序,其中包含公用函數hello,該函數將在屏幕上輸出"
Hello XXX!"。hello.h(見程序1)為該函數庫的頭文件。main.c(見程序3)為測試庫文件的
主程序,在主程序中調用了公用函數hello。
#ifndef HELLO_H
#define HELLO_H
void hello(const char *name);
#endif //HELLO_H
程序1: hello.h
#include <stdio.h>
void hello(const char *name)
{
printf("Hello %s!\n", name);
}
程序2: hello.c
#include "hello.h"
int main()
{
hello("everyone");
return 0;
}
程序3: main.c
第2步:將hello.c編譯成.o文件;
無論靜態庫,還是動態庫,都是由.o文件創建的。因此,我們必須將源程序hello.c通過g
cc先編譯成.o文件。
在系統提示符下鍵入以下命令得到hello.o文件。
# gcc -c hello.c
#
我們運行ls命令看看是否生存了hello.o文件。
# ls
hello.c hello.h hello.o main.c
#
在ls命令結果中,我們看到了hello.o文件,本步操作完成。
下面我們先來看看如何創建靜態庫,以及使用它。
第3步:由.o文件創建靜態庫;
靜態庫文件名的命名規范是以lib為前綴,緊接著跟靜態庫名,擴展名為.a。例如:我們將
創建的靜態庫名為myhello,則靜態庫文件名就是libmyhello.a。在創建和使用靜態庫時,
需要注意這點。創建靜態庫用ar命令。
在系統提示符下鍵入以下命令將創建靜態庫文件libmyhello.a。
# ar crv libmyhello.a hello.o
#
我們同樣運行ls命令查看結果:
# ls
hello.c hello.h hello.o libmyhello.a main.c
#
ls命令結果中有libmyhello.a。
第4步:在程序中使用靜態庫;
靜態庫制作完了,如何使用它內部的函數呢?只需要在使用到這些公用函數的源程序中包
含這些公用函數的原型聲明,然后在用gcc命令生成目標文件時指明靜態庫名,gcc將會從
靜態庫中將公用函數連接到目標文件中。注意,gcc會在靜態庫名前加上前綴lib,然后追
加擴展名.a得到的靜態庫文件名來查找靜態庫文件。
在程序3:main.c中,我們包含了靜態庫的頭文件hello.h,然后在主程序main中直接調用公
用函數hello。下面先生成目標程序hello,然后運行hello程序看看結果如何。
(# gcc -o hello main.c -L. -lmyhello??)
#gcc main.c libmyhello.a -o main
# ./hello
Hello everyone!
#
我們刪除靜態庫文件試試公用函數hello是否真的連接到目標文件 hello中了。
# rm libmyhello.a
rm: remove regular file `libmyhello.a'? y
# ./hello
Hello everyone!
#
程序照常運行,靜態庫中的公用函數已經連接到目標文件中了。
我們繼續看看如何在Linux中創建動態庫。我們還是從.o文件開始。
第5步:由.o文件創建動態庫文件;
動態庫文件名命名規范和靜態庫文件名命名規范類似,也是在動態庫名增加前綴lib,但其
文件擴展名為.so。例如:我們將創建的動態庫名為myhello,則動態庫文件名就是libmyh
ello.so。用gcc來創建動態庫。
在系統提示符下鍵入以下命令得到動態庫文件libmyhello.so。
# gcc -shared -fPCI -o libmyhello.so hello.o
#
我們照樣使用ls命令看看動態庫文件是否生成。
# ls
hello.c hello.h hello.o libmyhello.so main.c
#
第6步:在程序中使用動態庫;
在程序中使用動態庫和使用靜態庫完全一樣,也是在使用到這些公用函數的源程序中包含
這些公用函數的原型聲明,然后在用gcc命令生成目標文件時指明動態庫名進行編譯。我們
先運行gcc命令生成目標文件,再運行它看看結果。
# gcc -o hello main.c -L. -lmyhello
# ./hello
./hello: error while loading shared libraries: libmyhello.so: cannot open shar
ed object file: No such file or directory
#
哦!出錯了。快看看錯誤提示,原來是找不到動態庫文件libmyhello.so。程序在運行時,
會在/usr/lib和/lib等目錄中查找需要的動態庫文件。若找到,則載入動態庫,否則將提
示類似上述錯誤而終止程序運行。我們將文件libmyhello.so復制到目錄/usr/lib中,再試
試。
# mv libmyhello.so /usr/lib
# ./hello
Hello everyone!
#
成功了。這也進一步說明了動態庫在程序運行時是需要的。
我們回過頭看看,發現使用靜態庫和使用動態庫編譯成目標程序使用的gcc命令完全一樣,
那當靜態庫和動態庫同名時,gcc命令會使用哪個庫文件呢?抱著對問題必究到底的心情,
來試試看。
先刪除除.c和.h外的所有文件,恢復成我們剛剛編輯完舉例程序狀態。
# rm -f hello hello.o /usr/lib/libmyhello.so
# ls
hello.c hello.h main.c
#
在來創建靜態庫文件libmyhello.a和動態庫文件libmyhello.so。
# gcc -c hello.c
# ar cr libmyhello.a hello.o
# gcc -shared -fPCI -o libmyhello.so hello.o
# ls
hello.c hello.h hello.o libmyhello.a libmyhello.so main.c
#
通過上述最后一條ls命令,可以發現靜態庫文件libmyhello.a和動態庫文件libmyhello.s
o都已經生成,并都在當前目錄中。然后,我們運行gcc命令來使用函數庫myhello生成目標
文件hello,并運行程序 hello。
# gcc -o hello main.c -L. -lmyhello
# ./hello
./hello: error while loading shared libraries: libmyhello.so: cannot open shar
ed object file: No such file or directory
#
從程序hello運行的結果中很容易知道,當靜態庫和動態庫同名時, gcc命令將優先使用動
態庫。
Note:
編譯參數解析
最主要的是GCC命令行的一個選項:
-shared 該選項指定生成動態連接庫(讓連接器生成T類型的導出符號表,有時候也生成弱連接W類型的導出符號),不用該標志外部程序無法連接。相當于一個可執行文件
l -fPIC:表示編譯為位置獨立的代碼,不用此選項的話編譯后的代碼是位置相關的所以動態載入時是通過代碼拷貝的方式來滿足不同進程的需要,而不能達到真正代碼段共享的目的。
l -L.:表示要連接的庫在當前目錄中
l -ltest:編譯器查找動態連接庫時有隱含的命名規則,即在給出的名字前面加上lib,后面加上.so來確定庫的名稱
l LD_LIBRARY_PATH:這個環境變量指示動態連接器可以裝載動態庫的路徑。
l 當然如果有root權限的話,可以修改/etc/ld.so.conf文件,然后調用 /sbin/ldconfig來達到同樣的目的,不過如果沒有root權限,那么只能采用輸出LD_LIBRARY_PATH的方法了。
調用動態庫的時候有幾個問題會經常碰到,有時,明明已經將庫的頭文件所在目錄 通過 “-I” include進來了,庫所在文件通過 “-L”參數引導,并指定了“-l”的庫名,但通過ldd命令察看時,就是死活找不到你指定鏈接的so文件,這時你要作的就是通過修改 LD_LIBRARY_PATH或者/etc/ld.so.conf文件來指定動態庫的目錄。通常這樣做就可以解決庫無法鏈接的問題了。
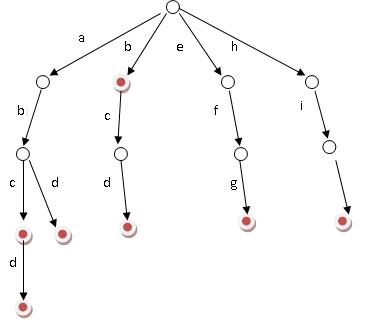
Trie,又稱字典樹、單詞查找樹,是一種樹形結構,用于保存大量的字符串。它的優點是:利用字符串的公共前綴來節約存儲空間。
相對來說,Trie樹是一種比較簡單的數據結構.理解起來比較簡單,正所謂簡單的東西也得付出代價.故Trie樹也有它的缺點,Trie樹的內存消耗非常大.當然,或許用左兒子右兄弟的方法建樹的話,可能會好點.
其基本性質可以歸納為:
1. 根節點不包含字符,除根節點外每一個節點都只包含一個字符。
2. 從根節點到某一節點,路徑上經過的字符連接起來,為該節點對應的字符串。
3. 每個節點的所有子節點包含的字符都不相同。
其基本操作有:查找 插入和刪除,當然刪除操作比較少見.我在這里只是實現了對整個樹的刪除操作,至于單個word的刪除操作也很簡單.
搜索字典項目的方法為:
(1) 從根結點開始一次搜索;
(2) 取得要查找關鍵詞的第一個字母,并根據該字母選擇對應的子樹并轉到該子樹繼續進行檢索;
(3) 在相應的子樹上,取得要查找關鍵詞的第二個字母,并進一步選擇對應的子樹進行檢索。
(4) 迭代過程……
(5) 在某個結點處,關鍵詞的所有字母已被取出,則讀取附在該結點上的信息,即完成查找。
其他操作類似處理.
1
 /**//*
/**//*
2 Name: Trie樹的基本實現
Name: Trie樹的基本實現
3 Author: MaiK
Author: MaiK
4 Description: Trie樹的基本實現 ,包括查找 插入和刪除操作*/
Description: Trie樹的基本實現 ,包括查找 插入和刪除操作*/
5 #include<algorithm>
#include<algorithm>
6 #include<iostream>
#include<iostream>
7 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
8
9 const int sonnum=26,base='a';
const int sonnum=26,base='a';
10 struct Trie
struct Trie
11

 {
{
12 int num;//to remember how many word can reach here,that is to say,prefix
int num;//to remember how many word can reach here,that is to say,prefix
13 bool terminal;//If terminal==true ,the current point has no following point
bool terminal;//If terminal==true ,the current point has no following point
14 struct Trie *son[sonnum];//the following point
struct Trie *son[sonnum];//the following point
15 };
};
16 Trie *NewTrie()// create a new node
Trie *NewTrie()// create a new node
17

 {
{
18 Trie *temp=new Trie;
Trie *temp=new Trie;
19 temp->num=1;temp->terminal=false;
temp->num=1;temp->terminal=false;
20 for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)temp->son[i]=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)temp->son[i]=NULL;
21 return temp;
return temp;
22 }
}
23 void Insert(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)// insert a new word to Trie tree
void Insert(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)// insert a new word to Trie tree
24

 {
{
25 Trie *temp=pnt;
Trie *temp=pnt;
26 for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
27

 {
{
28 if(temp->son[s[i]-base]==NULL)temp->son[s[i]-base]=NewTrie();
if(temp->son[s[i]-base]==NULL)temp->son[s[i]-base]=NewTrie();
29 else temp->son[s[i]-base]->num++;
else temp->son[s[i]-base]->num++;
30 temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
31 }
}
32 temp->terminal=true;
temp->terminal=true;
33 }
}
34 void Delete(Trie *pnt)// delete the whole tree
void Delete(Trie *pnt)// delete the whole tree
35

 {
{
36 if(pnt!=NULL)
if(pnt!=NULL)
37

 {
{
38 for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)if(pnt->son[i]!=NULL)Delete(pnt->son[i]);
for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)if(pnt->son[i]!=NULL)Delete(pnt->son[i]);
39 delete pnt;
delete pnt;
40 pnt=NULL;
pnt=NULL;
41 }
}
42 }
}
43 Trie* Find(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)//trie to find the current word
Trie* Find(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)//trie to find the current word
44

 {
{
45 Trie *temp=pnt;
Trie *temp=pnt;
46 for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
47 if(temp->son[s[i]-base]!=NULL)temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
if(temp->son[s[i]-base]!=NULL)temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
48 else return NULL;
else return NULL;
49 return temp;
return temp;
50 }
}
今天,終于達到150題啦(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……繼續加油
問題:
http://poj.org/problem?id=1016思路:
純模擬,需要細心...
代碼:
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<string.h>
4 #define NUM 10 /* 0..9 */
5 #define UP 15
6 #define INPUT_LEN 81
7 #define MAX_LEN 31
8 char input[INPUT_LEN], inv[UP][MAX_LEN];
9 int count[NUM];
10
11 void
12 generate(char *src, char *dst)
13 {
14 int i, index, len = strlen(src);
15 memset(count, 0, sizeof(count));
16 for(i=0; i<len; i++)
17 ++count[src[i]-'0'];
18
19 index = 0;
20 for(i=0; i<NUM; i++) {
21 if(count[i] > 0) {
22 if(count[i] >= 10) {
23 dst[index++] = (count[i]/10)+'0';
24 dst[index++] = (count[i]%10)+'0';
25 } else {
26 dst[index++] = count[i]+'0';
27 }
28 dst[index++] = i+'0';
29 }
30 }
31 }
32
33 void
34 solve()
35 {
36 int i, index = 0;
37 generate(input, inv[index]);
38 if(strcmp(input, inv[index]) == 0) {
39 printf("%s is self-inventorying\n", input);
40 return;
41 }
42 ++index;
43 while(index < UP) {
44 generate(inv[index-1], inv[index]);
45 if(strcmp(inv[index], inv[index-1]) == 0) {
46 printf("%s is self-inventorying after %d steps\n", input, index);
47 return;
48 }
49 for(i=index-2; i>=0; i--)
50 if(strcmp(inv[index], inv[i]) == 0) {
51 printf("%s enters an inventory loop of length %d\n", input, index-i);
52 return;
53 }
54 if(index >= 1)
55 if(strcmp(inv[index], input) == 0) {
56 printf("%s enters an inventory loop of length %d\n", input, index+1);
57 return;
58 }
59 ++index;
60 }
61 printf("%s can not be classified after 15 iterations\n", input);
62 }
63
64 int
65 main(int argc, char **argv)
66 {
67 while(scanf("%s", input) != EOF) {
68 if(strcmp(input, "-1") == 0)
69 break;
70 memset(inv, 0, sizeof(inv));
71 solve();
72 }
73 }
問題:
http://poj.org/problem?id=2418思路:
題意清晰明了,不難,用三種方法分別實現:
快速排序
動態生成節點的二叉查找樹
靜態分配節點的二叉查找樹
結果發現,原來對于快速排序與靜態分配節點都不是很熟悉,二維數組的快速排序分析見
http://www.shnenglu.com/Joe/archive/2010/10/29/131746.html,而動態生成節點則需要注意如果函數需要修改指針,那么必須傳遞指向指針的指針,因為C是值傳遞的
另外,我以為靜態分配節點應該比動態分配節點節約很多時間的,結果居然差不多...而快速排序在這題明顯是最耗時的
代碼(快排)
1 /* 35640K 1844MS */
2 #include<stdio.h>
3 #include<stdlib.h>
4 #include<string.h>
5 #define MAX_LEN 36
6 #define MAX_NUM 1000001
7 char species[MAX_NUM][MAX_LEN];
8
9 int
10 cmp(const void *arg1, const void *arg2)
11 {
12 return strcmp((char *)arg1, (char *)arg2);
13 }
14
15 int
16 main(int argc, char **argv)
17 {
18 int i, count, total = 0;
19 while(gets(species[total]) != NULL)
20 ++total;
21 qsort(species, total, sizeof(species[0]), cmp);
22 count = 1;
23 for(i=1; i<total; i++) {
24 if(strcmp(species[i], species[i-1]) == 0)
25 ++count;
26 else {
27 printf("%s %.4f\n", species[i-1], (count*100.0)/total);
28 count = 1;
29 }
30 }
31 printf("%s %.4f\n", species[total-1], (count*100.0)/total);
32 }
代碼(動態分配節點的BST,原本想實現下destroy函數的,結果怕麻煩就留給系統回收吧(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……)
1 /* binary search tree(dynamic allocation) */
2 /* 544K 1188MS */
3 #include<stdio.h>
4 #include<stdlib.h>
5 #include<string.h>
6 #include<assert.h>
7 #define MAX_LEN 36
8 struct Node {
9 char spec[MAX_LEN];
10 int count;
11 struct Node *left, *right;
12 };
13 int total;
14
15 struct Node *
16 create_node(char *str)
17 {
18 struct Node *node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
19 assert(node != NULL);
20 strcpy(node->spec, str);
21 node->left = node->right = NULL;
22 node->count = 1;
23 return node;
24 }
25
26 void
27 insert(struct Node **root, char *str)
28 {
29 int ret;
30 struct Node *node;
31 if(*root==NULL) {
32 *root = create_node(str);
33 return;
34 }
35 ret = strcmp((*root)->spec, str);
36 if(ret == 0)
37 ++((*root)->count);
38 else if(ret < 0)
39 insert(&((*root)->right), str);
40 else
41 insert(&((*root)->left), str);
42 }
43
44 void
45 inorder(struct Node *root)
46 {
47 if(root == NULL)
48 return;
49 inorder(root->left);
50 printf("%s %.4f\n", root->spec, (root->count)*100.0/total);
51 inorder(root->right);
52 }
53
54 void
55 destroy(struct Node **root)
56 {
57 }
58
59 int
60 main(int argc, char **argv)
61 {
62 char str[MAX_LEN];
63 struct Node *bst = NULL;
64 total = 0;
65 while(gets(str) != NULL) {
66 ++total;
67 insert(&bst, str);
68 }
69 inorder(bst);
70 }
代碼(靜態分配節點的BST)
1 /* binary search tree(static allocation) */
2 /* 492K 1188MS */
3 #include<stdio.h>
4 #include<stdlib.h>
5 #include<string.h>
6 #include<assert.h>
7 #define MAX_LEN 36
8 #define MAX_NUM 10007
9 #define ROOT 1
10 struct Node {
11 char spec[MAX_LEN];
12 int count;
13 int left, right;
14 }bst[MAX_NUM];
15 int cur_index, total;
16
17 int
18 find(int root, char *str)
19 {
20 int ret, parent, cur = root;
21 while(cur != 0) {
22 parent = cur;
23 ret = strcmp(bst[cur].spec, str);
24 if(ret == 0) {
25 ++bst[cur].count;
26 return 0;
27 } else if(ret < 0) {
28 cur = bst[cur].right;
29 } else {
30 cur = bst[cur].left;
31 }
32 }
33 return parent;
34 }
35
36 #define ADD(index, str) { \
37 strcpy(bst[index].spec, str); \
38 bst[index].left = bst[index].right = 0; \
39 bst[index].count = 1; \
40 ++index; }
41
42 void
43 insert(int parent, char *str)
44 {
45 int ret = strcmp(bst[parent].spec, str);
46 assert(ret != 0);
47 if(ret < 0)
48 bst[parent].right = cur_index;
49 else
50 bst[parent].left = cur_index;
51 ADD(cur_index, str);
52 }
53
54 void
55 inorder(int index)
56 {
57 if(index == 0)
58 return;
59 inorder(bst[index].left);
60 printf("%s %.4f\n", bst[index].spec, (bst[index].count*100.0)/total);
61 inorder(bst[index].right);
62 }
63
64 int
65 main(int argc, char **argv)
66 {
67 int parent;
68 char str[MAX_LEN];
69 total = 1;
70 cur_index = ROOT;
71 gets(str);
72 ADD(cur_index, str); /* create the root node first */
73 while(gets(str) != NULL) {
74 ++total;
75 if((parent=find(ROOT, str)) > 0)
76 insert(parent, str);
77 }
78 inorder(ROOT);
79 }
在將qsort函數應用于對指針數組與二維數組排序時,傳遞給compare函數的參數類型是不同的首先,我們舉個簡單的例子,先將qsort對整數數組排序:
1 int
2 cmp(const void *arg1, const void *arg2)
3 {
4 return (*(int *)arg1)-(*(int *)arg2);
5 }
6
7 int
8 main(int argc, char **argv)
9 {
10 int i;
11 int arr[] = {3, 1, 5, 2, 4};
12 qsort(arr, sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]), sizeof(int), cmp);
13 }
排序針對的是數組里的元素而言的,這里整數數組的元素就是整數,因此qsort的第三個參數就是sizeof(int),而傳遞給比較函數cmp的參數就是相對應的指向整數的指針
接著,我們來看看指針數組的情形:
1 int
2 cmp(const void *arg1, const void *arg2)
3 {
4 return strcmp((*(char **)arg1), (*(char **)arg2));
5 }
6
7 int
8 main(int argc, char **argv)
9 {
10 int i;
11 /* pointer array */
12 char *str[] = {"java", "c", "python", "perl"};
13 qsort(str, sizeof(str)/sizeof(str[0]), sizeof(char *), cmp);
14 }
這里的理解其實跟整數數組差不多,關鍵是抓住數組里元素的類型,既然稱之為指針數組,那數組元素的類型自然就是指針,因此qsort的第三個參數就是sizeof(char *),而傳遞給比較函數cmp的參數就是相對應的指向指針的指針,這里即char **類型
二維數組的理解最為復雜,代碼如下:
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<string.h>
4
5 int
6 cmp1(const void *arg1, const void *arg2)
7 {
8 return strcmp((*((char (*)[])arg1)), (*((char (*)[])arg2)));
9 }
10
11 int
12 cmp2(const void *arg1, const void *arg2)
13 {
14 return strcmp((char *)arg1, (char *)arg2);
15 }
16
17 int
18 main(int argc, char **argv)
19 {
20 int i;
21 char str1[4][8] = {"java", "c", "python", "peal"};
22 printf("COMPARE-FUNCTION-1\n");
23 qsort(str1, 4, sizeof(str1[0]), cmp1);
26
27 char str2[4][8] = {"java", "c", "python", "peal"};
28 printf("COMPARE-FUNCTION-2\n");
29 qsort(str2, 4, sizeof(str2[0]), cmp2);
34 }
這里cmp1與cmp2都能正常的工作(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……
還是按照上述方法來分析,抓住數組元素的類型來入手,二維數組實際上就是數組的數組,因此二維數組的元素類型就是一維數組,因此qsort的第三個參數就是sizeof(str1[0])或sizeof(str2[0]),那傳遞給比較函數的參數應該就是指向數組的指針,這點可以通過gdb設置斷點來得到證實:
1 (gdb) p &str1[0]
2 $1 = (char (*)[8]) 0xbffff2cc
3 (gdb) p &str1[1]
4 $2 = (char (*)[8]) 0xbffff2d4
5
6 Breakpoint 2, cmp1 (arg1=0xbffff2cc, arg2=0xbffff2d4) at char_test2.c:8
7 8 return strcmp((*((char (*)[])arg1)), (*((char (*)[])arg2)));
8 (gdb) p arg1
9 $3 = (const void *) 0xbffff2cc
10 (gdb) p arg2
11 $4 = (const void *) 0xbffff2d4
12 (gdb) p *(char (*)[])arg1
13 $5 = "j"
14 (gdb) p *(char (*)[8])arg1
15 $6 = "java\000\000\000"
通過第2行與第9行的比較可以發現,比較函數的參數arg1其實就是&str1[0],類型為char (*)[],這也是為什么cmp1能正常工作的原因
那么cmp2呢,它為什么正確呢?
在cmp1中:
strcmp((*((char (*)[])arg1)), (*((char (*)[])arg2))); 這里傳遞給strcmp的參數之所以不會出錯,是因為我們將arg1解地址操作獲得一個數組,而數組名其實是指向數組首元素的指針,arg1既然是指向str1[0]這個一維數組的指針,而str1[0]本身其實就是指向這個一維數組的指針,也就是說arg1其實就是str1[0],因此cmp2能夠正常工作
1 (gdb) p &str1[0]
2 $3 = (char (*)[8]) 0xbffff2cc
3 (gdb) p &str1[0][0]
4 $4 = 0xbffff2cc "java"
5 (gdb) p arg1
6 $5 = (const void *) 0xbffff2cc
7 (gdb) p (char *)arg1
8 $6 = 0xbffff2cc "java"
額...貌似越說越復雜的樣子,不過這是我理解的過程,見諒...
問題:
http://poj.org/problem?id=1657思路:
原本以為是搜索題,結果發現居然都可以推導出來(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……0MS
睡覺前AC個題,感覺蠻好
代碼(寫的比較繁瑣):
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<string.h>
4 #define Diff(a, b) ((a)>(b) ? ((a)-(b)) : ((b)-(a)))
5 #define Max(a, b) ((a)>(b) ? (a) : (b))
6 #define MAX_LEN 3
7 typedef enum {
8 Black,
9 White
10 }Color;
11
12 int
13 is_linear(char *src, char *dst)
14 {
15 if(src[0]==dst[0] || src[1]==dst[1])
16 return 1;
17 return 0;
18 }
19
20 int
21 is_oblique(char *src, char *dst)
22 {
23 int x_diff = Diff(src[0], dst[0]);
24 int y_diff = Diff(src[1], dst[1]);
25 if(x_diff == y_diff)
26 return 1;
27 return 0;
28 }
29
30 Color
31 black_or_white(char *src)
32 {
33 int x = src[0] - 'a' + 1;
34 int y = src[1] - '0';
35 if(x%2 == y%2)
36 return White;
37 return Black;
38 }
39
40 void
41 solve(char *src, char *dst)
42 {
43 int a, b, c, d, x_diff, y_diff;
44 x_diff = Diff(src[0], dst[0]);
45 y_diff = Diff(src[1], dst[1]);
46 a = Max(x_diff, y_diff); /* king */
47 if(is_linear(src, dst) || is_oblique(src, dst)) /* queen */
48 b = 1;
49 else
50 b = 2;
51
52 if(is_linear(src, dst)) /* rook */
53 c = 1;
54 else
55 c = 2;
56
57 if(is_oblique(src, dst)) /* bishop */
58 d = 1;
59 else if(black_or_white(src) != black_or_white(dst))
60 d = -1;
61 else
62 d = 2;
63
64 printf("%d %d %d ", a, b, c);
65 if(d == -1)
66 printf("Inf\n");
67 else
68 printf("%d\n", d);
69 }
70
71 int
72 main(int argc, char **argv)
73 {
74 int tests;
75 char begin[MAX_LEN], end[MAX_LEN];
76 scanf("%d", &tests);
77 while(tests--) {
78 scanf("%s %s", begin, end);
79 if(begin[0]==end[0] && begin[1]==end[1])
80 printf("0 0 0 0\n");
81 else
82 solve(begin, end);
83 }
84 }
問題:
http://poj.org/problem?id=3400思路:
這題就是個悲劇...
應該算是簡單的深搜題,結果花了我一個上午
畫了好幾顆遞歸調用樹也不知道為什么會出錯...抓狂...
最后發現,一直出錯的原因是在寫代碼的時候將遞歸函數的參數直接修改,導致后續的“同一層”的回溯調用出錯,啊啊啊...
代碼:
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<string.h>
4 #define MAX_LEN 11
5 struct Stone {
6 int weight;
7 int cost;
8 }stones[MAX_LEN];
9 int N, D;
10 int total_cost, max_cost, hash[MAX_LEN];
11
12 void
13 dfs(char bunker, int weight_a, int cost_a, int weight_b, int cost_b)
14 {
15 int i, w, c, mark = 0;
16 if(total_cost-cost_a<=max_cost)
17 return;
18 for(i=0; i<N; i++) {
19 if(!hash[i]) {
20 mark = 1;
21 hash[i] = 1;
22 switch(bunker) {
23 case 'A':
24 w = weight_a+stones[i].weight;
25 c = cost_a+stones[i].cost;
26 if(w-weight_b <= D)
27 dfs('A', w, c, weight_b, cost_b);
28 else
29 dfs('B', w, c, weight_b, cost_b);
30 break;
31 case 'B':
32 w = weight_b+stones[i].weight;
33 c = cost_b+stones[i].cost;
34 if(w-weight_a <= D)
35 dfs('B', weight_a, cost_a, w, c);
36 else
37 dfs('A', weight_a, cost_a, w, c);
38 break;
39 }
40 hash[i] = 0;
41 }
42 }
43 if(!mark)
44 max_cost = max_cost<cost_b ? cost_b : max_cost;
45 }
46
47 int
48 main(int argc, char **argv)
49 {
50 int i;
51 while(scanf("%d %d", &N, &D) != EOF) {
52 total_cost = 0;
53 for(i=0; i<N; i++) {
54 scanf("%d %d", &stones[i].weight, &stones[i].cost);
55 total_cost += stones[i].cost;
56 }
57 max_cost = 0;
58 memset(hash, 0, sizeof(hash));
59 dfs('A', 0, 0, 0, 0);
60 printf("%d\n", max_cost);
61 }
62 }
在圖書館偶見《系統程序員成長計劃》,作者是李先靜
記得之前曾經見過作者的博客,可惜沒能仔細查看
如今,趕緊借了回來,剛看了前幾章,覺得寫的很好,也頗有收獲(其實,Linux+Vim+C特別符合咱胃口(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……)
書中描述C語言的特點:簡單、高效、直觀,實在是言簡意賅
說實話,我最喜歡的就是C語言
Keep Fighting...
問題:
http://poj.org/problem?id=2312思路:
在
http://www.shnenglu.com/Joe/archive/2010/10/23/130973.html中,參考網上代碼采用了一種"新"的BFS方法來解題,該方法的一個缺點在于每個點可能多次進入隊列,這也直接導致了單個點的多次擴展
其實,這題可以采用原始的BFS方法來做,只是不能再用普通的隊列,而需要使用優先級隊列
通過這題,使我對于寬度優先搜索有了新的認識
普通的BFS之所以能夠找到最小的步數,關鍵在于它是單步擴展的,也就是說它首先羅列出所有在一步之內可以到達的點,然后再羅列所有在兩步之內可以到達的點,類似于"1-1-1...-2-2-2...-3-3-3..."的方式
這題在擴展的時候并非都是一步,所以普通的BFS并不能找出正確的解,例如:
Y B
E T
假如我們以右、下、左、上的順序進行擴展,那么我們將得出結果是3,而事實上只需要2
優先級隊列之所以能夠找出正確解,是因為它保證我們始終從最小步數的點開始擴展
代碼(C++)
1 /* 0MS */
2 #include<iostream>
3 #include<cstdio>
4 #include<cstring>
5 #include<queue> /* priority queue */
6 using namespace std;
7
8 #define MAX_LEN 301
9 #define is_valid(x, y) ((x)>=0 && (x)<M && (y)>=0 && (y)<N)
10 char map[MAX_LEN][MAX_LEN];
11 const int dx[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
12 const int dy[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
13 int M, N;
14 int you_x, you_y, target_x, target_y;
15 int visited[MAX_LEN][MAX_LEN];
16 struct Node {
17 int x, y;
18 int steps;
19 bool operator<(const Node &item) const {
20 return steps > item.steps;
21 }
22 }cur, next;
23 priority_queue<Node> states;
24
25 int
26 bfs()
27 {
28 int i;
29 memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
30 while(!states.empty()) /* empty the queue */
31 states.pop();
32 next.x = you_x;
33 next.y = you_y;
34 next.steps = 0;
35 visited[you_x][you_y] = 1;
36 states.push(next);
37 while(!states.empty()) {
38 cur = states.top();
39 states.pop();
40 if(cur.x==target_x && cur.y==target_y)
41 return cur.steps;
42 for(i=0; i<4; i++) {
43 next.x = cur.x + dx[i];
44 next.y = cur.y + dy[i];
45 if(!visited[next.x][next.y]) {
46 visited[next.x][next.y] = 1;
47 if(map[next.x][next.y]=='E' || map[next.x][next.y]=='T') {
48 next.steps = cur.steps+1;
49 states.push(next);
50 } else if(map[next.x][next.y]=='B') {
51 next.steps = cur.steps+2;
52 states.push(next);
53 }
54 }
55 }
56 }
57 return -1;
58 }
59
60 int
61 main(int argc, char **argv)
62 {
63 int i, j;
64 while(scanf("%d %d", &M, &N)!=EOF && M && N) {
65 for(i=0; i<M; i++) {
66 scanf("%s", map[i]);
67 for(j=0; j<N; j++) {
68 if(map[i][j] == 'Y') {
69 you_x = i;
70 you_y = j;
71 } else if(map[i][j] == 'T') {
72 target_x = i;
73 target_y = j;
74 }
75 }
76 }
77 printf("%d\n", bfs());
78 }
79 }