普通的有限责�Q公司�Q�最低注册资�?万元�Q�需�?个或2个以上的股东�Q?
�?6�q?月�v新的公司法规定,允许1个股东注册有限责��d��司,�q�种�Ҏ��的有限责��d��司又�U?#8220;一人有限公�?#8221;(但公司名�U�C��不会�?#8220;一�?#8221;字样�Q�执照上会注�?#8220;自然人独�?#8221;)�Q�最低注册资�?0万元。如果只有你一个�h作�ؓ股东�Q�则选择一人有限公司,最低注册资�?0万元�Q�如果你和朋友、家人合伙投资创业,可选择普通的有限公司�Q�最低注册资�?万元。徏议你准备好注册资�?万元�?
二、注册公司所需的注册资料:
(1)个�h资料�Q���n份证、法人户口本复印件或��L��证明、居住地址、电话号码)
(2)注册资金
(3)拟订注册公司名称若干
(4)公司�l�营范围
(5)�U�房房��证、租赁合�?
(6)公司住所
(7)股东名册及股东联�pȝ��话、联�p�d��址
(8)公司的机构及其��生办法、职权、议事规�?
(9)公司章程
三、注册公司的步骤�Q?
1.核名�Q�到工商局去领取一�?#8220;企业(字号)名称预先核准甌����?#8221;�Q�填写你准备取的公司名称�Q�由工商局上工商局内部�|�检索是否有重名�Q�如果没有重名,���可以��用这个名�U�ͼ���׃��核发一�?#8220;企业(字号)名称预先核准通知�?#8221;。工商名�U�核准费�?0元,交给工商局�?40元可以帮你检�?个名字,很多名字重复�Q�所以一般常见的名字��׃��用试了,免得花冤枉钱�?
2.�U�房�Q?��M��门的写字楼租一间办公室�Q�如果你自己有厂房或者办公室也可以,有的地方不允许在居民楼里办公�?你要交房�U�给所�U�办公室的房�?所有权�?�Q�假讑֊�公室的房�U�是1000�?�?一般�v�U�最��?个月,6个月的房�U�是6000元�?
3.�{�订�U�房合同�Q�你要与你所�U�的办公室的房东�{�֮��U�房合同,�q�让房东提供房��证的复印件。租房合同打印费5�?5元,房��证复��C�g5�?.5元�?
4.买租房的印花�E�:你要到税务局��M��印花�E�,按年�U�金的千分之一的税率购乎ͼ�贴在房租合同的首���c��例如你的每�q�房�U�是1.2万元�Q�那���p���?2元钱的印��q���Q�后面凡是需要用到房�U�合同的地方�Q�都需要是贴了印花�E�的合同复印件�?
5.�~�写“公司章程”�Q�可以在工商局�|�站下蝲“公司章程”的样本,修改一下就可以了。章�E�的最后由所有股东签名�?假设章程打印5�?股东2人各2份、工商局1份、银�?份、会计师事务所1�?�Q�章�E�打印费15元、下载公司章�E�的上网�?元�?
6.�ȝ��章: 去街上刻章的地方��M��个私章,�l�他们讲��L��人私�?方�Ş�?。刻章费�?0元�?
7.��C��计师事务所领取“银行询征�?#8221;�Q�联�p�M��家会计师事务所�Q�领取一�?#8220;银行询征�?#8221;�Q�必���L��原�g�Q�会计师事务所盖鲜章。如果你不清楚,可以看报�U怸�的分�c�d��告,有很多会计师事务所的广告。银行询征函10元�?
8.去银行开立公叔R��资户�Q?所有股东带上自己入股的那一部分钱到银行�Q�带上公司章�E�、工商局发的核名通知、法��Z��表的�U�章、��n份证、用于验资的钱、空白询征函表格�Q�到银行��d��立公司帐��P��你要告诉银行是开验资戗���开立好公司帐户后,各个股东按自己出资额向公司帐户中存入相应的钱�?银行会发�l�每个股东缴�Ƒ֍�、�ƈ在询征函上盖银行的章。公叔R��资户开戯���20元�?
注意�Q�公司法规定�Q�注册公司时�Q�投资�h(股东)必须�~�纳���额的资本,可以以贷币�Ş�?也就是�h民币)������Q�也可以以实�?如汽车、房产、知识��权等)�����。到银行办的只是货币������q�一部分�Q�如果你有实物、房产等作�ؓ�����的,需要到会计师事务所鉴定其�h值后再以其实际�h值出资,比较�ȝ���Q�因此徏议你直接拉K��来出资,公司法不���你用什么手�D�|��的钱�Q�自��q��也好、借的也好�Q�只要如数缴���_��资款卛_���?
9.办理验资报告�Q�拿着银行出具的股东缴�Ƒ֍�、银行盖章后的询征函�Q�以及公司章�E�、核名通知、房�U�合同、房产证复印�Ӟ����C��计师事务所办理验资报告�Q�会计师事务师验资报告按注册资本收费�?0万元以下注册资金验资�?00元�?
10.注册公司�Q�到工商局领取公司讄���登记的各�U�表��|��包括讄���登记甌���表、股�?发�v�?名单、董事经理监理情��c��法��Z��表登记表、指定代表或委托代理人登记表。注册登记费�Q�按注册资金的万分之8收取。填好后�Q�连同核名通知、公司章�E�、房�U�合同、房产证复印件、验资报告一起交�l�工商局。大�?个工作日后可领取执照。注册公司手�l�费300元�?
11.凭营业执照,到公安局特行�U�指定的�ȝ���C�,��d��公章、胦务章。后面步骤中�Q�均需要用到公章或财务章。公�?0元,财务�?0元�?
12.办理企业�l�织机构代码证:凭营业执照到技术监督局办理�l�织机构代码证,费用�?0元。办�q�个证需要半个月�Q�技术监督局会首先发一个预先受理代码证明文�Ӟ��凭这个文件就可以办理后面的税务登记证、银行基本户开��h���l�了�?
13.去银行开基本��P��凭营业执照、组�l�机构代码证�Q�去银行开立基本帐受���最好是在原来办理验资时的那个银行的同一�|�点��d��理,否则�Q�会多收100元的验资帐户费用�?开基本户需要填很多表,你最好把能带齐的东西全部带上�Q�要不然要跑很多���,包括营业执照正本原�g、��n份证、组�l�机构代码证、公财章、法人章�?
开基本��h���Q�还需要购��C��个密码器(�?005�q�下半年��P��大多银行都有�q�个规定)�Q�今后你的公司开支票、划�ƾ时�Q�都需要��用密码器来生成密码。公司基本帐号开戯���20元,密码�?80元�?
14.办理�E�务登记�Q�领取执照后�Q?0日内到当地税务局甌���领取�E�务登记证。一般的公司都需要办�?�U�税务登记证�Q�即国税和地�E�。费用是�?0元,�?0元�?
15.请兼职会计:办理�E�务登记证时�Q�必���L��一个会计,因�ؓ�E�务局要求提交的资料其中有一��Ҏ��会计资格证和�w�䆾证。你可先请一个兼职会计,���公司刚开始请的兼职会计一�?00元工资就可以了�?
16.甌���领购发票�Q�如果你的公司是销售商品的�Q�应该到国税�ȝ��请发���,如果是服务性质的公司,则到地税申领发票�?开始可先领�?00元的发票�?
最后就开始营业了�?
四、注册公司的费用�Q?
1、工商局工商名称核准�Q?0�?
2、公司办公室房租6个月�Q?000�?
3、租房合同打印费5�?5元,房��证复��C�g5�?.5�?
4、租房的印花�E?2�?
5、下载公司章�E�的上网�?元,公司章程打印�?5�?
6、刻法�h�U�章20�?
7、会计师事务所的银行询征函10�?
8、银行开立公叔R��资户开戯���20�?
9、会计师事务所办理验资报告500�?
10、工商局注册公司手箋�?00元,信息�?20�?
11、公�?�?20元,财务�?�?0�?
12、技术监督局办理�l�织机构代码�?48�?
13、银行开立公司基本帐号开戯���20元、密码器280�?
14、国�E�税务登记证60元,地税�E�务登记�?0�?
15、兼职会计工资,200�?
16、申请领购发���,500�?
合计�Q?502.5�?
如果不算房租、会计工资、发���,则合�?802.5元�?
注册资本最��?万元�?
注册登记�Ҏ��注册资本�?.08%(1000万以�?,0.04%(1000万以上的���过部分)收取
营业�E�:销售商品的公司�Q�按所开发票额的4%征收增殖�E�;提供服务的公司,按所开发票额的5%征收营业�E��?
所得税�Q�对企业的纯利润征收18-33%的企业所得税�?
利润收入�?万元�Q�含3万元�Q�以下的�E�率�?8%�Q�利润收入在3万元以上10万元�Q�含10万元�Q�的�E�率�?7%�Q?0万元以上的�ؓ33%�?
五、注册公司的相关说明�Q?
1.注册公司会不到半�q�时��_��最快需�?0天时间。地��Z��同注册公司的费用也有所不同�?
2.要注册一个公司,首先惛_���l�营什么,怎样�l�营好,再来注册。要不,注册了也没有用,注册了公司是需要很多成本的�Q�不是一�?#8220;好玩”的事情�?
3.注册个体���单易办;而注册公司要有章�E�、合同,要验资,�E�序挺多的�?在投入不是太多时�Q�还是注册个体�ؓ好�?
4.前期可行性分析调查,�����你自��p��真的考虑一�?
5.公司必须建立健全的会计制度,你可能担心自�׃��会,怎么办?刚开始成立的公司�Q�业务少�Q�对会计的工作量也非常小�Q�你可以请一个兼职会计,每个月到你的公司帮你建帐�Q�二、三天时间就够了�Q�给�?00-500左右的工资即可�?
6.每个�?�?10日按时向�E�务��x���E�,即��没有开展业务不需要缴�E�,也要�q�行零申报,否则会被�|�款的。罚���N��度超�q�一�?00元。营业执照办理下来后一个月内必���d��理税务登记。每�q?-6月年定时�q�检营业执照�?
7.对企业所得税�Q�做帐很关键�Q�如果帐面上你的利润很多�Q�那�E�率���高。所以,�q�_��的购买设备都要开发票�Q�你吃饭、坐车的���都留�v来,可以做�ؓ你的企业�q�作成本�?
8.营业�E�是对营业额征税�Q�不���你赚没有赚钱,只有发生了交易,开了发���,���p��征税�Q�所得税�Q�是对利润征�E�,利润���是营业额扣减各�U�成本后剩余的钱�Q�只有赚了钱�Q�才会征所得税�?
9.有限责�Q公司可以注册分公司�?
10.开办费是指企业在筹建期间发生的费用�Q�包括筹建期人员工资、办公费、培训费、差旅费、印刯���、注册登记费以及不计入固定资产和无�Ş资��购徏成本的汇兑损益和利息支出。筹建期是指企业被批准筹��Z��日�v臛_��始生产、经营(包括试生产、试营业�Q�之日的期间�?
One of the interesting features I found in C# is a �K�Events and Delegates�K?concept. The idea is good but not new in Object Oriented Programming, it is one of the most frequently used concepts in programming, sometimes referred to as �K�Observer�K?or �K�Document/View�K?design pattern. Classical formulation of it could be found in �K�Design Patterns, Elements of Reusable Object Oriented Software�K?by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson, and John Vlissides (The Gang of Four).
This concept is used when you want some information stored in one object, called �K�model�K?(subject) to be watched by others, called �K�views�K?(observers). Each time when information is changed in the �K�model�K? �K�views�K?attached to the model should receive notification and update there states accordingly to the changed �K�model�K?
Classical implementation described in �K�Design Patterns�K?
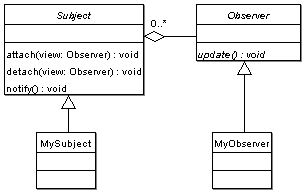
As it is seen from the class diagram, concrete models should be derived from Subject class and views from Observer. Any time the state of Subject is changed, it calls notify method which notifies all observers attached to the Subject.
void Subject::notify() { for(int i=0; i<observes.size(); i++) observers[i]->update(); }
In many applications, this straightforward implementation is good enough, but things are getting ugly when you have different kinds of changes in the �K�subject�K?and you want to pass different types of parameters to the �K�views�K?
One of the examples for complex �K�Model�K?�K�View�K?relations is a GUI control attached to its processing function. Each time the control�K�s state is changed, process function is called with parameters indicating new state of the control.
These kinds of problems are solved in C# by the introduction of �K�Events and Delegates�K?concept. The resolution of the problem is easier in C#, because all classes are inherited from the same �K�object�K?class.
At the beginning, I thought why we do not have this nice �K�Events and Delegates�K?thing in standard C++, but then I came to the conclusion that C++ does not need it.
C++ language is powerful enough to express �K�Events�K?and �K�Delegates�K?concept in terms of already existing primitives. Proposed design makes it possible to "connect" different methods with different number of parameters belonging to unrelated classes to the �K�model�K?
The keys for this solution are C++ templates (generic types) and pointes to member functions.
Using Code
Suppose we have a class MySubject that has internal information connected to different views, it produces three different types of events called int_event, double_event and triple_event with different types and numbers of parameters.
class MySubject { public: CppEvent1<bool,int> int_event; CppEvent2<bool,double,int> double_event; CppEvent3<bool,double,int,const char*> triple_event; void submit_int() { int_event.notify(1); } void submit_double() { double_event.notify(10.5,100); } void submit_triple() { triple_event.notify(10.5,100,"Oh ye"); } };
Views represented by MyListener1 and MyListener2 are unrelated. The only requirement is for callback (delegate) methods to have parameters signature similar to corresponding CppEvent.
class MyListener1 { public: bool update_int(int p) { Console::WriteLine(S"int update listener 1"); return true; } bool update_double(double p,int p1) { Console::WriteLine(S"double update listener 1"); return true; } bool update_triple(double p,int p1,const char* str) { Console::WriteLine(S"triple update listener 1"); return true; } }; class MyListener2 { public: bool fun(int p) { Console::WriteLine(S"int update listener 2"); return true; } };
The final step is to create viewers MyListener1 and MyListener2 and connect their member functions to corresponding events in MySubject model.
int main(void) { // create listeners (viewers) MyListener1* listener1 = new MyListener1; MyListener2* listener2 = new MyListener2; // create model MySubject subject; // connect different viewers to different events of the model CppEventHandler h1 = subject.int_event.attach(listener1, &MyListener1::update_int); CppEventHandler h2 = subject.int_event.attach(listener2, &MyListener2::fun); CppEventHandler h3 = subject.double_event.attach(listener1, &MyListener1::update_double); CppEventHandler h4 = subject.triple_event.attach(listener1, &MyListener1::update_triple); // generate events subject.submit_int(); subject.submit_double(); subject.submit_triple(); // detach handlers subject.int_event.detach(h1); subject.int_event.detach(h2); subject.double_event.detach(h3); subject.triple_event.detach(h4); return 0; }
Resulting output is:
> int update listener 1
> int update listener 2
> double update listener 1
> triple update listener 1
Implementation
First of all, if we want to attach different types of event handles (member functions with same types of parameters from different classes) to the same event, we should provide common base for them. We use templates to make it generic for any combination of parameter types in �K�delegate�K?or call back method. There are different event types for every number of arguments in callback function.
// Event handler base for delegate with 1 parameter template <typename ReturnT,typename ParamT> class EventHandlerBase1 { public: virtual ReturnT notify(ParamT param) = 0; };
Specific type of member function pointer within a pointer to the object is stored in the derived class.
template <typename ListenerT,typename ReturnT,typename ParamT> class EventHandler1 : public EventHandlerBase1<ReturnT,ParamT> { typedef ReturnT (ListenerT::*PtrMember)(ParamT); ListenerT* m_object; PtrMember m_member; public: EventHandler1(ListenerT* object, PtrMember member) : m_object(object), m_member(member) {} ReturnT notify(ParamT param) { return (m_object->*m_member)(param); } };
Event class stores map of event handlers and notifies all of them when notify method is called. Detach method is used to release handler from the map.
template <typename ReturnT,typename ParamT> class CppEvent1 { typedef std::map<int,EventHandlerBase1<ReturnT,ParamT> *> HandlersMap; HandlersMap m_handlers; int m_count; public: CppEvent1() : m_count(0) {} template <typename ListenerT> CppEventHandler attach(ListenerT* object,ReturnT (ListenerT::*member)(ParamT)) { typedef ReturnT (ListenerT::*PtrMember)(ParamT); m_handlers[m_count] = (new EventHandler1<ListenerT, ReturnT,ParamT>(object,member)); m_count++; return m_count-1; } bool detach(CppEventHandler id) { HandlersMap::iterator it = m_handlers.find(id); if(it == m_handlers.end()) return false; delete it->second; m_handlers.erase(it); return true; } ReturnT notify(ParamT param) { HandlersMap::iterator it = m_handlers.begin(); for(; it != m_handlers.end(); it++) { it->second->notify(param); } return true; } };
Comments
This implementation is quite similar to those in the article �K�Emulating C# delegates in Standard C++�K?/font>. I found out it after I already wrote the article. Actually, the fact that we have a similar way to deal with the problem means that it�K�s a very intuitive solution for this kind of problem in C++. An advantage of the current implementation is that it supports different number of arguments, so any member function of any class could be a callback (delegate). Probably to have this thing as a part of standard library is a good thing, but even if it�K�s not a part of the standard, you can use it as it is. This implementation is restricted to events up to 3 parameters, it can be easily extended to other numbers by just rewriting it with different number of parameters (see code for details).
定义对象间的一�U�一对多的依赖关�p�,当一个对象的状态发生改变时�Q�所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知�q�被自动更新�?/p>
UML�l�构图:

解析�Q?/p>
Observer模式定义的是一�U�一对多的关�p�,�q�里的一���是图中的Subject�c�,而多则是Obesrver�c�,当Subject�cȝ��状态发生变化的时候通知与之对应的Obesrver�c�M��也去相应的更新状态,同时支持动态的��d��和删除Observer对象的功能。Obesrver模式的实现要�Ҏ���Q�第一一般subject�c�都是采用链表等容器来存放Observer对象�Q�第二抽取出Observer对象的一些公��q��属性�Ş成Observer基类�Q�而Subject中保存的则是Observer�c�d��象的指针�Q�这样就使Subject和具体的Observer实现了解耦,也就是Subject不需要去兛_��到底是哪个Observer�Ҏ���q�了自己的容器中。生�z�M��有很多例子可以看做是Observer模式的运用,比方��_��一个班有一个班��M�Q�Q�Subject�Q�,他管理手下的一帮学生(Observer�Q�,当班里有一些事情发生需要通知学生的时候,班主任要做的不是逐个学生挨个的通知而是把学生召集�v来一起通知�Q�实��C��班主��d��具体学生的关�p�解耦�?/p>
实现�Q?/p>
1�Q�Observer.h
/**//********************************************************************
created: 2006/07/20
filename: Observer.h
author: 李创
http://www.shnenglu.com/converse/
purpose: Observer模式的演�C�Z���?br>*********************************************************************/
#ifndef OBSERVER_H
#define OBSERVER_H
#include <list>
typedef int STATE;
class Observer;
// Subject抽象基类,只需要知道Observer基类的声明就可以�?br>class Subject
{
public:
Subject() : m_nSubjectState(-1){}
virtual ~Subject();
void Notify(); // 通知对象改变状�?br> void Attach(Observer *pObserver); // 新增对象
void Detach(Observer *pObserver); // 删除对象
// 虚函�?提供默认的实�?�z�����c�d��以自己实现来覆盖基类的实�?br> virtual void SetState(STATE nState); // 讄���状�?br> virtual STATE GetState(); // 得到状�?/p>
protected:
STATE m_nSubjectState; // 模拟保存Subject状态的变量
std::list<Observer*> m_ListObserver; // 保存Observer指针的链�?br>};
// Observer抽象基类
class Observer
{
public:
Observer() : m_nObserverState(-1){}
virtual ~Observer(){}
// �U�虚函数,各个�z�����c�d��能有不同的实�?br> // 通知Observer状态发生了变化
virtual void Update(Subject* pSubject) = 0;
protected:
STATE m_nObserverState; // 模拟保存Observer状态的变量
};
// ConcreateSubject�c?�z����在Subject�c?br>class ConcreateSubject
: public Subject
{
public:
ConcreateSubject() : Subject(){}
virtual ~ConcreateSubject(){}
// �z�����c�自己实现来覆盖基类的实�?br> virtual void SetState(STATE nState); // 讄���状�?br> virtual STATE GetState(); // 得到状�?/p>
};
// ConcreateObserver�c�L��生自Observer
class ConcreateObserver
: public Observer
{
public:
ConcreateObserver() : Observer(){}
virtual ~ConcreateObserver(){}
// 虚函�?实现基类提供的接�?br> virtual void Update(Subject* pSubject);
};
#endif
2�Q�Observer.cpp
/**//********************************************************************
created: 2006/07/20
filename: Observer.cpp
author: 李创
http://www.shnenglu.com/converse/
purpose: Observer模式的演�C�Z���?br>*********************************************************************/
#include "Observer.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
/**//* --------------------------------------------------------------------
| Subject�c�L��员函数的实现
|
----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void Subject::Attach(Observer *pObserver)
{
std::cout << "Attach an Observern";
m_ListObserver.push_back(pObserver);
}
void Subject::Detach(Observer *pObserver)
{
std::list<Observer*>::iterator iter;
iter = std::find(m_ListObserver.begin(), m_ListObserver.end(), pObserver);
if (m_ListObserver.end() != iter)
{
m_ListObserver.erase(iter);
}
std::cout << "Detach an Observern";
}
void Subject::Notify()
{
std::cout << "Notify Observers''s Staten";
std::list<Observer*>::iterator iter1, iter2;
for (iter1 = m_ListObserver.begin(), iter2 = m_ListObserver.end();
iter1 != iter2;
++iter1)
{
(*iter1)->Update(this);
}
}
void Subject::SetState(STATE nState)
{
std::cout << "SetState By Subjectn";
m_nSubjectState = nState;
}
STATE Subject::GetState()
{
std::cout << "GetState By Subjectn";
return m_nSubjectState;
}
Subject::~Subject()
{
std::list<Observer*>::iterator iter1, iter2, temp;
for (iter1 = m_ListObserver.begin(), iter2 = m_ListObserver.end();
iter1 != iter2;
)
{
temp = iter1;
++iter1;
delete (*temp);
}
m_ListObserver.clear();
}
/**//* --------------------------------------------------------------------
| ConcreateSubject�c�L��员函数的实现
|
----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void ConcreateSubject::SetState(STATE nState)
{
std::cout << "SetState By ConcreateSubjectn";
m_nSubjectState = nState;
}
STATE ConcreateSubject::GetState()
{
std::cout << "GetState By ConcreateSubjectn";
return m_nSubjectState;
}
/**//* --------------------------------------------------------------------
| ConcreateObserver�c�L��员函数的实现
|
----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void ConcreateObserver::Update(Subject* pSubject)
{
if (NULL == pSubject)
return;
m_nObserverState = pSubject->GetState();
std::cout << "The ObeserverState is " << m_nObserverState << std::endl;
}
3�Q�Main.cpp
/**//********************************************************************
created: 2006/07/21
filename: Main.cpp
author: 李创
http://www.shnenglu.com/converse/
purpose: Observer模式的测试代�?br>*********************************************************************/
#include "Observer.h"
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
Observer *p1 = new ConcreateObserver;
Observer *p2 = new ConcreateObserver;
Subject* p = new ConcreateSubject;
p->Attach(p1);
p->Attach(p2);
p->SetState(4);
p->Notify();
p->Detach(p1);
p->SetState(10);
p->Notify();
delete p;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
在许多广泛应用的�E�序库,我们会看到类�?#pragma pack(push, 4) �{�这��L��标示。因为用户会��L��更改他们的结构成员对齐选项�Q�对于先于这些内容创建的�E�序库来��_��不能���保一定的内存布局���可能在预先书写的一些数据访问模块上��D��错误�Q�或者根本不可能实现�?br>
我在实现一�U?C++ �cȝ��实例的序列化工具�Ӟ��依赖了内存布局。我知道市面上很�?#8220;序列�?#8221;工具允许更�ؓ�q�泛的通信用途,但是它们也是用�v来最�ȝ��的,有很多限制条件。我实现的序列化工具用意很明显,为特定运行模块提供便捷高效的持久化存储能力�?br>
��Z��提供感性的认识�Q�提供了一个��用这个序列化工具的类型定义�?br>
class StorageDoc
: public SerialOwner
{
public:
Serializable(StorageDoc);
char c;
int i;
SerialString str;
};
它��承自 SerialOwner�Q�它声明�?Serializable�Q�隐含着实现了一些接口,为基�c�访问当前类型信息提供帮助。这是较早书写的一�U�方案,现在我会改用模板以便在编译时建立�c�d��信息�Q�不�q�原理完全一栗��?br>
现在�Q�StorageDoc 当中的内存布局需要可���定的,但是用户会选择不同的结构成员对齐选项�Q��ؓ此需要设定一个结构成员对齐的“子域”�Q�完成这��能力的伪指令是 #pragma pack�?br>
#pragma pack( [ show ] | [ push | pop ] [, identifier ] , n )
1�Q�当选用 show�Q�则��d��一条警告信息,指示当前�~�译域内的对齐属�?br>2�Q�仅仅设�|?n�Q�则重写�~�译器选项 /Zp�Q��ƈ影响到此声明以下的同一个编译单元内的所有结构定�?br>3�Q�push 以及 pop ���理了一�l?#8220;子域”堆栈�Q�可以不断加深嵌�?br>4�Q�identifier 命名了堆栈上的对齐项�Q�以便在特定需求中弹出合适的��目
以下是��用的注意事项�Q?br>
1�Q�不��Z���Ӟ��#pragma pack() ��L��恢复�?/Zp 的预讑ր�|��即��处于 push �?#8220;子域”
2�Q?pragma pack(push) 未指定对齐��|��则不改变
3�Q?pragma pack(pop) 可指定对齐值出栈后的设�|���|��若不指定则按嵌套�{���q�原�Q�直�?/Zp 预设�?br>
�l�g���Q?pragma pack(pop) ��L��能正���回退��C��一个作用域�Q�不���该作用域通过 #pragma pack(n) 声明或�?#pragma pack(push, n)。�?#pragma pack() ��L��取预讑ր�{��对于用户事先指定了一�?#8220;子域”�Q��ƈ在其中引入了一个���?#pragma pack(n) - #pragma pack() 对而非堆栈形式来声明局部结构成员对齐的头文�Ӟ��会��用户非常困惑�?d3d9types.h> ���是�q�样做的�?br>
当我们�ؓ�E�序库编译运行时�Q�有一些类型要求严格地遵守内存布局�Q�比如一些硬件允许我们传入的数据���需要这么做�Q�就可以把它们限定�v来:
#pragma pack(push, 8)
#include "Chain.h"
#include "ByteQueue.h"
#include "SerialOwner.h"
#include "SerialUser.h"
#include "SerialString.h"
#include "SerialStream.h"
#pragma pack(pop)
事情再回到序列化上面�Q�用户会多次���试�~�译他们的序列化应用模块�Q��ƈ指望前一�ơ编译之后运行所产生的文件仍然是可用的,所以还需要在用户文�g当中明确所选用的对齐��|���q�一旦确定就不再更改�Q?br>
#pragma pack(push, 8)
class StorageDoc
: public SerialOwner
{
public:
Serializable(StorageDoc);
char c;
int i;
SerialString str;
};
#pragma pack(pop)
�q���用它们:
StorageDoc doc;
doc.Load(t("doc.bin"));
std::cout << doc.str.Get() << std::endl;
doc.str = ss.str();
std::cout << doc.str.Get() << std::endl;
doc.Save(t("doc.bin"));
�q�就是全部了�Q�但是正如以上提到的�Q�不仅仅在序列化上,和硬件、链接库的通信也可能存在严格的内存布局的要求,如果你在��目设计上遭遇这些困惑,那么现在���可以立卛_��手解军_��们�?br>
如果�Ҏ��文提到的序列化能力感兴趣的话�Q�可以到以下链接了解详情�Q?br>
http://code.google.com/p/los-lib/source/browse/
目录是:
svn/trunk/Inc/Los/
文�g分别是:
_ISerialUser.h
ByteQueue.h
Chain.h
Serialization.h
SerialOwner.h
SerialStream.h
SerialString.h
SerialUser.h
不过在本文发布之�Ӟ��以上文�g所处版本没有针对结构成员对齐选项�q�行修改�Q�但�q�不影响阅读�?br>
* 补充一�Q?009-1-18 02:41�Q?br>
联合以及�l�构的结构成员对齐异�?br>
class Tick
{
static int _StaticID;
__int64 _StartLI; // __alignof(LARGE_INTEGER) != __alignof(__int64)
__int64 _CurrentLI;
__int64 _Frequency;
int _ID;
clock_t _Start;
clock_t _Current;
bool _Stop;
bool _HighPerformance;
...
}
LARGE_INTEGER 是分别对应两�?32bit 以及一�?64bit �c�d��的联合,奇怪的是随着全局寚w��选项的修改,LARGE_INTEGER �c�d��本��n的请求对�?__alignof(LARGE_INTEGER) ���取联合的成员的最大者同全局寚w��选项的最�����|��也就是说�Q�当 /Zp 讄����?2�Q�那�?LARGE_INTEGER 也将仅承诺在 2 字节边界上对齐,多么不幸啊。当然如果将�q�个�c�d���U�_�� #pragma pack 的限定域那就什么问题都没有了,不管联合的对齐算法多么的古怪,只要保证不修�Ҏ��需的对齐值那�����L��能获得确定的内存布局�?br>
不过正如上面的代码列出的�Q�我使用�?__int64 代替�?LARGE_INTEGER 的工作,�q�在��h�� Win32 API 的接口上强制指针转型�Q���用的时候亦如此�Q�但若访问联合成员刚好�ؓ __int64 �c�d��则直接��用便可。这�U�方式没有获得额外的好处�Q�算是一�U�抗议的行�ؓ�Q��ƈ且让后来的阅读者有��Z��了解到这个见不得光的问题�?br>
_HighPerformance = ::QueryPerformanceFrequency((LARGE_INTEGER*)&_Frequency) != 0;
当然作�ؓ严肃的代码写作者,也许你将在不止一处��用到 LARGE_INTEGER�Q��ؓ此我也不拒绝使用如下格式�Q?br>
#pragma pack(push, 8)
#include
#pragma pack(pop)
它可保证你万无一失�?br>
作�ؓ�Ҏ���Q�FILETIME 有如下定义:
typedef struct _FILETIME
{
DWORD dwLowDateTime;
DWORD dwHighDateTime;
} FILETIME;
且不论它所需的可能的最大结构成员对齐�ؓ 4�Q�它也将伴随着 /Zp 的更改而变动。因此,在不同的选项的媄响下�Q?br>
__alignof(LARGE_INTEGER) != __alignof(FILETIME) != __alignof(__int64)
有些人可能要指责会发生这��L��问题�U���a是用户在玩弄“�l�构成员寚w��选项”而导致的�Q�我真希望他能够��M��读这���文章�?br>
* 补充二(2009-1-18 02:41�Q?br>
D3D 与用户定义结构的协调
class VertexXYZ_N_T1
{
public:
float x, y, z;
float normal_x, normal_y, normal_z;
float u, v;
DeviceBitmap* bitmap;
Material* material;
float temp_val;
static const int FVF = D3DFVF_XYZ | D3DFVF_NORMAL | D3DFVF_TEX1;
};
�q�是一个自定义��点�l�构�Q�它的最大成员字节数�?4�Q�所有的成员也都�?4 字节边界�Q�不��Z��何选项�Q�始�l�保持紧凑存储,若其中一个成员扩展�ؓ 8 字节�Q�那么伴随着选项的更改,VertexXYZ_N_T1 要求的对齐边界可��D��部分�I�洞�Q�从而同����g所需的顶点缓存数据布局存在出入�Q�我不追�I�硬件是否���?double ��|��但是现在���应当���?br>
#pragma pack(push, 4)
...
#pragma pack(pop)
加以限定�?br>
我还定义�?Matrix, Material, Vector3, Colorf �{�类型,如果要��得这些数据同 D3D, D3DX 的相应类型在内存上兼容的�Q�也是需要限定的�?/p>
1�?sizeof应用在结构上的情�?/font>
��L��下面的结构:
struct MyStruct
{
double dda1;
char dda;
int type
};
对结构MyStruct采用sizeof会出��C��么结果呢�Q�sizeof(MyStruct)为多���呢�Q�也�怽�会这��h���Q?/font>
sizeof(MyStruct)=sizeof(double)+sizeof(char)+sizeof(int)=13
但是当在VC中测试上面结构的大小�Ӟ��你会发现sizeof(MyStruct)�?6。你知道��Z��么在VC中会得出�q�样一个结果吗�Q?/font>
其实�Q�这是VC对变量存储的一个特�D�处理。�ؓ了提高CPU的存储速度�Q�VC对一些变量的起始地址做了“寚w��”处理。在默认情况下,VC规定各成员变量存攄���起始地址相对于结构的起始地址的偏�U�量必须�����变量的类型所占用的字节数的倍数。下面列出常用类型的寚w��方式(vc6.0,32位系�l?�?/font>
�c�d��
寚w��方式�Q�变量存攄���起始地址相对于结构的起始地址的偏�U�量�Q?/font>
Char
偏移量必���Mؓsizeof(char)�?的倍数
int
偏移量必���Mؓsizeof(int)�?的倍数
float
偏移量必���Mؓsizeof(float)�?的倍数
double
偏移量必���Mؓsizeof(double)�?的倍数
Short
偏移量必���Mؓsizeof(short)�?的倍数
各成员变量在存放的时候根据在�l�构中出现的��序依次甌����I�间�Q�同时按照上面的寚w��方式调整位置�Q�空�~�的字节VC会自动填充。同时VC��Z�����保�l�构的大����ؓ�l�构的字节边界数�Q�即该结构中占用最大空间的�c�d��所占用的字节数�Q�的倍数�Q�所以在为最后一个成员变量申��L��间后�Q�还会根据需要自动填充空�~�的字节�?/font>
下面用前面的例子来说明VC到底怎么��h��存放�l�构的�?/font>
struct MyStruct
{
double dda1;
char dda;
int type
}�Q?/font>
��Z��面的�l�构分配�I�间的时候,VC�Ҏ��成员变量出现的顺序和寚w��方式�Q�先为第一个成员dda1分配�I�间�Q�其起始地址跟结构的起始地址相同�Q�刚好偏�U�量0刚好为sizeof(double)的倍数�Q�,该成员变量占用sizeof(double)=8个字节;接下来�ؓ�W�二个成员dda分配�I�间�Q�这时下一个可以分配的地址对于�l�构的�v始地址的偏�U�量�?�Q�是sizeof(char)的倍数�Q�所以把dda存放在偏�U�量�?的地�Ҏ�����_��齐方式,该成员变量占用sizeof(char)=1个字节;接下来�ؓ�W�三个成员type分配�I�间�Q�这时下一个可以分配的地址对于�l�构的�v始地址的偏�U�量�?�Q�不是sizeof(int)=4的倍数�Q��ؓ了满���_��齐方式对偏移量的�U�束问题�Q�VC自动填充3个字节(�q�三个字节没有放什么东西)�Q�这时下一个可以分配的地址对于�l�构的�v始地址的偏�U�量�?2�Q�刚好是sizeof(int)=4的倍数�Q�所以把type存放在偏�U�量�?2的地方,该成员变量占用sizeof(int)=4个字节;�q�时整个�l�构的成员变量已�l�都分配了空��_���ȝ��占用的空间大����ؓ�Q?+1+3+4=16�Q�刚好�ؓ�l�构的字节边界数�Q�即�l�构中占用最大空间的�c�d��所占用的字节数sizeof(double)=8�Q�的倍数�Q�所以没有空�~�的字节需要填充。所以整个结构的大小为:sizeof(MyStruct)=8+1+3+4=16�Q�其中有3个字节是VC自动填充的,没有放�Q何有意义的东�ѝ�?/font>
下面再�D个例子,交换一下上面的MyStruct的成员变量的位置�Q���它变成下面的情况�Q?/font>
struct MyStruct
{
char dda;
double dda1;
int type
}�Q?/font>
�q�个�l�构占用的空间�ؓ多大呢?在VC6.0环境下,可以得到sizeof(MyStruc)�?4。结合上面提到的分配�I�间的一些原则,分析下VC怎么样�ؓ上面的结构分配空间的。(���单说明)
struct MyStruct
{
char dda;//偏移量�ؓ0�Q�满���_��齐方式,dda占用1个字节;
double dda1;//下一个可用的地址的偏�U�量�?�Q�不是sizeof(double)=8
//的倍数�Q�需要补��?个字节才能��偏移量变�?�Q�满���_���?/font>
//方式�Q�,因此VC自动填充7个字节,dda1存放在偏�U�量�?
//的地址上,它占�?个字节�?/font>
int type�Q?/下一个可用的地址的偏�U�量�?6�Q�是sizeof(int)=4的�?/font>
//敎ͼ�满��int的对齐方式,所以不需要VC自动填充�Q�type�?/font>
//攑֜�偏移量�ؓ16的地址上,它占�?个字节�?/font>
}�Q?/所有成员变量都分配了空��_���I�间�ȝ��大小�?+7+8+4=20�Q�不是结�?/font>
//的节边界敎ͼ�即结构中占用最大空间的�c�d��所占用的字节数sizeof
//(double)=8�Q�的倍数�Q�所以需要填�?个字节,以满���结构的大小�?/font>
//sizeof(double)=8的倍数�?/font>
所以该�l�构�ȝ��大小为:sizeof(MyStruc)�?+7+8+4+4=24。其中�ȝ���?+4=11个字节是VC自动填充的,没有放�Q何有意义的东�ѝ�?/font>
VC对结构的存储的特�D�处理确实提高CPU存储变量的速度�Q�但是有时候也带来了一些麻烦,我们也屏蔽掉变量默认的对齐方式,自己可以讑֮�变量的对齐方式�?/font>
VC中提供了#pragma pack(n)来设定变量以n字节寚w��方式。n字节寚w�����是说变量存攄���起始地址的偏�U�量有两�U�情况:�W�一、如果n大于�{�于该变量所占用的字节数�Q�那么偏�U�量必须满��默认的对齐方式,�W�二、如果n���于该变量的�c�d��所占用的字节数�Q�那么偏�U�量为n的倍数�Q�不用满���默认的寚w��方式。结构的��d�����也有个�U�束条�g�Q�分下面两种情况�Q�如果n大于所有成员变量类型所占用的字节数�Q�那么结构的��d�����必���Mؓ占用�I�间最大的变量占用的空间数的倍数�Q?/font>
否则必须为n的倍数。下面�D例说明其用法�?/font>
#pragma pack(push) //保存寚w��状�?/font>
#pragma pack(4)//讑֮��?字节寚w��
struct test
{
char m1;
double m4;
int m3;
};
#pragma pack(pop)//恢复寚w��状�?/font>
以上�l�构的大����ؓ16�Q�下面分析其存储情况�Q�首先�ؓm1分配�I�间�Q�其偏移量�ؓ0�Q�满���x��们自��p��定的寚w��方式�Q?字节寚w���Q�,m1占用1个字节。接着开始�ؓm4分配�I�间�Q�这时其偏移量�ؓ1�Q�需要补��?个字节,�q�样使偏�U�量满��为n=4的倍数�Q�因为sizeof(double)大于n�Q?m4占用8个字节。接着为m3分配�I�间�Q�这时其偏移量�ؓ12�Q�满����ؓ4的倍数�Q�m3占用4个字节。这时已�l��ؓ所有成员变量分配了�I�间�Q�共分配�?6个字节,满��为n的倍数。如果把上面�?pragma pack(4)改�ؓ#pragma pack(16)�Q�那么我们可以得到结构的大小�?4。(误���者自己分析)
2�?sizeof用法�ȝ��
在VC中,sizeof有着许多的用法,而且很容易引起一些错误。下面根据sizeof后面的参数对sizeof的用法做个�ȝ���?/font>
A�Q?参数为数据类型或者�ؓ一般变量。例如sizeof(int),sizeof(long)�{�等。这�U�情况要注意的是不同�pȝ���pȝ��或者不同编译器得到的结果可能是不同的。例如int�c�d���?6位系�l�中�?个字节,�?2位系�l�中�?个字节�?/font>
B�Q?参数为数�l�或指针。下面�D例说�?
int a[50]; //sizeof(a)=4*50=200; 求数�l�所占的�I�间大小
int *a=new int[50];// sizeof(a)=4; a��Z��个指针,sizeof(a)是求指针
//的大��?�?2位系�l�中�Q�当然是�?个字节�?/font>
C�Q?参数为结构或�c�R��Sizeof应用在类和结构的处理情况是相同的。但有两炚w��要注意,�W�一、结构或者类中的静态成员不对结构或者类的大�����生媄响,因�ؓ静态变量的存储位置与结构或者类的实例地址无关�?/font>
�W�二、没有成员变量的�l�构或类的大����ؓ1�Q�因为必���M��证结构或�cȝ��每一
个实例在内存中都有唯一的地址�?/font>
下面举例说明�Q?/font>
Class Test{int a;static double c};//sizeof(Test)=4.
Test *s;//sizeof(s)=4,s��Z��个指针�?/font>
Class test1{ };//sizeof(test1)=1;
D�Q?参数为其他。下面�D例说明�?/font>
int func(char s[5]);
{
cout<< sizeof(s) << endl;
//数组参数在传递的时候系�l�处理�ؓ一个指针,所
//以sizeof(s)实际上�ؓ求指针的大小�?/font>
return 1;
}
sizeof(func(“1234”))=4//因�ؓfunc的返回类型�ؓint�Q�所以相当于
求sizeof(int).
以上为sizeof的基本用法,在实际的使用中要注意分析VC的分配变量的分配�{�略�Q�这��L��话可以避免一些错误�?/font>