2009年2月17日
John Borthwick 在 Google Next Victim Of Creative Destruction? 一文中闡述了AOL 的死亡以及產業的不斷循環, yahoo, ebay 等已經成為技術革新的受害者.
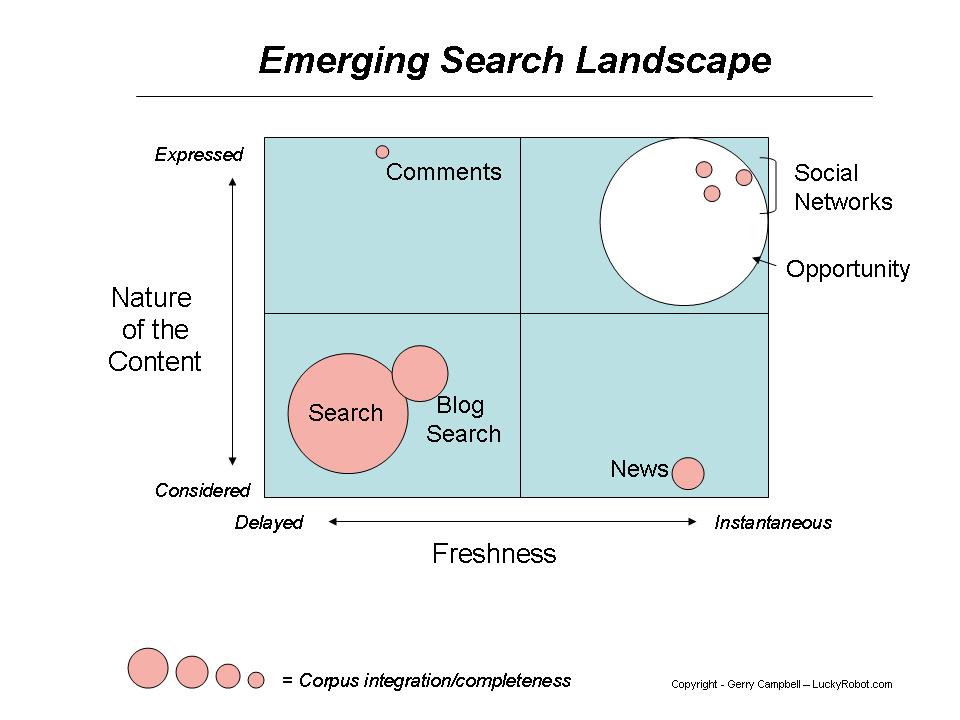
隨著搜索的垂直分割, 搜索市場也被細化
1. 視頻搜索的突起, youtube 從2007.10 到 2008.10 的搜索增長了114%, 占了google 搜索的26%.
2. 實時消息的發展, 以twitter 為代表, 市場對突發事件的要求的強烈, 使得twitter 迅速發展, twitter 的搜索(http://search.twitter.com/)與傳統引擎依賴內容相關以及鏈接關系相比, 更注重時間的相關性.
Gerry campbell 的文章 Search is broken – really broken. 的一個圖說明了這種趨勢
2008年12月19日
Python 的logging 模塊的Socket 和 Logging4cplus 的 socket 的格式是不一樣的, 現實中需要將日志發送到logging4cplus 的服務器, 不得已, 寫了個 Python logging 模塊到 logging4cplus的Adapter
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2 #-*- coding: gbk -*-
3 from struct import pack, unpack
4
5 class BufferPack(object):
6 def __init__(self):
7 self.buffer = ''
8
9 def addChar(self, s, unsigned=False):
10 self.buffer += pack(unsigned and '>b' or '>c', s )
11
12 def addShort(self, s, unsigned=False):
13 self.buffer += pack(unsigned and '>H' or '>h', s )
14
15 def addInt(self, s, unsigned=False):
16 self.buffer += pack(unsigned and '>I' or '>i', s )
17
18 def addLong(self, s, unsigned=False):
19 self.buffer += pack(unsigned and '>L' or '>l', s )
20
21 def addString(self, s):
22 self.addInt( len(s) )
23 self.buffer += s
24
25 def addBuffer(self, s):
26 self.buffer += s.buffer
27
28 class BufferUnpack(object):
29
30 char_bits = len( pack('>b', 0) )
31 short_bits = len( pack('>H', 0) )
32 int_bits = len( pack('>I', 0) )
33 long_bits = len( pack('>L', 0) )
34
35 def __init__(self, buffer):
36 self.buffer = buffer
37 self.pos = 0
38
39 def _read_item(self, unpackstr, len):
40 v = unpack(unpackstr, self.buffer[self.pos:self.pos+len] )
41 self.pos += len
42 return v
43
44 def readChar(self, unsigned=False):
45 return self._read_item(unsigned and '<b' or '<c', self.char_bits)
46
47 def readShort(self, unsigned=False):
48 return self._read_item(unsigned and '<H' or '<h', self.short_bits )
49
50 def readInt(self, unsigned=False):
51 return self._read_item(unsigned and '<I' or '<i', self.int_bits )
52
53 def readLong(self, unsigned=False):
54 return self._read_item(unsigned and '<L' or '<l', self.long_bits )
55
56 def readString(self):
57 len = self.readInt()
58 v = self.buffer[self.pos:self.pos+len]
59 self.pos += len
60 return v
61
62 def PackMessage( record ):
63 bp = BufferPack()
64 bp.addChar(2, True)
65 bp.addChar(1, True)
66
67 bp.addString("{log.servername}")
68 bp.addString(record.name)
69 bp.addInt(record.levelno*1000)
70 bp.addString("")
71 bp.addString(record.msg)
72 bp.addString(str(record.threadName))
73 bp.addString(str(record.process))
74 bp.addInt( record.created )
75 bp.addInt( record.msecs )
76 bp.addString(record.filename)
77 bp.addInt( 1 )
78
79 pkg = BufferPack()
80 pkg.addInt(len(bp.buffer), True)
81 pkg.addBuffer( bp )
82
83 return pkg.buffer
84
85 if __name__=="__main__":
86 import logging, logging.handlers
87
88 logger = logging.getLogger()
89 logging.handlers.SocketHandler.makePickle = lambda self,rc : PackMessage(rc)
90
91 hdlr = logging.handlers.SocketHandler('{logserver.ip}', 8888)
92 formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s')
93 hdlr.setFormatter(formatter)
94 logger.addHandler(hdlr)
95 logger.setLevel(logging.NOTSET)
96
97 logger.info("hello")
使用的時候.
1. 在logging 創建SocketHandler 的時候, 需要修改logging.handlers.SocketHandler.makePickle 為方法 PackMessage
logging.handlers.SocketHandler.makePickle = lambda self,rc : PackMessage(rc)
2. 需要修改代碼中的兩部分內容 {log.servername} 和 {logserver.ip}
2008年12月4日
BHO就是Browser Helper Object(瀏覽器輔助對象)
BHO關聯原理 (BHO關聯的是SHDOCVW,也就是說不只關聯IE,下面全部用IE來說明)
1.IE的窗口打開時,先尋找HKLM下的SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Browser Helper Objects\ 里的CLSID,這些CLSID,都對應著相應的BHO插件,然后根據這個CLSID到HKCR下的CLSIDs里找到此插件的信息,包括文件位置等。
2.IE根據找到的CLSID信息創建 BHO 對象,并且查找 IObjectWithSite 接口. (這個接口非常簡單,只有SetSite和GetSite兩個方法)
3.IE把IWebBrowser2(瀏覽器插件)傳到 BHO 的 SetSite 方法,用戶在此方法中可掛載自己的事件處理方法。
4.窗口關閉時,IE把 null 傳到 BHO 的 SetSite 方法,此方法用來去掉掛載的事件處理方法。
編寫BHO流程
1.創建IObjectWithSite顯式接口,創建 COM 類型,實現繼承IObjectWithSite接口
2.實現此接口并在SetSite方法里加上所要掛載的事件
3.處理事件
4.注冊此BHO到注冊表中HKLM下的Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Browser Helper Objects;(HKCR下的CLSIDs是根據上面的路徑自動注冊的)
5、.net 下須設置此BHO項目的 配置屬性_>生成 中為Interop注冊為True,這樣才能將.net 類庫文件注冊到COM
刪除BHO
打開注冊表項到:HKLM下的Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Browser Helper Objects 可以看到下面有一些CLSID值,這些值對應相關的插件,點擊可以在默認值后看到相關插件的名稱!可以復制相關CLSID到注冊表中搜索相關CLSID,找到后打開InprocServer32可以看到相關文件的路徑,至于DLL文件等可以用UEDIT32.exe工具打開查看具體信息,當然也可以用修改程序類的eXeScope.exe研究一下!
請根據具體情況刪除相關鍵值和相關文件!
REF:
BHO 的編寫
VCKBase 關于IE 編程文檔中心
C++中使用BHO來屏蔽特定網站
瀏覽器集成教學 自定義瀏覽器
2008年10月29日
zz http://littletutorials.com/2008/07/07/success-as-technical-lead/
分為3個部分
Set yourself up for success
Build your relationship with the team
Build your relationship with the management and business people
Set yourself up for success
1. Define early on what success means for you, the team and the business
You have to have a clear idea of what you want. You also have to understand what team members and the management want. You also have to be aware that what people really want, what they say the want and sometimes even what they think they want are very different things. Try to be very honest at least with yourself. Success has different definitions for different people. If there is a big disconnect between these definitions you have a problem before you start.
2. Believe in the project: idea, architecture, time, team
You cannot have any kind of success if you are convinced you lead a team of morons to implement a stupid idea using the wrong architecture in a ridiculously short time. You have to really believe in the project to have a chance to success. This does not mean lie to yourself. It means do whatever you can to understand your concerns and work on them with the management. As for the architecture, it is best if you have a heavy word or if you are the architect.
3. Understand the domain, the business requirements and the technical challenges
You should be an expert in the technologies used for implementation. You also have to become very knowledgeable in the problem domain and the business case. This will help you understand the business decisions dropped on your head from upstairs and also will help you stand a chance at negotiating them.
4. Know your team: strengths, weaknesses, ambitions and personalities
Software is created by people. Your job as a “tech lead” is to support them in doing that, both from a technical point of view and at a human level. You want to lead a team of motivated and enthusiastic people. But each person gets motivated by different things.
5. Have a plan as a result of a planning activity
“Plans are useless but planning is essential” - (Dwight D Eisenhower, US President, general 1890-1969). Planning will make you think about the problems you face in detail. Also keep in mind that “a plan is just a list of things that ain’t gonna happen” - (Benicio Del Torro in “The Way of the Gun”).
6. Be part in the design of everything
This does not mean do the whole design. You want to empower team members. But your job is to understand and influence each significant subsystem in order to maintain architectural integrity.
7. Get your hands dirty and code
Yes you should take parts of the code and implement them. Even the least glamorous parts. This will help you not getting stuck alone between management and the team. It will also help you gain respect in the team.
8. Act as a communication proxy for your team
In long complex projects with big teams communication is one of the most complicated aspects. The more people you have involved in solving a problem the bigger the communication matrix becomes. Since people need information to be able to make the right decisions this will lead to an exponential increase in the time consumed for communication. Agile methodologies alleviate this problem. But in the end it is up to you to propagate important information to the right people.
9. Make sure everybody understands the big picture: their work has implications
This will help you greatly because will allow team members to design and implement in a way that you don’t have to fight. It is also hard work from your part.
10. Fight for architecture and design consistency
Doing the right thing from the design and architecture point of view is not more costly. It is actually cheaper in every project longer than a couple of months. Every early investment in architecture pays for itself later during integration and maintenance. Even if you have to admit an occasional hack or prototype in the code base you should contain it in very specific modules.
11. Know the status of everybody’s work and detect slippage
This allows for corrective actions and for early communication with the management. You don’t want to be caught by surprise. Remember that during 90% of the allocated time for a task the code is 90% complete.
12. Record technical debt if you need shortcuts but try to maintain architectural integrity; report the debt
This one is very important for products that will have multiple releases. Technical debt should be analyzed at the beginning of each iteration.
13. Use the process that makes sense in your particular case
Tough one. Sometimes (most of the times?) the process is not up to you. In the enterprise usually the process is pre-decided. But always keep in mind that the process in itself means nothing. It is the people who give meaning to the process. Good people can make the worst process work while the wrong team cannot make any process work. Waterfall can be implemented in a very agile way and the agile methodologies can be applied with “rigor mortis” agility (see The Agile 800 Pounds Gorilla).
14. Avoid dogmas - question why everything is done the way is done; make sure everybody else knows the reasons
Sometimes I hear from programmers: we are agile and combine XP and Scrum and we also do TDD (Test Driven Development - I still hope for a TDD that means Thought Driven Development). The questions that pop up in my mind are: Do you need all those? Do you “really” do them by the book?
Anyway the point here is don’t do anything just because it is the way it has always been done. Understand why. Then explain the reasons to all team members. Rinse and repeat.
15. Avoid design by committee; listen to everybody but make your own decisions
No good design is born from referendum. There are lots of people making wild exotic suggestions when their a$$ is not on the line. There are also excessively prudent ideas born from fear. Even with good ideas you have to filter them and make them yours before you can include them in the design. A good architecture and a good design is usually born in one mind, an open mind that looks around. The obvious example is Linux.
Build your relationship with the team 16. Gain the team’s respect with the quality of your work and by doing what you are preaching17. Be fair
18. Admit your mistakes
19. Publicly recognize both team’s and individual members’ merits
20. Don’t blame anybody publicly for anything
21. Build morale and confidence by offering early victories to the team and to its individual members
22. Match people and tasks based on skills and their personal preference if possible; explain your decisions
23. Work the estimates with the team don’t come up with them
24. Mentor people
25. Listen to and learn from people
26. Explain your technical decisions
Build your relationship with the management and business people
27. Be sure you have authority along with responsibility
28. Be sure you get requirements and not architecture/design masked as requirements
29. Explain technical decisions in business terms
30. Try to be accurate in your estimates; avoid being too optimistic and don’t push it with hidden padding; explain the need for padding
31. Set reasonable expectations
32. Understand the relationships and dependencies with other teams or projects
33. Accurately report the status with alarms, explanations and solutions; report any technical debt
34. Resist pressure for change in requirements, and more important for shortcuts…
35. Be aware of politics
36. React to surprises with calm and with documented answers
zz http://www.whenpenguinsattack.com/2006/07/19/php-template-engine-roundup/
該文總結了 php 的一些模板. 我使用過的有smarty, template lib, 還有后來用的 Savant. 感覺smarty 太復雜了, template lib 需要學習一些標簽, 并且不是很強大, 綜合考慮還是Savant 最好, 既可以使用模板機制, 另外頁面模板直接使用php 函數來輸出. 功能也還可以.
Smarty
Smarty is a template engine that compiles the templates into PHP scripts, then executes those scripts. Very fast, very flexible.
Savant
A powerful but lightweight PEAR-compliant template system. It is non-compiling, and uses PHP itself as its template language.
Heyes Template Class
A very easy to use, yet powerful and quick template engine that enables you to separate your page layout and design from your code.
FastTemplate
A simple variable interpolation template class that parses your templates for variables and spits out HTML with their values
ShellPage
A simple and easy to use class that lets you make whole websites based on template files for layouts. Change the template and your whole site changes.
STP Simple Template Parser
A simple, light weight and easy to use template parser class. It can assemble a page from several templates, output result pages to the browser or write them to the filesystem.
OO Template Class
An object oriented template class you can use in your own programs.
SimpleTemplate
A template engine to create and structure websites and applications. It can translate and compile the templates.
bTemplate
A small and fast template class that allows you to separate your PHP logic from your HTML presentation code.
ETS - easy template system
A template system that allows you to reshuffle templates with exactly the same data.
EasyTemplatePHP
A simple, yet powerful templating system for your site.
vlibTemplate
A fast, full featured template system that includes a caching and debugging class.
AvanTemplate
A template engine that is multi-byte safe and consumes little computing resource. It supports variable replacement and content blocks that can be set to hidden or shown.
Grafx Software’s Fast Template
A modification of the popular Fast Template system, this includes a cache function, debug console, and silent removal of unassigned dynamic blocks.
TemplatePower
A fast, simple and powerful template class. Features nested dynamic block support, block/file include support and show/hide unassigned variables.
TagTemplate
This library function was designed for use with template files and allows you to retrieve info from HTML files.
htmltmpl: templating engine
A templating engine for Python and PHP. Targeted to web application developers, who want to separate program code and design of their projects.
PHP Class for Parsing Dreamweaver templates
A simple class to parse a Dreamweaver template for use in custom mods for a Gallery 2 and a WordPress blog.
MiniTemplator (Template Engine)
A compact template engine for HTML files. It features a simple syntax for template variables and blocks. Blocks can be nested.
Layout Solution
Simplifies website development and maintenance. It holds commonly used variables and page elements so you don’t need to duplicate common layouts over and over.
Cached Fast Template
This inclusion into FastTemplate allows for caching of the template files, and can even cache with different specifications on separate blocks of content.
TinyButStrong
A template engine that supports MySQL, Odbc, Sql-Server and ADODB. It includes seven methods and two properties.
Brian Lozier’s php based template engine
Only 2k in size, very fast and object-orientated.
WACT
a template engine that separates code from design.
PHPTAL
a XML/XHTML template library for PHP.
ref:
http://www.sitepoint.com/forums/showthread.php?t=123769 對其他的php 模板進行了討論
2008年10月6日
看條款38 的時候不是很理解, 于是寫了個測試代碼
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
virtual void show(int a=145)
{
cout<<"A: a="<<a<<endl;
}
};
class B: public A
{
public:
void show(int b)
{
cout<<"B: b="<<b<<endl;
}
};
class C: public B
{
public:
void show(int c=999)
{
cout<<"C: c="<<c<<endl;
}
};
class D: public C
{
public:
void show()
{
cout<<"D:\n";
}
};
void main()
{
A *pp;
A a;
B b;
C c;
D d;
a.show();
pp = &a; pp->show();
// b.show(); // error C2660: 'B::show' : function does not take 0 arguments
pp = &b; pp->show();
c.show();
pp = &c; pp->show();
d.show();
pp = &d; pp->show();
C *pc= &d;
pc->show();
system("pause");
}
輸出結果是
A: a=145
A: a=145
B: b=145
C: c=999
C: c=145
D:
C: c=145
C: c=999
回顧條款
虛函數是動態綁定而缺省參數值是靜態綁定的. 為什么C++堅持這種有違常規的做法呢?答案和運行效率有關。如果缺省參數值被動態綁定,編譯器就必須想辦法為虛函數在運行時確定合適的缺省值,這將比現在采用的在編譯階段確定缺省值的機制更慢更復雜。做出這種選擇是想求得速度上的提高和實現上的簡便,所以大家現在才能感受得到程序運行的高效;
所以
a. 靜態綁定 .vs. 動態綁定
A *pp
= new B;
這里 pp 靜態綁定是 A* , 而動態綁定卻是 B*
B *pb = new B;
這里 pb 靜態綁定和動態綁定是一樣的都是 B*
b. 缺省值是靜態綁定的, 而非動態綁定
所以
d.show() 輸出 D: 因為show 被 D override
pp
= &d; pp->show();
pp 被動態綁定到D *, 但是show 的缺省值卻是A* 的 145, 所以輸出的是 C: c=145, 而不是999 ( 函數 show 被C 給override 了)
而 C *pc = &d; pc->show() , pc 靜態綁定為C*, 而動態綁定為 D* , 所以輸出的是 C: c=999 , 999 是 C* 靜態綁定的缺省值
c. 所以調用b.show 的時候出現了如下的錯誤
// b.show(); // error C2660: 'B::show' : function does not take 0 arguments
因為 B* 沒有靜態綁定的函數
結論就是
決不要重新定義繼承而來的缺省參數值
ref:
從這里學了不少:)
http://bbs.chinaunix.net/viewthread.php?tid=439188
2008年10月3日
為了給黑莓導入iPhone 的通信錄(contacts) , 只能利用黑莓的桌面管理器, 通過ipd 來維護.
但是發現 ABC Amber BlackBerry Converter 只能轉換而無法修改, IPDManager 只能維護鈴聲和音樂啥的:( 只能自己寫了個小程序
ipd 的格式可以在 http://na.blackberry.com/eng/developers/resources/journals/jan_2006/ipd_file_format.jsp 這里找到, 后面是代碼, 只是生成datablock 列表, 還需要額外拷貝. 操作時最好只同步通信錄.
下面是代碼
#!/usr/local/bin/python2.5
#-*- coding: gbk -*-
from struct import *
class BBFile:
def __init__(self):
pass
def _contactblock(self, name, phone, uid):
s = ''
# name
name = name.encode("utf-16be")
s += pack('<HB', len(name)+1, 0xa0)
s += pack('<B', 0x01) + name
# ff * 8
s += pack('<HB', 8, 0x54)
s += '\xff'*8
# uid
s += pack('<HBI', 4, 0x55, uid)
# phone
phone = phone.encode("gbk")
s += pack('<HB', len(phone)+1, 0x08)
s += phone + '\x00'
return s
def save(self, filename, us, dbID=0, dbVer=0):
hf = open(filename, "w+b")
rs, uid = 1, 363797835 # 初始值
for u in us:
s = self._contactblock(u[0], u[1], uid)
h = pack('<HIBHI', dbID, len(s)+7, dbVer, rs, uid)
hf.write(h + s)
uid += 8 #
rs += 1 #
hf.close()
if __name__=='__main__':
bb = BBFile()
us = [ (u'寶寶1', u'13888888888'),(u'寶寶2', u'13888888888'),(u'寶寶3', u'13888888888'), ]
bb.save("bb.ipd", us, 0, 0)
1. 保存成文件就可以直接運行了:)
2. 如果要真的生成可以導入bb 的文件的話, 要使用高級-> 只同步通訊錄, 然后將這個文件生成的內容放在導出文件的頭的后面, 還是有點麻煩.... 有空做個全自動的 呵呵
因為只是測試, 所以很多硬編碼了:)
2008年9月25日
= HTTP 基礎
一個完整的 HTTP 請求可以分成4步:
1. 創建TCP socket, 連接到Web 服務器
2. 發送Http 請求頭
3. 接受Web 響應數據
4. 關閉socket 連接
整個流程可以通過telnet hostname 80 來模擬
一個完整的請求例子如下
* About to connect() to www.baidu.com port 80 (#0)
* Trying 202.108.22.5... connected
* Connected to www.baidu.com (202.108.22.5) port 80 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> User-Agent: curl/7.16.4 (i586-pc-mingw32msvc) libcurl/7.16.4 OpenSSL/0.9.7e zlib/1.2.2
> Host: www.baidu.com
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Date: Thu, 25 Sep 2008 05:14:30 GMT
< Server: BWS/1.0
< Content-Length: 3342
< Content-Type: text/html
< Cache-Control: private
< Expires: Thu, 25 Sep 2008 05:14:30 GMT
< Set-Cookie: BAIDUID=3A8165EF68FFEE5F605D33ADEF300BA1:FG=1; expires=Thu, 25-Sep-38 05:14:30 GMT; path=/; domain=.baidu.com
< P3P: CP=" OTI DSP COR IVA OUR IND COM "
<
<html><head><meta http-equiv=Content-Type content="text/html;charset=gb2312"><title>......
另外值得說明的是, HTTP 請求是無狀態的,表明在處理一個請求時,Web服務器并不記住來自同一客戶端的請求。
= Http 請求頭
包含4個部分: 請求行、請求頭、空行和請求數據
1. 請求行
由三個標記組成:請求方法、請求URI和HTTP版本,它們用空格分隔, 如:GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
HTTP 規范定義了8種請求方法:
GET 檢索URI中標識資源的一個簡單請求
HEAD 與GET方法相同,服務器只返回狀態行和頭標,并不返回請求文檔
POST 服務器接受被寫入客戶端輸出流中的數據的請求
PUT 服務器保存請求數據作為指定URI新內容的請求
DELETE 服務器刪除URI中命名的資源的請求
OPTIONS 關于服務器支持的請求方法信息的請求
TRACE Web服務器反饋Http請求和其頭標的請求
CONNECT 已文檔化但當前未實現的一個方法,預留做隧道處理
2. 請求頭 [ 可無 ]
由關鍵字及值對組成,每行一對,關鍵字和值用冒號(:)分隔。如
> User-Agent: curl/7.16.4 (i586-pc-mingw32msvc) libcurl/7.16.4 OpenSSL/0.9.7e zlib/1.2.2
> Host: www.baidu.com
> Accept: */*
具體請求頭如后所列
3. 空行
最后一個請求頭之后是一個空行,發送回車符和退行,通知服務器以下不再有頭標。
4. 請求數據 [ 可無 ]
使用POST傳送數據,最常使用的是Content-Type和Content-Length頭標
= Web 響應
由四個部分組成: 狀態行、響應頭、空行、響應數據, 如:
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Date: Thu, 25 Sep 2008 05:14:30 GMT
< Server: BWS/1.0
< Content-Length: 3342
< Content-Type: text/html
< Cache-Control: private
< Expires: Thu, 25 Sep 2008 05:14:30 GMT
< Set-Cookie: BAIDUID=3A8165EF68FFEE5F605D33ADEF300BA1:FG=1; expires=Thu, 25-Sep-38 05:14:30 GMT; path=/; domain=.baidu.com
< P3P: CP=" OTI DSP COR IVA OUR IND COM "
<
<html><head><meta http-equiv=Content-Type content="text/html;charset=gb2312"><title>......
1.狀態行
由三個標記組成:HTTP版本、響應代碼和響應描述
HTTP版本:: 向客戶端指明其可理解的最高版本。
響應代碼:: 3位的數字代碼,指出請求的成功或失敗,如果失敗則指出原因。
響應描述:: 為響應代碼的可讀性解釋。
如
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
HTTP響應碼劃分如下(祥見后):
1xx:信息,請求收到,繼續處理
2xx:成功,行為被成功地接受、理解和采納
3xx:重定向,為了完成請求,必須進一步執行的動作
4xx:客戶端錯誤
2.響應頭
跟請求頭一樣,它們指出服務器的功能,標識出響應數據的細節。
3.空行
最后一個響應頭標之后是一個空行,發送回車符和退行,表明服務器以下不再有頭標。
4.響應數據
HTML文檔和圖像等,就是HTML本身。
= HTTP頭
用以描述客戶端或者服務器的屬性、被傳輸的資源等, 分為
1.通用頭標:即可用于請求,也可用于響應,是作為一個整體而不是特定資源與事務相關聯。
2.請求頭標:允許客戶端傳遞關于自身的信息和希望的響應形式。
3.響應頭標:服務器和于傳遞自身信息的響應。
4.實體頭標:定義被傳送資源的信息。即可用于請求,也可用于響應。
下表描述在HTTP/1.1中用到的頭標
Accept 定義客戶端可以處理的媒體類型,按優先級排序;
在一個以逗號為分隔的列表中,可以定義多種類型和使用通配符。例如:Accept: image/jpeg,image/png,*/*
Accept-Charset 定義客戶端可以處理的字符集,按優先級排序;
在一個以逗號為分隔的列表中,可以定義多種類型和使用通配符。例如:Accept-Charset: iso-8859-1,*,utf-8
Accept-Encoding 定義客戶端可以理解的編碼機制。例如:Accept-Encoding:gzip,compress
Accept-Language 定義客戶端樂于接受的自然語言列表。例如:Accept-Language: en,de
Accept-Ranges 一個響應頭標,它允許服務器指明:將在給定的偏移和長度處,為資源組成部分的接受請求。
該頭標的值被理解為請求范圍的度量單位。例如Accept-Ranges: bytes或Accept-Ranges: none
Age 允許服務器規定自服務器生成該響應以來所經過的時間長度,以秒為單位。
該頭標主要用于緩存響應。例如:Age: 30
Allow 一個響應頭標,它定義一個由位于請求URI中的次源所支持的HTTP方法列表。例如:Allow: GET,PUT
AUTHORIZATION 一個響應頭標,用于定義訪問一種資源所必需的授權(域和被編碼的用戶ID與口令)。
例如:Authorization: Basic YXV0aG9yOnBoaWw=
Cache-Control 一個用于定義緩存指令的通用頭標。例如:Cache-Control: max-age=30
Connection 一個用于表明是否保存socket連接為開放的通用頭標。例如:Connection: close或Connection: keep-alive
Content-Base 一種定義基本URI的實體頭標,為了在實體范圍內解析相對URLs。
如果沒有定義Content-Base頭標解析相對URLs,使用Content-Location URI(存在且絕對)或使用URI請求。
例如:Content-Base: Http://www.myweb.com
Content-Encoding 一種介質類型修飾符,標明一個實體是如何編碼的。例如:Content-Encoding: zip
Content-Language 用于指定在輸入流中數據的自然語言類型。例如:Content-Language: en
Content-Length 指定包含于請求或響應中數據的字節長度。例如:Content-Length:382
Content-Location 指定包含于請求或響應中的資源定位(URI)。
如果是一絕。對URL它也作為被解析實體的相對URL的出發點。
例如:Content-Location: http://www.myweb.com/news
Content-MD5 實體的一種MD5摘要,用作校驗和。
發送方和接受方都計算MD5摘要,接受方將其計算的值與此頭標中傳遞的值進行比較。
例如:Content-MD5: <base64 of 128 MD5 digest>
Content-Range 隨部分實體一同發送;標明被插入字節的低位與高位字節偏移,也標明此實體的總長度。
例如:Content-Range: 1001-2000/5000
Contern-Type 標明發送或者接收的實體的MIME類型。例如:Content-Type: text/html
Date 發送HTTP消息的日期。例如:Date: Mon,10PR 18:42:51 GMT
ETag 一種實體頭標,它向被發送的資源分派一個唯一的標識符。
對于可以使用多種URL請求的資源,ETag可以用于確定實際被發送的資源是否為同一資源。
例如:ETag: "208f-419e-30f8dc99"
Expires 指定實體的有效期。例如:Expires: Mon,05 Dec 2008 12:00:00 GMT
Form 一種請求頭標,給定控制用戶代理的人工用戶的電子郵件地址。例如:From: webmaster@myweb.com
Host 被請求資源的主機名。對于使用HTTP/1.1的請求而言,此域是強制性的。例如:Host: www.myweb.com
If-Modified-Since 如果包含了GET請求,導致該請求條件性地依賴于資源上次修改日期。
如果出現了此頭標,并且自指定日期以來,此資源已被修改,應該反回一個304響應代碼。
例如:If-Modified-Since: Mon,10PR 18:42:51 GMT
If-Match 如果包含于一個請求,指定一個或者多個實體標記。只發送其ETag與列表中標記區配的資源。
例如:If-Match: "208f-419e-308dc99"
If-None-Match 如果包含一個請求,指定一個或者多個實體標記。資源的ETag不與列表中的任何一個條件匹配,操作才執行。
例如:If-None-Match: "208f-419e-308dc99"
If-Range 指定資源的一個實體標記,客戶端已經擁有此資源的一個拷貝。必須與Range頭標一同使用。
如果此實體自上次被客戶端檢索以來,還不曾修改過,那么服務器只發送指定的范圍,否則它將發送整個資源。
例如:Range: byte=0-499<CRLF>If-Range:"208f-419e-30f8dc99"
If-Unmodified-Since 只有自指定的日期以來,被請求的實體還不曾被修改過,才會返回此實體。
例如:If-Unmodified-Since:Mon,10PR 18:42:51 GMT
Last-Modified 指定被請求資源上次被修改的日期和時間。例如:Last-Modified: Mon,10PR 18:42:51 GMT
Location 對于一個已經移動的資源,用于重定向請求者至另一個位置。
與狀態編碼302(暫時移動)或者301(永久性移動)配合使用。
例如:Location: http://www2.myweb.com/index.jsp
Max-Forwards 一個用于TRACE方法的請求頭標,以指定代理或網關的最大數目,該請求通過網關才得以路由。
在通過請求傳遞之前,代理或網關應該減少此數目。例如:Max-Forwards: 3
Pragma 一個通用頭標,它發送實現相關的信息。例如:Pragma: no-cache
Proxy-Authenticate 類似于WWW-Authenticate,便是有意請求只來自請求鏈(代理)的下一個服務器的認證。
例如:Proxy-Authenticate: Basic realm-admin
Proxy-Proxy-Authorization 類似于授權,但并非有意傳遞任何比在即時服務器鏈中更進一步的內容。
例如:Proxy-Proxy-Authorization: Basic YXV0aG9yOnBoaWw=
Public 列表顯示服務器所支持的方法集。例如:Public: OPTIONS,MGET,MHEAD,GET,HEAD
Range 指定一種度量單位和一個部分被請求資源的偏移范圍。例如:Range: bytes=206-5513
Refener 一種請求頭標域,標明產生請求的初始資源。對于HTML表單,它包含此表單的Web頁面的地址。
例如:Refener: http://www.myweb.com/news/search.html
Retry-After 一種響應頭標域,由服務器與狀態編碼503(無法提供服務)配合發送,以標明再次請求之前應該等待多長時間。
此時間即可以是一種日期,也可以是一種秒單位。例如:Retry-After: 18
Server 一種標明Web服務器軟件及其版本號的頭標。例如:Server: Apache/2.0.46(Win32)
Transfer-Encoding 一種通用頭標,標明對應被接受方反向的消息體實施變換的類型。例如:Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Upgrade 允許服務器指定一種新的協議或者新的協議版本,與響應編碼101(切換協議)配合使用。
例如:Upgrade: HTTP/2.0
User-Agent 定義用于產生請求的軟件類型(典型的如Web瀏覽器)。
例如:User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0(compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows NT; DigExt)
Vary 一個響應頭標,用于表示使用服務器驅動的協商從可用的響應表示中選擇響應實體。例如:Vary: *
Via 一個包含所有中間主機和協議的通用頭標,用于滿足請求。例如:Via: 1.0 fred.com, 1.1 wilma.com
Warning 用于提供關于響應狀態補充信息的響應頭標。例如:Warning: 99 www.myweb.com Piano needs tuning
www-Authenticate 一個提示用戶代理提供用戶名和口令的響應頭標,與狀態編碼401(未授權)配合使用。響應一個授權頭標。
例如:www-Authenticate: Basic realm=zxm.mgmt
= HTTP碼應碼
響應碼由三位十進制數字組成,它們出現在由HTTP服務器發送的響應的第一行, 分五種類型,由它們的第一位數字表示:
- 1xx:信息,請求收到,繼續處理
- 2xx:成功,行為被成功地接受、理解和采納
- 3xx:重定向,為了完成請求,必須進一步執行的動作
- 4xx:客戶端錯誤,請求包含語法錯誤或者請求無法實現
- 5xx:服務器錯誤,服務器不能實現一種明顯無效的請求
下表顯示每個響應碼及其含義:
100 繼續
101 分組交換協
200 OK
201 被創建
202 被采納
203 非授權信息
204 無內容
205 重置內容
206 部分內容
300 多選項
301 永久地傳送
302 找到
303 參見其他
304 未改動
305 使用代理
307 暫時重定向
400 錯誤請求
401 未授權
402 要求付費
403 禁止
404 未找到
405 不允許的方法
406 不被采納
407 要求代理授權
408 請求超時
409 沖突
410 過期的
411 要求的長度
412 前提不成立
413 請求實例太大
414 請求URI太大
415 不支持的媒體類型
416 無法滿足的請求范圍
417 失敗的預期
500 內部服務器錯誤
501 未被使用
502 網關錯誤
503 不可用的服務
504 網關超時
505 HTTP版本未被支持
= 實例
== POST 數據
== 上傳一個文件
假設接受文件的網頁程序位于 a
bb
ccc
客戶端鏈接 192.168.29.65 后, 應該發送如下http 請求:
POST /upload_file/UploadFile HTTP/1.1
Accept: text/plain, */*
Accept-Language: zh-cn
Host: 192.168.29.65
Content-Type:multipart/form-data;boundary=---------------------------7d33a816d302b6
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; OpenOffice.org)
Content-Length: 333
Connection: Keep-Alive
-----------------------------7d33a816d302b6
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="userfile1"; filename="E:s"
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
a
bb
ccc
-----------------------------7d33a816d302b6
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="text1"
foo
-----------------------------7d33a816d302b6
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="password1"
bar
-----------------------------7d33a816d302b6--
(上面有一個回車)
此內容必須一字不差,包括最后的回車。
注意:Content-Length: 333 這里的333是紅色內容的總長度(包括最后的回車)
注意這一行:
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------7d33a816d302b6
根據 rfc1867, multipart/form-data是必須的.
---------------------------7d33a816d302b6 是分隔符,分隔多個文件、表單項。其中33a816d302b6 是即時生成的一個數字,用以確保整個分隔符不會在文件或表單項的內容中出現。Form每個部分用分隔符分割,分隔符之前必須加上"--"著兩個字符(即--{boundary})才能被http協議認為是Form的分隔符,表示結束的話用在正確的分隔符后面添加"--"表示結束。
前面的 ---------------------------7d 是 IE 特有的標志,Mozila 為---------------------------71.
每個分隔的數據的都可以用Content-Type來表示下面數據的類型,可以參考rfc1341 (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1341.txt) 例如:
Contect-Type:application/octet-stream 表示下面的數據是二進制數據
Contect-Type:text/plain 表示下面的數據是ASSCII碼數據
Contect-Type:text/richtext 表示下面的數據是RTF格式
2008年8月14日
想要在c++ 中嵌入script 代碼, 除了自己寫腳本引擎外, lua, python 都可以在c++ 中使用, 另外 MonoBind, AngelScript library 都是一些c++ script library, 可以嵌入到c++ 中使用 .
今天在c++ 中試著嵌入 python 代碼 (示例代碼在 Python-2.5.2\Demo\embed\ 下)
#include <Python.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// Py_NoSiteFlag = 1;
// Py_SetPythonHome("D:\\usr\\Python"); // PYTHONHOME
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("from time import time,ctime\n"
"print 'Today is',ctime(time())\n");
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
在運行時可能會產生類似 'import site' failed; use -v for traceback 的錯誤, 原因是python 在import module 的時候的路徑問題. 有3種方法可以解決(以前通過設置環境變量 PYTHONPATH 好像在2.5 已經無效了).
0. 取消注釋 Py_NoSiteFlag = 1;
這個只是取消import site , 當然如果在代碼中要import 啥的話, 還是會出現錯誤的.
a. 設置環境變量 PYTHONHOME = D:\usr\Python
b. 在調用 Py_Initialize 之前調用函數
Py_SetPythonHome("D:\\usr\\Python"); // 參數是python 的安裝目錄
2. 其他一些有用的資源
Python/C API Reference Manual (API 參考) , Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter (擴展及嵌入Python解釋器, 主要說明了如何擴展Python, 給Python 寫擴展, 其中 5. Embedding Python in Another Application 一章講述了在C++中嵌入/調用Python 代碼 )
使用C/C++擴展Python 對文 Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter 作了精簡, 很不錯的一篇文章, 但是跳過了一些基礎 .
Building Hybrid Systems with Boost.Python 介紹了使用boost.python 方便python 插件開發, python綁定c++程序 是其中文版本.
Embedding Python in Multi-Threaded C/C++ Applications 講了c++在多線程環境如何使用Python , 文 C++多線程中調用python api函數 提供了一個多線程的封裝.
SCXX - A Simple Python/C++ API
http://davidf.sjsoft.com/mirrors/mcmillan-inc/scxx.html
C++擴展和嵌入Python應用 (介紹了一些Python/C API 函數, 以及ext 例子, 一般般)
http://hi.baidu.com/yunsweet/blog/item/20b08aeebaa2b1282cf534c7.html
3. Python 多線程的使用
zz http://blog.csdn.net/liguangyi/archive/2007/06/20/1659697.aspx
今天看了近一天關于多線程的應用中,如何安全調用python方面的資料,開始的時候看的簡直頭大如斗,被python語言的全局鎖(Global Interpreter Lock)、線程狀態(Thread State )等都有點繞暈了,后來經過各方面文章和幫助文檔的相互參考,發現對于2.4/2.5版本,提供了PyGILState_Ensure, PyGILState_Release,哎,這下可方便大發了。
一、首先定義一個封裝類,主要是保證PyGILState_Ensure, PyGILState_Release配對使用,而且這個類是可以嵌套使用的。
#include <python.h>
class PyThreadStateLock
{
public:
PyThreadStateLock(void)
{
state = PyGILState_Ensure( );
}
~PyThreadStateLock(void)
{
PyGILState_Release( state );
}
private:
PyGILState_STATE state;
};
二、在主線程中,這樣處理
// 初始化
Py_Initialize();
// 初始化線程支持
PyEval_InitThreads();
// 啟動子線程前執行,為了釋放PyEval_InitThreads獲得的全局鎖,否則子線程可能無法獲取到全局鎖。
PyEval_ReleaseThread(PyThreadState_Get());
// 其他的處理,如啟動子線程等
......
// 保證子線程調用都結束后
PyGILState_Ensure();
Py_Finalize();
// 之后不能再調用任何python的API
三、在主線程,或者子線程中,調用python本身函數的都采用如下處理
{
class PyThreadStateLock PyThreadLock;
// 調用python的API函數處理
......
}
呵呵,看這樣是否非常簡單了。
另外還有兩個和全局鎖有關的宏,Py_BEGIN_ALLOW_THREADS 和 Py_END_ALLOW_THREADS。這兩個宏是為了在較長時間的C函數調用前,臨時釋放全局鎖,完成后重新獲取全局鎖,以避免阻塞其他python的線程繼續運行。這兩個宏可以這樣調用
{
class PyThreadStateLock PyThreadLock;
// 調用python的API函數處理
......
Py_BEGIN_ALLOW_THREADS
// 調用需要長時間的C函數
......
Py_END_ALLOW_THREADS
// 調用python的API函數處理
......
}
4. 可能的錯誤及解決
a. 在vs 200x 下 debug 模式出現鏈接問題
extmodule.obj : error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol __imp___Py_Dealloc referenced in function _PySwigObject_format
extmodule.obj : error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol __imp___Py_NegativeRefcount referenced in function _PySwigObject_format
extmodule.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol __imp___Py_RefTotal
extmodule.obj : error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol __imp___PyObject_DebugFree referenced in function _PySwigObject_dealloc
extmodule.obj : error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol __imp___PyObject_DebugMalloc referenced in function _PySwigObject_New
extmodule.obj : error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol __imp__Py_InitModule4TraceRefs referenced in function _init_extmodule
主要是因為 Py_DEBUG/Py_TRACE_REFS 引起, 修改 Python\include 下的 pyconfig.h, object.h 兩個文件就行了 ... 詳見 http://www.nabble.com/link-error-in-debug-mode-td3126668.html
Python 支持Com調用(client com) 以及撰寫COM 組件(server com).
1. com 調用示例(使用Windows Media Player 播放音樂)
from win32com.client import Dispatch
mp = Dispatch("WMPlayer.OCX")
tune = mp.newMedia("C:/WINDOWS/system32/oobe/images/title.wma")
mp.currentPlaylist.appendItem(tune)
mp.controls.play()
2. com server 的編寫
主要可以參考 <<
Python Programming on Win32 之 Chapter 12 Advanced Python and COM http://oreilly.com/catalog/pythonwin32/chapter/ch12.html >>
示例(分割字符串)
- 代碼
class PythonUtilities:
_public_methods_ = [ 'SplitString' ]
_reg_progid_ = "PythonDemos.Utilities"
# NEVER copy the following ID
# Use "print pythoncom.CreateGuid()" to make a new one.
_reg_clsid_ = "{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}"
def SplitString(self, val, item=None):
import string
if item != None: item = str(item)
return string.split(str(val), item)
# Add code so that when this script is run by
# Python.exe, it self-registers.
if __name__=='__main__':
print "Registering COM server "
"
import win32com.server.register
win32com.server.register.UseCommandLine(PythonUtilities)
- 注冊/注銷Com
|
Command-Line Option
|
Description
|
|
|
The default is to register the COM objects.
|
|
--unregister
|
Unregisters the objects. This removes all references to the objects from the Windows registry.
|
|
--debug
|
Registers the COM servers in debug mode. We discuss debugging COM servers later in this chapter.
|
|
--quiet
|
Register (or unregister) the object quietly (i.e., don't report success).
|
- 使用COM 可以在python 命令行下運行
>>> import win32com.client
>>> s = win32com.client.Dispatch("PythonDemos.Utilities")
>>> s.SplitString("a,b,c", ",")
((u'a', u'a,b,c'),)
>>>
3. python server com 原理
其實在注冊表中查找到python com 的實現內幕
 Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}]
 @="PythonDemos.Utilities"
@="PythonDemos.Utilities"

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\Debugging]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\Debugging]
 @="0"
@="0"

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\Implemented Categories]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\Implemented Categories]

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\Implemented Categories\{B3EF80D0-68E2-11D0-A689-00C04FD658FF}]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\Implemented Categories\{B3EF80D0-68E2-11D0-A689-00C04FD658FF}]

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\InprocServer32]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\InprocServer32]
 @="pythoncom25.dll"
@="pythoncom25.dll"
 "ThreadingModel"="both"
"ThreadingModel"="both"

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\LocalServer32]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\LocalServer32]
 @="D:\\usr\\Python\\pythonw.exe \"D:\\usr\\Python\\lib\\site-packages\\win32com\\server\\localserver.py\" {41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}"
@="D:\\usr\\Python\\pythonw.exe \"D:\\usr\\Python\\lib\\site-packages\\win32com\\server\\localserver.py\" {41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}"

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\ProgID]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\ProgID]
 @="PythonDemos.Utilities"
@="PythonDemos.Utilities"

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\PythonCOM]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\PythonCOM]
 @="PythonDemos.PythonUtilities"
@="PythonDemos.PythonUtilities"

 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\PythonCOMPath]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{41E24E95-D45A-11D2-852C-204C4F4F5020}\PythonCOMPath]
 @="D:\\"
@="D:\\"


inproc server 是通過pythoncom25.dll 實現
local server 通過localserver.py 實現
com 對應的python 源文件信息在 PythonCOMPath & PythonCOM
4. 使用問題
用PHP 或者 c 調用com 的時候
 <?php
<?php
 $com = new COM("PythonDemos.Utilities");
$com = new COM("PythonDemos.Utilities");
 $rs = $com->SplitString("a b c");
$rs = $com->SplitString("a b c");
 foreach($rs as $r)
foreach($rs as $r)
 echo $r."\n";
echo $r."\n";
 ?>
?>
會碰到下面的一些錯誤.
pythoncom error: PythonCOM Server - The 'win32com.server.policy' module could not be loaded.
<type 'exceptions.ImportError'>: No module named server.policy pythoncom error: CPyFactory::CreateInstance failed to create instance. (80004005)
可以通過2種方式解決:
a. 設置環境 PYTHONHOME = D:\usr\Python
另外在c ++ 使用python 的時候, 如果import module 出現錯誤
'import site' failed; use -v for traceback 的話, 也可以通過設置這個變量解決.
b. 為com 生產exe, dll 可執行文件, setup.py 代碼如下 :
 from distutils.core import setup
from distutils.core import setup
 import py2exe
import py2exe

 import sys
import sys
 import shutil
import shutil

 # Remove the build tree
# Remove the build tree ALWAYS do that!
ALWAYS do that!
 shutil.rmtree("build", ignore_errors=True)
shutil.rmtree("build", ignore_errors=True)

 # List of modules to exclude from the executable
# List of modules to exclude from the executable
 excludes = ["pywin", "pywin.debugger", "pywin.debugger.dbgcon", "pywin.dialogs", "pywin.dialogs.list"]
excludes = ["pywin", "pywin.debugger", "pywin.debugger.dbgcon", "pywin.dialogs", "pywin.dialogs.list"]

 # List of modules to include in the executable
# List of modules to include in the executable
 includes = ["win32com.server"]
includes = ["win32com.server"]

 # ModuleFinder can't handle runtime changes to __path__, but win32com uses them
# ModuleFinder can't handle runtime changes to __path__, but win32com uses them
 try:
try:
 # if this doesn't work, try import modulefinder
# if this doesn't work, try import modulefinder
 import py2exe.mf as modulefinder
import py2exe.mf as modulefinder
 import win32com
import win32com

 for p in win32com.__path__[1:]:
for p in win32com.__path__[1:]:
 modulefinder.AddPackagePath("win32com", p)
modulefinder.AddPackagePath("win32com", p)

 for extra in ["win32com.shell", "win32com.server"]: #,"win32com.mapi"
for extra in ["win32com.shell", "win32com.server"]: #,"win32com.mapi"
 __import__(extra)
__import__(extra)
 m = sys.modules[extra]
m = sys.modules[extra]
 for p in m.__path__[1:]:
for p in m.__path__[1:]:
 modulefinder.AddPackagePath(extra, p)
modulefinder.AddPackagePath(extra, p)

 except ImportError:
except ImportError:
 # no build path setup, no worries.
# no build path setup, no worries.
 pass
pass

 # Set up py2exe with all the options
# Set up py2exe with all the options
 setup(
setup(
 options = {"py2exe": {"compressed": 2,
options = {"py2exe": {"compressed": 2,
 "optimize": 2,
"optimize": 2,
 #"bundle_files": 1,
#"bundle_files": 1,
 "dist_dir": "COMDist",
"dist_dir": "COMDist",
 "excludes": excludes,
"excludes": excludes,
 "includes": includes}},
"includes": includes}},
 # The lib directory contains everything except the executables and the python dll.
# The lib directory contains everything except the executables and the python dll.
 # Can include a subdirectory name.
# Can include a subdirectory name.
 zipfile = None,
zipfile = None,
 com_server = ['PythonDemos'], # 文件名!!
com_server = ['PythonDemos'], # 文件名!!
 )
)

ref:
http://oreilly.com/catalog/pythonwin32/chapter/ch12.html http://blog.donews.com/limodou/archive/2005/09/02/537571.aspx